Are you interested in knowing who owns Amazon?
This article is for you.
This article delves into Amazon’s ownership structure, major shareholders, and the control mechanisms that drive its success.
Amazon History
Amazon began as an online bookstore and rapidly diversified its offerings to include electronics, apparel, and more.
Over the years, it expanded into cloud computing with Amazon Web Services (AWS), ventured into physical retail by acquiring Whole Foods Market, and developed various consumer electronics like the Kindle and Echo devices. This diversification has solidified Amazon’s position as a leader in multiple sectors.
Key Milestones in Amazon’s History
- 1994: Amazon is founded by Jeff Bezos.
- 1995: The company launches as an online bookstore.
- 1997: Amazon goes public with its IPO.
- 1998: Expands into music, videos, and electronics.
- 2002: Launches AWS as an internal tool.
- 2005: Introduces Amazon Prime.
- 2006: Public launch of AWS.
- 2007: Releases the Kindle e-reader.
- 2017: Acquires Whole Foods Market.
- 2021: Jeff Bezos steps down as CEO; Andy Jassy takes over.
Who Owns Amazon: Largest Shareholders
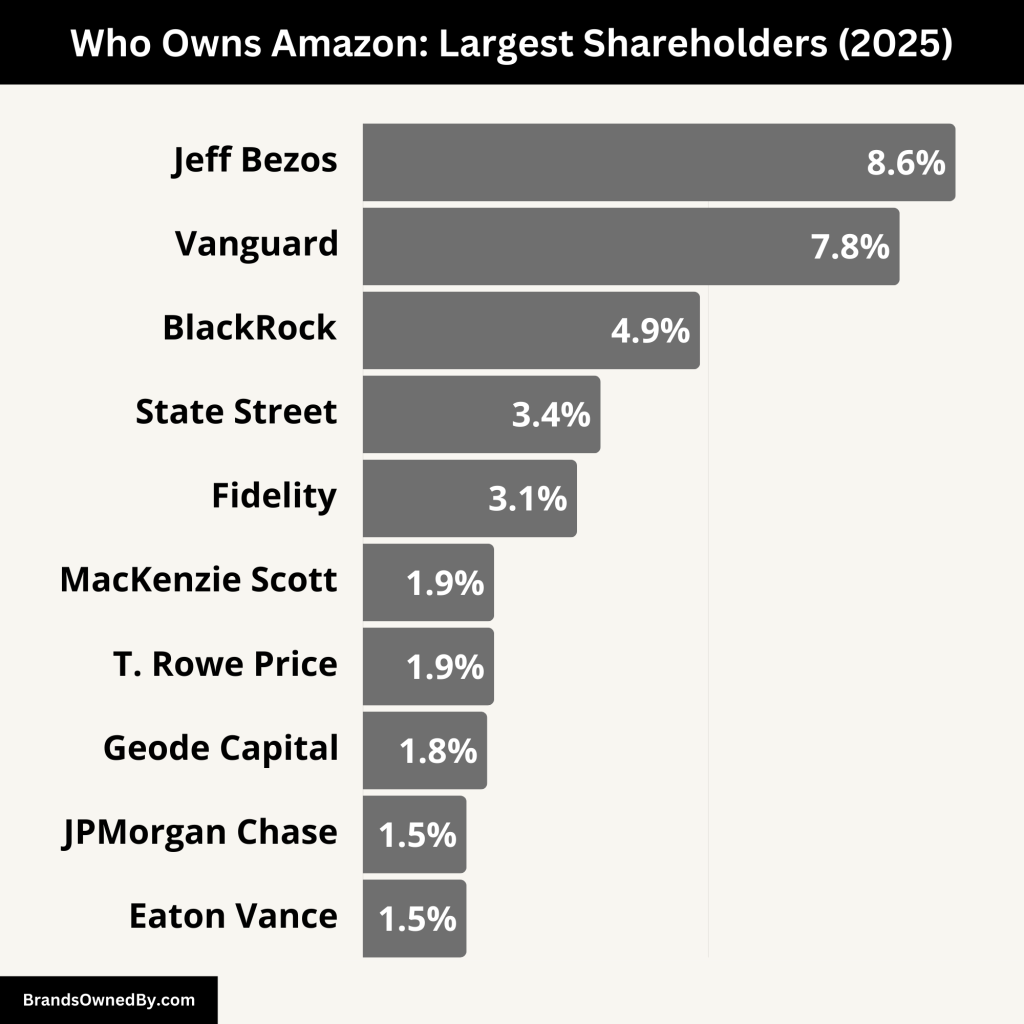
The ownership of Amazon is a blend of individual and institutional shareholders. Founder Jeff Bezos remains the largest individual shareholder, holding approximately 9.1% of the company’s shares. Institutional investors collectively own a significant portion, with The Vanguard Group and BlackRock being notable stakeholders.
