- Hummer is fully owned by General Motors, with 100% ownership held at the corporate level. It is a brand, not a separate company, and has no independent shareholders, board, or legal structure.
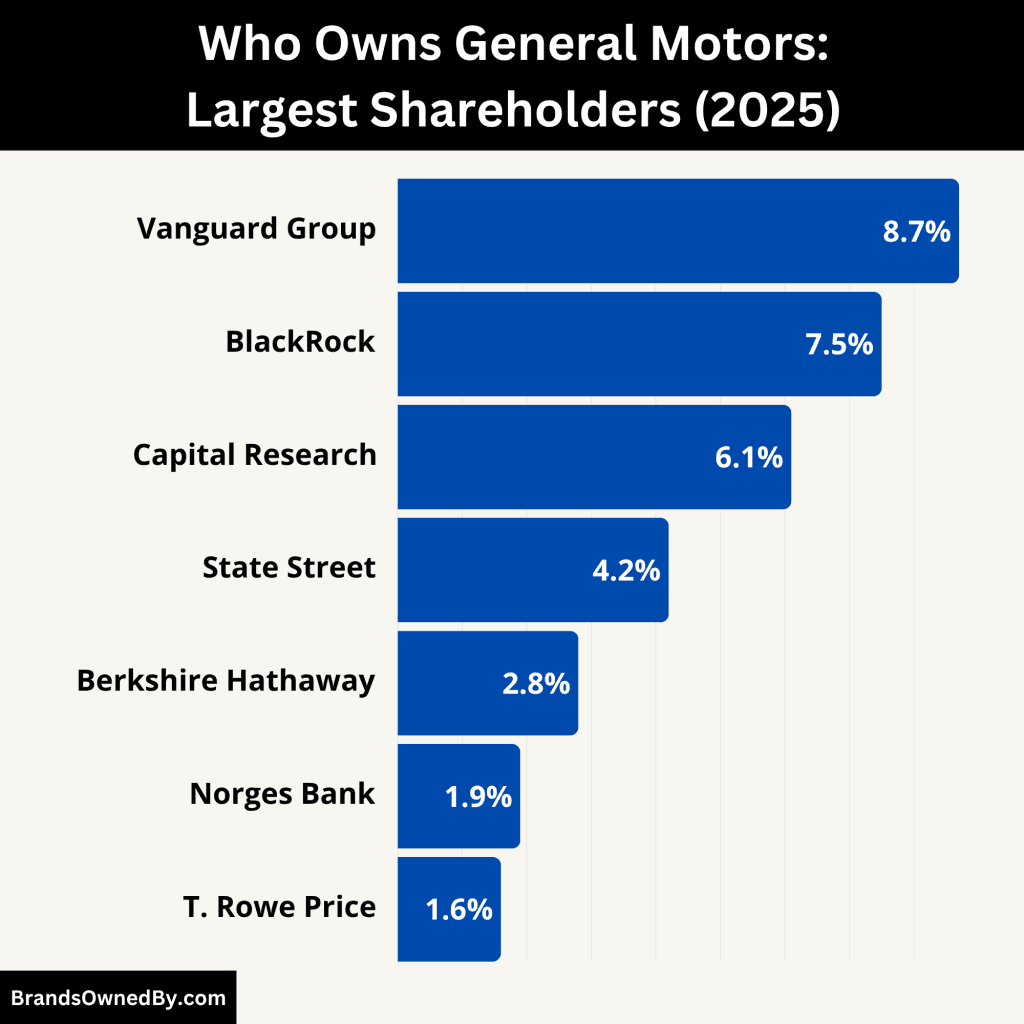
- All shareholder exposure to Hummer is indirect, coming through General Motors’ public shareholders. Institutional investors such as Vanguard Group and BlackRock are among GM’s largest shareholders, but none hold stakes in Hummer itself.
- Ownership and control have remained unchanged since 1999, when General Motors acquired the Hummer brand. Despite discontinuation and revival, Hummer has never been sold, spun off, or diluted through partnerships or external investors.
