Curious to know the list of companies owned by Elon Musk? Well, he owns quite a few companies and much more…
Elon Musk owns multiple companies including Tesla, SpaceX, The Boring Company, SolarCity, and many others.
He is an inventor and investor who has made great strides in the fields of technology and space exploration.
He is most famous for his founding roles at companies such as Tesla Motors, SpaceX, The Boring Company, Neuralink, OpenAI, and SolarCity.
Musk’s vision for Tesla Motors focuses on accelerating the world’s transition to renewable energy with electric cars, solar panels, and home batteries.
This article explores the companies that Elon Musk owns or has invested in.
Let’s find out what companies he owns…
Who is Elon Musk?

Elon Musk is one of the most influential and controversial figures in modern technology and business. A billionaire entrepreneur, inventor, and industrial designer, Musk is best known for founding companies that challenge conventional industries—from space travel to electric vehicles. His bold vision, outspoken nature, and groundbreaking ventures have made him a global icon and a subject of intense media interest.
Early Life and Background
Elon Reeve Musk was born on June 28, 1971, in Pretoria, South Africa. He developed an early interest in computers and technology. By age 12, he had created and sold a video game. After attending high school in South Africa, Musk moved to Canada and later the United States, where he pursued higher education at the University of Pennsylvania.
He earned degrees in both physics and economics before dropping out of a PhD program at Stanford to dive into the startup world.
First Ventures: Zip2 and PayPal
Elon’s first major company was Zip2, an online city guide software provider, which he co-founded with his brother Kimbal in 1996. Compaq acquired Zip2 in 1999 for $307 million.
He then co-founded X.com, an online banking platform that later became PayPal after a merger. PayPal was acquired by eBay in 2002 for $1.5 billion in stock, giving Musk his first major fortune.
Founding of SpaceX: Making Space Travel Affordable
In 2002, Musk launched Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) with the aim of reducing space travel costs and enabling human colonization of Mars. Initially met with skepticism, SpaceX became the first private company to send a spacecraft to the International Space Station in 2012.
Today, SpaceX is a leading aerospace innovator, known for reusable rockets like the Falcon 9 and ambitious projects like Starship and Starlink, a satellite internet service.
Tesla Inc.: Revolutionizing the Auto Industry
Musk joined Tesla Motors (now Tesla Inc.) in 2004 as chairman and later became CEO. Tesla’s mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Under Musk’s leadership, Tesla developed popular electric cars like the Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y.
Tesla has also invested in energy products, including solar panels and battery storage systems. Despite criticism over delays and production issues, Musk has turned Tesla into the world’s most valuable car company.
Other Ventures: Neuralink, The Boring Company, xAI
Musk’s interests go beyond space and electric cars. He founded Neuralink in 2016 to develop brain-machine interfaces. The goal is to merge the human brain with AI to treat neurological conditions and potentially enhance human capabilities.
In 2017, he launched The Boring Company, which focuses on tunneling and infrastructure to reduce traffic congestion in urban areas.
In 2023, Musk founded xAI, an artificial intelligence company meant to challenge the dominance of OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and others. xAI works closely with Musk’s other companies, particularly X (formerly Twitter).
Acquisition of Twitter: A Bold Move in Social Media
In 2022, Musk acquired Twitter Inc. for $44 billion, citing the need to protect free speech and reform the platform. He rebranded the platform as X and has since implemented sweeping changes, including staff cuts, new monetization strategies, and algorithmic updates. His approach to Twitter has attracted both praise and criticism.
Net Worth and Global Influence
Elon Musk is consistently ranked among the richest people in the world. His net worth fluctuates with the value of Tesla stock, but it often exceeds $200 billion. Musk’s influence spans technology, finance, space exploration, social media, and public policy. He is a polarizing figure—praised for his ambition, but often criticized for his social media behavior and management style.