As of February 2025, Amazon.com, Inc. (NASDAQ: AMZN) boasts a diverse ownership structure, comprising individual insiders, institutional investors, and retail shareholders.
This blend reflects the company’s expansive growth and appeal across various investor classes.
Here’s a list of the major shareholders of Amazon:
| Shareholder | Ownership Percentage | Role |
|---|
| Jeff Bezos | 8.58% | Founder, Former CEO, Largest Individual Shareholder |
| The Vanguard Group | 7.77% | Largest Institutional Shareholder, Passive Investor |
| BlackRock | 4.88% | Institutional Investor, Passive Stakeholder |
| State Street Corp. | 3.44% | Institutional Investor, Corporate Governance Influencer |
| Fidelity Investments | 3.1% | Mutual Fund Investor, Active in Shareholder Engagement |
| MacKenzie Scott | 1.9% | Individual Shareholder, Philanthropist |
| T. Rowe Price | 1.9% | Investment Management Firm, Portfolio Manager |
| Geode Capital Mgmt. | 1.8% | Quantitative Investment Firm, Systematic Strategy |
| JPMorgan Chase & Co. | 1.5% | Institutional Investor, Financial Services Provider |
| Eaton Vance | 1.5% | Investment Firm, Focused on Fund Management |
1. Jeff Bezos
Founder and former CEO Jeff Bezos remains the largest individual shareholder of Amazon.
As of November 2024, he owned over a billion shares, valued at approximately $213 billion. Bezos has periodically sold portions of his holdings; notably, between July and November 2024, he sold $5.1 billion worth of stock under a prearranged trading plan.
Despite these sales, his substantial stake reflects his enduring influence over the company’s direction.
2. The Vanguard Group
The Vanguard Group, a leading global investment management firm, is Amazon’s largest institutional shareholder. It owns about 7.77% of the company’s shares, amounting to over 823 million shares. Vanguard’s investment in Amazon reflects its confidence in the company’s long-term performance and stability. As a passive investor, Vanguard’s influence is primarily through voting rights associated with its shareholding.
3. BlackRock
BlackRock, another global investment powerhouse, holds approximately 4.88% of Amazon’s shares, equating to over 517 million shares. BlackRock’s stake signifies its strategic interest in Amazon’s diverse business model and growth prospects. Similar to Vanguard, BlackRock’s role is largely passive, focusing on long-term value creation for its clients.
4. State Street Corporation
State Street Corporation owns around 3.44% of Amazon’s shares, totaling over 364 million shares. As one of the world’s largest asset managers, State Street’s investment indicates a strong belief in Amazon’s market position and future growth. The firm exercises its voting rights to influence corporate governance practices positively.
5. Fidelity Investments
Fidelity Investments holds approximately 3.1% of Amazon’s shares. As a prominent mutual fund and financial services provider, Fidelity’s investment showcases its confidence in Amazon’s continued innovation and market leadership. Fidelity engages with Amazon’s management to ensure alignment with shareholder interests.
6. MacKenzie Scott
MacKenzie Scott, philanthropist and former spouse of Jeff Bezos, owns about 1.9% of Amazon’s shares. Her stake, resulting from the couple’s divorce settlement in 2019, reflects her significant wealth derived from the company’s success. Scott has been actively using her fortune to support various charitable causes worldwide.
7. T. Rowe Price
T. Rowe Price, a global investment management firm, holds around 1.9% of Amazon’s shares. The firm’s investment in Amazon indicates its positive outlook on the company’s financial health and strategic initiatives. T. Rowe Price engages in active portfolio management to maximize returns for its investors.
8. Geode Capital Management
Geode Capital Management owns approximately 1.8% of Amazon’s shares. As a quantitative investment manager, Geode’s stake in Amazon suggests data-driven confidence in the company’s performance metrics and market trajectory. The firm employs systematic investment strategies to manage its holdings.
