BYD has emerged as one of the leading electric vehicle manufacturers in the world. If you’re wondering who owns BYD, the answer involves a mix of founders, strategic investors, and large institutional shareholders. This article explores the ownership structure, company control, and the vast reach of BYD across industries.
History of BYD
BYD, short for “Build Your Dreams,” was founded in February 1995 by Wang Chuanfu, a former researcher at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Starting with just 20 employees in Shenzhen, the company focused on producing rechargeable nickel-cadmium batteries for mobile phones. Within a few years, BYD had become a top supplier of batteries to major electronics brands, including Motorola, Nokia, and Samsung.
The company’s low-cost manufacturing model and in-house research capabilities allowed it to quickly outpace Japanese competitors. By the early 2000s, BYD had captured a significant share of the global battery market.
Here’s a year-wise history of BYD company:
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1995 | BYD was founded in Shenzhen by Wang Chuanfu with 20 employees. Initially focused on rechargeable nickel-cadmium batteries. |
| 1997 | Became a major battery supplier to mobile phone giants like Motorola and Nokia. |
| 2000 | Captured a significant share of the global battery market. Began exploring diversification. |
| 2002 | Listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX), raising international capital. |
| 2003 | Acquired Qinchuan Automobile Company, marking BYD’s entry into the automotive industry. |
| 2005 | Launched the BYD F3, its first mass-market gasoline vehicle. It became a top-seller in China. |
| 2008 | Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway invested $232 million for nearly a 10% stake. |
| 2009 | Released the F3DM, the first commercially available plug-in hybrid in the world. |
| 2010 | Entered the electric bus market with the launch of the K9 e-bus. |
| 2013 | Launched the Qin plug-in hybrid, which quickly became one of China’s best-selling NEVs. |
| 2015 | Became the top-selling EV manufacturer globally for the first time. |
| 2017 | Launched SkyRail, a monorail system for urban transit, diversifying into infrastructure. |
| 2018 | Reached over 500,000 NEV units sold. Expanded into Europe and Latin America. |
| 2020 | Unveiled the Blade Battery, a safer and more efficient LFP battery technology. |
| 2021 | Began supplying batteries to automakers like Toyota. Strengthened battery division. |
| 2022 | Ended production of gasoline-only cars, becoming a pure NEV manufacturer. |
| 2023 | Surpassed Tesla in global EV sales for the first time in a single quarter. Expanded in global markets. |
| 2024 | Reported revenue of $85 billion. Launched luxury EV brands Yangwang and Fang Cheng Bao. |
| 2025 | Continues to lead in EV innovation, public transport, and battery production. Expanding rail, chip, and energy storage businesses. |