Advisory Role in the Trump Administration
In 2025, Elon Musk’s relationship with President Donald Trump was marked by both collaboration and conflict. After Trump’s re-election, Musk was appointed as a senior advisor to a new initiative called the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), alongside Vivek Ramaswamy. This role was intended to bring Musk’s private-sector expertise into streamlining federal bureaucracy. However, despite Trump stating that Musk was “in charge” of DOGE, the White House later clarified that Musk held no formal authority and could only advise the President.
Tensions escalated when Musk publicly opposed Trump’s sweeping trade tariffs, which significantly impacted tech and automotive sectors, including Tesla. Musk argued for free trade and criticized the administration’s policies for harming American innovation and increasing costs. His efforts to persuade Trump to change course were unsuccessful, and Tesla’s stock value suffered amid broader economic ripple effects. While Musk’s involvement with the administration initially suggested alignment, their conflicting views on key economic policies revealed deeper divisions.
List of Companies Owned by Elon Musk
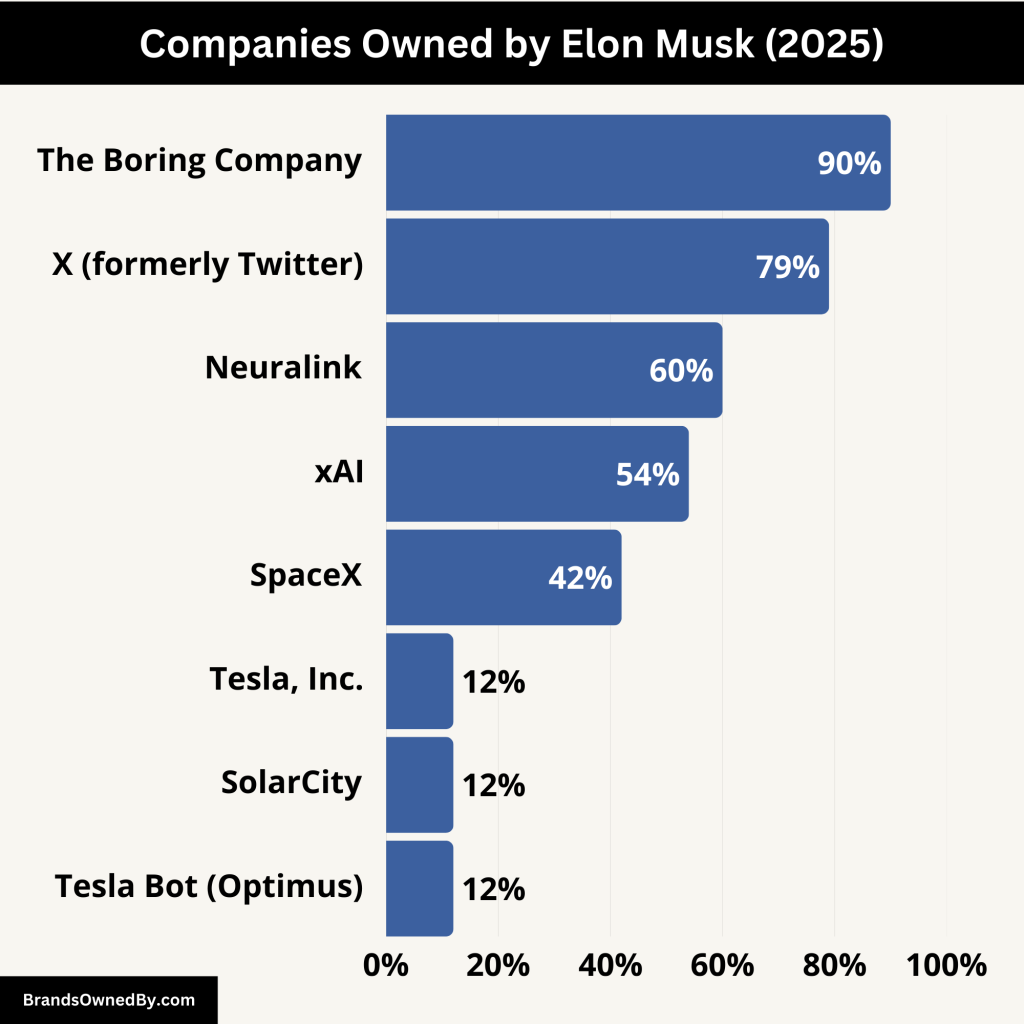
Here’s a list of companies owned by Elon Musk including businesses he has invested in or has been associated with:
| Company | Status | Musk’s Estimated Stake | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla, Inc. | Public | ~12% | CEO and Product Architect; largest individual shareholder |
| SpaceX | Private | ~42% (majority voting control) | CEO and Chief Engineer; dominant commercial space company |
| X (formerly Twitter) | Private | ~79% | Owner and Executive Chairman; fully privatized social platform |
| Neuralink | Private | ~60% | Co-founder; developing brain-computer interface technology |
| The Boring Company | Private | ~90%+ | Founder; focused on tunnel infrastructure and transit |
| xAI | Private | Undisclosed (majority expected) | Founder; developing truth-seeking AI, creator of Grok |
| SolarCity | Acquired by Tesla | Indirect via Tesla (~12%) | Merged into Tesla Energy in 2016 |
| Zip2 Corporation | Acquired (Sold in 1999) | 0% | Co-founder; sold to Compaq |
| X.com / PayPal | Acquired (Sold in 2002) | 0% | Founder of X.com; merged to become PayPal, sold to eBay |
| DeepMind | Investment (Rumored) | Unknown | Unconfirmed early investment or acquisition interest |