9. JPMorgan Chase & Co.
JPMorgan Chase & Co. holds about 1.5% of Amazon’s shares. As a leading global financial services firm, JPMorgan’s investment reflects its strategic interest in Amazon’s expansive operations and revenue streams. The firm provides a range of financial services that may intersect with Amazon’s business ventures.
10. Eaton Vance
Eaton Vance owns around 1.5% of Amazon’s shares. As an investment management firm, Eaton Vance’s stake signifies its belief in Amazon’s ability to deliver consistent returns. The firm focuses on managing investment funds and offering advisory services.
Who Controls Amazon?
Although Amazon’s ownership is divided among individual and institutional shareholders, control over the company’s strategic direction and operations rests primarily with its Board of Directors, executive leadership team, and major shareholders.
Board of Directors
Amazon’s Board of Directors is responsible for making key business decisions, setting long-term strategies, and overseeing corporate governance. The board includes industry leaders, finance experts, and technology professionals who ensure that Amazon remains competitive and aligned with its mission.
Some key board members include:
- Andy Jassy (President & CEO, Board Member) – Succeeded Jeff Bezos as CEO in 2021 and has been instrumental in leading Amazon Web Services (AWS) and expanding Amazon’s global footprint.
- Jeff Bezos (Executive Chairman, Founder) – While no longer CEO, Bezos retains influence as Executive Chairman, focusing on innovation, long-term vision, and major strategic decisions.
- Judy McGrath (Former CEO of MTV Networks) – Brings expertise in media, branding, and content strategy, supporting Amazon’s entertainment and streaming ventures.
- Indra Nooyi (Former CEO of PepsiCo) – Adds experience in global business management, corporate strategy, and sustainability.
- Brad Smith (President of Microsoft) – Provides insights on cloud computing, AI, and cybersecurity.
- Jamie Gorelick (Former U.S. Deputy Attorney General) – Plays a role in corporate governance and regulatory compliance.
The board makes decisions by voting, with majority votes determining Amazon’s corporate direction. Major shareholders, particularly institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock, also influence these decisions through their voting power.
Executive Leadership Team
Amazon’s day-to-day operations and long-term vision are guided by its executive leadership team. This group is responsible for different business divisions, ensuring Amazon’s dominance across e-commerce, cloud computing, logistics, and AI.
Some key executives include:
- Andy Jassy (CEO) – Leads Amazon globally, overseeing innovation, financial growth, and expansion into new markets.
- Brian Olsavsky (CFO) – Manages Amazon’s financial health, investments, and revenue growth strategies.
- Adam Selipsky (CEO of AWS) – Heads Amazon Web Services, the company’s most profitable division, driving cloud dominance.
- Doug Herrington (CEO of Worldwide Amazon Stores) – Manages Amazon’s core retail business, marketplace strategies, and Prime services.
- David Limp (SVP of Devices & Services) – Oversees Alexa, Kindle, and other Amazon consumer electronics.
Each executive controls a major part of Amazon’s operations, working closely with the board and shareholders.
Institutional Shareholder Influence
Major institutional investors like Vanguard Group (7.77%), BlackRock (4.88%), and State Street Corporation (3.44%) hold significant stakes in Amazon. While they do not directly manage the company, they exercise corporate influence through voting rights at shareholder meetings.
These investors advocate for decisions that align with their financial interests, such as stock buybacks, leadership appointments, and corporate policies.
Jeff Bezos’ Remaining Influence
Even though Jeff Bezos stepped down as CEO in 2021, he continues to exert considerable control over Amazon’s future. As the largest individual shareholder (8.58%) and Executive Chairman, he remains involved in high-level strategic decisions, innovation, and expansion efforts. His voting power, combined with his legacy, gives him an outsized influence over Amazon’s trajectory.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Amazon
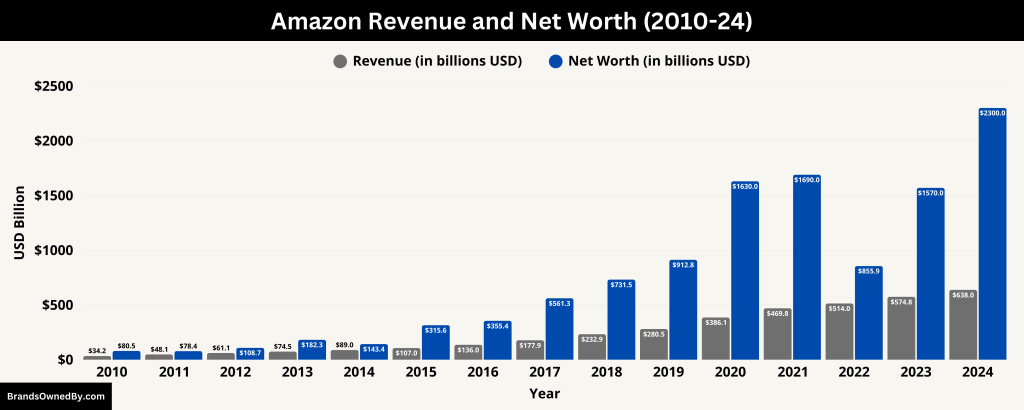
In 2024, Amazon reported an annual revenue of approximately $637.96 billion, positioning it as one of the world’s most significant companies by revenue. The company’s diverse ventures, from e-commerce to cloud computing, contribute to its substantial financial standing.
