When it comes to the global investment landscape, few names stand out quite like Vanguard Group. Known for its low-cost investment approach and index funds, Vanguard has cemented itself as a pivotal player in the financial sector. But have you ever wondered exactly what companies Vanguard owns?
This post explores the key details of Vanguard’s ownership, lists the major companies and brands in which it holds significant stakes, explains how Vanguard operates, and sheds light on its revenue and primary owners. Whether you’re an investor, a curious researcher, or someone who appreciates the inner workings of finance, this post will provide valuable insights.
Who Owns Vanguard?
Vanguard Group is unique in the investment world because it operates as a client-owned organization. Unlike traditional publicly traded firms that issue stock to external investors, Vanguard’s mutual funds own the company. This means its shareholders are effectively its clients. This structure has enabled Vanguard to focus on minimizing costs for its investors rather than maximizing profits for external shareholders.
John C. “Jack” Bogle founded Vanguard in 1975 to revolutionize investment management. Since then, Vanguard has grown exponentially and currently manages over $8 trillion in global assets.
- Investors: The clients holding mutual fund shares collectively “own” Vanguard. With over 30 million investors worldwide, ownership is widely distributed.
- Leadership: While the investors technically own Vanguard, the firm operates under a team of professional executives, led by its CEO, Tim Buckley. The board of directors oversees its operations.
What Companies Are Owned by Vanguard Group?
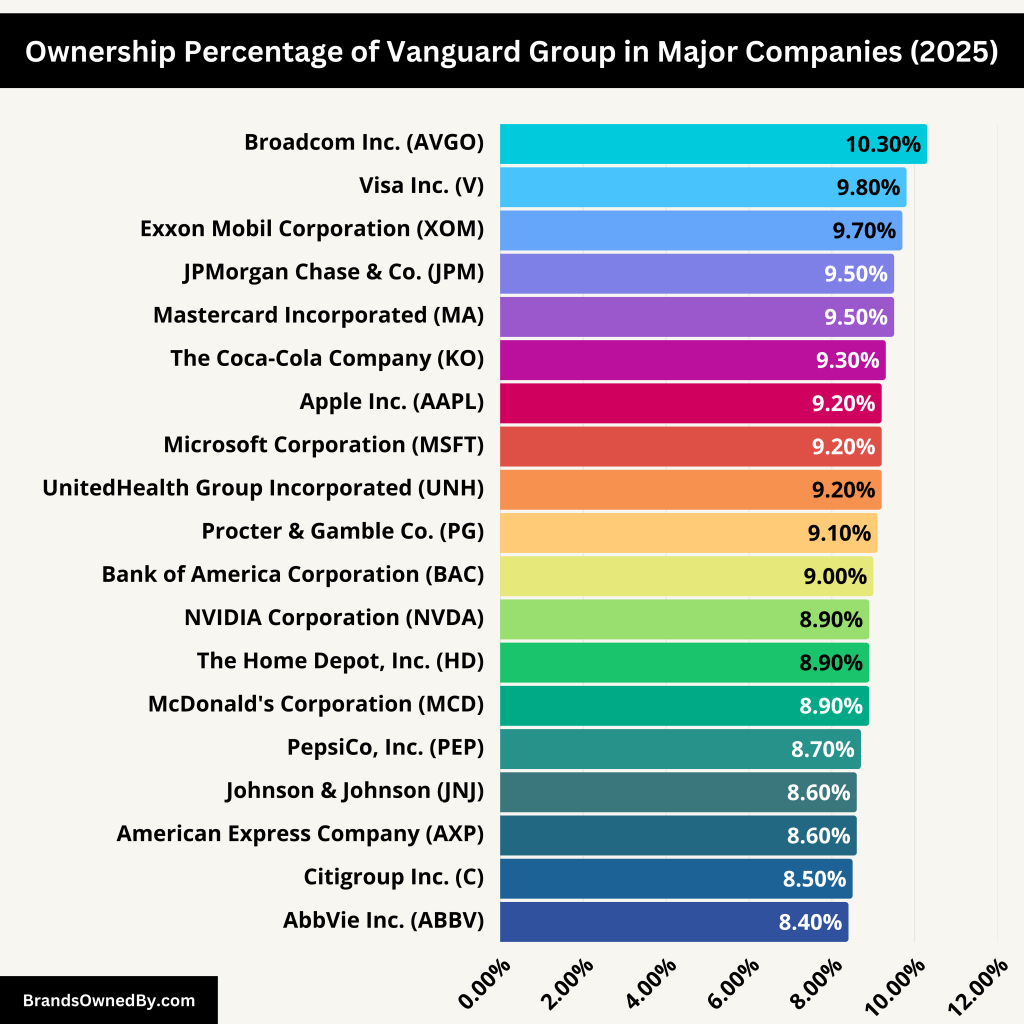
Vanguard itself isn’t a company that engages in areas like manufacturing or retail, it holds significant stakes in some of the most well-known corporations worldwide. The firm doesn’t “own” these companies in the traditional sense. Instead, it holds shares on behalf of its investors through mutual funds and ETFs (exchange-traded funds). Because of its massive scale, Vanguard is often one of the largest shareholders in the companies it invests in.
Here’s a list of some major brands and companies owned by Vanguard Group:
| Company Name | Vanguard Ownership (%) |
|---|
| Apple Inc. (AAPL) | 9.2% |
