Many sports fans often wonder who owns ESPN, the biggest name in sports broadcasting. With its wide range of programming, ESPN has become a central part of global sports culture. Understanding the ownership and structure behind ESPN can help fans and investors see how the company operates today.
History of ESPN
ESPN, which stands for Entertainment and Sports Programming Network, launched on September 7, 1979.
It was founded by Bill Rasmussen, his son Scott Rasmussen, and Ed Eagan. Their idea was to create a 24-hour sports channel, something unheard of at the time.
Originally headquartered in Bristol, Connecticut, ESPN started with broadcasting sports news and minor sports events.
Over the years, it grew into a giant, covering major leagues like the NFL, NBA, MLB, and global events like the FIFA World Cup. Throughout its journey, several larger corporations took an interest in ESPN and eventually acquired it.
Who Owns ESPN?
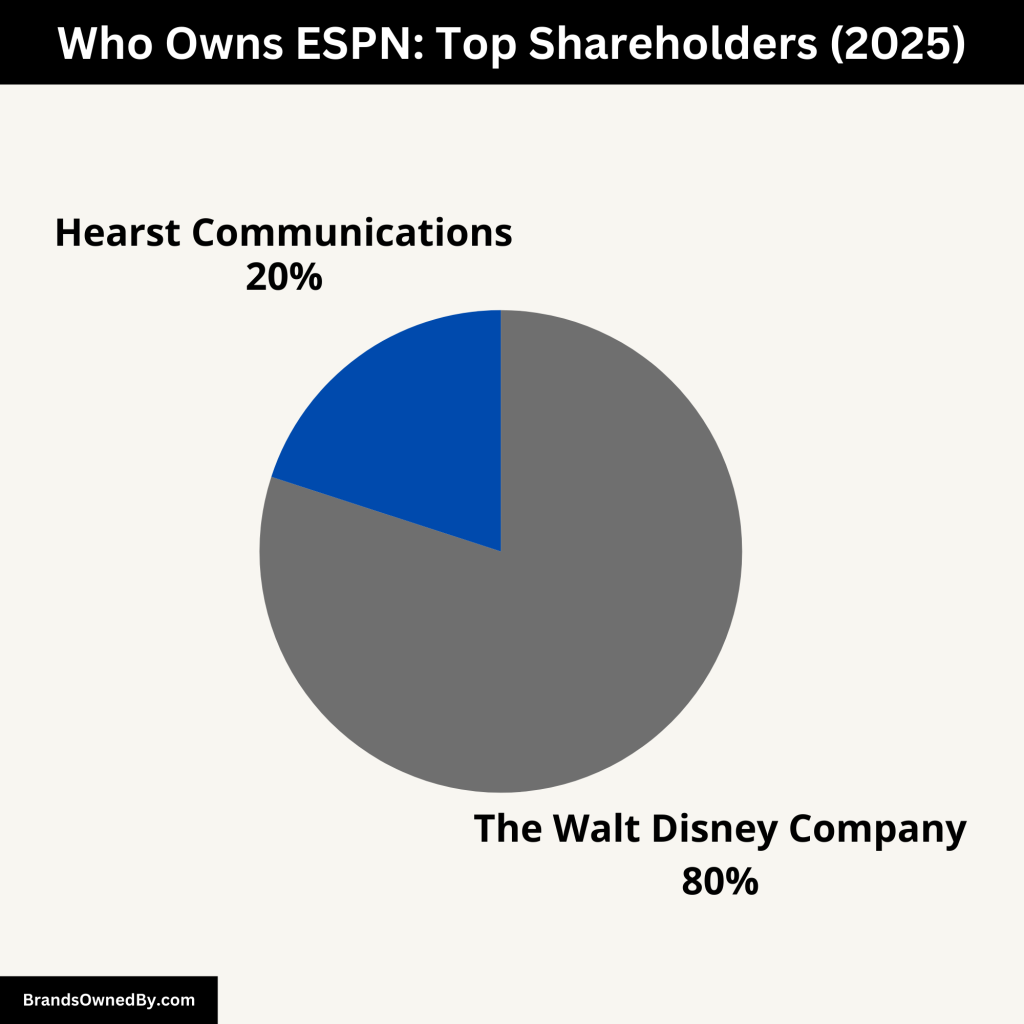
Today, The Walt Disney Company owns the majority of ESPN. Disney controls about 80% of ESPN Inc. The remaining 20% is held by Hearst Communications. Disney’s involvement began in 1995 when it acquired Capital Cities/ABC Inc., which had previously bought ESPN.
