Tesla, Inc., founded in 2003, has revolutionized the automotive industry with its electric vehicles (EVs) and energy solutions. Understanding who owns Tesla provides insight into the company’s direction and governance.
Tesla History
Tesla began its journey in 2003, aiming to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. The company introduced its first car, the Roadster, in 2008, showcasing the potential of electric mobility.
Subsequent models like the Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y have solidified Tesla’s position in the EV market.
Beyond automobiles, Tesla has ventured into energy storage and solar energy products, broadening its impact on sustainable solutions.
Who Owns Tesla?
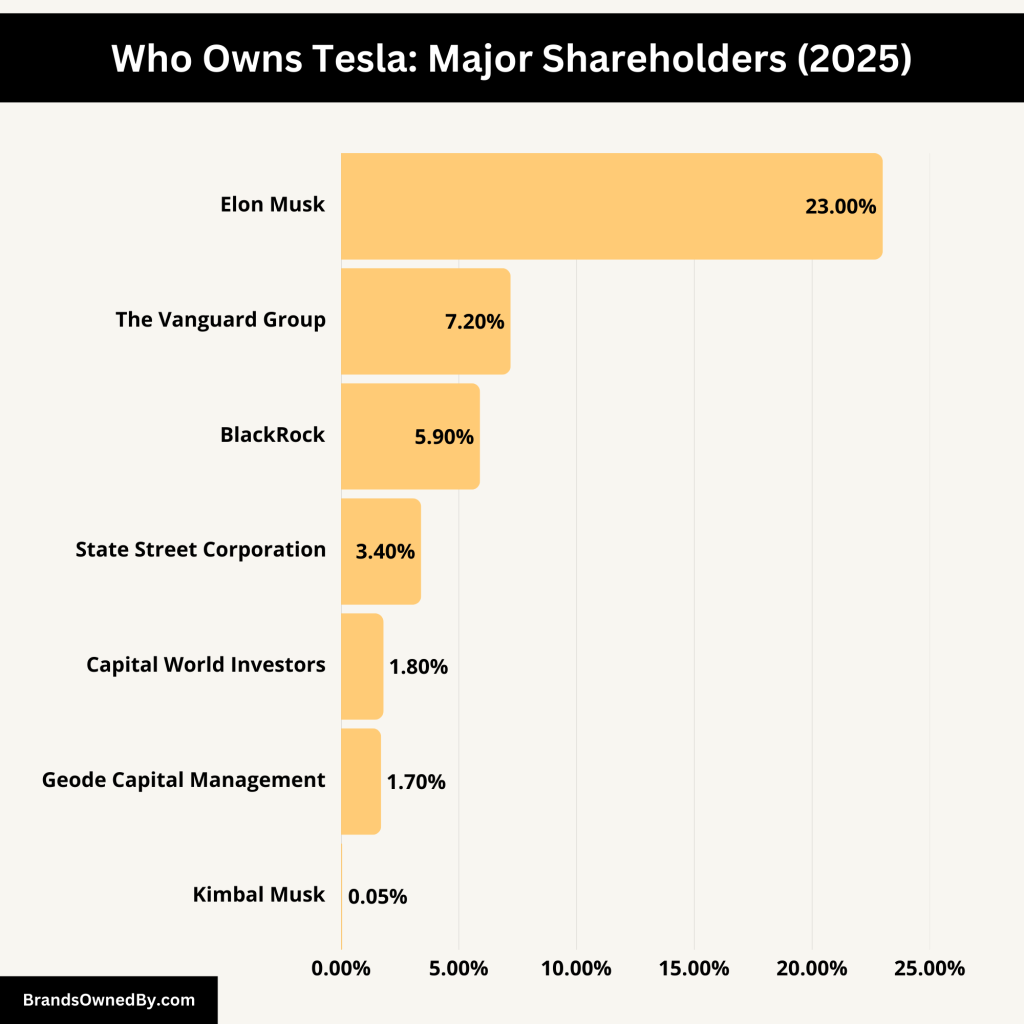
Tesla, Inc.’s ownership structure comprises both individual insiders and institutional investors, each playing a pivotal role in the company’s strategic direction and governance.
