Facebook, now part of Meta Platforms Inc., is one of the most influential social media platforms in the world. If you’re wondering who owns Facebook, the answer is more layered than it seems.
This article breaks down the history, shareholders, control structure, and business empire of the company.
History of Facebook
Facebook was launched in February 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg along with his Harvard classmates Eduardo Saverin, Andrew McCollum, Dustin Moskovitz, and Chris Hughes. Initially created as a social networking site for Harvard students, it quickly expanded to other universities and eventually to the public.
The Harvard Beginnings (2004)
Facebook began in a Harvard dorm room. Mark Zuckerberg, along with fellow students Eduardo Saverin, Andrew McCollum, Dustin Moskovitz, and Chris Hughes, launched “TheFacebook” on February 4, 2004. It started as a social networking site exclusive to Harvard students, allowing them to create profiles, connect, and share basic information. Within a month, it expanded to other Ivy League schools, and soon to most U.S. universities.
Early Growth and Expansion (2005–2006)
In 2005, the company dropped “The” from its name and became simply Facebook. It secured its first major investment from Peter Thiel, co-founder of PayPal. The platform opened to high school students and eventually to anyone over the age of 13 with a valid email address. By 2006, Facebook was no longer a college-exclusive platform. Its user base began growing rapidly across the globe.
Funding and Monetization (2007–2011)
Facebook attracted the attention of major investors. In 2007, Microsoft bought a 1.6% stake in the company, valuing it at $15 billion. During this period, Facebook introduced several key features, including the News Feed, the Like button, and Pages. It also launched its advertising platform, which became a significant revenue source. By 2010, Facebook had over 500 million users.
IPO and Global Dominance (2012)
On May 18, 2012, Facebook went public with an initial public offering (IPO) that raised $16 billion, one of the largest in tech history. It started trading on the NASDAQ under the symbol FB. The IPO gave Facebook a market valuation of over $100 billion. Despite some early trading issues, the move solidified Facebook’s position as a tech giant.
Major Acquisitions (2012–2014)
To strengthen its portfolio and eliminate competition, Facebook made major acquisitions. In 2012, it bought Instagram for $1 billion. In 2014, it acquired WhatsApp for $19 billion and Oculus VR for $2 billion. These strategic moves helped Facebook expand into messaging, photo sharing, and virtual reality.
Data Scandals and Regulatory Scrutiny (2016–2020)
Facebook faced major controversies in the latter half of the 2010s. The Cambridge Analytica scandal in 2018 revealed how user data was harvested and used for political profiling. This led to a global backlash, congressional hearings, and regulatory fines. The platform was criticized for misinformation, privacy concerns, and its role in elections. Despite the setbacks, Facebook continued to grow.
Rebranding to Meta (2021)
In October 2021, Facebook Inc. was renamed Meta Platforms Inc. The rebranding reflected a broader vision focused on the “metaverse” — an immersive digital world combining augmented and virtual reality. While Facebook remained the core social platform, Meta became the parent company overseeing Instagram, WhatsApp, Oculus (now Meta Quest), and more.
Recent Developments (2022–2025)
In recent years, Meta has doubled down on artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and short-form video content to compete with platforms like TikTok. Despite economic headwinds and workforce reductions, the company remains financially strong. Facebook itself continues to be one of the world’s most visited platforms, especially for social networking and advertising.