As of 2025, Disney has expressed interest in finding strategic partners to invest in ESPN, potentially selling up to a 36% stake to new investors, while retaining majority control. Potential investors include tech companies like Apple and Amazon, as well as telecom firms like Verizon and Comcast.
Here’s a breakdown of the major shareholders of ESPN:
| Shareholder | Ownership Percentage | Role and Details | Status (2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Walt Disney Company | 80% | Majority owner; full operational control; drives strategy, management, and bundling with Disney assets | Active |
| Hearst Communications | 20% | Minority owner; limited operational involvement; influence on major strategic corporate decisions | Active |
| Apple (Potential) | To be determined (part of up to 30–36% stake available) | Interested in minority investment to expand sports content streaming | Negotiations ongoing |
| Amazon (Potential) | To be determined | Exploring investment to enhance sports offerings on Prime Video | Negotiations ongoing |
| Verizon (Potential) | To be determined | Considering investment to integrate exclusive content with wireless services | Negotiations ongoing |
| Comcast/NBCUniversal (Potential) | To be determined | Possible minority investment; competitive and regulatory considerations in play | Negotiations ongoing |
| Capital Cities/ABC (Past Owner) | Former full owner | Purchased ESPN in 1984; later acquired by Disney in 1995 | Historical shareholder (no longer active) |
The Walt Disney Company – 80% Ownership
The Walt Disney Company is the dominant owner of ESPN, holding 80% of ESPN Inc. Disney’s ownership dates back to 1995 when it acquired Capital Cities/ABC, which had already taken control of ESPN in 1984. This majority stake gives Disney almost full operational and financial control over ESPN’s day-to-day activities, strategic direction, and brand management.
Under Disney’s leadership, ESPN has expanded into digital streaming with ESPN+, international broadcasting, and large-scale rights acquisitions for leagues like the NFL, NBA, and UFC. Disney’s stake allows it to bundle ESPN with other Disney assets like Disney+ and Hulu, offering a competitive streaming package known as the Disney Bundle.
In 2025, Disney has been exploring bringing in new minority partners for ESPN to fund further streaming expansions, but it has made clear it intends to maintain majority control.
Hearst Communications – 20% Ownership
Hearst Communications owns the remaining 20% stake in ESPN. Hearst is a large media company that operates newspapers, magazines, television channels, and digital media. Its involvement with ESPN started in the early 1990s when Hearst invested alongside Capital Cities/ABC.
Although Hearst is a minority owner, its shareholding grants it certain voting rights and influence, particularly on major strategic initiatives like mergers, acquisitions, and changes to ESPN’s core business structure. However, day-to-day operations are primarily led by Disney.
Hearst benefits financially from ESPN’s profitability but does not involve itself in programming or management decisions unless major corporate actions are proposed.
Potential New Investors – Strategic Partnerships Under Discussion (2025)
In 2024 and 2025, Disney announced plans to sell up to 30–36% of ESPN to strategic partners. This move is intended to boost ESPN’s ability to invest in streaming technology and content rights as traditional cable TV subscriptions decline.
While no new deals have been finalized yet, several companies have been reported as interested:
- Apple: Apple has discussed investing in ESPN as part of its broader push into sports broadcasting through Apple TV+. Apple’s interest would focus on enhancing streaming content and technology partnerships.
- Amazon: Amazon, already strong in sports broadcasting with NFL Thursday Night Football, has explored a minority stake to expand its Prime Video offerings.
- Verizon: Verizon, a major telecom operator, has considered investing to combine its wireless services with exclusive sports content for customers.
- Comcast (NBCUniversal): Comcast is another potential investor, although regulatory and competitive concerns might complicate any direct partnership.
If these partnerships materialize, ESPN’s ownership structure could change, but Disney plans to retain majority control (above 50%) to direct the network’s future.
Past Shareholders: Capital Cities/ABC
Before Disney’s acquisition, Capital Cities/ABC was the primary owner of ESPN. Capital Cities/ABC bought ESPN from its original founders and early investors in 1984. The Capital Cities/ABC era helped ESPN expand nationally and sign its first major sports league broadcasting contracts.
Disney absorbed Capital Cities/ABC entirely in 1995 for $19 billion, thus acquiring ESPN as a major part of that deal.
Who is the CEO of ESPN?
As of 2025, Jimmy Pitaro serves as the Chairman of ESPN. He has held this position since March 2018. Under his leadership, ESPN has expanded further into digital media and streaming services.
The CEO or Chairman of ESPN reports directly to the President of Disney Entertainment. This structure places ESPN firmly within Disney’s broader media operations.
