Wondering who owns Google?
This article is for you.
Google is owned by its parent company, Alphabet Inc. Since its restructuring in 2015, Google has become a subsidiary of Alphabet, which oversees its core businesses including search, YouTube, and Android.
This article breaks down the ownership structure of Google and Alphabet, detailing major shareholders, financial performance, market share, and competition.
Google Company Profile
Google is a global technology company known primarily for its internet-related services and products. It dominates the online search industry and plays a significant role in cloud computing, digital advertising, mobile operating systems, and artificial intelligence. Google’s mission is “to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
The company operates under Alphabet Inc., a holding structure created in 2015 to allow greater focus on various business units. Today, Google remains Alphabet’s largest and most profitable subsidiary, responsible for the majority of its revenue.
Google Founders
Google was founded in September 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, who were Ph.D. students at Stanford University. Their breakthrough was the PageRank algorithm, which ranked web pages based on how many other pages linked to them, offering more relevant search results compared to existing search engines at the time.
They started the company from a garage in Menlo Park, California, and rapidly grew from a search engine into a tech giant.
Major Milestones
- 1996: Larry Page and Sergey Brin began working on Backrub, the precursor to Google, at Stanford University.
- 1998: Google was officially incorporated as a company.
- 2000: Google launched AdWords, its advertising platform that would become a massive revenue driver.
- 2001: Eric Schmidt was hired as CEO to bring managerial experience.
- 2004: Google went public with its IPO, raising $1.67 billion.
- 2005: Google acquired Android, setting the foundation for mobile dominance.
- 2006: Acquired YouTube, now the world’s leading video platform.
- 2008: Launched Google Chrome browser.
- 2012: Introduced Google Now, a precursor to Google Assistant.
- 2015: Created Alphabet Inc. as a parent company, restructuring its business model.
- 2019: Sundar Pichai became CEO of both Google and Alphabet.
- 2023–2024: Rapid expansion into AI with Google Bard (now Gemini) and major enhancements to Google Cloud and Workspace platforms.
Company Details
- Parent Company: Alphabet Inc.
- Headquarters: Mountain View, California, USA
- Founders: Larry Page and Sergey Brin
- CEO: Sundar Pichai (as of 2025)
- Number of Employees: Over 180,000 (Alphabet-wide, 2025 estimate)
- Key Business Segments:
- Google Search
- YouTube
- Google Ads
- Google Cloud
- Android
- Google Play
- Chrome
- Google Maps
- Google Workspace
- Core Revenue Model: Digital advertising through Google Ads and YouTube Ads accounts for the majority of revenue. Cloud computing and enterprise software are growing segments.
- Stock Information: Alphabet Inc. trades on NASDAQ under tickers GOOGL (Class A shares) and GOOG (Class C shares).
Google continues to lead the way in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and digital health. Through its products, acquisitions, and innovation, it remains at the forefront of the global tech industry.
History of Google
Google’s journey began in 1998 when Stanford University students Larry Page and Sergey Brin launched a search engine designed to organize the world’s information. Originally named “Backrub,” it was rebranded as “Google,” a play on the mathematical term “googol,” reflecting their mission to manage infinite data.
In its early years, Google revolutionized search with its PageRank algorithm, which ranked websites based on relevance and popularity. By 2000, it introduced AdWords, a groundbreaking advertising platform that became its primary revenue source. The company went public in 2004, solidifying its place as a tech giant.
Over the years, Google expanded beyond search. It acquired YouTube in 2006, launched Android in 2008, and introduced Chrome in 2009. The 2010s saw innovations like Google Drive, Google Maps, and the AI-powered Google Assistant. In 2015, it restructured under Alphabet Inc., allowing its diverse ventures—like Waymo (self-driving cars) and Verily (health tech)—to flourish independently.
Today, Google remains a leader in AI, cloud computing, and digital services, continually shaping how we interact with technology and information. From a dorm-room project to a global powerhouse, Google’s story is one of relentless innovation and ambition.
1995-1997: The Early Days
- 1995: Larry Page and Sergey Brin meet at Stanford University and begin collaborating on a search engine called Backrub.
- 1996: Backrub launches on Stanford’s servers, using the PageRank algorithm to rank web pages based on links.
- 1997: The name Google is officially adopted, inspired by the term “googol” (a 1 followed by 100 zeros).
1998: Google is Born
- Google Inc. is officially founded on September 4, 1998, in Menlo Park, California. The first Google Doodle is created to notify users of the founders’ absence during the Burning Man festival.
1999-2000: Rapid Growth
- 1999: Google moves to Palo Alto and secures $25 million in funding. It introduces its first major office culture perk: free food.
- 2000: Google launches AdWords, its advertising platform, and becomes the world’s largest search engine by indexing over 1 billion web pages.
2001-2004: Expanding Horizons
- 2001: Google hires Eric Schmidt as CEO, forming the iconic trio of Page, Brin, and Schmidt.
- 2002: AOL adopts Google’s search technology, boosting its user base.
- 2004: Google goes public on August 19, 2004, with an IPO that raises $1.67 billion. Gmail is launched with 1GB of free storage, a game-changer at the time.
2005-2007: Innovation Explosion
- 2005: Google Maps and Google Earth are introduced, revolutionizing navigation and geospatial data.
- 2006: Google acquires YouTube for $1.65 billion and launches Google Translate.