Hummer is an American automotive brand known for its rugged, military-inspired vehicles and, more recently, its transition into electric trucks and SUVs. The brand’s identity is rooted in off-road capability, bold design, and a distinct presence on the road. Hummer vehicles became cultural icons in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, appealing to buyers who valued durability and commanding performance.
Although frequently referred to as a standalone brand, Hummer has operated under larger parent companies throughout its history. It began as a civilian offshoot of a military vehicle manufacturer and later became part of one of the world’s largest automakers.
Today, Hummer exists as a sub-brand under the GMC lineup of General Motors, focusing on electric vehicles that carry forward the rugged ethos of earlier models.
Hummer Founder
Hummer’s origins trace back to AM General, a company with deep ties to military vehicle production. AM General did not “found” Hummer as a brand in the traditional startup sense. Rather, the brand emerged from the evolution of the High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV), commonly known as the Humvee, which AM General developed for the U.S. military in the 1980s.
Key figures in Hummer’s early development were engineers and executives at AM General who worked on military contracts and oversaw the adaptation of the Humvee for civilian use. The Humvee’s reputation for durability and all-terrain performance led AM General to pursue a civilian version in the early 1990s.
In 1999, General Motors (GM) acquired the rights to the Hummer name from AM General. GM did not start the brand, but it became the steward of Hummer’s evolution in the civilian automotive market. Under GM, Hummer expanded its product lineup with models such as the H1, H2, and H3.
Ownership History
Hummer’s ownership history spans multiple phases. These include its origins as a military vehicle, its growth under a civilian manufacturer, its acquisition by a global automaker, its discontinuation, and its reimagining as an electric brand. Each phase reflects shifts in strategy, market forces, and corporate priorities.
| Time Period | Owner / Controller | Ownership Status | Key Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Late 1970s – 1991 | AM General | Military program | Development of the HMMWV (Humvee) for the U.S. military. No civilian brand existed at this stage. |
| 1992 – 1998 | AM General | Full brand control | Launch of the civilian Hummer H1. AM General handled design, manufacturing, and limited distribution. |
| 1999 – 2009 | General Motors | Full ownership | GM acquired the Hummer brand rights. Expanded lineup with H2 and H3. Global marketing and dealership integration. |
| 2010 | General Motors | Brand discontinued | GM shut down Hummer during bankruptcy restructuring. Production ended. |
| 2010 – 2019 | General Motors | Dormant ownership | Brand trademarks retained by GM. No vehicles produced or sold. |
| 2020 – Present | General Motors (via GMC) | Full ownership | Revival as an electric vehicle sub-brand under GMC. Focus on electric trucks and SUVs. |
Military Origins and Early Development
Hummer’s story begins not as a consumer brand but as a military program. In the late 1970s and early 1980s, the U.S. Department of Defense sought a rugged, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle. This led to the development of the High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV). AM General, a defense contractor with expertise in heavy vehicles, won the contract.
The HMMWV earned widespread use by the U.S. military and allied forces. Its versatility and performance under harsh conditions helped it become an icon of military mobility. While not a consumer brand at this stage, the HMMWV laid the foundation for what would later become the Hummer name.
Civilian Introduction Through AM General
AM General recognized that public interest in the military Humvee could translate into a consumer market. In 1992, the company introduced the Hummer H1 for civilian sale. The H1 was essentially a modified Humvee, adapted with certain features for legal road use and consumer comfort.
AM General oversaw design, manufacturing, and initial sales. The brand quickly attracted attention for its unique military heritage and bold looks. However, AM General lacked the global marketing reach and dealership infrastructure of established consumer automakers. As interest grew, this limitation became increasingly visible.
Acquisition by General Motors
In 1999, General Motors (GM) acquired the marketing and distribution rights for Hummer from AM General. The deal transferred the civilian brand to GM while AM General continued producing military vehicles under defense contracts.
GM’s acquisition marked a turning point. The company had vast production capacity, a global dealer network, and deep marketing resources. Under GM, Hummer evolved with new models and broader distribution. The H2 and H3 launched in the early 2000s, expanding the brand’s appeal beyond niche buyers of the H1.