| Microsoft Corporation (MSFT) | 9.2% |
| NVIDIA Corporation (NVDA) | 8.9% |
| Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) | 7.8% |
| Meta Platforms, Inc. (META) | 7.6% |
| Alphabet Inc. Class A (GOOGL) | 4.0% |
| Alphabet Inc. Class C (GOOG) | 3.3% |
| Broadcom Inc. (AVGO) | 10.3% |
| Tesla, Inc. (TSLA) | 7.6% |
| Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (BRK.B) | 6.9% |
| JPMorgan Chase & Co. (JPM) | 9.5% |
| Eli Lilly and Company (LLY) | 8.2% |
| Visa Inc. (V) | 9.8% |
| UnitedHealth Group Incorporated (UNH) | 9.2% |
| Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) | 8.6% |
| Procter & Gamble Co. (PG) | 9.1% |
| The Home Depot, Inc. (HD) | 8.9% |
| Mastercard Incorporated (MA) | 9.5% |
| The Coca-Cola Company (KO) | 9.3% |
| PepsiCo, Inc. (PEP) | 8.7% |
| AbbVie Inc. (ABBV) | 8.4% |
| Chevron Corporation (CVX) | 6.9% |
| Exxon Mobil Corporation (XOM) | 9.7% |
| Intel Corporation (INTC) | 8.2% |
| Cisco Systems, Inc. (CSCO) | 7.6% |
| Pfizer Inc. (PFE) | 7.9% |
| The Walt Disney Company (DIS) | 7.4% |
| Merck & Co., Inc. (MRK) | 5.0% |
| The Wendy’s Company (WEN) | 7.8% |
| SoftBank Group Corp. (9984.T) | 2.19% |
| Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. (WBD) | 6.79% |
| International Business Machines Corp. (IBM) | 7.5% |
| Adobe Inc. (ADBE) | 7.4% |
| Verizon Communications Inc. (VZ) | 7.2% |
| AT&T Inc. (T) | 6.5% |
| Salesforce, Inc. (CRM) | 8.1% |
| McDonald’s Corporation (MCD) | 8.9% |
| The Boeing Company (BA) | 7.3% |
| The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. (GS) | 7.8% |
| Bank of America Corporation (BAC) | 9.0% |
| Citigroup Inc. (C) | 8.5% |
| Walmart Inc. (WMT) | 8.4% |
| General Electric Company (GE) | 7.7% |
| 3M Company (MMM) | 8.2% |
| Honeywell International Inc. (HON) | 8.0% |
| QUALCOMM Incorporated (QCOM) | 7.9% |
| Netflix, Inc. (NFLX) | 7.1% |
| PayPal Holdings, Inc. (PYPL) | 7.4% |
Apple Inc. (AAPL)
Apple Inc., headquartered in Cupertino, California, is a global leader in consumer electronics, software, and services. Renowned for products like the iPhone, iPad, Mac, and services such as the App Store and iCloud, Apple has revolutionized technology consumption worldwide. As of Q4 2024, Vanguard holds approximately 1.395 billion shares in Apple, valued at around $350 billion, accounting for 6.27% of its portfolio.