Who Owns BYD?
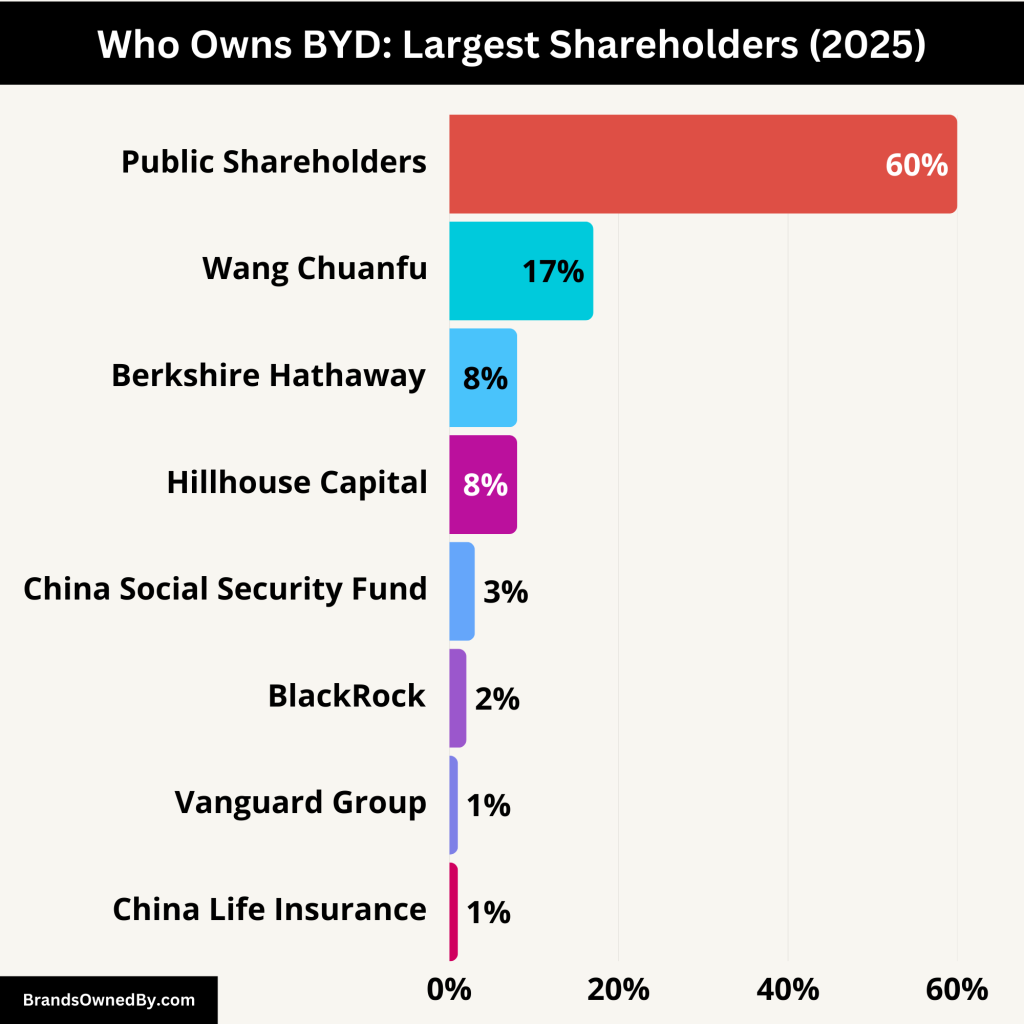
Ownership of BYD is shared among founders, foreign investors, Chinese institutions, and public shareholders. The largest shareholder is its founder and CEO, Wang Chuanfu, who holds significant voting power through direct and indirect holdings. Another major player is Berkshire Hathaway, Warren Buffett’s firm, which made a notable investment in BYD in 2008.
The company is listed on both the Hong Kong Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exchange, attracting a mix of domestic and international investors.
BYD Largest Shareholders
Here’s a list of the top shareholders of BYD company:
| Shareholder | Ownership (%) | Type | Role/Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wang Chuanfu | ~17% | Individual (Founder/Chairman) | Largest individual shareholder; key decision-maker and strategist. |
| BYD Industry Company Limited | Included in above | Corporate (Founder-controlled) | Consolidates founder’s stake; aids in long-term control. |
| Berkshire Hathaway | ~6–8% (H-shares) | Foreign Institutional Investor | Strategic partner; global credibility but no direct control. |
| China Social Security Fund (NSSF) | ~2–3% | Chinese State Institutional Fund | Long-term strategic investor; supports national clean energy goals. |
| BlackRock | ~1–2% | Global Asset Manager | Passive investor; reflects global ESG fund interest. |
| Vanguard Group | ~1% | Passive Institutional Investor | Holds H-shares via ETFs and index funds; no active influence. |
| Hillhouse Capital | Variable | Private Equity / Investment Fund | Periodic strategic investor; focused on high-growth sectors. |
| China Life Insurance | ~1% | State-Linked Financial Institution | Strategic institutional support; aligned with government policies. |
| Public Shareholders | Remainder (~60%) | Retail and Institutional (A & H shares) | No direct control; provide liquidity and valuation support. |
Wang Chuanfu – Founder and Largest Individual Shareholder (17%)
Wang Chuanfu, BYD’s founder, chairman, and CEO, holds approximately 17% of the company through direct ownership and entities like BYD Industry Company Limited. His holdings make him the largest single shareholder and the central decision-maker.
Wang’s influence is not just financial. As the founder, he plays a key role in strategic direction, technology development, and day-to-day leadership. His long-term vision has shaped BYD’s rise from a battery supplier to a global EV and tech giant.
Berkshire Hathaway – Strategic Foreign Investor (8%)
Berkshire Hathaway, Warren Buffett’s investment firm, entered BYD in 2008 through its subsidiary MidAmerican Energy Holdings (now part of Berkshire Hathaway Energy). It initially acquired a 9.89% stake for $232 million. Over time, Berkshire has reduced its stake slightly, and as of 2024, it holds around 6% to 8% of BYD’s H-shares listed in Hong Kong.