| Halcyon Molecular | Past Investment | Unknown (company shut down) | Early-stage biotech startup; now defunct |
| Vicarious | Past Investment | Passive investor (undisclosed) | AI startup; acquired by Alphabet’s Intrinsic |
| Thud | Defunct (funded project) | Initially 100% → 0% | Funded by Musk but later dropped ownership |
| Hyperloop | Concept (Open source) | 0% | Created and open-sourced idea; no ownership in Hyperloop companies |
| Dogecoin | Cryptocurrency | 0% (but significant influence) | No formal stake; public support influences adoption and price |
| Tesla Bot (Optimus) | Tesla Subdivision | ~12% (via Tesla) | Humanoid robot project under Tesla |
Tesla, Inc.
Tesla was founded in 2003 by engineers Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, but Elon Musk joined shortly after as lead investor during its Series A funding round in 2004. Since then, Musk has become the public face of the company and serves as its CEO and Product Architect.
As of 2024, Musk owns around 12% of Tesla but remains its largest individual shareholder. Tesla is best known for its electric vehicles like the Model S, 3, X, Y, and Cybertruck.
Beyond cars, Tesla operates in solar energy, energy storage, and autonomous driving technology, making it a dominant force in sustainable energy and transportation.
SpaceX (Space Exploration Technologies Corp.)
Founded by Elon Musk in 2002 using proceeds from his PayPal sale, SpaceX aims to make space travel more affordable and ultimately enable human life on Mars. Musk serves as CEO and Chief Engineer, overseeing everything from rocket design to interplanetary missions.
Though privately held, SpaceX has raised billions in funding and is valued at over $180 billion. Musk reportedly owns about 42% of the company but retains majority voting control. SpaceX operates Starlink, a growing satellite internet service, and is pioneering the reusable rocket market with its Falcon 9 and Starship vehicles.
X (formerly Twitter)
In October 2022, Elon Musk acquired Twitter for $44 billion and subsequently rebranded it as “X” in 2023 to reflect his broader ambitions of turning it into an “everything app.” Musk currently owns around 79% of the company and holds the role of Executive Chairman.
Under his leadership, X has undergone significant changes including monetization programs for creators, reduced content moderation, and integrations with AI tools like Grok. He plans to expand X’s functionality into payments, messaging, and news aggregation.