- 2007: Android is unveiled, and the Open Handset Alliance is formed to promote open-source mobile operating systems.
2008-2010: Dominance in Tech
- 2008: The first Android-powered phone, the T-Mobile G1 (HTC Dream), is released. Google Chrome, a fast and minimalist browser, is launched.
- 2009: Google Voice and Google Wave (later discontinued) are introduced.
- 2010: Google starts testing self-driving cars and launches Google Photos as part of Google+.
2011-2014: Beyond Search
- 2011: Larry Page becomes CEO, and Google+ is launched as a social network (later shut down in 2019).
- 2012: Google acquires Motorola Mobility for $12.5 billion and releases the Nexus 7 tablet.
- 2013: Google Glass is unveiled, and Chromecast is launched.
- 2014: Google acquires DeepMind, a leading AI research company.
2015-2017: Restructuring and AI Focus
- 2015: Google restructures under Alphabet Inc., with Sundar Pichai becoming CEO of Google. Projects like Waymo (self-driving cars) and Verily (health tech) are spun off.
- 2016: Google Assistant is launched, and the company introduces Pixel smartphones.
- 2017: Google’s AlphaGo AI defeats the world champion in the complex board game Go.
2018-2020: Cloud and Controversies
- 2018: Google faces scrutiny over data privacy and antitrust issues. It launches Google Duplex, an AI system capable of making phone calls.
- 2019: Google announces Stadia, a cloud gaming platform, and achieves quantum supremacy with its Sycamore processor.
- 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerates Google’s focus on remote work tools like Google Meet and Google Classroom.
2021-2023: AI and Sustainability
- 2021: Google launches LaMDA, an advanced conversational AI, and invests heavily in sustainability, aiming for carbon neutrality.
- 2022: Google introduces Bard, its AI chatbot, and expands its AI integration into search and productivity tools.
- 2023: Google faces increasing competition in AI from OpenAI and Microsoft but continues to innovate with Gemini, its next-gen AI model.
2024-2025: The Future
- 2024: Google deepens its focus on AI-powered services, including enhanced search capabilities, personalized AI assistants, and advancements in quantum computing. It also expands its presence in healthcare and autonomous vehicles.
- 2025 (Projected): Google is expected to achieve breakthroughs in AI ethics, sustainability, and quantum computing, solidifying its role as a leader in shaping the future of technology.
Who Owns Google: Major Shareholders
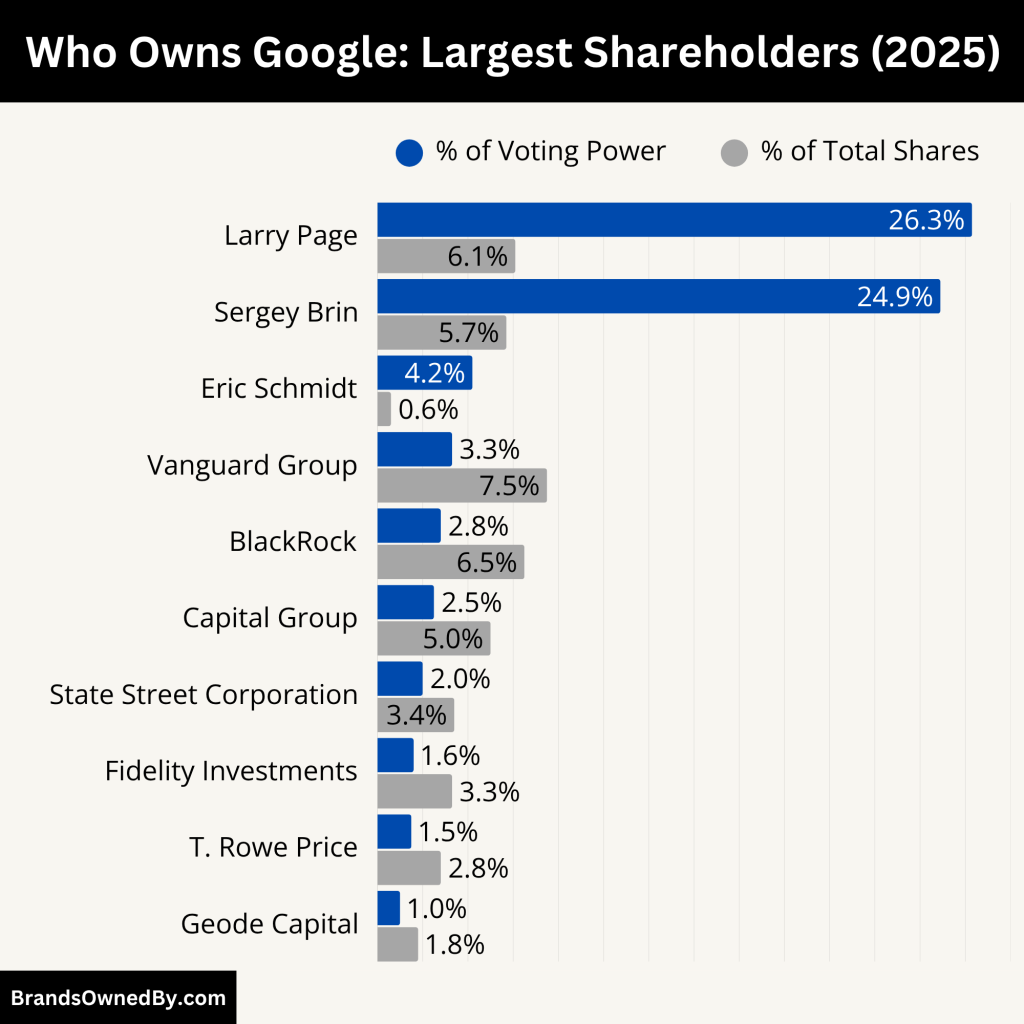
Alphabet Inc., Google’s parent company, is publicly traded on the Nasdaq stock exchange under the tickers GOOGL (Class A shares) and GOOG (Class C shares). The company has a dual-class share structure, which allows its founders and key executives to retain control despite owning a minority of the total shares.