Although Berkshire is not involved in BYD’s operational decisions, its continued investment is seen as a strong vote of confidence. The partnership also helped boost BYD’s global image and attract other long-term investors.
BYD Industry Company Limited – Founder-Linked Entity
This private entity is closely associated with Wang Chuanfu and acts as a vehicle for his holdings. It is one of the largest shareholders and often appears in official ownership reports. It plays a vital role in consolidating voting rights and maintaining control within Wang’s circle.
China Social Security Fund – Institutional State Investor (3%)
The National Social Security Fund of China (NSSF) owns around 2–3% of BYD shares. It invests in key strategic sectors, including clean energy and infrastructure, as part of its long-term mandate to support China’s aging population.
NSSF’s stake in BYD signals government support without direct control. It provides financial stability and aligns BYD with national green energy goals.
BlackRock – Global Asset Manager (2%)
BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, holds a minor but important stake in BYD through various index funds and ETFs. As of recent filings, it owns between 1% and 2%, mainly in the H-shares listed in Hong Kong.
While BlackRock is a passive investor, its presence reflects strong international institutional interest in BYD, especially from ESG-aligned funds that prioritize electric mobility and sustainability.
Vanguard Group – Passive Institutional Investor (1%)
Similar to BlackRock, The Vanguard Group holds a small stake (around 1%) in BYD through index funds. Its investment is mostly in the H-shares and held passively, meaning it doesn’t influence the company’s strategy or governance.
Vanguard’s stake reflects BYD’s growing inclusion in global ESG and green tech indices, making it attractive to long-term investors seeking exposure to the EV sector.
Hillhouse Capital – Chinese Investment Fund (Variable Stake)
Hillhouse Capital, a major Chinese investment group, has at times held positions in BYD, particularly through private placements and strategic investments. Its stake varies over time based on its portfolio rebalancing.
Hillhouse is known for investing in high-growth technology and consumer brands. Its involvement often signals strong expectations for long-term innovation and profitability.
China Life Insurance – State-Linked Financial Institution (1%)
China Life Insurance, one of China’s biggest insurers, holds a stake in BYD through its asset management arm. With roughly 1% ownership, it serves as another example of state-affiliated financial institutions supporting BYD’s long-term success.
The investment reflects alignment with China’s push for electric vehicles, sustainable development, and technological self-reliance.
Public Shareholders – Thousands of Retail and Institutional Investors
The remaining ownership is held by a mix of public investors across BYD’s dual listings:
- H-shares (Hong Kong Stock Exchange): Available to international and institutional investors.
- A-shares (Shenzhen Stock Exchange): Held mostly by domestic Chinese investors.
This segment includes retail shareholders, domestic mutual funds, pension funds, and global index-tracking funds. While these investors don’t exert control, they provide liquidity and contribute to BYD’s market valuation.
Who Controls BYD?
BYD is controlled by its founder, Wang Chuanfu. As chairman and CEO, he oversees strategic decisions, R&D direction, and global expansion. The board of directors includes both executive and independent members, but Wang’s influence is dominant due to his equity and leadership role.
Although Berkshire Hathaway is a major shareholder, it takes a passive approach and does not interfere in daily governance.
Wang Chuanfu – Founder, Chairman, and CEO
Wang Chuanfu is the primary force behind BYD’s strategic direction and operations. As the founder, chairman, and chief executive officer, he holds a dual leadership role. With approximately 17% ownership, his financial stake supports his executive power.
Wang is known for his hands-on leadership style. He oversees product development, innovation strategy, and expansion plans. His technical background in battery chemistry and engineering also enables him to lead on the R&D front. Most major decisions at BYD—from the Blade Battery launch to the shift away from gasoline vehicles—bear his influence.
Wang’s voting power, combined with his shareholding through BYD Industry Company Limited, secures his practical control over boardroom decisions.
Board of Directors – Formal Corporate Governance
BYD is governed by a Board of Directors, which includes executives, independent directors, and supervisory board members. The board is responsible for corporate governance, strategy oversight, risk management, and approving key business initiatives.
While Wang chairs the board, other board members play a role in ensuring compliance, internal checks, and long-term planning. Several board members bring expertise in finance, legal affairs, and public policy, enhancing governance and stakeholder trust.
However, given Wang’s founder status and large shareholding, the board typically aligns with his strategic vision, making him the de facto leader.