Jimmy Pitaro: Chairman of ESPN
As of 2025, Jimmy Pitaro serves as the Chairman of ESPN. He was appointed to this role in February 2023, having previously held positions such as President of ESPN and Co-Chair of Disney Media Networks. Pitaro oversees all aspects of ESPN’s operations, including its domestic and international television networks, digital platforms, streaming services like ESPN+, and other related ventures.
Leadership and Strategic Vision
Under Pitaro’s leadership, ESPN has focused on several key strategic priorities:
- Direct-to-Consumer Innovation: Pitaro has championed the development of ESPN’s direct-to-consumer streaming services, including the upcoming “Flagship” platform, which aims to offer a comprehensive and personalized sports viewing experience.
- Content Expansion: He has secured long-term broadcasting rights with major sports leagues, such as the NFL, NBA, and UFC, ensuring ESPN’s continued prominence in sports media.
- Digital and Social Media Growth: Pitaro has emphasized the importance of digital platforms, leading to ESPN becoming the top U.S. digital sports property with significant monthly unique users and social media engagement.
- Diversity and Inclusion: He has prioritized diversity, equity, and inclusion within ESPN’s workforce and content offerings.
Previous Leadership
Before Pitaro, ESPN was led by several notable executives:
- John Skipper: Served as President from 2012 to 2017, focusing on expanding ESPN’s digital presence and securing key sports rights.
- George Bodenheimer: Held leadership roles from 1998 to 2011 and briefly in 2017-2018, overseeing ESPN’s growth into a global sports media powerhouse.
The Walt Disney Company’s Role
The Walt Disney Company holds an 80% ownership stake in ESPN, granting it significant control over the network’s operations and strategic direction. Disney’s influence extends to major decisions regarding content, distribution, and technological innovation within ESPN.
Hearst Communications’ Involvement
Hearst Communications owns the remaining 20% of ESPN. While it is a minority stakeholder, Hearst participates in certain strategic decisions and benefits from ESPN’s financial success.
Potential Strategic Partnerships
In recent developments, Disney has explored the possibility of bringing in strategic partners to invest in ESPN, potentially selling up to a 36% stake. This move aims to enhance ESPN’s streaming capabilities and adapt to the evolving media landscape. Potential investors include tech giants like Apple and Amazon, as well as telecom companies such as Verizon and Comcast.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of ESPN
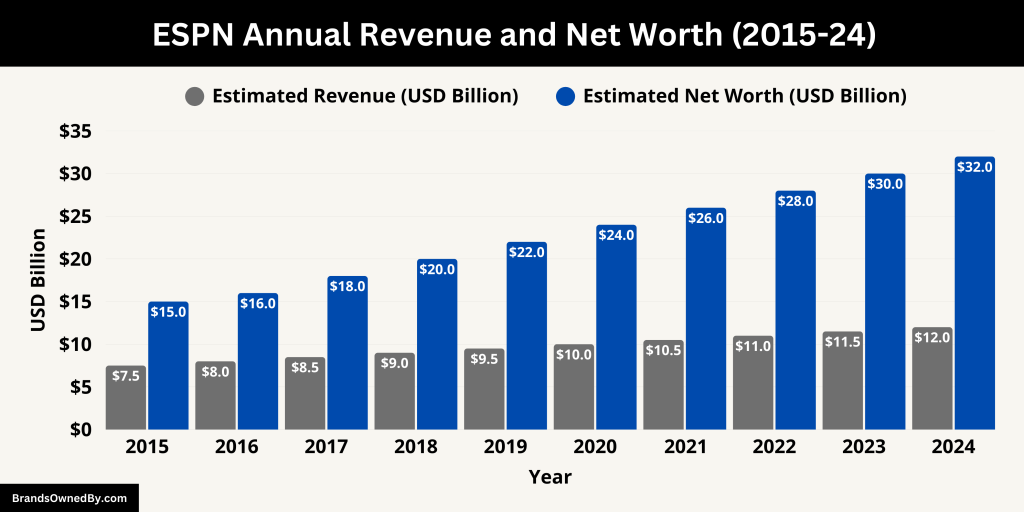
In the fiscal year 2024, ESPN generated approximately $17.6 billion in revenue, marking a 3% increase from the previous year’s $17.1 billion. This growth was driven by strong affiliate fees, advertising revenue, and subscription fees from services like ESPN+.
Despite facing challenges such as subscriber losses on ESPN+, the network maintained robust financial performance. In the final quarter of 2024, ESPN reported revenues of $4.85 billion, consistent with the same quarter in the previous year.