List of Tesla Shareholders
Here’s a list of the major individual and institutional shareholders and investors of Tesla:
| Shareholder | Role | Ownership Percentage | Shares Owned (Approx.) |
|---|
| Elon Musk | CEO & Co-founder | 23% | 715 million |
| Kimbal Musk | Board Member, Entrepreneur | 0.05% | 1.54 million |
| Vaibhav Taneja | Chief Financial Officer (CFO) | 0.003% | 108,965 |
| Tom Zhu | SVP of Automotive | 0.002% | 67,491 |
| Andrew Baglino | SVP of Powertrain & Energy Engineering | 0.001% | 31,230 |
| The Vanguard Group | Institutional Investor | 7.2% | 230 million |
| BlackRock | Institutional Investor | 5.9% | 188 million |
| State Street Corporation | Institutional Investor | 3.4% | 108 million |
| Geode Capital Management | Institutional Investor | 1.7% | 55.25 million |
| Capital World Investors | Institutional Investor | 1.8% | 59.35 million |
Elon Musk (Approximately 23%)
As Tesla’s CEO and co-founder, Elon Musk holds around 23% of the company’s shares, amounting to 715 million shares as of December 31, 2023. This substantial stake gives him significant influence over Tesla’s vision and operations.
Kimbal Musk (Approximately 0.05%)
Elon’s younger brother, Kimbal Musk, serves on Tesla’s Board of Directors. As of December 2024, he owned 1,538,220 shares, representing about 0.05% of Tesla’s outstanding stock. Beyond Tesla, Kimbal is an entrepreneur in the food and sustainability sector.
Vaibhav Taneja (Approximately 0.003%)
Appointed as Tesla’s Chief Financial Officer in August 2023, Vaibhav Taneja held 108,965 shares, approximately 0.003% of Tesla’s common stock as of December 2024. His financial expertise supports Tesla’s fiscal management and growth strategies.
Tom Zhu (Approximately 0.002%)
Serving as Senior Vice President of Automotive since April 2023, Tom Zhu owned 67,491 shares, about 0.002% of Tesla’s stock as of September 2024. He oversees Tesla’s global automotive operations, ensuring production efficiency and market expansion.
Andrew Baglino (Approximately 0.001%)
As Tesla’s Senior Vice President of Powertrain and Energy Engineering, Andrew Baglino held 31,230 shares as of April 2024, representing about 0.001% of Tesla’s stock. He plays a crucial role in Tesla’s battery development and energy solutions.
The Vanguard Group (Approximately 7.2%)
As of December 30, 2023, Vanguard Group held nearly 230 million shares of Tesla stock, accounting for about 7.2% of all outstanding shares. This investment reflects Vanguard’s confidence in Tesla’s long-term potential.
BlackRock (Approximately 5.9%)
BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, held 188 million shares of Tesla stock as of December 30, 2023, representing 5.9% of all Tesla shares. Their substantial stake signifies support for Tesla’s strategic initiatives.
State Street Corporation (Approximately 3.4%)
As the third-largest institutional shareholder, State Street held 108 million shares of Tesla, accounting for 3.4% of the total as of December 30, 2023. Their investment underscores State Street’s belief in Tesla’s market position.
Geode Capital Management (Approximately 1.7%)
Managing Fidelity Investments’ stock index funds, Geode owned 55,256,335 shares of Tesla stock, representing an ownership stake of more than 1.7% as of December 2024. Their investment highlights Tesla’s inclusion in major index funds.
Capital World Investors (Approximately 1.8%)
With a longstanding history in wealth management, Capital World owned 59,356,401 shares, about 1.8% of Tesla’s outstanding stock as of December 2024. This stake reflects their positive outlook on Tesla’s growth prospects.
Who Controls Tesla?
Tesla’s ownership structure is divided between individual and institutional shareholders. However, control over the company primarily rests in the hands of its leadership, board of directors, and key shareholders. These entities shape Tesla’s strategy, operations, and major decisions.
Tesla remains heavily controlled by Elon Musk. His large stake, combined with his position as CEO and influence over Tesla’s culture, gives him significant authority over the company’s direction.
Elon Musk: The Driving Force
Elon Musk, Tesla’s co-founder and CEO, is the most influential figure in the company. With a 23% stake, he holds the largest individual ownership. His vision and leadership define Tesla’s innovation, expansion, and market strategies.