GM’s stewardship accelerated Hummer’s visibility. Dealerships across the United States and other markets sold the vehicles with GM’s sales, financing, and service support.
Discontinuation and Failed Sale
By the late 2000s, multiple pressures converged on Hummer. Rising fuel prices, shifting consumer preferences, and economic recession weakened demand for large, fuel-intensive SUVs. GM faced financial distress and entered bankruptcy protection in 2009.
During GM’s restructuring, the company announced plans to discontinue the Hummer brand. A sale to a Chinese company, Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPG), was proposed but ultimately fell through. Regulatory issues and financing difficulties prevented completion of the deal.
With no viable buyer, GM shut down Hummer as a civilian brand. Production of all models ceased by 2010. The brand entered a dormant phase, with trademarks and intellectual property held by GM.
Revival Under GM as an Electric Brand
After a decade of inactivity, General Motors opted to revive Hummer — but in a radically different form. In 2020, GM announced that Hummer would return as an electric vehicle sub-brand under its GMC division.
This revival was part of GM’s broader electrification strategy. The revived Hummer would leverage GM’s new Ultium battery platform and focus on zero-emission performance trucks and SUVs. GM maintained full ownership throughout the revival. No external entity acquired the dormant brand.
The first new-generation vehicles, including the Hummer EV pickup, began deliveries in the early 2020s. This shift reframed Hummer from a symbol of gas-powered excess to a high-end electric performance line.
Who Owns Hummer?
Hummer is fully owned by General Motors and operates as a brand, not a standalone company. General Motors controls all Hummer trademarks, vehicle programs, manufacturing decisions, and long-term strategy. The brand has no independent shareholders, board, or legal structure. All ownership authority flows directly through GM and its executive leadership.
Parent Company: General Motors
General Motors is the controlling entity behind every aspect of Hummer’s existence. GM determines whether the brand expands, contracts, or pauses production. This control is structural, operational, and strategic.
Hummer sits within GM’s North American operations and is commercially aligned with the GMC division. However, this alignment is functional, not legal. GMC does not own Hummer. It acts as the retail and branding channel through which Hummer vehicles are sold.
GM integrates Hummer into its broader vehicle architecture strategy. The Hummer EV lineup is built on GM-developed electric platforms, uses GM proprietary battery systems, and relies on GM-owned or GM-contracted manufacturing facilities. Engineering teams working on Hummer vehicles are GM employees, not a separate Hummer workforce.
From a governance standpoint, Hummer has no executive authority. Decisions related to product cadence, pricing tiers, regional availability, and production volume are approved through GM’s centralized leadership structure. Final authority rests with GM’s CEO and executive committee.
Hummer also plays a strategic role inside GM. It is positioned as a halo brand. Its purpose is not mass-market volume but brand signaling. GM uses Hummer to demonstrate technical capabilities in electric performance, off-road engineering, and large-scale EV platforms.
Acquisition Insights and Details
General Motors acquired the Hummer brand in 1999 from AM General.
Before the acquisition, AM General controlled the civilian Hummer H1, which was derived from the military Humvee. AM General specialized in defense manufacturing and limited civilian production. It did not have the dealer network or consumer marketing infrastructure required to scale Hummer globally.
The 1999 acquisition transferred the civilian Hummer brand rights to GM. This included the Hummer name, consumer vehicle branding, and marketing control. AM General retained its military contracts and continued producing military vehicles. It did not retain ownership of the Hummer consumer brand.
This acquisition allowed GM to fully commercialize Hummer. GM redesigned the brand for mass-market visibility. It introduced new models engineered on GM platforms, not military chassis. This shift fundamentally changed Hummer from a niche military-derived vehicle into a mainstream consumer SUV brand.
Expansion Under GM Ownership
Following the acquisition, GM launched the Hummer H2 and later the H3. These vehicles were developed using GM engineering resources and produced at GM-controlled facilities. Distribution expanded through GM dealerships rather than specialty outlets.