As of April 2025, the net worth of Amazon is around $2.3 trillion.
Below is a comprehensive table detailing Amazon’s annual revenue, net income, and market capitalization over the past 15 years, along with the year-over-year (YoY) percentage changes:
| Year | Revenue (in billions USD) | YoY Revenue Growth | Net Income (in billions USD) | YoY Net Income Growth | Market Capitalization (in billions USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | $34.20 | — | $1.15 | — | $80.46 |
| 2011 | $48.08 | 40.6% | $0.63 | -45.2% | $78.37 |
| 2012 | $61.09 | 27.1% | -$0.039 | -106.2% | $108.68 |
| 2013 | $74.45 | 21.9% | $0.27 | 794.9% | $182.25 |
| 2014 | $88.99 | 19.5% | -$0.24 | -188.0% | $143.40 |
| 2015 | $107.01 | 20.2% | $0.60 | 349.0% | $315.60 |
| 2016 | $135.99 | 27.1% | $2.37 | 297.7% | $355.41 |
| 2017 | $177.87 | 30.8% | $3.03 | 27.8% | $561.31 |
| 2018 | $232.89 | 30.9% | $10.07 | 232.2% | $731.47 |
| 2019 | $280.52 | 20.4% | $11.59 | 15.1% | $912.81 |
| 2020 | $386.06 | 37.6% | $21.33 | 84.0% | $1,630.00 |
| 2021 | $469.82 | 21.7% | $33.36 | 56.4% | $1,690.00 |
| 2022 | $514.00 | 9.4% | -$2.72 | -108.2% | $855.88 |
| 2023 | $574.79 | 11.8% | $30.43 | 1217.7% | $1,570.00 |
| 2024 | $637.96 | 11.0% | $59.25 | 94.7% | $2,300.00 |
Amazon’s Market Share and Competitors
Amazon is a global leader in e-commerce, cloud computing, digital advertising, and AI-driven services. The company’s dominance spans multiple industries, with significant market share in several key sectors.
Global E-Commerce Market Share
Amazon is the largest e-commerce company in the world, holding approximately 37.6% of the U.S. e-commerce market as of 2024. Globally, its share is lower due to competition from regional giants like Alibaba, Flipkart, and MercadoLibre.
- United States – 37.6%
- United Kingdom – 30%
- Germany – 25%
- Japan – 23%
- India – ~5% (competing with Flipkart and Reliance Jio)
Despite increasing competition, Amazon continues to dominate in North America and Europe due to Prime membership, fast logistics, and a vast product selection. The company’s e-commerce growth is fueled by new technologies, including AI-driven recommendations, drone delivery, and same-day shipping networks.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Market Share
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the largest cloud computing provider worldwide, with a 31% market share in the global cloud infrastructure industry. AWS generates a significant portion of Amazon’s total revenue and remains a high-margin business.
- AWS – 31% (Amazon)
- Microsoft Azure – 25%
- Google Cloud – 11%
- Alibaba Cloud – 4%
AWS maintains its lead through a robust infrastructure, AI-powered cloud solutions, and enterprise partnerships. The service powers major organizations, including Netflix, NASA, and the U.S. government.
Amazon’s Digital Advertising Market Share
Amazon is the third-largest digital advertising company, trailing behind Google and Meta. Its share of the global digital ad market is around 7.5%, growing rapidly as brands shift advertising budgets to Amazon’s platform.