Microsoft Corporation (MSFT)
Based in Redmond, Washington, Microsoft is a leading technology company known for its software products like Windows, Office Suite, and cloud services through Azure. It plays a pivotal role in personal and enterprise computing globally. Vanguard’s investment in Microsoft includes about 684 million shares, valued at approximately $288 billion, representing 5.17% of its portfolio.
NVIDIA Corporation (NVDA)
NVIDIA, headquartered in Santa Clara, California, specializes in designing graphics processing units (GPUs) for gaming, artificial intelligence, and data centers. Its innovations have significantly advanced visual computing technology. Vanguard holds roughly 2.179 billion shares in NVIDIA, valued at about $293 billion, making up 5.25% of its holdings.
Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN)
Seattle-based Amazon is a multinational technology company focusing on e-commerce, cloud computing, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence. Known for its customer-centric approach, Amazon has transformed the retail industry. Vanguard’s stake in Amazon comprises approximately 823 million shares, valued at around $181 billion, accounting for 3.24% of its portfolio.
Meta Platforms Inc. (META)
Formerly known as Facebook, Meta Platforms, headquartered in Menlo Park, California, is a social media conglomerate owning platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp. It focuses on building communities and connecting people globally. Vanguard holds about 191 million shares in Meta, valued at approximately $113 billion, representing 2.02% of its holdings.
Alphabet Inc. Class A (GOOGL) and Class C (GOOG)
Alphabet Inc., based in Mountain View, California, is the parent company of Google and various subsidiaries. It dominates the online advertising market and is a leader in search, cloud computing, and technological innovations. Vanguard’s combined investment in Alphabet’s Class A and Class C shares totals approximately $170.3 billion, accounting for a significant portion of its portfolio.
Broadcom Inc. (AVGO)
Broadcom, headquartered in San Jose, California, is a global technology company that designs, develops, and supplies a broad range of semiconductor and infrastructure software solutions. Its products are integral to data center, networking, software, broadband, wireless, and storage applications. Vanguard’s investment in Broadcom includes approximately 475 million shares, valued at around $110 billion, representing 1.98% of its portfolio.
Tesla Inc. (TSLA)
Tesla, based in Palo Alto, California, is an electric vehicle and clean energy company. It designs and manufactures electric cars, battery energy storage, and solar products, aiming to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Vanguard holds about 243 million shares in Tesla, valued at approximately $98.2 billion, accounting for 1.76% of its holdings.
Berkshire Hathaway Inc. Class B (BRK.B)
Berkshire Hathaway, headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska, is a multinational conglomerate holding company led by Warren Buffett. It owns diverse businesses, including insurance, rail transportation, energy, manufacturing, and retailing. Vanguard’s investment in Berkshire Hathaway comprises approximately 148 million shares, valued at around $67.1 billion, representing 1.2% of its portfolio.
JPMorgan Chase & Co. (JPM)
JPMorgan Chase, based in New York City, is a leading global financial services firm offering investment banking, financial services for consumers and businesses, financial transaction processing, asset management, and private equity. Vanguard holds approximately 272 million shares in JPMorgan Chase, valued at about $65.3 billion, accounting for 1.17% of its portfolio.
Visa Inc. (V)
Visa, headquartered in Foster City, California, is a multinational financial services corporation facilitating electronic funds transfers worldwide through its branded credit, debit, and prepaid cards. Vanguard’s investment in Visa includes approximately 159 million shares, valued at around $50.4 billion, representing 0.9% of its portfolio.