Who Owns Facebook: Major Shareholders
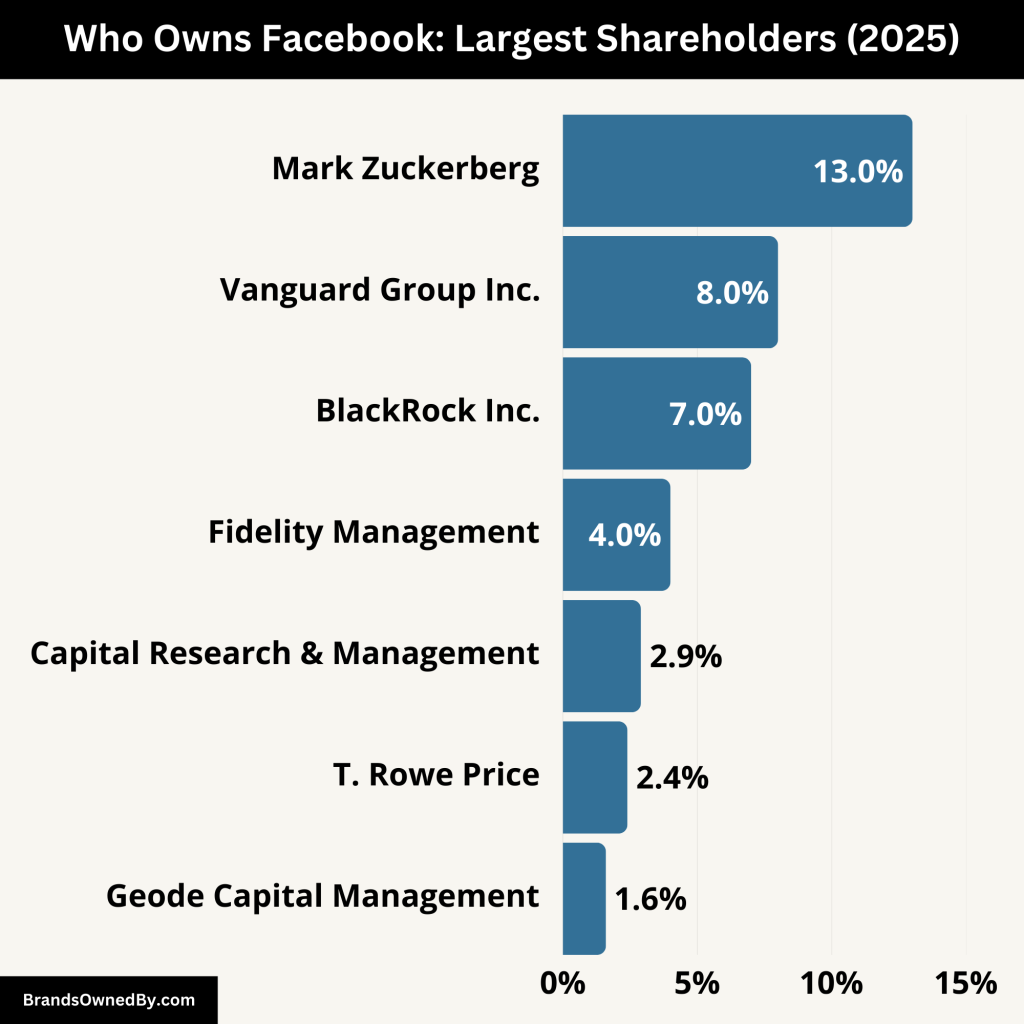
Facebook is owned by Meta Platforms Inc., a publicly traded company listed on NASDAQ under the ticker symbol META. While millions of investors hold shares in Meta, Mark Zuckerberg remains the largest individual shareholder. Through a dual-class share structure, Zuckerberg retains majority voting power, giving him effective control over Facebook and its parent company, Meta.