Senior Executive Team – Operational Control
BYD’s executive team includes vice presidents, division heads, and department directors who manage daily operations across units like EVs, batteries, rail transit, and international business. Key roles include:
- Stella Li – Head of international operations, especially North America and Latin America.
- Lian Yubo – Executive VP and Head of R&D, overseeing battery technology and EV platforms.
- He Long – President of BYD Battery Division, key to battery innovation and supply chain.
These executives implement Wang’s vision and ensure that BYD operates efficiently at scale across different markets and industries.
Chinese Government – Indirect Strategic Influence
While the Chinese government does not directly control BYD, it plays a significant role through policy, subsidies, and institutional investors. Bodies like the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) and the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) influence BYD’s strategic direction by shaping regulations and electric vehicle incentives.
Institutions such as the China Social Security Fund and China Life Insurance also hold minority stakes, giving the government some indirect financial interest in BYD’s long-term success.
The government’s strong support for clean energy and new energy vehicles has closely aligned with BYD’s growth strategy. This alignment enhances BYD’s access to resources, licenses, and urban transport contracts.
No Dual-Class Share Structure
Unlike companies such as Alibaba or Meta, BYD does not have a dual-class share structure. Voting rights are proportional to shareholding. This means that Wang Chuanfu’s control stems from his significant equity and leadership role, not from special voting rights.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of BYD
In 2024, BYD reported a record revenue of approximately $107 billion USD (around CNY 765 billion), marking one of the fastest growth years in its history. This 2024 revenue figure represented a ~29% increase compared to the previous year. The growth was driven by soaring global EV sales, rapid overseas expansion, and booming demand for BYD’s battery and energy storage solutions.
The company sold over 3.6 million new energy vehicles (NEVs) during the year and continued its diversification into sectors like monorail systems (SkyRail), semiconductors, and battery supply for other automakers.
BYD’s net profit in 2024 rose to approximately $4.9 billion USD (around CNY 35 billion), fueled by higher-margin luxury models (like Yangwang U8), export volumes, and strong cost efficiency in battery production.
As of April 2025, BYD’s market capitalization is around $148 billion placing it among the top global EV manufacturers alongside Tesla.
Here’s an overview of the last 10 years of revenue:
| Year | Revenue (CNY Billion) | Revenue (USD Billion) | Key Highlights |
|---|
| 2014 | 55.4 | 8.8 | Qin plug-in hybrid sales surged. |
| 2015 | 77.6 | 12.5 | Global EV leadership begins. |
| 2016 | 100.2 | 15.2 | Strong NEV and battery growth. |
| 2017 | 105.9 | 16.3 | SkyRail project launched. |
| 2018 | 130.1 | 19.6 | Expanded to Europe and Latin America. |
| 2019 | 127.7 | 18.5 | Market slowdown, innovation in batteries. |
| 2020 | 156.6 | 22.4 | Blade Battery launched during pandemic. |
| 2021 | 216.1 | 33.2 | Massive jump in NEV demand. |
| 2022 | 424.1 | 62.8 | Ended ICE production, NEV-only company. |
| 2023 | 602.3 | 83.1 | Surpassed Tesla in EV sales. |
| 2024 | 765.0 | 107.0 | Highest revenue in BYD’s history. |
Companies Owned by BYD: Major Subsidiaries and Brands
BYD operates through a broad set of subsidiaries and product lines. The major companies owned by BYD include:
BYD Auto Co., Ltd.
BYD Auto is BYD’s flagship automotive subsidiary. It was founded in 2003 after BYD acquired the Tsinchuan Automobile Company. BYD Auto designs, manufactures, and sells electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles across passenger and commercial categories.
The company leads China’s NEV market and has expanded globally, selling in over 60 countries by 2024. Popular models include:
- BYD Qin, Song, and Han – Plug-in hybrids and EV sedans
- BYD Tang – Mid-size SUV
- BYD Dolphin and Seagull – Affordable city EVs
- BYD Seal – Premium electric sedan competing with Tesla Model 3
- Yangwang U8 and U9 – Luxury electric SUV and supercar under the Yangwang sub-brand
- Denza – A premium sub-brand co-developed with Mercedes-Benz (Daimler)
BYD Auto plays a central role in BYD’s revenue, contributing over 65% of the group’s 2024 income.
FinDreams Battery Co., Ltd.