Here’s a breakdown of the major shareholders of Google as of June 2025:
| Shareholder | % of Total Shares | % of Voting Power | Share Class(es) Held | Role / Influence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Larry Page | ~6.1% | ~26.3% | Mostly Class B | Co-founder, board member, high strategic control |
| Sergey Brin | ~5.7% | ~24.9% | Mostly Class B | Co-founder, board member, high strategic control |
| Eric Schmidt | ~0.6% | ~4.2% | Class B | Former CEO, retains insider influence |
| Vanguard Group | ~7.5% | ~3.3% | Class A & Class C | Largest institutional investor, passive role |
| BlackRock, Inc. | ~6.5% | ~2.8% | Class A & Class C | Large institutional investor, passive governance influence |
| State Street Corporation | ~3.4% | ~1.5–2.0% | Class A & Class C | Passive institutional investor |
| Fidelity Investments | ~3.3% | ~1.4–1.6% | Class A | Active/passive fund manager, minor voting influence |
| T. Rowe Price | ~2.8% | ~1.2–1.5% | Class A | Long-term fund manager, standard voting rights |
| Capital Group (Capital Research) | ~5.0% | ~2.0–2.5% | Class A | Influential institutional investor |
| Geode Capital Management | ~1.8% | ~0.8–1.0% | Class A | Index fund sub-advisor, limited influence |
| Norges Bank (Norway SWF) | ~1.5% | ~0.7–0.8% | Class A | Active ESG advocate, minor ownership |
| JPMorgan Chase | ~1.4% | ~0.6–0.7% | Class A | Institutional investor, minimal influence |
| Morgan Stanley | ~1.2% | ~0.5–0.6% | Class A | Institutional investor, limited role |
| Northern Trust | ~1.0% | ~0.4–0.5% | Class A | Institutional investor, passive role |
Larry Page
Larry Page is the co-founder of Google and played a central role in its early technical development, including the creation of the PageRank algorithm. As of 2025, Page owns approximately 6.1% of Alphabet’s total outstanding shares, mostly in Class B stock. These shares are not publicly traded and carry 10 votes per share, giving him around 26.3% of total voting power.
Despite stepping down as CEO of Alphabet in 2019, Page remains a board member and retains significant influence over strategic decisions due to his voting power. His voting stake ensures he can veto or steer company’s direction if needed. His holdings are valued at over $229 billion as of mid-2025.
Sergey Brin
Sergey Brin, the other co-founder of Google, has maintained a similarly large stake in Alphabet. Brin controls approximately 5.7% of Alphabet’s total equity, with most of his shares also in Class B, giving him about 24.9% of the voting power.
Brin stepped away from day-to-day operations in 2019 but, like Page, remains on Alphabet’s board and holds considerable control through super-voting rights. In 2025, Brin donated more than 4 million shares (a mix of Class A and C) to charitable foundations, showing active management of his holdings without significantly reducing his voting influence.
Eric Schmidt
Eric Schmidt served as Google’s CEO from 2001 to 2011 and later as Executive Chairman until 2017. Though no longer in executive leadership, he retains a notable stake in Alphabet, primarily through Class B shares.
As of 2025, Schmidt owns around 0.6% of Alphabet’s total shares, which gives him approximately 4.2% of the voting power. His continued involvement as a key insider ensures that he holds some influence in strategic matters despite not being involved in operations.
Vanguard Group
The Vanguard Group is Alphabet’s largest institutional investor, managing billions in index funds and ETFs. As of 2025, Vanguard owns about 7.5% of Alphabet’s total shares, mostly in Class A (GOOGL) and Class C (GOOG) shares, which carry one vote or no vote respectively.
Vanguard’s voting power is around 3.3%, making it the most influential institutional investor in shareholder meetings. However, it does not have insider control and plays a passive role, acting on behalf of its fund shareholders.
BlackRock, Inc.
BlackRock is another leading institutional investor in Alphabet, with holdings totaling around 6.5% of total shares in 2025. Like Vanguard, BlackRock’s holdings are mostly in Class A and C shares, with limited voting influence.
Its voting power stands at roughly 2.8%, and it represents investors via funds such as iShares ETFs. BlackRock typically supports management but has the scale to influence corporate governance matters during proxy votes.
State Street Corporation
State Street holds about 3.4% of Alphabet’s shares as of 2025. The firm invests primarily through passive index funds, with exposure mostly to Class A shares. Its voting power is proportionate to its share count, and it typically aligns its voting behavior with other institutional firms on governance and ESG issues.