Beyond shareholding, Musk’s influence extends through his role as CEO and product architect. He directly oversees critical areas such as vehicle development, battery technology, and artificial intelligence. His control over Tesla is reinforced by his ability to sway investor sentiment, market perception, and internal decision-making.
Board of Directors: Governance and Oversight
Tesla’s Board of Directors plays a crucial role in governing the company. The board ensures compliance, approves major strategic moves, and oversees executive performance. As of recent filings, the board includes:
- Robyn Denholm (Chairwoman) – Ensures Musk’s decisions align with shareholder interests.
- Kimbal Musk – Elon Musk’s brother and an advocate for Tesla’s sustainability goals.
- James Murdoch – Brings expertise in media and global business strategy.
- Ira Ehrenpreis & Kathleen Wilson-Thompson – Provide financial and operational oversight.
While Musk has significant sway, the board serves as a check on his power, ensuring corporate governance standards are met.
Institutional Investors: Indirect Influence
Tesla’s institutional shareholders, such as The Vanguard Group (7.2%) and BlackRock (5.9%), have a say in corporate matters through voting rights. These firms manage investments on behalf of millions of investors. Though they don’t dictate daily operations, their voting power in key resolutions—such as executive compensation and corporate policies—affects Tesla’s direction.
Retail Investors: A Decentralized Influence
Tesla has a large base of retail investors, who own shares individually through stock market purchases. While no single retail investor has major control, their collective voice impacts Tesla’s stock price and shareholder meetings. Many are loyal supporters of Musk’s vision, reinforcing his leadership.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Tesla
In the fiscal year 2024, Tesla reported revenues of approximately $97.7 billion, marking a 1% increase from the previous year.
As of March 2025, Tesla’s market capitalization stands at approximately $777 billion, reflecting a significant decline of nearly 49% from December 2024’s valuation of $1.54 trillion.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of Tesla’s historical revenue and YoY growth:
| Fiscal Year | Annual Revenue (USD) | YoY Growth (%) |
|---|
| 2015 | 4.05 billion | +26.50 |
| 2016 | 7.00 billion | +73.01 |
| 2017 | 11.76 billion | +67.98 |
| 2018 | 21.46 billion | +82.51 |
| 2019 | 24.58 billion | +14.52 |
| 2020 | 31.54 billion | +28.31 |
| 2021 | 53.82 billion | +70.67 |
| 2022 | 81.46 billion | +51.35 |
| 2023 | 96.77 billion | +18.80 |
| 2024 | 97.69 billion | +0.95 |
Tesla Market Share and Competitors
Tesla has been a dominant force in the EV market. However, its market share has seen some decline due to increased competition. In 2023, Tesla retained a 55% market share for electric vehicles, down from 62% in the previous year.
As of September 2024, Tesla held an 18% share of the global battery electric vehicle (BEV) market, slightly down from 19% in 2023.
This shift reflects the intensifying competition in the electric vehicle (EV) industry.
Competitors such as Ford, General Motors, and China’s BYD Company have introduced compelling EV models, intensifying market dynamics.
BYD Company Limited
BYD has emerged as a formidable competitor in the global EV market. Between January and May 2024, BYD sold approximately 625,596 units, capturing about 11% of total EV sales during that period.
The company’s diverse lineup, ranging from affordable models to luxury vehicles, has contributed to its rapid growth. BYD’s strong presence in China and its expansion into international markets have further solidified its position in the EV sector.
General Motors (GM)
General Motors has made significant strides in the EV market. In 2024, GM reported a 50% increase in EV sales year-over-year, reflecting its commitment to electrification.
The company’s investments in battery technology and plans to introduce a range of electric models across its brands indicate its strategic focus on capturing a larger share of the EV market.
Ford Motor Company
Ford has been proactive in its EV initiatives. The company reported a 38% increase in EV sales year-over-year in 2024.
Ford’s introduction of electric versions of its popular models, such as the Mustang Mach-E and the F-150 Lightning, has resonated with consumers and positioned the company as a strong competitor in the EV landscape.