FinDreams Battery is BYD’s dedicated power battery subsidiary. It manufactures lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, including the innovative Blade Battery, which offers superior thermal safety and lifespan.
The company supplies batteries to BYD’s own vehicles and external partners, such as Toyota, Hyundai, Tesla (rumored), and Changan Auto. FinDreams has become one of the top three EV battery makers globally by installed capacity.
It operates several giga-factories across China and is building new plants in Hungary and Brazil to support international demand.
FinDreams Powertrain Co., Ltd.
FinDreams Powertrain develops and produces BYD’s in-house electric motors, drive systems, and controllers. These components are core to BYD’s DM-i and DM-p hybrid technologies, known for fuel efficiency and acceleration.
The vertical integration of motors and controllers allows BYD to optimize vehicle performance and reduce costs.
FinDreams Vision Co., Ltd.
This BYD subsidiary focuses on automotive electronics, intelligent driving systems, and cockpit technologies. It develops instrument panels, displays, infotainment, and ADAS (advanced driver assistance systems).
The unit is integral to BYD’s strategy to advance smart cars and autonomous capabilities, especially in high-end models like the Yangwang U8.
FinDreams Moduling Co., Ltd.
This company focuses on battery pack assembly and module manufacturing, converting cells into usable systems for EVs and energy storage. It ensures the efficiency, durability, and safety of BYD’s Blade Battery systems before they’re installed in vehicles or sent to commercial partners.
BYD Electronics (International) Co., Ltd.
Listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, BYD Electronics is a major global supplier of smartphone parts, tablets, laptops, wearables, and consumer electronics components. Its clients include Apple, Huawei, Xiaomi, and Dell.
It manufactures:
- Precision metal and plastic parts
- Batteries for phones and laptops
- Flexible PCBs and assembly services
In recent years, the division expanded into automotive electronics, integrating its strengths into BYD’s vehicles.
BYD Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
BYD Semiconductor develops automotive-grade chips, such as IGBTs (insulated gate bipolar transistors), MCUs, and sensors for power electronics and electric drive systems.
It was initially spun off for IPO, but due to volatile markets, BYD postponed its listing. The semiconductor unit is seen as strategic in China’s push for tech self-sufficiency, especially in the EV sector.
BYD SkyRail and SkyShuttle
These two divisions focus on urban rail transit solutions:
- SkyRail is BYD’s straddle-type monorail system, designed for medium-capacity urban transit.
- SkyShuttle is a smaller, rubber-tired autonomous tram for short urban routes and last-mile transport.
SkyRail has been deployed in cities like Shenzhen, Yinchuan, and São Paulo, with more international projects under planning.
These businesses are part of BYD’s vision to solve city congestion and offer clean, automated transport.
BYD Energy (BYD Solar and Storage)
BYD also owns a growing renewable energy division that develops:
- Solar panels (photovoltaic solutions)
- Home and commercial energy storage systems
- Large-scale grid storage for utilities
BYD Energy serves clients in Europe, Australia, Africa, and Southeast Asia. The division leverages BYD’s battery technology to power off-grid systems, microgrids, and renewable backup power solutions.
Denza
Denza is a premium electric vehicle brand co-developed by BYD and Mercedes-Benz. Denza is known for its luxury EVs, such as the Denza 500, which was launched as a high-end electric sedan for the Chinese market. The brand positions itself as a premium alternative to Tesla, combining BYD’s battery technology and Mercedes-Benz’s luxury design elements.
Denza is a significant part of BYD’s strategy to offer high-end EVs to affluent consumers in China and eventually in other global markets.
Fangchengbao
Fangchengbao is BYD’s real estate and infrastructure development arm, which focuses on the construction of housing projects, commercial properties, and industrial parks. The subsidiary is involved in the development of EV-related infrastructure, such as battery manufacturing facilities and EV charging stations.
As part of BYD’s broader ecosystem, Fangchengbao is positioned to support sustainable urbanization and enhance the overall infrastructure needed for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
BYD Intelligent Electronics
BYD’s Intelligent Electronics division specializes in the development and manufacture of smart devices, wearables, and IoT (Internet of Things) solutions. The division plays an integral role in BYD’s smart car ecosystem, providing sensors, navigation systems, and infotainment technologies for its electric vehicle lineup.
Other Notable BYD Subsidiaries and Ventures
- BYD Energy Technology Co., Ltd. – The company focuses on expanding BYD’s presence in renewable energy sectors, specifically in grid storage and solar energy solutions.