Fidelity Investments
Fidelity is another significant institutional shareholder, owning an estimated 3.3% of Alphabet’s equity. It manages both active and passive funds and invests in Class A shares, providing limited voting power.
Fidelity does not influence Alphabet’s strategic direction, but is important in annual general meetings and shareholder proposals.
T. Rowe Price
T. Rowe Price manages long-term mutual funds and retirement accounts and holds about 2.8% of Alphabet’s total shares. Its voting power is tied to Class A stock, which gives it a standard one-vote-per-share influence.
T. Rowe typically maintains a neutral stance in shareholder voting but can support or oppose board proposals if concerns arise about corporate governance or performance.
Capital Research & Management (Capital Group)
Capital Group owns close to 5% of Alphabet’s equity and is one of the more active large fund managers. Its stake includes Class A shares, making it one of the top voting institutional investors.
Though its voting power remains lower than the founders’, Capital Group can rally support for or against board-level decisions in tandem with other institutional investors.
Geode Capital Management
Geode Capital, a sub-adviser to Fidelity, holds around 1.8% of Alphabet’s equity. It manages a wide range of index portfolios, mainly through Class A shares. Its influence is minor, though not insignificant, when participating in proxy voting.
Norges Bank Investment Management (Norway’s Sovereign Wealth Fund)
Norges Bank is a globally influential investor and owns about 1.5% of Alphabet’s shares in 2025. It frequently advocates for transparency, environmental policies, and corporate accountability. Although its voting power is low, it is an active voice in ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) matters.
JPMorgan Chase, Morgan Stanley, and Northern Trust
These financial institutions each hold between 1.0% and 1.4% of Alphabet’s total shares. Their stakes are held through institutional portfolios and funds. While they do not exert control, their voting participation collectively adds to institutional oversight during shareholder meetings.
Who is the CEO of Google?
As of 2025, Sundar Pichai is the CEO of both Google LLC and its parent company, Alphabet Inc.. He first took over as CEO of Google in 2015 and became CEO of Alphabet in December 2019 when co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin stepped down from executive roles. Under his leadership, Google has entered a new era focused on artificial intelligence, global cloud services, and responsible technology development.
Background and Education
Sundar Pichai was born in Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India in 1972. He holds a degree in metallurgical engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur. He later earned a Master’s degree in material sciences and engineering from Stanford University and an MBA from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania, where he was named both a Siebel Scholar and a Palmer Scholar. His academic background laid the foundation for his strategic and analytical approach to tech leadership.
Career at Google
Pichai joined Google in 2004. He initially worked on the Google Toolbar and quickly moved up the ranks to oversee the development of Google Chrome, which became the world’s most-used web browser. Over the years, he also led the teams responsible for Gmail, Google Maps, Google Drive, and Android. His calm demeanor, diplomatic style, and deep product knowledge helped him gain the trust of Google’s founders and board of directors. His promotion to CEO in 2015 marked the beginning of a more structured management era at Google.
Role as CEO of Alphabet
After the corporate restructuring that created Alphabet Inc. in 2015, Larry Page served as CEO of Alphabet while Pichai led Google. In 2019, Page and Brin stepped away from day-to-day operations and appointed Pichai as CEO of Alphabet as well. Since then, Pichai has overseen all of Alphabet’s businesses, including Google, YouTube, Waymo, DeepMind, and Verily. He works closely with the board and key product leaders while reporting directly to Alphabet shareholders.
Decision-Making and Leadership Style
Pichai is known for his calm, collaborative leadership style. Unlike the more visionary and hands-on approach of the co-founders, Pichai is pragmatic and team-oriented. He emphasizes transparency, long-term thinking, and product scalability. In 2025, Pichai continues to champion artificial intelligence and cloud computing as the core focus areas for Alphabet. At the 2025 Google I/O conference, he unveiled several major AI advancements, including real-time translation in Google Meet and new features in the Gemini AI platform. He believes AI will transform engineering productivity, stating that over 30% of new code at Google is now AI-generated.
Past CEOs of Google and Alphabet
Before Sundar Pichai, Google was led by its co-founders. Larry Page served as the first CEO from 1998 until 2001, before handing over the role to Eric Schmidt, who served from 2001 to 2011. Page returned as CEO from 2011 until the creation of Alphabet in 2015. Eric Schmidt remained a major figure at the company, later serving as Executive Chairman. When Alphabet was formed, Page took over as CEO of the parent company, with Pichai leading Google. The full transition to Pichai as CEO of both entities occurred in late 2019.
Who Controls Google (and Who Makes the Decisions)
Google’s control lies in the hands of its founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, who wield significant power through their Class B shares.
Page and Brin hold Class B shares, which carry 10 votes per share, compared to the single vote per share of Class A shares held by the public. This structure ensures that the founders retain significant control over Alphabet’s decisions, even as their ownership stake has decreased over time.
Collectively, Page and Brin control over 50% of Alphabet’s voting power, giving them the final say on major decisions, including board appointments, mergers, and acquisitions.
While both founders stepped down from day-to-day roles in 2019 (with Sundar Pichai taking over as CEO of Alphabet), they remain actively involved in strategic decisions through their board positions and voting power.
The Role of Alphabet Inc.
In 2015, Google underwent a significant restructuring, creating Alphabet Inc. as its parent company. This move allowed Google to focus on its core businesses while giving other ventures room to grow independently.