- Google Ads – 28%
- Meta (Facebook & Instagram) – 18%
- Amazon Ads – 7.5%
- TikTok & Others – 6%
Amazon’s advertising strength lies in its retail media network, where brands pay to advertise products directly on Amazon’s platform. This ad business is expected to keep growing due to Amazon’s vast shopping data and AI-driven targeting capabilities.
Amazon’s Competitors by Industry
Amazon faces strong competition across its business segments. Here’s a breakdown of its key rivals:
1. E-Commerce Competitors
- Walmart (U.S.) – Amazon’s biggest rival in the U.S., focusing on omnichannel retail with strong brick-and-mortar operations.
- Alibaba (China, Global) – Dominates the Chinese market and competes with Amazon globally through AliExpress and cloud services.
- eBay (Global) – Focuses on auctions and reselling but competes in select e-commerce categories.
- Target (U.S.) – Competes in the retail sector, especially in categories like grocery and home essentials.
2. Cloud Computing Competitors
- Microsoft Azure – Amazon’s biggest rival in the cloud market, growing rapidly with enterprise and AI-powered solutions.
- Google Cloud – Competes in AI-driven cloud computing but lags behind AWS and Azure in market share.
- Alibaba Cloud – The dominant cloud provider in China, expanding globally.
3. Digital Advertising Competitors
- Google Ads – The market leader in search and display ads, competing directly with Amazon’s product ads.
- Meta (Facebook & Instagram Ads) – Focuses on social media advertising but faces pressure from Amazon’s retail ads.
- TikTok Ads – Growing rapidly in video-based advertising and social commerce.
4. Streaming & Entertainment Competitors
- Netflix – Leads the global streaming industry, competing with Amazon Prime Video for subscribers.
- Disney+ – A major rival in the streaming space, offering exclusive content from Disney, Marvel, and Star Wars.
- HBO Max – Competes in premium content with a strong focus on original programming.
5. Smart Devices & AI Competitors
- Apple (Siri, HomePod, Apple TV) – Competes with Amazon’s Alexa and Echo devices in smart home technology.
- Google (Google Assistant, Nest Devices) – A direct rival in voice assistants and smart home ecosystems.
Amazon’s Competitive Strategy
To maintain its market dominance, Amazon continuously invests in:
- AI and automation – Enhancing customer experience with AI-driven search, recommendation engines, and chatbots.
- Logistics and fulfillment – Expanding same-day and one-hour delivery services.
- Subscription services – Growing Amazon Prime, which offers fast shipping, exclusive content, and cloud storage.
- Acquisitions and partnerships – Expanding its reach through strategic purchases like Whole Foods, MGM Studios, and One Medical.
Brands Owned by Amazon
Here’s a list of the brands and companies owned by Amazon:
1. Whole Foods Market
- Acquisition Year: 2017
- Purchase Price: $13.7 billion
- Overview: Whole Foods Market is a leading organic and natural grocery store chain. Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods marked its entry into the physical retail space and allowed it to expand its grocery delivery services. The brand is known for its high-quality products and commitment to sustainability.
- Impact: The acquisition strengthened Amazon’s presence in the grocery sector and enabled the integration of Whole Foods into Amazon Prime, offering discounts and delivery options to Prime members.
2. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Launch Year: 2006 (publicly launched)
- Overview: AWS is Amazon’s cloud computing division, providing on-demand cloud services to businesses, governments, and individuals. It offers a wide range of services, including storage, computing power, machine learning, and analytics.
- Impact: AWS is Amazon’s most profitable division, contributing a significant portion of the company’s operating income. It dominates the cloud computing market, with a 32% global market share as of 2023.
3. Twitch
- Acquisition Year: 2014
- Purchase Price: $970 million
- Overview: Twitch is a live-streaming platform primarily focused on video games, esports, and creative content. It allows users to broadcast and watch live streams, interact with streamers, and participate in communities.
- Impact: Twitch has become the go-to platform for gamers and content creators, with millions of daily active users. It has also expanded into music, art, and other forms of entertainment.
4. Zappos
- Acquisition Year: 2009
- Purchase Price: $1.2 billion
- Overview: Zappos is an online retailer specializing in shoes, clothing, and accessories. It is known for its exceptional customer service, including free shipping and a 365-day return policy.
- Impact: Zappos operates as an independent subsidiary of Amazon, maintaining its unique culture while benefiting from Amazon’s logistics and infrastructure.