- BYD Auto Sales Co., Ltd. – A sales subsidiary that focuses on domestic and international distribution of BYD’s electric vehicles.
- BYD Li-ion Battery Co., Ltd. – Responsible for the manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries used in EVs, consumer electronics, and energy storage systems.
- BYD Aluminum – Focuses on producing aluminum parts for automotive applications, ensuring lightweight, durable, and energy-efficient vehicle designs.
Conclusion
If you’re trying to understand who owns BYD, the picture includes its visionary founder Wang Chuanfu, global powerhouse Berkshire Hathaway, and a mix of Chinese institutions. Control remains firmly with Wang, ensuring strategic alignment and consistent innovation. BYD is not just an EV company—it’s a diversified tech and transportation conglomerate with global reach.
FAQs
Is BYD owned by Mercedes?
No, BYD is not owned by Mercedes-Benz. However, the two companies have a joint venture called Denza, which was established in 2010. BYD and Mercedes-Benz (through its parent company Daimler AG) co-developed the Denza brand to produce premium electric vehicles specifically for the Chinese market. While Mercedes-Benz holds a minority stake in the brand, BYD remains the majority shareholder and fully owns BYD Auto.
Why did Mercedes leave BYD?
Mercedes-Benz did not exactly “leave” BYD, but it reduced its involvement in the Denza brand after initially co-developing it. The Denza brand was part of a strategy for Mercedes-Benz to enter the Chinese electric vehicle market. However, as BYD’s own success and expertise in the EV sector grew, Mercedes-Benz chose to reduce its direct involvement. Despite this, the partnership still exists in the form of a collaboration under the Denza name, but Mercedes-Benz has gradually phased out its participation as BYD took the lead in product development.
Is BYD related to Toyota?
BYD and Toyota are not directly related in terms of ownership, but they have formed a partnership. BYD and Toyota signed an agreement in 2020 to jointly develop electric vehicles for the Chinese market. This collaboration aims to combine BYD’s expertise in electric battery technology with Toyota’s advanced engineering in vehicle manufacturing. BYD also supplies batteries for Toyota’s electric vehicles, which strengthens their business relationship.
What is BYD full form?
BYD stands for Build Your Dreams. The name reflects the company’s focus on innovation and the ambition to provide sustainable, green technology solutions in the fields of electric vehicles, renewable energy, and batteries. The name has become synonymous with eco-friendly technologies and future mobility.
Who manufactures BYD cars?
BYD cars are manufactured by BYD Auto Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of BYD Company Limited. BYD Auto is responsible for the design, production, and sale of BYD’s electric and hybrid vehicles. The cars are produced in several factories across China and at various international locations, reflecting BYD’s global manufacturing capabilities. The company also develops and produces all critical components of its vehicles, such as batteries, electric motors, and powertrains in-house, ensuring complete control over the production process.
Is BYD state-owned?
No, BYD is not a state-owned enterprise. It is a privately held company, but it does have significant backing from Chinese state-owned entities in certain areas, such as investment and policy support related to green technologies. While BYD has received government incentives for its clean energy efforts, it operates independently as a publicly traded company on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. The company’s leadership remains largely in the hands of its founder and private shareholders.
Why did Berkshire sell BYD?
Berkshire Hathaway did not entirely sell its stake in BYD, but it has reduced its ownership over the years. Berkshire Hathaway originally invested in BYD in 2008, and their stake grew significantly. However, in 2022, Berkshire Hathaway sold some of its shares in BYD to diversify its portfolio. Despite this reduction, the firm still holds a significant minority stake in the company. Berkshire’s decision was primarily driven by the goal of rebalancing its portfolio and capitalizing on profits from its successful investment in BYD, rather than signaling a complete exit from the company.
Who is the largest shareholder of BYD?
Wang Chuanfu, the founder, is the largest shareholder. He owns about 17% of the company and leads it as chairman and CEO.
Does Warren Buffett still own BYD?
Yes, Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway still holds a major stake in BYD, although it has reduced its position slightly over the years. The current holding is around 6-8%.
Is BYD a Chinese state-owned company?
No, BYD is a privately owned company. However, Chinese state funds are minority shareholders.
Is BYD bigger than Tesla?
In terms of vehicle sales, BYD surpassed Tesla in global EV sales in 2023. However, Tesla still has a larger global market capitalization.