Neuralink
Neuralink was co-founded by Elon Musk in 2016 with the aim of developing brain-computer interface technology that could help treat neurological disorders and, eventually, merge human cognition with artificial intelligence. Musk holds an estimated 60% stake and plays an active role in product vision.
Neuralink’s first implant, the N1 device, has been approved for human trials and is designed to help individuals with paralysis control devices with their thoughts. The long-term vision is to achieve a symbiosis between humans and AI.
The Boring Company
The Boring Company was launched by Elon Musk in 2016 as a solution to urban congestion. Frustrated with traffic in Los Angeles, Musk proposed building underground tunnels to create a new transportation system called “Loop.” Musk reportedly owns over 90% of the company. The Boring Company has completed small-scale tunnels in Las Vegas and is exploring similar projects in Texas and California. It also sells novelty products like flamethrowers and perfume, which Musk has used to fund early operations in unorthodox ways.
xAI (x Artificial Intelligence)
xAI is Elon Musk’s latest venture, launched in 2023 as a competitor to OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Anthropic. Created to build a “maximum truth-seeking AI,” xAI is developing language models designed to work closely with X (Twitter) and Tesla’s self-driving systems. Musk has not publicly disclosed his exact stake in xAI, but it’s presumed he holds a controlling interest. The company has already introduced Grok, a conversational AI integrated directly into the X platform. In 2024, xAI raised $6 billion, signaling serious intent to challenge Big Tech in the AI arms race.
Zip2 Corporation
Zip2 was Elon Musk’s first startup, founded in 1996 alongside his brother Kimbal. The company provided online business directories and maps for newspapers. Compaq (later HP) acquired Zip2 in 1999 for $307 million. Musk received $22 million from the deal, which he used to start his next venture, X.com. While Musk no longer owns Zip2, it marked the beginning of his entrepreneurial path.
X.com and PayPal
X.com was founded by Musk in 1999 as an online financial services platform. It later merged with Confinity, the company behind PayPal, and shifted its focus to payments. Musk was briefly CEO before being ousted in a boardroom shake-up. In 2002, eBay acquired PayPal for $1.5 billion, earning Musk about $180 million. While he no longer owns PayPal, the experience shaped his future in fintech and startups. Musk later repurchased the X.com domain in 2017, indicating its lasting symbolic value.
OpenAI (Former Association)
Although not an owner, Elon Musk was a co-founder of OpenAI in 2015, contributing funding and strategic direction during its early development. He stepped away from the organization in 2018 due to disagreements over its direction, particularly its partnership with Microsoft. Musk has since criticized OpenAI’s shift toward commercialization and used xAI to offer an open alternative. While not currently involved, his legacy at OpenAI remains significant.
SolarCity
SolarCity was co-founded in 2006 by Lyndon and Peter Rive, Elon Musk’s cousins, with Musk acting as chairman and initial funder. The company specialized in solar panel installation and was backed heavily by Musk, who saw solar as a crucial part of sustainable energy. In 2016, Tesla acquired SolarCity for $2.6 billion, effectively merging the two entities. Though controversial at the time, the acquisition helped Tesla launch Tesla Energy, integrating solar panels, solar roofs, and Powerwall battery storage into its business model.
DeepMind (Early Investor, Reported Interest)
While not officially confirmed, several reports suggest that Musk was either a very early backer or showed acquisition interest in DeepMind before it was acquired by Google in 2014. Musk has often cited DeepMind as one of the key reasons he grew concerned about AI safety, leading to his co-founding of OpenAI and later, xAI.
Halcyon Molecular (Past Investment)
Elon Musk invested in Halcyon Molecular, a biotech company founded in 2008 that aimed to make DNA sequencing cheaper and more efficient. While the company eventually shut down in 2012, it was part of Musk’s broader interest in transformative, science-based companies.