Ownership during this period remained unchanged. GM did not spin off Hummer or bring in partners. The brand operated entirely under GM’s balance sheet and governance.
GM’s ownership also meant full exposure to market risk. When fuel prices rose and consumer demand shifted away from large SUVs, Hummer’s performance directly impacted GM’s portfolio. This ownership structure played a key role in later decisions to discontinue the brand.
Attempted Sale and Retained Ownership
During GM’s financial restructuring in 2009, the company announced its intent to divest Hummer. A proposed sale to a Chinese-backed investor was negotiated but never completed.
Critically, ownership never transferred. No assets changed hands. No regulatory approvals were finalized. When the deal collapsed, GM retained full ownership of Hummer without interruption.
As a result, when Hummer was discontinued in 2010, it was not sold or spun off. GM simply ceased production while keeping all intellectual property rights intact.
Revival Without Acquisition
When GM revived Hummer in 2020, no acquisition occurred.
The revival was an internal decision made by GM leadership. The brand was reintroduced as an electric-only lineup under GM’s direct control. No external investors were involved. No joint ventures were created. No equity restructuring took place.
This makes Hummer’s revival unusual. Most discontinued auto brands return through licensing or third-party ownership. Hummer returned under the same parent company that originally shut it down.
Who Manufactures Hummer?
Hummers are manufactured through a multi-plant U.S. production network consisting of Factory ZERO, Brownstown Battery Assembly, Ultium Cells plants in Lordstown and Spring Hill, Toledo Propulsion Systems, and Pontiac Stamping. Each facility has a specific, documented role, and all manufacturing is controlled by General Motors, with zero outsourcing of vehicle assembly.
Final Vehicle Assembly
All Hummer EV Pickup and Hummer EV SUV vehicles are fully assembled at Factory ZERO.
This is the only plant in the world where complete Hummer EV vehicles are built.
Factory ZERO performs:
- Body shop welding and structural assembly
- Paint operations
- Installation of battery packs
- Installation of electric drive units
- Interior, electronics, and software integration
- Final inspection and validation.
No other GM facility performs final Hummer assembly.
Battery Cell Manufacturing (Exact Plants)
Hummer EV battery cells are produced by Ultium Cells, a GM-controlled battery manufacturer.
Ultium Cells – Lordstown, Ohio
This facility manufactures lithium-ion battery cells used in:
- Hummer EV Pickup
- Hummer EV SUV.
It is one of GM’s primary high-volume EV battery cell plants.
Ultium Cells – Spring Hill, Tennessee
This plant also produces Ultium battery cells and supports:
- Hummer EV production
- Other GM electric vehicle programs.
Cells from both plants are shipped onward for pack assembly.
Brownstown Battery Assembly Plant (Michigan)
Battery modules and complete battery packs for Hummer EVs are assembled at Brownstown Battery Assembly Plant.
This facility:
- Assembles battery cells into modules
- Builds full battery packs
- Integrates cooling and structural housings
Completed packs are then transported to Factory ZERO for vehicle installation.
Toledo Propulsion Systems (Ohio)
Electric drive units used in Hummer EVs are produced at Toledo Propulsion Systems.
This facility manufactures:
- Electric motors
- Drive units
- Propulsion components for GM EVs.
These units are shipped directly to Factory ZERO.
Stamping and Body Components
Major stamped body panels and structural components for Hummer EVs are produced at Pontiac Stamping.
These include:
- Large body panels
- Structural metal components.
Stamped parts are shipped to Factory ZERO for body assembly.