Eli Lilly and Company (LLY)
Eli Lilly, based in Indianapolis, Indiana, is a pharmaceutical company known for its innovations in developing medications for diabetes, oncology, immunology, and neuroscience. Vanguard holds approximately 74 million shares in Eli Lilly, valued at about $57.3 billion, accounting for 1.03% of its portfolio.
Procter & Gamble Co. (PG)
Procter & Gamble (P&G), headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio, is a multinational consumer goods company specializing in personal health, hygiene, and home care products. The company owns well-known brands such as Pampers, Tide, Gillette, and Head & Shoulders. P&G’s vast portfolio makes it a leader in the consumer goods industry, with strong global brand recognition. Vanguard holds approximately 225 million shares in P&G, valued at around $37 billion, representing a significant portion of its consumer sector investments.
The Coca-Cola Company (KO)
Coca-Cola, headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, is one of the world’s largest beverage companies. It owns a vast portfolio of non-alcoholic beverages, including brands like Sprite, Fanta, Dasani, and Minute Maid. Coca-Cola’s distribution network reaches over 200 countries, making it a dominant player in the global beverage market. Vanguard holds about 280 million shares in Coca-Cola, valued at approximately $35 billion.
PepsiCo Inc. (PEP)
PepsiCo, based in Purchase, New York, is a leading global food and beverage company known for brands such as Pepsi, Mountain Dew, Lay’s, Tropicana, and Gatorade. The company operates in over 200 countries and generates revenue from its diversified product lines. Vanguard owns around 212 million shares of PepsiCo, worth about $40 billion.
Johnson & Johnson (JNJ)
Johnson & Johnson (J&J), headquartered in New Brunswick, New Jersey, is a global healthcare and pharmaceutical giant. It specializes in medical devices, consumer health products, and pharmaceuticals, with well-known brands like Band-Aid, Tylenol, and Neutrogena. Vanguard holds approximately 178 million shares of J&J, valued at around $42 billion.
ExxonMobil Corporation (XOM)
ExxonMobil, headquartered in Irving, Texas, is one of the largest publicly traded international oil and gas companies. The company engages in oil exploration, production, refining, and distribution worldwide. It also invests in renewable energy solutions. Vanguard holds around 330 million shares in ExxonMobil, valued at approximately $37 billion.
Chevron Corporation (CVX)
Chevron, based in San Ramon, California, is another major player in the energy sector. The company is involved in all aspects of the oil and gas industry, including exploration, refining, and distribution. Chevron also invests in alternative energy sources such as hydrogen and carbon capture technology. Vanguard’s stake in Chevron consists of about 180 million shares, worth around $31 billion.
United Parcel Service (UPS)
UPS, headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, is a global leader in logistics and package delivery services. The company operates a vast transportation and distribution network that serves businesses and consumers worldwide. Vanguard holds approximately 95 million shares of UPS, valued at around $18 billion.
Boeing Co. (BA)
Boeing, based in Chicago, Illinois, is a major aerospace and defense manufacturer. It produces commercial airplanes, military aircraft, satellites, and defense systems. Boeing plays a crucial role in both commercial and government aviation. Vanguard owns about 85 million shares in Boeing, valued at approximately $15 billion.
AT&T Inc. (T)
AT&T, headquartered in Dallas, Texas, is a multinational telecommunications company offering wireless, broadband, and digital entertainment services. It operates one of the largest telecommunications networks in the U.S. Vanguard holds around 190 million shares in AT&T, valued at approximately $20 billion.
Verizon Communications Inc. (VZ)
Verizon, based in New York City, is a leading telecommunications company providing wireless and broadband services. It is a key player in 5G network expansion and digital communications. Vanguard has a stake of about 210 million shares in Verizon, worth around $22 billion.
Walmart Inc. (WMT)
Walmart, headquartered in Bentonville, Arkansas, is the world’s largest retailer by revenue. It operates a chain of hypermarkets, discount department stores, and grocery stores across the globe. Walmart’s business model focuses on cost leadership and high-volume sales. Vanguard holds approximately 140 million shares in Walmart, valued at around $24 billion.