Vicarious (AI Startup, Past Investor)
Vicarious was an AI research startup focused on building general artificial intelligence. Musk was an early investor, alongside people like Mark Zuckerberg and Jeff Bezos. The company was later acquired by Alphabet’s Intrinsic in 2021. Musk’s involvement was passive, but it helped shape his views on AI safety and the need for aligned intelligence.
Thud (Media Company)
Thud was a short-lived satirical media venture launched in 2017 with funding from Elon Musk. It was founded by former Onion editors and was meant to be a platform for satirical content. Musk later distanced himself from the project due to creative differences, and the site was shut down after a brief existence.
Hyperloop (Concept, Not a Company)
While Musk doesn’t own Hyperloop as a formal company, he published a white paper in 2013 proposing the high-speed vacuum tube transport system. He open-sourced the idea, encouraging private companies like Virgin Hyperloop and HyperloopTT to develop it. The Boring Company has integrated some Hyperloop-like concepts into its Loop projects.
Dogecoin (Significant Influence)
Although not a company, Elon Musk has been a major public supporter and indirect promoter of Dogecoin. Through tweets and public commentary, he’s heavily influenced its market value and adoption. SpaceX and Tesla have both accepted Dogecoin for select merchandise, and Musk has hinted at using Dogecoin in X’s future payment infrastructure.
Tesla Bot (Optimus)
Tesla Bot, also known as Optimus, is a humanoid robot under development by Tesla. It isn’t a separate company, but the project reflects Musk’s broader ambitions to bring AI and robotics together. Optimus is part of Tesla’s internal roadmap to expand beyond vehicles into labor automation.
Elon Musk Net Worth
As of April 2025, Elon Musk has an estimated net worth of around $362.5 billion. This places him consistently among the top two richest people on Earth, often trading spots with Bernard Arnault and Jeff Bezos, depending on market shifts.
Composition of Musk’s Net Worth
Musk’s wealth is heavily tied to his equity holdings in the companies he leads. The breakdown is approximately as follows:
- Tesla, Inc.: By far his largest asset. Despite owning roughly 12% of Tesla’s shares, the company’s massive valuation—hovering around $500 billion—makes this stake worth over $60 billion. Tesla stock’s volatility has a major influence on Musk’s daily net worth.
- SpaceX: As a private company, SpaceX is valued at over $180 billion. Musk owns about 42%, which gives him a stake worth approximately $75 billion. SpaceX is expected to increase in value as Starlink expands and Starship advances toward commercial viability.
- X (formerly Twitter): Musk acquired Twitter for $44 billion in 2022 and now owns around 79% of the private company. Although its current estimated value has declined (ranging between $15 to $25 billion based on investor write-downs), Musk’s stake could be worth $12–20 billion depending on market perception and monetization progress.
- Other Ventures (Neuralink, The Boring Company, xAI): These private companies are not as large in valuation yet, but their future potential is considerable. Combined, his stakes across Neuralink, xAI, and The Boring Company may add $5 to $10 billion to his net worth, with xAI drawing increased investor attention after raising $6 billion.
- Cash & Other Investments: Musk is famously “cash-poor” in conventional terms, often borrowing against his stock holdings for liquidity. Still, he retains hundreds of millions in liquid assets, real estate, and cryptocurrency (particularly Dogecoin and Bitcoin, which he has acknowledged owning). His crypto holdings are volatile but add an estimated $500 million to $1 billion to his portfolio.
Volatility and Unique Financial Behavior
Elon Musk’s net worth is highly volatile. A single movement in Tesla stock or a funding round at SpaceX can increase or erase billions in hours. Unlike other billionaires who diversify or cash out, Musk rarely sells his holdings and instead leverages them as collateral to fund projects and personal expenses.
He has previously stated:
“I own no house. I’m literally staying at friends’ places. If my companies go bankrupt, so do I.”
This demonstrates Musk’s high-risk, high-conviction financial philosophy. His net worth is not simply a measure of stored wealth—it reflects the valuation of bold, long-term bets on humanity’s future.
