Apple Inc., is a globally renowned technology company known for its innovative products like the iPhone, iPad, and Mac. Given its prominence, many are curious about who owns Apple and the structure of its ownership.
Whether you’re an investor, a tech enthusiast, or a financial analyst, this blog post dives deep into the details of Apple’s shareholder structure, who owns Apple, its major players, and who ultimately holds power within the company.
History of Apple
Apple Inc. was founded on April 1, 1976, by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne in Los Altos, California. The company started in Jobs’ parents’ garage with the vision of making computers accessible to individuals, not just businesses and large institutions.
Early Years (1976–1980)
Apple’s first product was the Apple I, a hand-built computer designed by Steve Wozniak. Unlike later models, it lacked a monitor, keyboard, and case. Jobs saw the potential for selling a more user-friendly version and convinced Wozniak to refine the design. This led to the Apple II, launched in 1977. It became one of the first mass-market personal computers, featuring color graphics and an easy-to-use design. The success of Apple II made Apple a major player in the industry.
In 1978, Apple secured venture capital funding and rapidly grew. By 1980, it went public, raising over $100 million, one of the largest IPOs of that time.
The Macintosh Revolution (1981–1990)
Apple continued innovating with new computers, but competition increased. In 1983, the company introduced the Lisa computer, one of the first with a graphical user interface (GUI). However, it was expensive and failed commercially.
In 1984, Apple launched the Macintosh, featuring a GUI, mouse, and compact design. The famous “1984” Super Bowl ad positioned it as a revolutionary product. Though initially successful, Mac sales struggled against IBM PCs and Microsoft’s growing influence.
Tensions grew between Jobs and Apple’s board, leading to Jobs’ resignation in 1985. He went on to start NeXT, a company that would later play a crucial role in Apple’s revival.
Struggles and Near Bankruptcy (1990–1997)
Without Jobs, Apple struggled with internal conflicts and poor product decisions. Microsoft’s Windows operating system dominated the market, and Apple failed to compete effectively. During the mid-90s, Apple’s expensive and fragmented product lineup hurt its reputation.
By 1996, Apple was near bankruptcy. In a desperate move, it acquired NeXT for $429 million, bringing Steve Jobs back to the company as an advisor.
The Steve Jobs Era and the iPod Revolution (1997–2010)
Jobs quickly took control, becoming interim CEO in 1997. He simplified Apple’s product lineup and introduced the iMac in 1998, a stylish all-in-one computer that revived the company.
In 2001, Apple launched the iPod, a portable music player that transformed the industry. The same year, it opened the first Apple Store, providing a unique retail experience.
The real turning point came in 2007 with the launch of the iPhone. Combining a phone, music player, and internet device, the iPhone revolutionized technology. Apple followed with the App Store in 2008, further strengthening its ecosystem.
Modern Era and Continued Growth (2011–Present)
In 2011, Steve Jobs stepped down due to health issues and passed away later that year. Tim Cook took over as CEO. Under Cook, Apple continued expanding, launching the iPad, Apple Watch, AirPods, and new iPhone models.
Today, Apple is one of the world’s most valuable companies, with a market capitalization exceeding $3 trillion. It dominates multiple tech industries, including smartphones, personal computing, and digital services. Apple’s history is a story of innovation, struggle, and resurgence, making it one of the most influential companies of all time.
Who Owns Apple?