As of 2025, ESPN’s estimated net worth is approximately $32 billion, based on its social media presence and related earnings. However, considering ESPN’s extensive operations, including broadcasting rights, advertising, and subscriptions, its overall valuation is likely significantly higher.
ESPN’s financial strength is further underscored by its recent $7.8 billion deal to broadcast the College Football Playoffs through 2031, solidifying its position as a leader in sports media.
Below is an overview of the historical revenue and net worth of ESPN:
| Year | Estimated Revenue (USD) | Estimated Net Worth (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | $7.5 billion | $15 billion |
| 2016 | $8.0 billion | $16 billion |
| 2017 | $8.5 billion | $18 billion |
| 2018 | $9.0 billion | $20 billion |
| 2019 | $9.5 billion | $22 billion |
| 2020 | $10.0 billion | $24 billion |
| 2021 | $10.5 billion | $26 billion |
| 2022 | $11.0 billion | $28 billion |
| 2023 | $11.5 billion | $30 billion |
| 2024 | $12.0 billion | $32 billion |
Brands Owned by ESPN
As of 2025, ESPN owns and operates a diverse portfolio of media properties, digital platforms, and sports services. These assets are designed to cater to a wide range of sports fans, from traditional cable viewers to digital-first audiences.
Below is an overview of ESPN’s major brands and subsidiaries:
Of course! Here’s a full expansion for each ESPN-owned brand, with more detailed descriptions for each subheading:
| Brand/Company | ESPN Ownership (%) | Details |
|---|---|---|
| ESPN Flagship | 100% (Direct Ownership) | New direct-to-consumer streaming platform launching Fall 2025. Full ESPN channels accessible without cable. Fully developed and owned by ESPN. |
| ESPN+ | 100% (Direct Ownership) | Subscription-based streaming service offering exclusive live events, originals, and additional sports coverage. Part of Disney’s broader streaming strategy. |
| ESPN Deportes | 100% (Direct Ownership) | Spanish-language sports channel offering international soccer, MLB, NBA, boxing, and NFL in Spanish. |
| ESPNU | 100% (Direct Ownership) | College sports-focused cable channel under ESPN. Dedicated to NCAA football, basketball, baseball, and studio programming. |
| Andscape | 100% (Direct Ownership) | Multiplatform content initiative focusing on race, culture, and sports. Expanded into publishing, music, film, and TV. |
| ESPN Radio | 100% (Direct Ownership) | National sports radio network broadcasting via terrestrial radio, satellite, and streaming. Offers live sports and syndicated shows. |
| ESPN International | 100% (Direct Ownership, varies by region) | Global ESPN-branded operations, fully owned but sometimes partnered with local broadcasters. Manages international sports channels in Latin America, Brazil, Australia, Africa, and more. |
ESPN Flagship (Launching Fall 2025)
ESPN Flagship is ESPN’s boldest step into the direct-to-consumer space. Scheduled to launch in Fall 2025, this standalone streaming service will allow users to access the full ESPN suite without a cable subscription. Subscribers will be able to watch ESPN, ESPN2, ESPNU, ESPNEWS, SEC Network, ACC Network, and other associated channels. The platform will offer highly personalized features such as real-time stats, fantasy sports integrations, live betting options, and e-commerce for fan merchandise. With a subscription expected around $20/month, ESPN Flagship aims to redefine how fans consume sports content digitally.
ESPN+
ESPN+ is ESPN’s first successful foray into streaming. Launched in April 2018, ESPN+ offers a broad range of exclusive live sports events including UFC fights, PGA Tour golf, Top Rank Boxing, NHL, Bundesliga, La Liga, and college sports. It also features original programming like Peyton’s Places, Man in the Arena: Tom Brady, and 30 for 30 documentaries. As of early 2025, ESPN+ has over 25 million subscribers, making it a cornerstone of Disney’s streaming strategy alongside Disney+ and Hulu. ESPN+ complements the traditional ESPN channels by offering additional coverage not available elsewhere.
ESPN Deportes
ESPN Deportes is ESPN’s Spanish-language television network, catering to the United States’ Hispanic population. Launched in 2004, ESPN Deportes offers coverage of international sports events including Mexican soccer (Liga MX), UEFA Champions League, Major League Baseball, NBA games, NFL matches, boxing events, and more. It also features news shows like SportsCenter Deportes and original analysis programs. ESPN Deportes plays a vital role in diversifying ESPN’s audience reach and ensuring cultural representation in sports media.