Competitor Ownership Comparison
Hummer competes in the electric pickup and large electric SUV segment. This space is defined not only by vehicle capability but also by very different ownership and control structures. Comparing Hummer’s ownership with its key competitors helps clarify how strategy, funding, and decision-making differ across the segment.
| Brand / Model | Owner | Ownership Type | Corporate Structure | Key Ownership Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hummer EV | General Motors | 100% parent-owned | Sub-brand under GM (via GMC) | No autonomy. Strategy, production, and investment decisions are controlled by GM’s executive leadership. |
| Ford F-150 Lightning | Ford Motor Company | 100% parent-owned | Core product within Ford | Electrified extension of an existing flagship truck. Fully integrated into Ford’s mass-market strategy. |
| Tesla Cybertruck | Tesla | Public company ownership | Single-brand automaker | No sub-brand structure. Faster decision-making but higher exposure to execution risk. |
| Rivian R1T / R1S | Rivian Automotive | Public + institutional investors | Independent EV manufacturer | Full brand autonomy but limited scale and higher capital sensitivity. |
| GMC Sierra EV | General Motors | 100% parent-owned | GM internal brand | Shares platforms and ownership with Hummer but targets a more traditional truck buyer. |
Hummer (Owned by General Motors)
Hummer is fully owned by General Motors. It operates as a brand within GM and has no independent corporate structure.
This means Hummer benefits from GM’s scale, manufacturing infrastructure, supply chain, and long-term capital planning. At the same time, it does not have autonomy. Product timelines, production volumes, and geographic expansion are decided at the GM level, not by a standalone Hummer leadership team.
Hummer’s ownership model prioritizes stability and long-term integration over speed or independence.
Ford F-150 Lightning (Owned by Ford Motor Company)
The Ford F-150 Lightning is owned and produced by Ford Motor Company. Like Hummer, it is not a standalone brand but part of a larger automotive group.
Ford’s ownership structure mirrors GM’s in many ways. The Lightning benefits from Ford’s existing truck dominance, dealer network, and manufacturing scale. However, unlike Hummer, the F-150 Lightning is an electrified version of an existing mass-market product rather than a revived niche brand.
Ownership-wise, both Hummer and Ford Lightning sit under legacy automakers with centralized control and long-term planning horizons.
Tesla Cybertruck (Owned by Tesla, Inc.)
The Cybertruck is produced by Tesla, which operates under a very different ownership and governance model.
Tesla is a publicly traded company, but functions with a highly centralized leadership structure. Product decisions are driven internally rather than through brand-level divisions. The Cybertruck is not a sub-brand. It is a core Tesla product.
Compared to Hummer, Tesla’s ownership model allows faster decision-making and more aggressive timelines. However, Tesla lacks the multi-brand legacy structure and dealer network that GM provides to Hummer.
Rivian R1T and R1S (Independent Ownership)
Rivian vehicles are produced by Rivian Automotive, an independent automaker.
Rivian’s ownership is split among public shareholders and major institutional investors. Unlike Hummer, Rivian is not backed by a traditional legacy automaker. This gives Rivian full brand autonomy but also exposes it to higher financial and operational risk.
Hummer’s ownership under GM provides insulation from market volatility that Rivian does not have. In contrast, Rivian can pivot faster without legacy constraints.
GMC Sierra EV (Internal GM Comparison)
The GMC Sierra EV is also owned by General Motors. This makes it a direct internal competitor to Hummer rather than an external one.
Both brands share ownership, technology platforms, and manufacturing resources. The difference lies in positioning. Hummer is designed as a bold, extreme, halo product. Sierra EV targets more traditional premium truck buyers.
This internal competition highlights how GM uses multiple brands under one ownership structure to cover different customer segments.
Who Controls Hummer?
Control of Hummer is highly centralized and corporate-led. Unlike independent automakers or EV startups, Hummer does not function as a self-governing brand. Every meaningful decision related to the brand is made within the leadership, governance, and operational systems of its parent company.
Ultimate Authority: General Motors
Hummer is fully controlled by General Motors, which owns the brand outright and retains absolute authority over its direction.
This control is legal, strategic, and operational. GM owns all Hummer-related intellectual property, including trademarks, vehicle names, design rights, and future product concepts. Hummer cannot exist, expand, or pivot independently. If GM chooses to pause production, change positioning, or discontinue the brand again, it can do so unilaterally.
Hummer does not have its own incorporation documents, regulatory filings, or governance framework. It is treated internally as a brand program rather than a business unit with autonomy.
Corporate Executive Control and Strategic Decision-Making
At the highest level, strategic control of Hummer resides with GM’s executive leadership, led by Mary Barra.