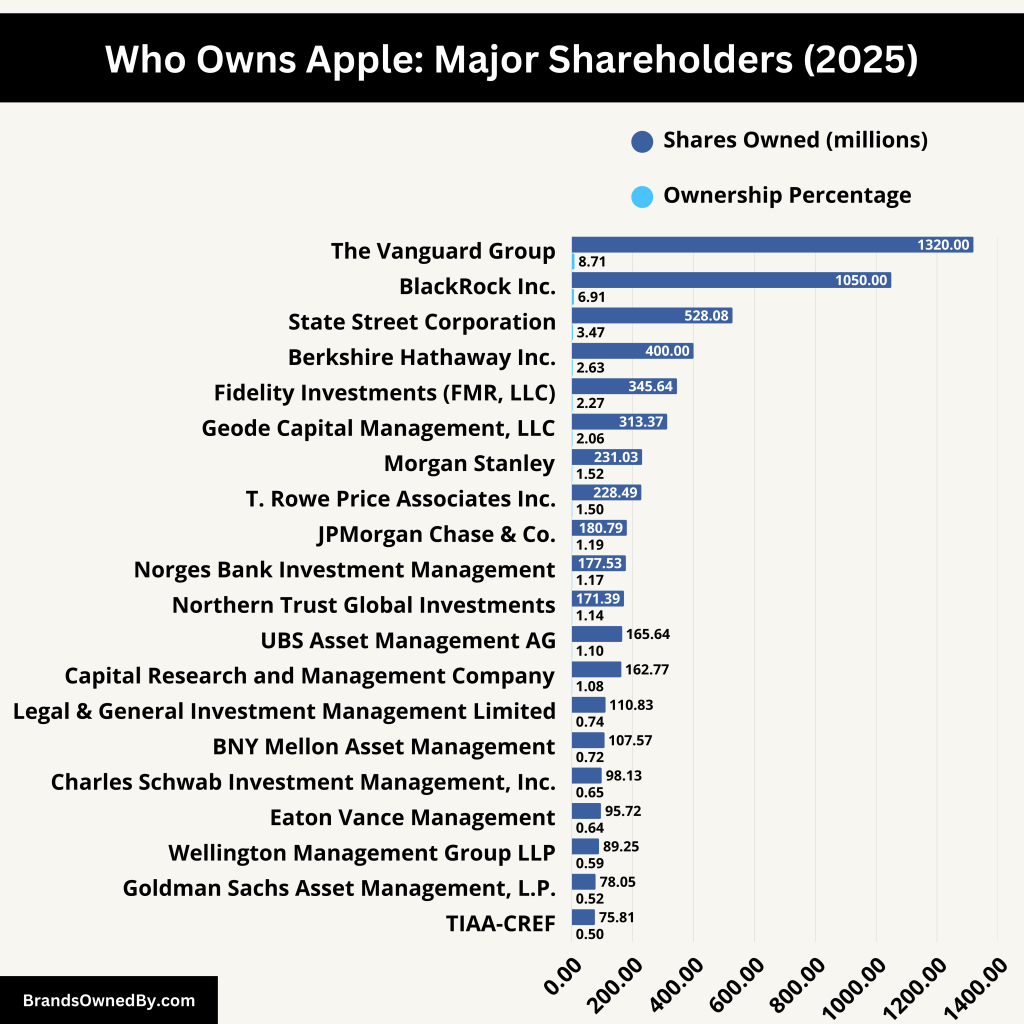
The ownership of Apple is defined by a complex structure of institutional investors, mutual funds, and individual stakeholders. However, institutional investors and mutual funds dominate the shareholder landscape, owning the vast majority of Apple shares.
The company’s largest shareholder is The Vanguard Group, a major asset management firm that owns approximately 8.71% of Apple, equating to billions of dollars in company value. Other institutional investors like BlackRock Inc. also hold significant stakes.
Institutional investors typically purchase large quantities of shares making them key stakeholders in Apple. These shares are often part of retirement and index funds, meaning that individual investors indirectly invest in Apple through their 401(k)s or mutual funds.
Major Apple Shareholders
Here’s a breakdown of Apple’s major shareholders, their percentage ownership, and their influence on the company:
| Shareholder | Shares Owned (millions) | Ownership Percentage |
|---|
| The Vanguard Group | 1,320 | 8.71% |
| BlackRock Inc. | 1,050 | 6.91% |
| State Street Corporation | 528.08 | 3.47% |
| Berkshire Hathaway Inc. | 400 | 2.63% |
| Fidelity Investments (FMR, LLC) | 345.64 | 2.27% |
| Geode Capital Management, LLC | 313.37 | 2.06% |
| Morgan Stanley | 231.03 | 1.52% |
| T. Rowe Price Associates Inc. | 228.49 | 1.50% |
| JPMorgan Chase & Co. | 180.79 | 1.19% |
| Norges Bank Investment Management | 177.53 | 1.17% |
| Northern Trust Global Investments | 171.39 | 1.14% |
| UBS Asset Management AG | 165.64 | 1.10% |
| Capital Research and Management Company | 162.77 | 1.08% |
| Legal & General Investment Management Limited | 110.83 | 0.74% |
| BNY Mellon Asset Management | 107.57 | 0.72% |
| Charles Schwab Investment Management, Inc. | 98.13 | 0.65% |
| Eaton Vance Management | 95.72 | 0.64% |
| Wellington Management Group LLP | 89.25 | 0.59% |
| Goldman Sachs Asset Management, L.P. | 78.05 | 0.52% |
| TIAA-CREF (Teachers Insurance and Annuity Association-College Retirement Equities Fund) | 75.81 | 0.50% |
The Vanguard Group
The Vanguard Group is Apple’s largest shareholder, holding approximately 1.32 billion shares, which represents about 8.71% of the company. As a leading investment management company, Vanguard offers a range of mutual funds and ETFs. Its substantial stake in Apple underscores its confidence in the company’s long-term growth and stability.