Tax, Philanthropy, and Controversies
Musk has drawn attention for paying relatively little in income tax in some years, which he explains is due to borrowing rather than selling assets. He made headlines in 2021 by paying over $11 billion in taxes, likely the largest individual tax bill in U.S. history.
Philanthropically, Musk pledged to donate at least half of his wealth under the Giving Pledge. However, critics argue that his charitable donations have been limited relative to his net worth. That said, he has made large anonymous gifts to schools, science initiatives, and climate-focused causes, and he donated $5.7 billion worth of Tesla stock to an unnamed charity in 2021.
Final Thoughts
Elon Musk’s business empire is unlike any other. Spanning electric vehicles, AI, aerospace, neurotech, and infrastructure, his companies are built to tackle the world’s most pressing challenges.
Though ownership percentages vary, Musk maintains effective control across the board. Each venture reflects a part of his grander mission—to accelerate humanity’s transition to a multi-planetary, AI-integrated, sustainable future.
FAQs
What Are 3 Important Things About Elon Musk?
1. Elon Musk is a technology entrepreneur, investor, and engineer who has founded, co-founded, and led several companies.
2. He has a mission to revolutionize space technology with the ultimate goal of enabling people to live on other planets.
3. His companies have disrupted various industries such as electric car manufacturing, energy storage systems, and artificial intelligence research laboratory.
What’s Unique About Elon Musk?
Elon Musk looks at problems from a different perspective and solves them by taking bold risks. He revolutionized industries using innovative ideas and cutting-edge technologies.
How Did Elon Musk Become Successful?
Elon Musk became successful by taking risks, innovating, and having a clear vision for the future.
What is Elon Musk’s Main Goal?
Elon Musk’s main goal is to make humanity a multi-planetary species. He seeks to make space travel possible for everyone and plans to set up colonies on Mars.
What is Elon Musk’s Mindset?
Elon Musk has a “universe-centric” mindset as he looks at problems from a bigger perspective. Additionally, he takes calculated risks and recognizes failure as an opportunity to learn.
Why is Elon Musk so Popular?
Elon Musk founded companies that have revolutionized their respective industries such as Tesla and SpaceX.
How Did Elon Musk Impact the World?
Elon Musk has had a major impact on the world with his revolutionary ideas, incredible projects, and innovative technologies. Tesla and SpaceX have revolutionized their respective industries.
How Does Elon Musk Learn Things?
Elon Musk is a self-taught learner and quickly grasps concepts. He thinks out of the box to develop solutions, which have changed the world.
What is Elon Musk’s Genius?
Elon Musk’s genius lies in his ability to think differently and take risks that others would not dare. He is constantly pushing the boundaries of technology and coming up with new ideas.
What Can We Learn From Elon Musk?
Elon Musk is a great example of determination and courage to pursue your dreams. He has shown marvels of hard work, dedication, and an unwavering focus on the task at hand.
What is Elon Musk’s IQ Number?
Although Elon Musk’s exact IQ is unknown, it has been estimated to be around 155. This places him within the top 2% of the population when it comes to intelligence and creativity.
Is Elon Musk an Engineer?
Elon Musk is an entrepreneur and investor but not an engineer. He holds a Bachelor of Science degree in Physics from the University of Pennsylvania as well as a business degree.
How Many Degrees Does Elon Musk Have?
Elon Musk has five degrees: a Bachelor of Science degree in Physics from the University of Pennsylvania, two Bachelor of Arts degrees in Economics and Physics from the Wharton School of Business at the University of Pennsylvania, and two Master’s degrees in Applied Physics and Materials Science also from the University of Pennsylvania.
What Was Elon Musk’s First Job?
Elon Musk’s first job was as an intern at a software firm called Pinnacle Research Institute.
How Much Money Did Elon Musk Start With?
Elon Musk started his entrepreneurial journey with just $28,000, which he received from selling his first company called Zip2 Corporation.