- Sundar Pichai: As CEO of both Alphabet and Google, Pichai is the face of the company’s day-to-day operations. While he owns a smaller stake in Alphabet (less than 1%), his leadership is critical in executing the founders’ vision.
- Board of Directors: Alphabet’s board includes influential figures like John Hennessy (Chairman), Diane Greene, and Roger Ferguson. However, the founders’ voting power ensures they have the final say on board decisions.
Institutional Investors: Passive but Powerful
While the founders hold the reins, institutional investors own the majority of Alphabet’s shares. These include asset management giants like The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and Fidelity Investments.
Institutional investors collectively own over 70% of Alphabet’s shares making them significant stakeholders.
Despite their large ownership, these investors are primarily passive, focusing on long-term growth rather than direct involvement in company decisions. However, their collective voice can influence corporate governance and strategic direction.
The Dual-Class Share Structure
Alphabet’s control mechanism is built on its dual-class share structure, which is common among tech companies but often criticized for concentrating power in the hands of a few.
- Class A Shares (GOOGL): Available to the public, these shares carry 1 vote per share.
- Class B Shares: Held by insiders (primarily Page and Brin), these shares carry 10 votes per share.
- Class C Shares (GOOG): These shares have no voting rights and are often used for employee compensation and acquisitions.
This structure ensures that the founders retain control even as the company grows and issues more shares to the public.
Google Annual Revenue and Net Worth
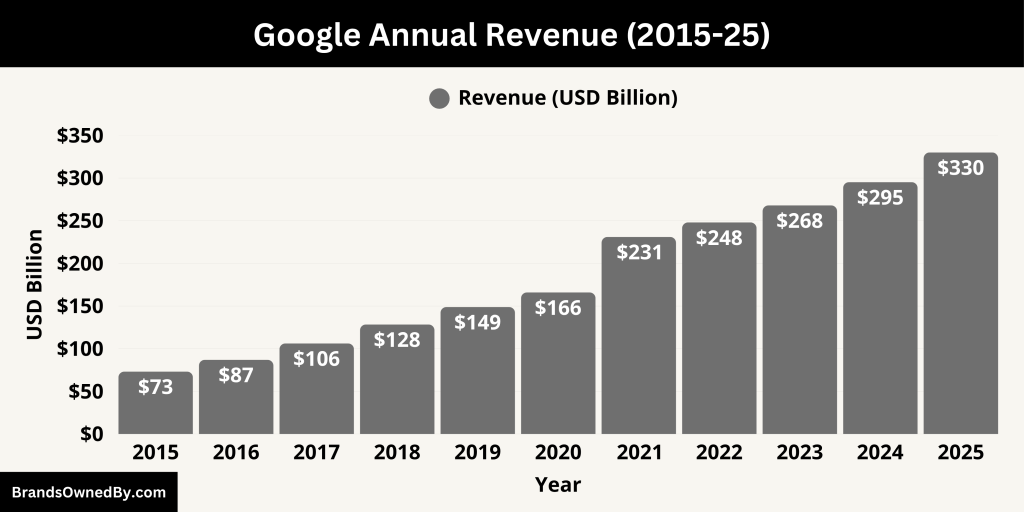
In the first quarter of 2025, Alphabet Inc. reported record earnings. Total revenue for Q1 reached $90.23 billion, marking a 12% year-over-year increase from $80.54 billion in Q1 2024. Breaking it down: Search and other services generated $50.7 billion, YouTube advertising contributed $8.93 billion, and Google Cloud brought in $12.26 billion.
According to the latest twelve-month data ending Q1 2025:
- Google Search & Other: $202.6 billion (12% growth)
- Google Cloud: $45.9 billion (30% growth)
- YouTube Ads: $37.0 billion (12% growth)
- Subscriptions, Platforms & Devices: $42.0 billion (17% growth).
Over the trailing twelve months ending March 31, 2025, total revenue amounted to approximately $359.71 billion, showing a 13% increase compared to the previous year. In 2024, Alphabet recorded full-year revenue of $350.02 billion, also reflecting strong growth.
During Q1 2025, operating income rose to $30.6 billion, with a healthy margin of 34%, compared to $25.47 billion and a 32% margin in Q1 2024. Net income reached an impressive $34.54 billion, representing a 46% increase year-over-year, with diluted earnings per share at $2.81.
Net Worth – Market Capitalization
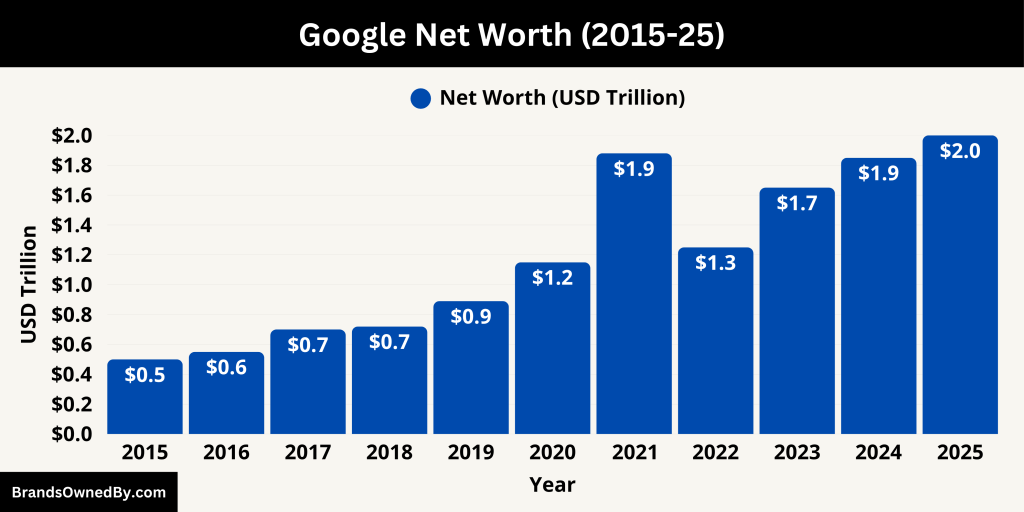
Alphabet’s net worth, as measured by market capitalization, stands at approximately $2.11 trillion as of June 2025. This makes it one of the most valuable public companies globally. Market trackers estimate the enterprise value at approximately $2.04 trillion.