BlackRock Inc.
BlackRock Inc. holds roughly 1.05 billion shares of Apple, accounting for about 6.91% ownership. As one of the world’s largest asset managers, BlackRock’s significant investment in Apple highlights the tech giant’s appeal to institutional investors seeking robust returns.
State Street Corporation
State Street Corporation owns approximately 528.08 million shares, representing around 3.47% of Apple’s outstanding shares. State Street is a major financial services firm, and its investment reflects a strategic position in a leading technology company.
Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
Berkshire Hathaway Inc., led by Warren Buffett, holds about 400 million shares of Apple, equating to a 2.63% stake. Berkshire’s investment in Apple has been one of its most profitable, with the stake valued at approximately $89 billion. This investment signifies Buffett’s recognition of Apple’s strong brand and consistent performance.
Fidelity Investments (FMR, LLC)
Fidelity Investments, through FMR, LLC, owns around 345.64 million shares of Apple, representing about 2.27% ownership. As a multinational financial services corporation, Fidelity’s stake in Apple aligns with its strategy of investing in high-performing companies.
Geode Capital Management, LLC
Geode Capital Management holds approximately 313.37 million shares, accounting for about 2.06% of Apple’s shares. Geode is known for providing investment management services, and its holding in Apple reflects its focus on stable and profitable enterprises.
Morgan Stanley
Morgan Stanley owns about 231.03 million shares of Apple, representing a 1.52% stake. As a leading global financial services firm, Morgan Stanley’s investment indicates its confidence in Apple’s market position and future prospects.
T. Rowe Price Associates Inc.
T. Rowe Price holds approximately 228.49 million shares, equating to about 1.50% ownership in Apple. This investment aligns with T. Rowe Price’s strategy of investing in companies with strong growth potential.
JPMorgan Chase & Co.
JPMorgan Chase & Co. owns around 180.79 million shares of Apple, representing about 1.19% of the company’s shares. As a leading global financial services firm, JPMorgan’s stake in Apple underscores its confidence in the company’s performance and future growth.
Norges Bank Investment Management
Norges Bank Investment Management holds approximately 177.53 million shares, accounting for about 1.17% of Apple’s shares. This investment reflects the Norwegian sovereign wealth fund’s strategy of investing in globally influential companies.
Northern Trust Global Investments
Northern Trust Global Investments holds approximately 171.39 million shares of Apple, representing about 1.14% ownership. As a global asset management firm, Northern Trust’s investment underscores its confidence in Apple’s market position and future prospects.
UBS Asset Management AG
UBS Asset Management AG owns around 165.64 million shares, accounting for approximately 1.10% of Apple’s outstanding shares. UBS’s significant stake reflects its strategic investment in leading technology companies.
Capital Research and Management Company
Capital Research and Management Company holds about 162.77 million shares, equating to roughly 1.08% ownership in Apple. This investment aligns with its focus on companies demonstrating strong growth potential.
Legal & General Investment Management Limited
Legal & General Investment Management Limited possesses approximately 110.83 million shares, representing around 0.74% of Apple’s shares. As one of Europe’s largest asset managers, its stake in Apple highlights the company’s global appeal to institutional investors.
Bank of New York Mellon (BNY) Asset Management
BNY Asset Management holds about 107.57 million shares, accounting for approximately 0.72% ownership in Apple. This investment reflects BNY’s strategy of investing in high-performing technology firms.
Charles Schwab Investment Management, Inc.
Charles Schwab Investment Management owns around 98.13 million shares, representing about 0.65% of Apple’s outstanding shares. This stake underscores Charles Schwab’s confidence in Apple’s continued innovation and market leadership.
Eaton Vance Management
Eaton Vance Management holds approximately 95.72 million shares, equating to roughly 0.64% ownership in Apple. As a prominent investment management firm, Eaton Vance’s investment signifies its belief in Apple’s long-term growth trajectory.