5. Ring
- Acquisition Year: 2018
- Purchase Price: $1 billion
- Overview: Ring is a smart home security company that produces video doorbells, security cameras, and alarm systems. Its products are designed to enhance home security and provide real-time monitoring.
- Impact: Ring has become a key player in Amazon’s smart home ecosystem, integrating with Alexa and other Amazon devices. It also contributes to Amazon’s efforts in neighborhood safety through its Neighbors app.
6. Audible
- Acquisition Year: 2008
- Purchase Price: $300 million
- Overview: Audible is the leading provider of audiobooks and spoken-word content. It offers a vast library of audiobooks, podcasts, and original content.
- Impact: Audible has revolutionized the audiobook industry, making it accessible to millions of listeners worldwide. It is a key component of Amazon’s digital content strategy.
7. PillPack
- Acquisition Year: 2018
- Purchase Price: $753 million
- Overview: PillPack is an online pharmacy that delivers pre-sorted medications to customers’ doors. It simplifies medication management, especially for individuals with chronic conditions.
- Impact: The acquisition of PillPack marked Amazon’s entry into the healthcare sector. It laid the foundation for Amazon Pharmacy, launched in 2020, which offers prescription delivery and discounts to Prime members.
8. IMDb (Internet Movie Database)
- Acquisition Year: 1998
- Purchase Price: Undisclosed
- Overview: IMDb is an online database of information related to movies, TV shows, and celebrities. It also offers streaming services through IMDb TV (now rebranded as Amazon Freevee).
- Impact: IMDb has become a trusted resource for entertainment information and a platform for streaming free, ad-supported content.
9. Goodreads
- Acquisition Year: 2013
- Purchase Price: Undisclosed
- Overview: Goodreads is a social networking site for book lovers. It allows users to track their reading, write reviews, and discover new books.
- Impact: Goodreads integrates with Amazon’s Kindle ecosystem, enabling seamless book recommendations and purchases. It has become a vital tool for authors and readers alike.
10. Woot
- Acquisition Year: 2010
- Purchase Price: $110 million
- Overview: Woot is an e-commerce website known for its daily deals and limited-time offers. It sells a variety of products, including electronics, home goods, and apparel.
- Impact: Woot operates as a subsidiary of Amazon, offering unique deals and maintaining its quirky brand identity.
11. Kiva Systems (now Amazon Robotics)
- Acquisition Year: 2012
- Purchase Price: $775 million
- Overview: Kiva Systems developed robots used in warehouses for inventory management and order fulfillment. After the acquisition, it was rebranded as Amazon Robotics.
- Impact: Amazon Robotics has transformed Amazon’s logistics operations, improving efficiency and reducing costs in its fulfillment centers.
12. Souq.com
- Acquisition Year: 2017
- Purchase Price: $580 million
- Overview: Souq.com was the largest e-commerce platform in the Middle East, often referred to as the “Amazon of the Middle East.”
- Impact: The acquisition allowed Amazon to establish a strong presence in the Middle East, rebranding Souq.com as Amazon.ae in 2019.
13. MGM Studios
- Acquisition Year: 2021
- Purchase Price: $8.45 billion
- Overview: MGM Studios is a renowned film and television production company with a vast library of content, including iconic franchises like James Bond and Rocky.
- Impact: The acquisition bolstered Amazon’s entertainment division, providing exclusive content for Amazon Prime Video and enhancing its competitiveness in the streaming wars.
14. One Medical
- Acquisition Year: 2022
- Purchase Price: $3.9 billion
- Overview: One Medical is a primary care provider offering in-person and virtual healthcare services. It focuses on providing a seamless patient experience through technology.
- Impact: The acquisition is part of Amazon’s broader strategy to expand into healthcare, offering affordable and accessible services to its customers.
15. Blink
- Acquisition Year: 2017
- Purchase Price: $90 million
- Overview: Blink produces affordable, battery-powered home security cameras and video doorbells.
- Impact: Blink complements Amazon’s smart home ecosystem, offering budget-friendly alternatives to Ring’s products.
16. Eero
- Acquisition Year: 2019
- Purchase Price: $97 million
- Overview: Eero manufactures Wi-Fi mesh networking systems designed to improve home internet coverage.
- Impact: Eero enhances Amazon’s smart home offerings by providing reliable connectivity for Alexa-enabled devices.