Net Worth Drivers and Trends
Alphabet’s market cap of over $2.1 trillion reflects strong investor confidence, driven by its leadership in digital advertising and rapid growth in cloud and AI services. Analysts point to YouTube subscriptions, AI platform integration, and profitability in cloud computing as the main drivers of future value.
Alphabet posted strong revenue and earnings growth in Q1 2025. Core businesses—Search, YouTube, and Cloud—are thriving. Cloud profit margins and subscription growth reinforce long-term stability. The company’s $2.1 trillion valuation places it among the world’s elite tech giants. AI investments, particularly in Gemini and Meet enhancements, are expected to further boost productivity and innovation.
Here is an overview of Google’s historical revenue and net worth (market capitalization) for the last 10 years, from 2015 to 2025:
| Year | Estimated Google Revenue (USD Billion) | YoY Revenue Growth | Estimated Net Worth (USD Trillion) | Key Business Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025 | $330.0 | +12% | $2.00 | AI integration, Google Cloud, YouTube |
| 2024 | $295.2 | +10% | $1.85 | Gemini AI, Search and YouTube gains |
| 2023 | $268.0 | +8% | $1.65 | Recovery in ads, Cloud breakeven |
| 2022 | $248.0 | +7% | $1.25 | Strong YouTube and Play Store sales |
| 2021 | $231.0 | +39% | $1.88 | Post-pandemic ad surge |
| 2020 | $166.0 | +12% | $1.15 | Resilient ad business during COVID-19 |
| 2019 | $148.9 | +16% | $0.89 | YouTube and Search ad growth |
| 2018 | $128.4 | +21% | $0.72 | Play Store expansion, hardware push |
| 2017 | $106.2 | +22% | $0.70 | Mobile Search, Google Ads |
| 2016 | $87.0 | +19% | $0.55 | Android dominance, ad targeting |
| 2015 | $73.2 | +13% | $0.50 | Transition to Alphabet, search ads growth |
Companies Owned by Google
Google owns a wide range of companies and services under the Alphabet umbrella. Here is a detailed list of the major companies and brands owned by Google:
| Name | Type | Year Launched/Acquired | Function / Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| YouTube | Video-sharing platform | Acquired 2006 | Global leader in video streaming, ads, subscriptions (YouTube Premium, TV, Music). |
| Android | Mobile operating system | Acquired 2005 | World’s most-used mobile OS, powering billions of devices. |
| Google Play | App & digital content store | Launched 2012 | Distribution of apps, games, books, movies, and music. |
| Google Chrome | Web browser | Launched 2008 | Most popular browser globally, basis for ChromeOS. |
| Gmail | Email service | Launched 2004 | Free and enterprise email platform with advanced features. |
| Google Maps | Mapping & navigation service | Launched 2005 | Global digital maps, navigation, traffic, and AR directions. |
| Google Ads | Advertising platform | Launched 2000 | Core revenue driver through paid search and display ads. |
| AdSense | Publisher monetization tool | Launched 2003 | Allows websites to earn revenue through Google ad placement. |
| Google Cloud | Cloud computing services | Launched 2008 | Cloud infrastructure, AI, and enterprise solutions. |
| Google Workspace | Productivity software suite | Launched 2006 (as G Suite) | Tools like Gmail, Docs, Meet, Sheets, Calendar for business use. |
| Google Hardware | Consumer hardware division | Established 2016 | Makes Pixel, Nest, Chromecast, and other devices. |
| Google Assistant | Virtual AI assistant | Launched 2016 | Powers voice commands across Google and smart devices. |
| Google Meet | Video conferencing tool | Launched 2017 (evolved from Hangouts) | Video meetings for individuals and businesses. |
| Google Pay | Digital wallet & payments | Launched 2015 (rebranded) | Contactless payments, P2P transfers, loyalty cards, transit. |
| Google Photos | Photo and video storage | Launched 2015 | Smart photo storage with AI search and editing. |
| Google Translate | Language translation service | Launched 2006 | Translates over 130+ languages, includes camera-based translation. |
| Google News | News aggregator | Launched 2002 | Personalized news feed from global sources. |
| Google Discover | Content discovery engine | Launched 2017 | Displays personalized search-related content on mobile. |
| Google Lens | Visual search & AR tool | Launched 2017 | Recognizes text, objects, products, and locations via camera. |
| Google Domains | Domain registration service | Launched 2015 | Enables domain name registration and DNS management. |
| Google Nest | Smart home devices | Acquired 2014 | Thermostats, security cameras, smart doorbells, part of smart home ecosystem. |
| Stadia | Cloud gaming platform | Launched 2019 | Allows high-end gaming via cloud on various devices. |
| Files by Google | File management app | Launched 2017 | Tool for file cleanup, transfer, and management on Android. |
| Google Fit | Health tracking platform | Launched 2014 | Tracks steps, workouts, and integrates with wearables. |
YouTube
Acquired in 2006, YouTube is the world’s leading video-sharing platform. Google has significantly expanded its features, introducing YouTube Shorts, YouTube Music, YouTube TV, and premium subscriptions. It remains a major revenue generator through advertising, subscriptions, and content partnerships.