Wellington Management Group LLP
Wellington Management Group LLP possesses about 89.25 million shares, representing around 0.59% of Apple’s shares. This stake aligns with Wellington’s strategy of investing in companies with strong fundamentals and growth prospects.
Goldman Sachs Asset Management, L.P.
Goldman Sachs Asset Management holds approximately 78.05 million shares, accounting for about 0.52% ownership in Apple. As a leading global investment management firm, Goldman’s stake reflects its confidence in Apple’s market position.
Teachers Insurance and Annuity Association-College Retirement Equities Fund (TIAA-CREF)
TIAA-CREF owns around 75.81 million shares, equating to roughly 0.50% of Apple’s outstanding shares. This investment highlights TIAA-CREF’s commitment to including stable and profitable companies in its portfolio.
Who Controls Apple?
Apple Inc. is a publicly traded company, meaning its control is shared among various stakeholders, including shareholders, the board of directors, and the executive leadership team. While no single individual has absolute control, decision-making power is concentrated within Apple’s leadership structure.
Board of Directors
Apple’s board of directors oversees the company’s strategic direction, approves major corporate decisions, and ensures that executive management acts in the best interest of shareholders. The board consists of prominent business leaders, each bringing expertise in various fields.
Some key members include:
- Arthur D. Levinson (Chairman) – Former CEO of Genentech, serving as Apple’s chairman since 2011. He plays a critical role in guiding the company’s long-term vision.
- Tim Cook (CEO & Director) – As Apple’s CEO and a board member, Cook influences strategic and operational decisions while managing the company’s day-to-day affairs.
- Al Gore (Director) – Former U.S. Vice President, contributing expertise in sustainability and policy matters.
- Other Directors – The board includes executives from major industries, such as Susan L. Wagner (co-founder of BlackRock) and James Bell (former CFO of Boeing).
Executive Leadership Team
The executive team, led by Tim Cook, controls Apple’s daily operations and strategic initiatives. This group is responsible for innovation, financial growth, and global expansion.
- Tim Cook (Chief Executive Officer) – Cook took over as CEO in 2011 following Steve Jobs’ resignation. He oversees all major business decisions and corporate strategy. Under his leadership, Apple has expanded into services, artificial intelligence, and augmented reality.
- Luca Maestri (Chief Financial Officer) – Manages Apple’s financial health, investments, and shareholder relations.
- Jeff Williams (Chief Operating Officer) – Oversees Apple’s global supply chain, manufacturing, and logistics. He is also involved in product development.
- Craig Federighi (Senior VP of Software Engineering) – Leads iOS, macOS, and software innovation, playing a crucial role in Apple’s ecosystem.
- John Ternus (Senior VP of Hardware Engineering) – Responsible for designing and engineering Apple’s hardware products, including iPhones, iPads, and Macs.
Major Shareholders’ Influence
Institutional investors, such as The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and Berkshire Hathaway, hold significant shares in Apple. While these investors do not directly control daily operations, their voting power influences major corporate decisions, including leadership appointments and strategic changes.
Tim Cook’s Role in Control
Although Apple is not controlled by a single individual, Tim Cook wields considerable influence as CEO. His decisions shape product innovation, corporate policies, and expansion strategies. He also represents Apple’s interests in dealings with governments, suppliers, and industry partners.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Apple
As of February 28, 2025, Apple’s 12-month trailing revenue was approximately $391.04 billion with a net income of about $93.74 billion.
In the fiscal year ending September 28, 2024, Apple reported a revenue of $391 billion, marking a 2% increase from the previous year.
The breakdown of Apple’s revenue by product category for this period is as follows:
- iPhone: $201.2 billion (51% of total revenue)
- Services: $96.2 billion (25%)
- Wearables, Home, and Accessories: $37.0 billion (9%)
- Mac: $30.0 billion (8%)
- iPad: $26.7 billion (7%)
In the first quarter of fiscal year 2025, which ended on December 28, 2024, Apple achieved a quarterly revenue of $124.3 billion, representing a 4% year-over-year growth. The net income for this quarter was approximately $36.33 billion, up from $33.92 billion in the same quarter the previous year.
The net worth or market capitalization of Apple as of March 2025 stood at roughly $3.61 trillion reflecting its substantial net worth.