Here’s a list of the primary Facebook shareholders via Meta:
| Shareholder | Approximate Ownership (%) | Role and Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Mark Zuckerberg | 13% (financial) | Founder, CEO, and Chairman. Holds over 60% of voting power through Class B shares, controlling company decisions. |
| Vanguard Group Inc. | 7.8% | Largest institutional investor. Passive investor with voting rights on major corporate matters. |
| BlackRock Inc. | 6.6% | Major institutional investor. Passive investor with voting rights, primarily on governance matters. |
| Fidelity Management & Research | 4.3% | Long-term institutional holder. Primarily represents mutual funds and retirement accounts. |
| T. Rowe Price | 2.4% | Growth-oriented fund manager. Active investor with long-term confidence in Meta’s potential. |
| Capital Research & Management | 2.9% | Active mutual fund manager. Invests for long-term growth in Meta’s expanding business ecosystem. |
| Geode Capital Management | 1.6% | Passive stakeholder, often participating in index-based strategies through Vanguard. |
| Public Shareholders | Majority (remaining shares) | Includes retail investors and smaller institutions. Limited influence due to lack of voting rights. |
| Other Insiders and Executives | Small percentage | Includes early employees and executives, with limited voting power. |
Mark Zuckerberg – Founder, CEO, and Controlling Shareholder
Mark Zuckerberg is the largest and most powerful shareholder in Meta. He owns around 13% of Meta’s total outstanding shares, but due to Meta’s dual-class share structure, he holds over 60% of the voting power. His shares are primarily Class B shares, which carry 10 votes per share, compared to 1 vote per share for Class A shares held by the public.
This voting control allows Zuckerberg to effectively steer company decisions on strategy, leadership, mergers, and acquisitions. Despite owning less than a majority of the financial equity, his influence is unrivaled. He also serves as Chairman and CEO, giving him both legal and practical control over Meta and its platforms, including Facebook.
Vanguard Group Inc.
The Vanguard Group is one of the most prominent asset management companies in the world and the largest institutional investor in Meta. It holds approximately 7.8% of Meta’s Class A shares. Vanguard’s stake is passive, meaning it does not influence daily operations but does vote on major decisions like board elections and corporate policy proposals.
As a fund manager, Vanguard represents millions of investors, including pension plans and retirement accounts. Its stake in Meta reflects strong investor confidence in the company’s long-term profitability.
BlackRock Inc.
BlackRock is another major institutional investor, holding about 6.6% of Meta’s shares. Like Vanguard, BlackRock doesn’t engage in day-to-day management but can influence shareholder proposals and vote on corporate governance matters.
BlackRock’s investments often reflect broad market trends, and its presence in Meta underscores the stock’s importance in global investment portfolios. It also plays a role in ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) activism, though its influence on Meta’s direction is limited due to Zuckerberg’s voting power.
Fidelity Management & Research
Fidelity owns approximately 4.3% of Meta’s Class A shares. It is one of the largest privately owned financial services firms and a long-time investor in technology companies. Fidelity manages various mutual funds and retirement accounts that include Meta as a top holding.
Although it lacks decision-making power, Fidelity’s continued investment signals institutional trust in Meta’s business strategy, especially as it shifts toward AI and virtual reality.
T. Rowe Price
T. Rowe Price holds close to 2.4% of Meta’s shares. The firm is known for investing in high-growth companies with long-term potential. It has been a consistent institutional investor in Meta since its early post-IPO days.
While T. Rowe Price is smaller compared to Vanguard and BlackRock in terms of Meta shares, it remains a key player in shareholder votes and market confidence.
Capital Research & Management
Capital Research and Management Company, part of the Capital Group, owns around 2.9% of Meta shares. Capital Group is known for its active management style and typically takes long positions in promising tech companies. Its investment reflects a belief in Meta’s evolving product ecosystem and revenue potential.
Geode Capital Management
Geode Capital Management, which often manages assets on behalf of Vanguard, owns about 1.6% of Meta. It is a lesser-known but significant institutional investor that participates in passive index-based strategies. Geode’s presence shows the popularity of Meta shares in index funds and ETFs.
Public Shareholders
A large portion of Meta’s Class A shares is held by public investors, including individual retail traders and smaller institutions. These shareholders have limited influence due to the lack of voting rights associated with Class B shares, which are almost entirely held by Zuckerberg and a few insiders. Still, public investment provides liquidity and plays a vital role in Meta’s stock market value.
Other Insiders and Executives
While Mark Zuckerberg is the most significant insider, other Meta executives and early employees also hold shares, though none have major voting power. People like Sheryl Sandberg (former COO) and David Wehner (former CFO) have owned or still own smaller stakes. Their influence was primarily through management roles, not ownership.