As Chair and CEO, Mary Barra oversees GM’s long-term corporate strategy, electrification roadmap, and capital deployment. The decision to revive Hummer as an all-electric brand was made within this executive framework. That decision aligned Hummer with GM’s broader shift toward electric vehicles rather than nostalgia or short-term demand.
Major questions about Hummer’s future are answered at this level. These include whether new Hummer models will be approved, how long the brand remains active, how much investment it receives, and how it fits into GM’s EV portfolio alongside Chevrolet, GMC, and Cadillac.
Below the CEO, GM’s executive committee and senior vice presidents play a direct role. Leaders responsible for North American operations, electric vehicle development, manufacturing, and global supply chain influence Hummer’s priorities. Their focus is not brand storytelling but portfolio optimization.
Brand-Level Oversight Within GMC
Day-to-day brand oversight for Hummer is handled within GM’s GMC division.
GMC leadership manages how Hummer is positioned in the market. This includes branding tone, marketing campaigns, dealer messaging, trim structure, and customer experience. GMC also coordinates how Hummer vehicles are presented alongside other GMC products in showrooms.
However, this oversight is operational, not authoritative. GMC does not control Hummer’s existence or product approval. It cannot independently launch a new Hummer model or cancel one. Those decisions must be approved higher up within GM.
This layered structure means Hummer’s identity is shaped at the GMC level, while its survival and scope are decided at the GM corporate level.
Product Planning and Engineering Control
Engineering control of Hummer sits entirely within GM’s centralized product development organization.
Hummer vehicles are designed using GM-wide engineering standards. Battery architecture, electric motors, software systems, vehicle platforms, and safety systems are developed centrally and then adapted for Hummer-specific use cases.
Even features that feel unique to Hummer, such as extreme off-road modes or specialized performance systems, are engineered within GM teams. There is no independent Hummer engineering division setting its own technical roadmap.
This centralized control ensures consistency and cost efficiency. It also means Hummer cannot pursue experimental or niche technologies unless they align with GM’s broader engineering priorities.
Manufacturing and Production Control
Manufacturing control is one of the most tightly held areas within GM’s structure.
GM decides where Hummer vehicles are built, how many units are produced, and how production capacity is allocated relative to other GM vehicles. Hummer does not own factories. It does not negotiate supplier contracts. It does not control its own production schedule.
If GM needs to reallocate battery supply, labor, or factory capacity to higher-volume or higher-priority models, Hummer production can be adjusted accordingly. This reflects its role as a halo product rather than a core revenue driver.
Financial and Investment Control
Hummer has no independent budget.
All investment decisions related to Hummer flow through GM’s internal capital allocation process. Research spending, tooling costs, marketing budgets, and technology investments are approved alongside other GM programs.
Hummer cannot raise funds, borrow capital, or attract outside investors. Its future depends entirely on GM’s willingness to continue allocating resources to the brand.
This also means Hummer is insulated from short-term financial pressure. Poor performance at the brand level does not automatically threaten its existence, as long as GM sees strategic value in maintaining it.
Brands Owned by Hummer
Hummer owns and operates a wide range of sub-brands and product lines as stated below:
Hummer EV Pickup Line
The Hummer EV Pickup is the foundation of the modern Hummer brand.
It represents the most extreme interpretation of Hummer’s off-road and performance identity. This product line is engineered for maximum torque, ground clearance, and terrain adaptability. The pickup format allows Hummer to target buyers who associate capability with utility and size.
Within this line, Hummer emphasizes:
- Extreme off-road readiness
- High-performance electric output
- Distinctive, oversized design language.
The pickup is positioned as a statement vehicle rather than a mass-market truck. Production volumes are intentionally limited compared to mainstream pickups.
Hummer EV SUV Line
The Hummer EV SUV line expands the brand into a more lifestyle-oriented segment.
This product line retains the same core identity as the pickup but adapts it to an enclosed SUV format. It targets buyers who want off-road performance without a truck bed.
Key characteristics of this line include:
- Shorter wheelbase for maneuverability
- Enhanced trail and rock-crawling focus
- Premium interior configuration.