Below is a breakdown of Apple’s historical revenue with YoY:
| Fiscal Year | Annual Revenue (in billions USD) | YoY Growth (%) |
|---|
| 2024 | 391.04 | +2.02 |
| 2023 | 383.28 | -2.80 |
| 2022 | 394.33 | +7.79 |
| 2021 | 365.82 | +33.26 |
| 2020 | 274.52 | +5.51 |
| 2019 | 260.17 | -2.04 |
| 2018 | 265.60 | +15.86 |
| 2017 | 229.23 | +6.30 |
| 2016 | 215.64 | -7.73 |
| 2015 | 233.72 | +27.86 |
| 2014 | 182.80 | +6.95 |
| 2013 | 170.91 | +9.20 |
| 2012 | 156.51 | +44.58 |
| 2011 | 108.25 | +65.96 |
| 2010 | 65.22 | +52.02 |
Apple’s Market Share and Competitors
Apple Inc. holds a significant position in the global smartphone market, competing with several key players. As of the second quarter of 2024, Apple secured a 17.7% share of the global smartphone market. In the United States, Apple’s dominance is more pronounced, with a 57.39% market share as of September 2024.
The company’s main competitors include:
Samsung
Samsung is Apple’s primary competitor in the smartphone industry. In the second quarter of 2024, Samsung led the global market with an 18.3% share, slightly ahead of Apple’s 17.7%. In the U.S., Samsung holds a 23.27% market share as of September 2024, making it the second-largest player in that market. Samsung’s diverse product lineup, spanning various price points, contributes to its substantial market presence.
Xiaomi
Xiaomi has emerged as a formidable competitor, particularly in Asian markets. In 2023, Xiaomi held a 12.5% global market share, with 145.9 million units sold. The company’s strategy of offering feature-rich smartphones at competitive prices has fueled its rapid growth and appeal among cost-conscious consumers.
Oppo
Oppo is another significant player in the global smartphone market. In 2023, Oppo captured an 8.8% market share, selling 103.1 million units. Known for its innovative camera technology and sleek designs, Oppo has gained a strong foothold, particularly in Asian markets.
Vivo
Vivo, like Oppo, has established a notable presence in the smartphone industry. In 2023, Vivo accounted for 8.2% of the global market share, with 99.0 million units sold. The company’s focus on high-quality audio and photography features has resonated with a broad consumer base.
Google’s Pixel smartphones have carved out a niche in the market. As of September 2024, Google holds a 4.97% market share in the U.S. The Pixel series is renowned for its pure Android experience and advanced camera capabilities, appealing to users seeking seamless integration with Google’s ecosystem.
Motorola
Motorola maintains a presence in the U.S. smartphone market with a 3.59% share as of September 2024. The brand’s focus on budget-friendly and mid-range devices has attracted consumers looking for reliable performance without a premium price tag.
Xiaomi (U.S. Market)
In the U.S., Xiaomi holds a smaller market share of 1.86% as of September 2024. While its presence is limited compared to other regions, Xiaomi continues to expand its footprint by offering competitively priced devices with robust features.
Companies Owned by Apple
Apple Inc. owns several companies, brands, and subsidiaries, each playing a vital role in its ecosystem. These brands contribute to Apple’s dominance in hardware, software, and services.
Below are some of Apple’s key brands and companies:
Beats by Dre
Apple acquired Beats Electronics in 2014 for $3 billion, marking one of its largest acquisitions. The brand, founded by Dr. Dre and Jimmy Iovine, specializes in premium audio products, including headphones, earphones, and speakers. Apple has integrated Beats technology into its ecosystem, and while the Beats brand continues to exist, many of its innovations have influenced Apple’s AirPods lineup.
Shazam
Shazam, a popular music identification app, was acquired by Apple in 2018 for $400 million. The app allows users to identify songs, movies, and advertisements by analyzing audio snippets. Apple integrated Shazam’s technology into Siri and Apple Music, making it easier for users to discover music seamlessly.
Dark Sky
Apple acquired Dark Sky, a highly accurate weather forecasting app, in 2020. The company integrated Dark Sky’s technology into the Apple Weather app, significantly improving its real-time and hyper-local weather data. Apple officially shut down the standalone Dark Sky app in 2023 after fully merging its features into its default Weather application.
PrimeSense
PrimeSense, an Israeli technology company specializing in 3D sensing and motion tracking, was acquired by Apple in 2013 for $360 million. Its technology played a crucial role in developing Face ID and ARKit, which power Apple’s facial recognition and augmented reality capabilities on iPhones and iPads.