Who Controls Facebook?
Although Meta Platforms Inc. is a publicly traded company with thousands of shareholders, the control of Facebook, its flagship social media platform, is primarily in the hands of Mark Zuckerberg, thanks to the company’s unique governance structure. However, other key individuals and bodies play significant roles in shaping the company’s direction.
Mark Zuckerberg – The Ultimate Decision-Maker
Mark Zuckerberg is the founder, CEO, and Chairman of Meta Platforms Inc. He exerts primary control over the company, despite owning only around 13% of its financial shares. This control stems from Meta’s dual-class share structure, which grants Class B shares (owned by Zuckerberg and a few insiders) 10 votes per share, compared to 1 vote per share for the Class A shares held by the public.
Zuckerberg’s voting power enables him to make significant corporate decisions, including:
- Appointing the board of directors
- Approving or blocking mergers and acquisitions
- Overseeing long-term strategic goals and product development
His near-total voting control has made him the unquestionable decision-maker at Meta, even as the company has grown into a global tech giant.
CEO Role – Mark Zuckerberg
As CEO, Mark Zuckerberg is responsible for overseeing the day-to-day operations of Meta, including its various social media platforms (Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp) and its long-term initiatives, such as the metaverse. He manages the executive team and ensures that the company’s vision and strategies align with business goals.
Zuckerberg’s leadership is characterized by his focus on innovation, particularly in artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and the metaverse. He’s the face of Meta’s initiatives, and his influence is not only limited to company decisions but also extends to global policy discussions about privacy, misinformation, and tech regulation.
Zuckerberg’s compensation package includes both salary and stock options, but his primary wealth is tied to his substantial stake in the company, which allows him to maintain control over Meta’s corporate direction.
The Role of the Board of Directors
While Mark Zuckerberg holds significant power, Meta also has a Board of Directors that is responsible for overseeing company performance, ensuring shareholder interests are met, and offering advice to the CEO. The board includes both insiders (such as Zuckerberg) and independent directors, although Zuckerberg’s voting power allows him to maintain substantial influence over board decisions.
The current board includes several key figures, such as:
- Sheryl Sandberg (former COO, until 2022): Sandberg was instrumental in Facebook’s growth, particularly in monetizing the platform through advertising. Although she stepped down as COO, she remains influential in Meta’s broader strategy.
- Susan Wojcicki (former CEO of YouTube): Although no longer actively involved, Wojcicki had influence as a director.
- Other notable members of the board come from various backgrounds, including technology, finance, and academia. However, Zuckerberg holds the power to appoint or remove board members, further consolidating his control.
The Role of Executives
Apart from Zuckerberg, several key executives help shape the day-to-day operations of Meta:
- Andrew Bosworth (Boz) – Chief Technology Officer (CTO): Boz oversees Meta’s hardware and infrastructure development, including efforts related to virtual reality and artificial intelligence.
- David Wehner – Chief Financial Officer (CFO): Wehner manages Meta’s finances, including revenue from advertising and investments in new technologies.
- Chris Cox – Chief Product Officer (CPO): Cox oversees product strategy for Meta’s platforms, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
While these executives are integral to Meta’s operations, their influence is ultimately guided by Zuckerberg’s strategic vision and the company’s board of directors.
The Role of Institutional Investors
Institutional investors like Vanguard, BlackRock, and Fidelity do not directly control Meta but can influence its decision-making process, especially in areas like corporate governance, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices, and executive compensation. These investors can vote on major shareholder resolutions, though their power is limited by the dominance of Zuckerberg’s voting rights.
While these investors generally respect Zuckerberg’s leadership and vision for Meta, they may intervene in situations concerning shareholder rights or company performance. However, their influence is often more passive than active, given the structure of Meta’s governance.