The Home Depot Inc. (HD)
Home Depot, based in Atlanta, Georgia, is the largest home improvement retailer in the U.S. The company provides building materials, tools, and services for homeowners and contractors. Vanguard owns about 95 million shares in Home Depot, worth around $26 billion.
Costco Wholesale Corporation (COST)
Costco, headquartered in Issaquah, Washington, operates a membership-based wholesale retail chain. It is known for offering bulk products at competitive prices. Vanguard has approximately 60 million shares in Costco, valued at around $25 billion.
The Walt Disney Company (DIS)
Vanguard holds a substantial stake in The Walt Disney Company, one of the world’s leading entertainment conglomerates. As of recent filings, Vanguard owns around 7.4% of Disney’s total shares, making it one of the company’s largest institutional investors. This significant investment underscores Vanguard’s confidence in Disney’s diversified revenue streams, which include theme parks, television networks, and streaming services such as Disney+, Hulu, and ESPN+.
Merck & Co., Inc. (MRK)
Vanguard owns a 5.0% stake in Merck & Co., Inc., a global pharmaceutical giant known for its innovations in oncology, vaccines, and immunology. Merck has consistently delivered strong financial performance, with blockbuster drugs like Keytruda (cancer treatment) and Gardasil (HPV vaccine) contributing significantly to its revenue.
The Wendy’s Company (WEN)
Vanguard holds a 7.8% stake in The Wendy’s Company, making it one of the fast-food chain’s most significant institutional investors. Wendy’s has built a strong brand presence in the quick-service restaurant industry, competing with McDonald’s and Burger King through its focus on fresh ingredients, menu innovation, and digital expansion.
SoftBank Group Corp. (9984.T)
Vanguard holds a 2.19% stake in SoftBank Group, a Japanese multinational conglomerate known for its aggressive investments in technology, AI, and venture capital. SoftBank’s Vision Fund has invested in companies like Uber, Alibaba, and Arm Holdings, making it a major player in the global tech ecosystem.
Warner Bros. Discovery, Inc. (WBD)
Vanguard holds a 6.79% stake in Warner Bros. Discovery, a major media and entertainment company formed from the merger of WarnerMedia and Discovery, Inc. The company owns major content brands such as HBO, Warner Bros. Studios, CNN, Discovery Channel, and DC Comics, giving it a dominant presence in both traditional and streaming media.
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM)
Vanguard holds a 7.5% stake in IBM, a global leader in enterprise computing, artificial intelligence, and cloud services. IBM has undergone significant transformations, shifting from its traditional hardware and software business to focus on cloud computing, AI, and cybersecurity.
Vanguard’s investment in IBM highlights confidence in its long-term strategy, particularly with its hybrid cloud and AI business led by Red Hat and Watson AI. Despite facing competition from Microsoft, Amazon, and Google in cloud computing, IBM continues to leverage its enterprise partnerships and government contracts. Vanguard’s sustained investment signals belief in IBM’s ability to capitalize on AI-driven automation and cloud services in the enterprise sector.
Pfizer Inc. (PFE)
Vanguard holds a 7.9% stake in Pfizer, one of the world’s largest pharmaceutical companies. Pfizer gained significant global attention for its COVID-19 vaccine (Comirnaty), developed in collaboration with BioNTech, as well as its antiviral treatment Paxlovid.
Beyond COVID-19 treatments, Pfizer remains a dominant force in oncology, immunology, and cardiovascular drugs. Vanguard’s investment reflects its confidence in Pfizer’s robust research pipeline and acquisitions, including its $43 billion purchase of Seagen to expand its cancer drug portfolio. Pfizer’s consistent dividends and focus on long-term drug development align with Vanguard’s investment philosophy.
Intel Corporation (INTC)
Vanguard holds an 8.2% stake in Intel, one of the world’s leading semiconductor manufacturers. Intel has faced intense competition from AMD, NVIDIA, and Qualcomm, but it remains a key player in the CPU, AI, and data center markets.