Android
Google purchased Android Inc. in 2005. Android is now the most widely used mobile operating system globally. Google releases major OS updates, manages Google Play Store, and partners with hardware manufacturers to integrate its ecosystem, including Google Mobile Services.
Google Play
This digital storefront for apps, games, books, movies, and music launched in 2012 by merging Android Market with Google Music. Google Play drives revenue via app sales, in-app purchases, subscription services, and digital content licensing.
Google Chrome
Released in 2008, Google’s browser quickly became dominant worldwide. It supports powerful features like Chrome Sync, developer tools, extensions, and regular updates across platforms—desktop and mobile. Many Chrome technologies feed into other Google services.
Gmail
Launched in 2004, Gmail revolutionized email with generous storage, threading, and powerful search functionality. It now supports smart replies, integrated tasks and calendar, and advanced spam filtering, serving billions of users worldwide.
Google Maps
Introduced in 2005, Google Maps offers detailed global mapping, real-time traffic, navigation, Street View, business listings, and integration with ride-hailing services. Updates include Live View AR directions and eco-friendly routing.
Google Ads & AdSense
Google Ads (formerly AdWords) powers the company’s core ad revenue. It enables advertisers to bid on search-related keywords. AdSense allows publishers to monetize content by displaying Google ads. Both platforms benefit from AI-driven ad targeting and analytics.
Google Cloud
Though some functionality overlaps with Alphabet reporting, Google Cloud is largely operated by Google itself. It includes infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), AI tools, and enterprise workloads. Clients range from startups to large enterprises.
Google Workspace
Formerly G Suite, Workspace is Google’s productivity suite. It includes Gmail, Calendar, Drive, Docs, Sheets, Slides, Meet, and Chat. It serves businesses and education sectors with collaboration tools, admin controls, and enterprise-level support.
Google Hardware
Google designs and sells hardware products such as Pixel smartphones, Pixelbooks, Nest smart home devices, Chromecast streaming devices, and Pixel Buds. Hardware integrates tightly with Google’s software and services.
Google Assistant
This virtual assistant leverages advanced AI to power voice commands on phones, speakers, smart displays, cars, and other devices. It supports smart home control and is deeply embedded in Android and Google services.
Google Meet
Originally part of Workspace, Meet is now positioned as Google’s primary video-conferencing product. It includes features like real-time captions, noise cancellation, and integrations with Gmail and Calendar.
Google Pay
Google Pay is the company’s digital wallet platform. It supports online payments, peer-to-peer money transfers, and contactless payments in stores. It integrates with Android devices and supports loyalty cards and transit passes.
Google Photos
This photo and video storage service offers free and paid backup options, smart organization, search by content, editing tools, and sharing options. It integrates with Google Drive and often receives AI-powered enhancements.
Google Translate
A translation service supporting over 133 languages. Key features include camera-based translation, offline translation packs, and auto-detection. It’s widely used in education and travel.
Google News & Discover
Google News aggregates news content in personalized feeds, while Discover presents search-like information before users make a query. Both continue to evolve with AI-driven curation and multimedia features.
Google Lens
An image recognition technology that allows users to search using their camera. Features include live translation, shopping via visual search, identifying landmarks, plants, animals, and solving homework problems.
Google Domains
A domain registration service that launched to simplify the purchase and management of website domains. It includes DNS management, email forwarding, and integrations with hosting services.
Google Nest (Smart Home)
Originally acquired in 2014 and now branded under Google Hardware, Nest provides smart thermostats, security cameras, doorbells, smoke detectors, and home security hubs. It tightly integrates with Google Home and Assistant.
Stadia
Google’s cloud gaming platform launched in 2019. It allows users to stream video games to multiple devices. Even though it struggled with market traction, as of 2025 it continues to operate with incremental improvements and content partnerships.
Google Curve or Other Miscellaneous Apps
Google maintains several other consumer apps like Google Fit (health tracking), Google Pay for transit in select cities, and Files by Google (file management). Many are supported by core data and AI infrastructure from Google.
Final Words on Who Owns Google
Understanding who owns Google reveals a layered corporate structure. While Alphabet Inc. is the parent company, founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin maintain significant control. Sundar Pichai leads day-to-day operations, but major decisions still reflect the original vision of the co-founders. With a diverse portfolio and massive global presence, Google remains one of the most powerful companies in modern tech.
FAQs
Who owns Google?
Google is owned by its shareholders, including institutional investors, mutual funds, insiders, and individual investors. Its parent company, Alphabet Inc., was created in 2015 to oversee Google and its other ventures.
Is Google a publicly traded company?