Board Decisions and Corporate Governance
Despite Zuckerberg’s dominance, Meta is still subject to public company governance norms. This means regular shareholder meetings, annual votes on key matters, and oversight by external regulators. Meta also faces scrutiny from government bodies, such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and European regulators, on matters like data privacy, antitrust issues, and content moderation.
Meta has at times faced shareholder proposals for increased transparency and stronger governance measures, but Zuckerberg’s control has consistently kept those proposals from significantly altering company operations.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Facebook
Meta Platforms Inc., the parent company of Facebook, reported a revenue of approximately $164.5 billion in 2024. As of April 2025, Meta’s market capitalization stood near $1.45 trillion making it one of the most valuable tech companies globally. Facebook, as a product within Meta’s ecosystem, contributes significantly to this revenue, mainly through digital advertising.
In 2024, advertising continued to be Meta’s primary revenue driver, contributing approximately 98% of total revenue. CEO Mark Zuckerberg has projected capital expenditures between $37 billion and $40 billion for 2024, with significant investments in artificial intelligence and data center expansion.
Meta’s revenue growth has been largely driven by its advertising business. Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp have become advertising powerhouses, attracting billions of dollars annually from marketers worldwide.
Over time, Meta has also diversified its revenue streams, focusing on acquisitions like Instagram, WhatsApp, and Oculus (now Meta Quest) to maintain growth. In recent years, Meta has ramped up its investments in the metaverse and virtual reality products, which, although currently a smaller portion of the business, are expected to contribute significantly to future revenue.
Here is a detailed breakdown of Meta’s annual revenue and market capitalization (net worth) for the past decade:
| Year | Annual Revenue (in billions) | Net Worth/Market Capitalization (in billions) | Key Milestones |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | $12.47 | $200 | Mobile-first transition, Instagram growth |
| 2015 | $17.93 | $250 | Facebook hits 1 billion users, mobile ads grow |
| 2016 | $27.64 | $370 | Expansion into virtual reality with Oculus |
| 2017 | $40.65 | $500 | Instagram’s revenue contribution increases |
| 2018 | $55.84 | $600 | Privacy issues (Cambridge Analytica) impact stock |
| 2019 | $70.70 | $620 | Focus on AI and automated ads, WhatsApp business |
| 2020 | $86.00 | $700 | COVID-19 boosts online advertising revenue |
| 2021 | $117.93 | $1,000 | Highest market cap, major investment in metaverse |
| 2022 | $116.61 | $850 | Economic challenges, metaverse investment ramped |
| 2023 | $117.90 | $700 | Decline in market cap, cost-cutting, AI investment |
| 2024 | $164.50 | $1,450 | Continued growth, significant AI investments |
Companies Owned by Facebook
Facebook itself doesn’t own any companies. Its parent company Meta, however, owns several other companies and brands.