17. Fabric.com
- Acquisition Year: 2008
- Purchase Price: Undisclosed
- Overview: Fabric.com is an online retailer specializing in fabrics, sewing supplies, and craft materials.
- Impact: The acquisition allowed Amazon to expand its product offerings in the arts and crafts category.
18. AbeBooks
- Acquisition Year: 2008
- Purchase Price: Undisclosed
- Overview: AbeBooks is an online marketplace for rare, used, and out-of-print books.
- Impact: AbeBooks caters to book collectors and enthusiasts, complementing Amazon’s broader book-selling business.
19. ComiXology
- Acquisition Year: 2014
- Purchase Price: Undisclosed
- Overview: ComiXology is a digital comics platform offering a vast library of comic books and graphic novels.
- Impact: The acquisition strengthened Amazon’s digital content offerings, particularly in the comics and graphic novels space.
20. Amazon Pharmacy
- Launch Year: 2020
- Overview: Amazon Pharmacy is an online pharmacy service offering prescription medications, with discounts for Prime members.
- Impact: The service leverages Amazon’s logistics network to provide convenient and affordable healthcare solutions.
Conclusion
Amazon’s ownership is a complex blend of individual and institutional stakeholders. Founder Jeff Bezos remains the largest individual shareholder, holding approximately 8.58% of the company’s shares.
Significant institutional investors include The Vanguard Group and BlackRock, owning about 7.77% and 4.88% of shares, respectively. This diversified ownership structure ensures a balance of influence, with both individual and institutional investors playing pivotal roles in shaping Amazon’s strategic direction.
FAQs
Who is the largest individual shareholder of Amazon?
Jeff Bezos, the founder and former CEO of Amazon, is the largest individual shareholder, owning approximately 8.58% of the company’s shares.
Which institutional investors hold significant shares in Amazon?
Major institutional investors in Amazon include The Vanguard Group, holding about 7.77% of shares, and BlackRock, with approximately 4.88%.
How is Amazon’s ownership structured?
Amazon’s ownership comprises a mix of individual insiders and institutional investors. Individual insiders, including Jeff Bezos, own about 11% of the shares, while institutional investors hold approximately 61.7%. The general public owns around 27.1% of the shares.
Does Jeff Bezos still control Amazon?
While Jeff Bezos stepped down as CEO in 2021, he remains the largest individual shareholder and serves as the Executive Chairman of Amazon’s Board of Directors, retaining significant influence over the company’s strategic decisions.
Who are the key members of Amazon’s Board of Directors?
As of 2025, key members of Amazon’s Board of Directors include:
- Andy Jassy: President and CEO
- Keith B. Alexander: CEO of IronNet Cybersecurity and former NSA director
- Edith W. Cooper: Co-founder of Medley and former EVP of Goldman Sachs
- Jamie Gorelick: Partner at Wilmer Cutler Pickering Hale and Dorr
- Daniel Huttenlocher: Dean of the MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
- Judy McGrath: Former CEO of Paramount Media Networks
- Indra Nooyi: Former CEO of PepsiCo
What percentage of Amazon’s shares does the general public own?
The general public holds approximately 27.1% of Amazon’s shares.
How has Amazon’s ownership structure evolved over the years?
Since its founding in 1994, Amazon’s ownership has transitioned from being predominantly controlled by its founder, Jeff Bezos, to a more diversified structure. Over the years, significant shares have been acquired by institutional investors, and the general public’s ownership has increased, reflecting the company’s growth and public trading history.
What role do institutional investors play in Amazon’s decision-making?
Institutional investors, holding approximately 61.7% of Amazon’s shares, play a crucial role in the company’s governance. Through their voting rights, they influence major corporate decisions, including board member elections and significant policy changes. Their substantial ownership stakes ensure they have a vested interest in Amazon’s strategic direction and performance.
Has Jeff Bezos sold any of his Amazon shares recently?
Yes, Jeff Bezos has periodically sold portions of his Amazon shares. For instance, in late 2024, he sold shares worth approximately $214 million. Despite these sales, he remains the largest individual shareholder.
How does Amazon’s ownership impact its corporate strategy?
The diverse ownership structure of Amazon, combining significant individual and institutional shareholders, fosters a balanced approach to corporate strategy. While Jeff Bezos provides visionary leadership and long-term strategic direction, institutional investors ensure financial discipline and accountability, influencing decisions that aim to enhance shareholder value.