Volkswagen Group
Volkswagen has been expanding its EV offerings through its ID series, aiming to become a leader in the global EV market. The company’s focus on scalable electric platforms and substantial investments in battery technology underscores its commitment to electrification.
Hyundai Motor Company
Hyundai, along with its subsidiary Kia, has introduced several successful EV models, such as the Hyundai Ioniq 5 and the Kia EV6. These models have received positive reviews for their design, performance, and affordability, contributing to Hyundai’s growing presence in the EV market.
Rivian Automotive
Rivian, a newer entrant in the EV market, focuses on electric trucks and SUVs. With backing from major investors and partnerships, Rivian has garnered attention for its innovative designs and commitment to sustainability.
Lucid Motors
Lucid Motors targets the luxury EV segment with its flagship model, the Lucid Air. Known for its impressive range and performance, Lucid aims to compete with high-end offerings from Tesla and other luxury automakers.
Brands Owned by Tesla
Tesla, Inc. has strategically acquired and developed several brands and subsidiaries to enhance its capabilities in electric vehicles, energy storage, and solar energy solutions. Below is an overview of these entities:
Tesla Energy
Tesla Energy is the clean energy division of Tesla, focusing on the development, manufacturing, and sale of solar energy generation systems and battery energy storage products.
Established on April 30, 2015, Tesla Energy offers products such as solar panels, the Solar Roof, the Powerwall (a home energy storage device), and the Megapack (a large-scale energy storage system). In 2024, Tesla Energy deployed 31.4 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of battery energy storage products, marking a 113% increase over 2023.
SolarCity
Founded in 2006 by Peter and Lyndon Rive, cousins of Elon Musk, SolarCity specializes in selling and installing solar energy systems for residential, commercial, and industrial customers.
In 2016, Tesla acquired SolarCity for approximately $2.6 billion, integrating it into Tesla Energy to bolster its solar energy offerings.
Maxwell Technologies Inc.
Maxwell Technologies, established in 1965, specialized in energy storage and power delivery products, notably ultracapacitors.
Tesla acquired Maxwell in 2019 for $207 million, aiming to leverage its technology to enhance electric vehicle performance and reduce production costs.
Grohmann Engineering GmbH
Grohmann Engineering, founded in 1963, specialized in automated manufacturing systems.
Tesla acquired the company in 2017 for $135.3 million, renaming it Tesla Grohmann Automation. This acquisition aimed to improve Tesla’s manufacturing efficiency and reduce production costs through advanced automation.
Perbix Machine Co. Inc.
Perbix, established in 1976, focused on designing and building custom automated manufacturing equipment. Tesla acquired Perbix in 2017 to further its goal of manufacturing process automation, allowing more vehicle parts to be produced in-house and enhancing production efficiency.
Conclusion
Tesla’s ownership structure is characterized by significant individual and institutional investments. Elon Musk’s substantial stake and leadership influence the company’s strategic direction. With a strong financial performance and a commitment to innovation, Tesla continues to navigate a competitive landscape, maintaining its role as a leader in sustainable energy solutions.
FAQs
Who is the largest shareholder of Tesla?
Elon Musk is the largest shareholder, holding approximately 13% of Tesla’s stock.
Which institutional investors hold significant stakes in Tesla?
Major institutional investors include The Vanguard Group (7.5%) and BlackRock (6.1%).
Who leads Tesla’s Board of Directors?
Robyn Denholm has chaired Tesla’s Board since 2018, overseeing corporate governance and strategic decisions.
Is Tesla owned by Elon Musk?
Elon Musk does not fully own Tesla but remains its largest shareholder and most influential leader. Tesla is a publicly traded company, meaning ownership is divided among institutional investors, retail investors, and executives.
How much of Tesla does Kimbal Musk own?
Kimbal Musk, Elon Musk’s brother and a Tesla board member, owns approximately 0.05% of Tesla, amounting to around 1.54 million shares.
How does Tesla make money?
Tesla generates revenue from multiple sources, including:
- Electric vehicle sales – The company’s primary revenue stream.
- Energy solutions – Solar panels, Solar Roof, and battery storage.
- Software & services – Full Self-Driving (FSD) subscriptions and Supercharging fees.
- Regulatory credits – Selling zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) credits to other automakers.