Here’s a list of the companies and brands owned by Meta:
| Company | Description | Acquisition Year | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| The world’s largest social networking platform. Known for its advertising business, content sharing, and community. | 2004 | Social networking, advertising, content sharing, Facebook Groups, Marketplace, Messenger. | |
| A photo and video-sharing platform with over 2 billion active users. Major platform for visual content and ads. | 2012 | Social networking, influencer marketing, visual content, shopping, advertising. | |
| A widely used messaging app with over 2 billion users, offering secure messaging and business communication tools. | 2014 | Messaging, voice and video calls, end-to-end encryption, business communication. | |
| Oculus (Meta Quest) | A leading virtual reality company now branded as Meta Quest, known for VR headsets and immersive experiences. | 2014 | Virtual reality (VR), metaverse, immersive technology, gaming, and educational experiences. |
| Messenger | Meta’s standalone messaging app that evolved from Facebook’s Chat feature, supporting texts, voice, and video calls. | 2011 | Instant messaging, voice and video calls, multimedia sharing, cross-platform communication. |
| Portal | A smart video-calling device for Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp, with AI-enhanced features for social interaction. | 2018 | Video calling, smart home integration, social interaction, remote work communication. |
| Giphy | A platform for creating and sharing GIFs, integrated into Meta’s apps like Facebook and Instagram. | 2020 | GIF creation and sharing, social messaging, internet culture. |
| NPE Team | Meta’s experimental division focused on developing new social platforms and digital tools for niche audiences. | 2018 | Product experimentation, social networking apps, testing new digital communication concepts. |
| Workplace by Meta | A business-focused platform offering collaboration and communication tools for companies and teams. | 2016 | Workplace collaboration, enterprise communication, video calls, project management. |
| Building 8 (Meta Reality Labs) | Meta’s internal division developing augmented reality (AR) technologies and new consumer hardware. | 2017 | Augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), brain-computer interface, metaverse technologies. |
| Fayvo | A social platform for sharing and discovering interests, like books, movies, and restaurants. | 2022 | Niche social networking, shared interests, discovery, and community-based interaction. |
Instagram, acquired by Facebook (now Meta) in 2012 for around $1 billion, is a photo and video-sharing platform that has grown into one of the most popular social media networks globally. With over 2 billion active users, Instagram is Meta’s second-largest platform in terms of user base.
Instagram is a key part of Meta’s advertising strategy. The platform’s stories, posts, Reels, and shopping features provide users with a range of engagement tools, while advertisers utilize Instagram to reach younger audiences through visually engaging content. Instagram has been pivotal in driving Meta’s expansion in e-commerce and influencer marketing.
Meta acquired WhatsApp, the global messaging app, in 2014 for about $19 billion, making it one of the largest technology acquisitions at the time. WhatsApp boasts over 2 billion monthly active users and remains one of the most widely used messaging platforms in the world.
WhatsApp enables text messaging, voice, and video calls, as well as file sharing, and it is particularly popular in markets outside the United States. Meta has invested in WhatsApp for Business, helping companies communicate with customers via the app. Additionally, WhatsApp’s integration into Meta’s broader ecosystem plays a role in the company’s push towards end-to-end encryption and secure messaging services.
Oculus (Now Meta Quest)
Acquired by Meta in 2014 for $2 billion, Oculus is now branded as Meta Quest. It is a leading virtual reality (VR) company known for developing VR headsets and platforms that help create immersive experiences. Meta’s focus on VR has been a significant part of its transition toward the metaverse, a virtual world where people can interact in real-time.
The Meta Quest series includes popular products like the Meta Quest 2 and Meta Quest Pro, which have garnered strong market interest. Meta continues to invest heavily in the VR and AR space, aiming to create the next generation of social and work experiences. Oculus is a key piece of Meta’s vision for a immersive digital future, with virtual spaces, gaming, and education being potential growth areas.
Messenger
Messenger is Meta’s instant messaging app that evolved from the Facebook Chat feature. Launched as a standalone app in 2011, Messenger allows users to send text messages, make voice and video calls, and send multimedia messages, including images and stickers. It has grown to become one of the world’s most popular messaging platforms, with over 1.3 billion monthly active users.
Messenger has been integrated with Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp to allow cross-platform messaging. Meta has also explored using Messenger for business communication, with features like Messenger Bots and payment integration. The app plays an important role in Meta’s strategy to provide all-in-one communication tools across its platforms.
Portal
Portal is a series of smart video calling devices developed by Meta. Launched in 2018, Portal allows users to make high-quality video calls through Facebook Messenger or WhatsApp, using features like auto-framing and smart sound to improve call quality. Meta has marketed Portal as a way to enhance social interactions and family communication, particularly in the context of remote work and long-distance relationships.
Portal devices come in different models, including the Portal TV and Portal+, and have been integrated with Amazon’s Alexa for smart home capabilities. While its market share is relatively small compared to other smart devices like Amazon Echo and Google Nest, Portal represents Meta’s entry into the hardware market and reflects the company’s broader vision of connecting people through technology.