Yes, Google is part of Alphabet Inc., which is publicly traded on the NASDAQ under the ticker symbols GOOGL (Class A shares) and GOOG (Class C shares).
Do Larry Page and Sergey Brin still own Google?
Yes, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, the co-founders of Google, still own a significant portion of Alphabet Inc. (Google’s parent company). Each holds approximately 6% of the shares and retains control through Class B shares, which carry 10 votes per share.
What is the difference between GOOGL and GOOG?
- GOOGL (Class A shares): These shares are publicly traded and carry 1 vote per share.
- GOOG (Class C shares): These shares are also publicly traded but have no voting rights. They are often used for employee compensation and acquisitions.
How much of Google does Sundar Pichai own?
Sundar Pichai, the CEO of Alphabet and Google, owns less than 1% of the company. While his stake is relatively small, his leadership role gives him significant influence over the company’s operations.
Can individuals buy shares in Google?
Yes, individuals can buy shares in Alphabet Inc. (Google) through brokerage accounts, retirement plans, or direct stock purchase programs. They can purchase either GOOGL (voting shares) or GOOG (non-voting shares).
Who controls Google’s decision-making?
Despite owning a smaller percentage of shares, Larry Page and Sergey Brin control Alphabet’s decision-making through their Class B shares, which carry 10 votes per share. This structure ensures the founders retain significant influence.
Does Google pay dividends to its shareholders?
No, Alphabet Inc. (Google) does not currently pay dividends. Instead, the company reinvests its profits into growth initiatives, acquisitions, and innovation.
Are there any restrictions on buying Google shares?
No, there are no specific restrictions on buying Google shares. However, investors should be aware of the differences between GOOGL (voting shares) and GOOG (non-voting shares) before purchasing.
Who founded Google?
Google was founded by Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1998 while they were students at Stanford University.
What is Alphabet Inc.?
Alphabet Inc. is the parent company of Google. It was created in 2015 to separate core businesses from experimental ventures.
Does Google have a parent company?
Yes, Alphabet Inc. is Google’s parent company and owns all of Google’s business units.
Who is the CEO of Alphabet?
Sundar Pichai is the CEO of both Google and Alphabet as of 2025.
How much is Google worth?
As of 2025, Alphabet Inc. has a net worth exceeding $2.2 trillion.
Who has the most shares in Google?
Larry Page and Sergey Brin hold the most voting shares, mainly through Class B stock.
Who is the Google owner?
Google is owned by Alphabet Inc., its parent company. Alphabet was created in 2015 to restructure Google’s expanding businesses. The largest individual shareholders are Larry Page and Sergey Brin, Google’s co-founders, who still control most of the voting power through special Class B shares.
Is Jeff Bezos the owner of Google?
No, Jeff Bezos is not the owner of Google. He is the founder of Amazon, one of Google’s main tech rivals. He has no known stake or executive role in Google or Alphabet.
Who owns 51% of Google?
No single person owns 51% of Google. However, Larry Page and Sergey Brin together control over 50% of Alphabet’s voting shares, giving them effective control over major decisions. This is done through Class B shares, which carry 10 times the voting power of regular shares.
Does Zuckerberg own Google?
No, Mark Zuckerberg does not own Google. He is the founder and CEO of Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook), a competing tech company. He has no financial or ownership stake in Google.
Is the Google CEO a billionaire?
Yes, Sundar Pichai, the CEO of Google and Alphabet, is a billionaire. As of 2025, his net worth is estimated to be over $1.3 billion, primarily due to his compensation, stock awards, and long tenure in top executive roles.
Who is the CEO of YouTube?
As of 2025, Neal Mohan is the CEO of YouTube. He succeeded Susan Wojcicki in 2023. Neal has been with Google for years and previously led product management at YouTube.
What is the full form of Google?
Google does not have an official full form. However, a popular backronym is “Global Organization of Oriented Group Language of Earth.” Originally, the name “Google” was derived from “googol,” a mathematical term for the number 1 followed by 100 zeros.
What 7 companies are owned by Google Alphabet?
Google LLC owns many companies and services, but 7 of the most prominent ones under Google itself include:
- YouTube
- Android
- Google Play
- Google Maps
- Google Ads
- Gmail
- Google Chrome
(If referring to Alphabet’s broader portfolio, other companies like Waymo, DeepMind, Verily, and X also apply.)
Who is the Alphabet CEO?
As of 2025, Sundar Pichai serves as the CEO of Alphabet Inc. in addition to his role as CEO of Google. He has held both positions since 2019.
Who owns Google Maps?
Google Maps is owned and operated by Google LLC. It was launched in 2005 and continues to be one of the most widely used mapping services in the world.
Who created Google?
Google was created by Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1998 while they were PhD students at Stanford University. Their original project was a search engine called “Backrub” which evolved into Google.
Who owns Google in 2025?
As of 2025, Alphabet Inc. owns Google. The largest and most powerful shareholders are Larry Page and Sergey Brin, who maintain majority voting control through Class B shares.
Who originally owned Google?
Google was originally owned by its founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, along with early investors like Andy Bechtolsheim, Sequoia Capital, and Kleiner Perkins. They incorporated Google in 1998.
Who owns Google phones?
Google LLC owns and manufactures Google Pixel phones. These are part of Google’s hardware division, which also includes devices like Nest, Pixelbook, and Chromecast.