AuthenTec
Apple acquired AuthenTec in 2012 for $356 million, focusing on fingerprint recognition technology. This acquisition led to the development of Touch ID, first introduced on the iPhone 5s in 2013. While Face ID has largely replaced Touch ID on newer devices, fingerprint recognition remains in use on some iPads and MacBooks.
Beddit
Beddit, a sleep-tracking company, was acquired by Apple in 2017. Its technology has been incorporated into Apple’s Health app and Apple Watch sleep tracking features. Apple discontinued Beddit’s standalone hardware in 2022 but continues using its research to improve sleep monitoring on Apple devices.
Claris International (formerly FileMaker Inc.)
Claris International, a wholly owned Apple subsidiary, develops FileMaker, a relational database software used for business applications. The brand continues to operate independently, catering to businesses and organizations that require database management solutions.
Anobit
Apple purchased Anobit, an Israeli flash memory technology company, in 2011 for $500 million. The acquisition improved Apple’s NAND flash storage technology, enhancing performance and efficiency in iPhones, iPads, and MacBooks.
Apple Pay and Financial Services
Apple’s financial services, including Apple Pay, Apple Card, and Apple Pay Later, are part of its growing fintech ecosystem. Although Apple partners with banks like Goldman Sachs, these services are integral to Apple’s brand and are expanding into digital banking solutions.
Mobeewave
Apple acquired Mobeewave, a Canadian startup specializing in contactless payments, in 2020 for $100 million. This acquisition has allowed Apple to develop tap-to-pay features, enabling iPhones to accept payments without additional hardware.
NextVR
NextVR, a virtual reality company specializing in sports and entertainment experiences, was acquired by Apple in 2020. Its technology has contributed to Apple’s Vision Pro headset and the development of spatial computing applications.
Swell
Apple acquired Swell, a podcast discovery platform, in 2014 for $30 million. The acquisition helped improve Apple Podcasts, enhancing its recommendation algorithms and user experience.
Akonia Holographics
Akonia Holographics, a company specializing in augmented reality (AR) lenses, was acquired by Apple in 2018. This acquisition played a role in the development of Apple Vision Pro, Apple’s first mixed-reality headset.
Camel Audio
Apple acquired Camel Audio, a music software company, in 2015. Its technology has been integrated into Logic Pro and GarageBand, enhancing Apple’s professional music production tools.
Drive.ai
Apple acquired Drive.ai, an autonomous vehicle startup, in 2019. This acquisition strengthened Apple’s Project Titan, its secretive self-driving car initiative, which focuses on developing autonomous vehicle technology.
Spaces
Spaces, a virtual reality startup, was acquired by Apple in 2020. The company’s expertise in immersive VR experiences has been incorporated into Apple’s AR/VR initiatives, particularly with the development of Vision Pro.
Final Thoughts
Understanding who owns and controls Apple provides valuable insights into how this tech giant functions. With institutional investors like The Vanguard Group and BlackRock holding significant stakes, and visionary leadership from Tim Cook and Apple’s Board, the company remains a pioneer and market leader.
For investors, Apple represents a robust and lucrative opportunity in the tech world, offering stability, innovation, and potential long-term growth.
Are you passionate about investing and analyzing companies like Apple? Stay informed about market trends to make the most of opportunities by following our blog.
FAQs
Who is Apple’s largest shareholder?
The Vanguard Group is the largest shareholder of Apple, owning approximately 8.36% of the company.
Does Tim Cook own Apple?
No, Tim Cook is Apple’s CEO and holds shares in the company, but ownership is divided among institutional investors and other shareholders.
How much of Apple does Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway own?
Berkshire Hathaway owns about 5.57% of Apple, making it one of the company’s largest shareholders.
Who controls Apple’s decisions?
Apple’s Board of Directors and executive team, led by CEO Tim Cook, control the company’s strategic and operational decisions, with input from major shareholders during meetings.
What is Apple’s market share in the global smartphone market?
Apple holds approximately 20% of the global smartphone market share, making it one of the top players alongside Samsung.
Who was Apple’s first CEO?
Apple’s first official CEO was Michael Scott, who led the company from 1977 to 1981. Steve Jobs later became the most famous Apple CEO, taking over in 1997 and transforming the company with products like the iMac, iPhone, and iPad.
Does Apple make its own chips?
Yes, Apple designs its own chips, including the M-series chips for MacBooks and A-series chips for iPhones. These chips have improved performance and efficiency, reducing Apple’s reliance on third-party suppliers like Intel.