Giphy
In 2020, Meta acquired Giphy, the popular platform for creating and sharing animated GIFs, for $400 million. Giphy integrates with various Meta-owned platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Messenger to allow users to easily share GIFs in their posts and messages.
Giphy helps to enhance the user experience on Meta’s platforms by offering fun and expressive ways for users to communicate. In 2021, Meta was forced to halt the acquisition after facing an antitrust review by the UK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA), but the deal was ultimately approved in 2022. Giphy represents Meta’s push toward becoming an integral part of internet culture, particularly in social messaging and digital content.
NPE Team (New Product Experimentation)
Meta’s NPE Team is an experimental division focused on building new social media platforms and products. Its goal is to explore innovative concepts that may evolve into future flagship products for Meta. The NPE team has worked on several small-scale products, including:
- Tuned: A private messaging app for couples.
- CatchUp: A voice-only social app for friends to catch up on calls.
- Bump: A platform for sharing music preferences.
While many of these products have been discontinued, the NPE team continues to explore new ways to keep Meta at the cutting edge of social media and digital communication.
Workplace by Meta
Launched in 2016, Workplace by Meta is a business-focused platform designed to provide communication and collaboration tools for companies. It combines features from Facebook, such as groups, messenger, and video calls, but tailored for a corporate environment. Workplace offers businesses a secure way to collaborate and is widely used in industries like healthcare, education, and retail.
Workplace by Meta competes with enterprise communication platforms like Slack and Microsoft Teams, and has seen increasing adoption as more companies embrace remote and hybrid work models.
Building 8 (Now Meta Reality Labs)
Meta’s Building 8 was an internal research and development division focused on developing new consumer hardware products, including AR glasses and brain-machine interfaces. The division has now been rebranded as Meta Reality Labs and plays a key role in Meta’s development of cutting-edge technologies for the metaverse.
One of the division’s most ambitious projects includes the development of augmented reality (AR) glasses. Meta has also made significant investments into brain-computer interface technology, aiming to create a future where users can interact with digital content through thought alone.
Fayvo
Meta acquired Fayvo in 2022, a social networking platform built around shared interests. The platform allows users to create lists of things they love—such as books, movies, or restaurants—and share these with friends. Fayvo was designed to foster discovery and community based on shared passions, helping Meta expand into the niche social networking space.
Though Fayvo’s success has been somewhat limited, its integration into Meta’s broader portfolio highlights the company’s focus on improving social interaction beyond the mainstream. It is part of Meta’s ongoing experimentation in the social network landscape.
Final Words
Technically, Meta Platforms Inc. owns Facebook but the real control lies with Mark Zuckerberg. With the majority of voting power, he has near-total influence over the platform’s direction. Institutional investors hold large chunks of Meta’s shares, but none match the authority Zuckerberg holds. Facebook continues to be a pillar of Meta’s revenue, even as the company expands into AI, VR, and the metaverse.
FAQs
Who founded Facebook?
Facebook was founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg, along with Eduardo Saverin, Dustin Moskovitz, Andrew McCollum, and Chris Hughes.
Is Facebook privately owned?
No, Facebook is owned by Meta Platforms Inc., a publicly traded company. However, Mark Zuckerberg controls it through a special share structure.
What is Meta?
Meta is the parent company of Facebook. It was rebranded in 2021 to reflect a shift toward virtual reality and the metaverse.
How much of Facebook does Zuckerberg own?
Mark Zuckerberg owns around 13% of Meta’s shares but controls over 60% of the company’s voting rights.
Does Facebook still make money?
Yes, Facebook remains a major source of income for Meta, primarily through digital advertising.
Who owns Facebook and Instagram?
Both Facebook and Instagram are owned by Meta Platforms Inc., which is led by Mark Zuckerberg. Meta is the parent company of both platforms. Zuckerberg, through Meta, controls these platforms alongside other acquisitions like WhatsApp and Oculus (Meta Quest).