Cisco Systems, Inc. (CSCO)
Vanguard holds a 7.6% stake in Cisco, one of the largest networking and cybersecurity companies in the world. Cisco dominates the enterprise networking industry, providing essential infrastructure for data centers, cloud computing, and cybersecurity solutions.
Adobe Inc. (ADBE)
Vanguard owns a 7.4% stake in Adobe, a leader in digital media, creative software, and cloud-based marketing solutions. Adobe’s suite of products, including Photoshop, Illustrator, Premiere Pro, and Adobe Creative Cloud, dominates the professional design and content creation market.
How Does Vanguard Operate?
The Vanguard Group operates differently from most other financial firms. Here’s how it works:
- Mutual Funds Ownership: Unlike other investment firms, Vanguard is owned by its mutual funds, which are in turn owned by their investors. This structure allows Vanguard to prioritize customer interests while minimizing fee structures.
- Passive Investing: Vanguard pioneered index fund investing. Its investment strategies focus on closely tracking the performance of an index (e.g., S&P 500) rather than actively trying to beat it. This results in stable, long-term growth.
- Low Costs: Vanguard is synonymous with low fees. Its client-owned structure allows it to reduce operational costs and pass these savings directly to its investors.
- Global Reach: Vanguard offers over 400 funds, including traditional mutual funds, ETFs, and international investments.
Vanguard’s Annual Revenue
While Vanguard Group isn’t a publicly traded company, estimates suggest its annual revenue exceeds $7 billion. A significant portion of this comes from the expense ratios clients pay for its funds, though these ratios are significantly lower compared to industry averages.
The firm’s low-cost strategy and growth in assets under management (AUM) have consistently fueled its financial success.
Why Vanguard’s Ownership Matters
The Vanguard Group is more than just an investor; it’s a key player in shaping the global economy. With stakes in everything from technology to healthcare, its influence on markets and industries is undeniable. Its client-owned model prioritizes investor interests, setting an example for corporate governance and ethical investing.
Want to explore more about Vanguard Group subsidiaries and investment strategies? Use this newfound knowledge to your advantage when assessing Vanguard’s influence—and perhaps even consider becoming an investor yourself.
Why Vanguard’s Influence Matters
With ownership in such a vast array of industries and companies, Vanguard Group wields substantial influence in corporate governance and decision-making. This has sparked debates about the concentration of economic power among institutional investors like Vanguard, and whether such power serves broader societal interests.
For investors, though, Vanguard’s influence is often seen as an advantage. Its ability to push for long-term, sustainable strategies benefits both the companies it invests in and the individuals whose savings fuel these investments.
Your Window into Corporate Power
Vanguard Group’s massive influence over publicly traded companies reflects not just its scale but also the trust millions of investors place in it. From reshaping industries to advocating for sustainability, Vanguard’s reach extends beyond mere profits—it shapes the future of the global economy.
Are you thinking about exploring Vanguard’s investment products? Delve deeper into the world of institutional-scale investing through their website or a financial advisor.
FAQ About Vanguard Group
1. Does Vanguard directly own companies?
No, Vanguard holds stock in hundreds of companies through its investment funds. These stocks are owned on behalf of millions of investors.
2. Why is Vanguard one of the top shareholders in many companies?
Due to its sheer size and the popularity of its index funds and ETFs, Vanguard naturally becomes a significant investor in major corporations.
3. How is Vanguard different from other asset management firms?
Vanguard’s client-owned structure and focus on low-cost investing set it apart. Unlike profit-driven firms, Vanguard reinvests profits to lower fees for investors.
4. Can anyone invest with Vanguard?
Yes, investors of all experience levels can open an account with Vanguard and invest in its mutual funds and ETFs.
5. How can I see what companies Vanguard funds invest in?
Most funds hold a prospectus and regular reports that detail their holdings. You can access this information on Vanguard’s official website.