The SUV line broadens Hummer’s appeal while maintaining brand consistency. It is not designed as a softer or urban variant. It remains firmly positioned in the extreme-capability category.
EV3X Performance Sub-Brand
EV3X functions as Hummer’s highest-performance sub-brand.
Vehicles under the EV3X designation represent the most powerful and feature-rich versions available. This sub-brand is used to signal maximum output, advanced off-road systems, and exclusive performance hardware.
EV3X is defined by:
- Top-tier electric power output
- Advanced terrain management systems
- Performance-focused tuning and features.
This sub-brand sits at the top of the Hummer hierarchy. It establishes the brand’s technological ceiling and reinforces its halo status.
Off-Road Capability Identity
Rather than launching a named off-road sub-brand, Hummer integrates off-road capability as a core identity layer across all product lines.
This identity is built around:
- Multi-mode terrain adaptability
- Extreme approach and departure angles
- Reinforced underbody and suspension systems.
Off-road capability is not optional within Hummer. It is embedded into every product line rather than isolated to a single trim or variant.
Edition and Trim-Based Differentiation
Hummer also operates through edition-based positioning rather than permanent sub-brands.
These editions differentiate vehicles based on:
- Launch status
- Feature availability
- Performance emphasis.
Such editions allow Hummer to create exclusivity, manage production pacing, and generate sustained interest without fragmenting the brand into multiple standalone lines.
Importantly, these trims do not dilute the core Hummer identity. Even lower-tier configurations retain the brand’s extreme positioning.
Technology Identity as a Sub-Layer
Hummer uses technology as a defining internal sub-layer rather than branding it as a separate company or platform.
This includes:
- Advanced electric drivetrain integration
- Specialized vehicle software interfaces
- Driver-selectable performance and terrain systems.
These technologies are branded and marketed within the Hummer identity itself, reinforcing the perception that Hummer is technologically distinct, even though development is centralized at the corporate level.
Final Thoughts
Hummer’s modern identity reflects a dramatic transformation shaped by ownership, control, and strategic repositioning. For anyone asking who owns Hummer, the answer clearly shows a brand that is fully owned and tightly controlled by General Motors, operating as a focused electric vehicle program rather than an independent automaker. With no subsidiaries, acquisitions, or standalone governance, Hummer’s value lies in its brand strength, extreme electric capability, and role as a halo product within GM’s broader strategy, positioning it as a distinctive and carefully managed nameplate in the evolving EV landscape.
FAQs
Who currently owns Hummer?
Hummer is fully owned by General Motors. It is not a separate company and has no independent shareholders. All ownership, trademarks, and decision-making authority belong to GM.
What brand is Hummer?
Hummer is an electric vehicle brand operated within GM’s GMC division. It exists as a sub-brand focused on high-performance electric trucks and SUVs, not as a standalone automaker.
Where is Hummer made?
Modern Hummer EV vehicles are manufactured in the United States. Final vehicle assembly takes place at GM’s Factory ZERO (Detroit–Hamtramck Assembly Center) in Michigan. Major components, including battery cells, battery packs, propulsion systems, and stamped body parts, are produced at multiple named GM and GM-controlled facilities across Michigan, Ohio, and Tennessee before final assembly.
Why was Hummer discontinued?
Hummer was discontinued in 2010 due to declining demand for large gasoline-powered SUVs, rising fuel prices, environmental concerns, and General Motors’ bankruptcy restructuring. The brand was paused, not sold. GM retained ownership and later revived Hummer as an all-electric brand.
Who made the original Hummer?
The original Hummer was developed and built by AM General. It was based on the military Humvee (HMMWV) designed for the U.S. armed forces. AM General produced the civilian Hummer H1 before GM acquired the brand rights.
Is Hummer owned by Toyota?
No. Hummer has never been owned by Toyota. It is entirely owned and controlled by General Motors.
Is Hummer GM or Ford?
Hummer is a GM brand. It has no connection to Ford in terms of ownership, manufacturing, or control.