ESPNU
ESPNU focuses specifically on college sports. Launched in March 2005, it broadcasts NCAA football, basketball, baseball, softball, lacrosse, and other college athletics. ESPNU has built a loyal following among fans of college sports, and it plays a critical role in showcasing emerging athletes before they turn professional. In addition to live games, ESPNU features studio programming such as College Football Live and The College Basketball Show.
Andscape
Andscape, originally known as The Undefeated, is ESPN’s multiplatform content initiative exploring the intersection of sports, race, and culture. Rebranded as Andscape in 2022, it has expanded beyond articles into book publishing (in partnership with Disney’s publishing arms), music production, television shows, and feature films. It provides thoughtful commentary and storytelling centered on African American experiences in sports and society. Notable projects include collaborations with filmmakers and authors to create socially impactful media.
ESPN Radio
ESPN Radio is ESPN’s 24/7 national sports talk and event coverage network. Founded in 1992, it broadcasts via hundreds of AM and FM stations nationwide and is also available via streaming. ESPN Radio features nationally syndicated shows like Greeny with Mike Greenberg, The Dan Le Batard Show (formerly hosted here), and The Will Cain Show. It also offers live play-by-play coverage for major sports leagues like the NBA Finals, MLB World Series, and college football playoffs.
ESPN International
ESPN International represents ESPN’s global footprint. It includes over 20 branded television networks and regional partnerships worldwide. Key international networks include ESPN Latin America, ESPN Brasil, ESPN Australia, and ESPN Africa. The company tailors content based on regional preferences, offering coverage of soccer, cricket, rugby, basketball, and American sports. ESPN International has local language programming and partnerships with leagues like the English Premier League, Indian Premier League, and Formula 1 to provide regionally relevant content.
Final Thoughts
If you are wondering who owns ESPN today, the simple answer is The Walt Disney Company, with Hearst Communications holding a minority stake. Through strong leadership, diversified assets, and global operations, ESPN remains a leader in sports broadcasting. Its future looks promising as it continues to adapt to the changing media landscape.
FAQs
Does Hearst Communications have control over ESPN?
Hearst Communications owns 20% of ESPN but does not control operations. It does have some influence on major strategic decisions.
How much is ESPN worth?
As of April 2025, ESPN has an estimated net worth of $32 billion based on brand strength, revenue, and market influence.
Is ESPN owned by Disney?
Yes, ESPN is owned by The Walt Disney Company. Disney holds an 80% controlling stake in ESPN, with Hearst Communications owning the remaining 20%.
Does ABC own ESPN?
While ABC and ESPN are both part of The Walt Disney Company, ABC does not directly own ESPN. ESPN operates as a separate subsidiary under Disney, though the two brands collaborate on sports programming and events.
Is TSN owned by ESPN?
No, TSN (The Sports Network) is not owned by ESPN. TSN is owned by BCE Inc. (Bell Media) in Canada. However, ESPN and TSN sometimes share content, particularly related to broadcasting American sports leagues in Canada.
Which country is the owner of ESPN?
ESPN is owned by The United States through The Walt Disney Company, which is based in Burbank, California.
Who created ESPN?
ESPN was created by Scott Rasmussen, a sports broadcaster, and Chad Hurley, a businessman, alongside co-founder Tom Yorton. The network launched on September 7, 1979, with the aim of providing 24/7 sports coverage.
How does ESPN make money?
ESPN generates revenue through several key streams:
- Affiliate Fees: ESPN charges cable and satellite providers fees for including ESPN channels in their packages.
- Advertising: ESPN earns money by selling advertising slots during sports events, which is its biggest source of revenue.
- Subscription Services: Revenue from ESPN+, its streaming service, which offers exclusive content and live events.
- Licensing and Broadcasting Rights: ESPN secures high-value broadcasting deals with sports leagues, such as the NFL, NBA, and UFC, paying large sums to retain exclusive rights.
Who owns ESPN TV?
ESPN TV is owned by The Walt Disney Company. Disney owns the entire ESPN network of channels, including ESPN1, ESPN2, ESPN3, ESPNEWS, SEC Network, ACC Network, and more.
Is ESPN still part of Disney+?
ESPN is not part of Disney+, but it is part of Disney’s broader streaming strategy. ESPN’s content is offered through its own streaming service, ESPN+, which is a separate service from Disney+. However, Disney bundles Disney+, Hulu, and ESPN+ together in certain subscription packages.
When did Disney acquire ESPN?
Disney acquired ESPN in 1996 as part of its purchase of Capital Cities/ABC, which owned ESPN at the time. Disney has since increased its stake, eventually reaching 80% ownership of ESPN as of 2025.

