Uber is one of the most well-known ride-hailing platforms in the world. If you’re wondering who owns Uber, the answer includes a mix of public shareholders, investment firms, and company insiders. This article explores Uber’s ownership, leadership, revenue, and more.
Uber Company Profile
Uber Technologies Inc., commonly known as Uber, is a global technology company headquartered in San Francisco, California. It operates in the ride-sharing, food delivery, and logistics sectors. Uber connects passengers with drivers through a mobile app, making transportation more accessible and cashless. Its business model has revolutionized urban mobility.
Founders
Uber was founded in March 2009 by Garrett Camp and Travis Kalanick. The idea originated when Garrett Camp, a co-founder of StumbleUpon, had trouble finding a cab on a snowy night in Paris. He thought of a service where people could request a ride from their phones. He teamed up with Travis Kalanick to turn that vision into reality. The service launched as UberCab in San Francisco in 2010.
Company Details
- Full Name: Uber Technologies Inc.
- Founded: March 2009
- Founders: Garrett Camp and Travis Kalanick
- Headquarters: San Francisco, California, United States
- CEO (2025): Dara Khosrowshahi
- Industry: Mobility as a service, Technology
- Stock Ticker: UBER (NYSE)
- Key Services: Ride-hailing, Food delivery (Uber Eats), Freight logistics (Uber Freight)
- Global Reach: Operates in over 70 countries and 10,000+ cities.
Major Milestones
- 2010: UberCab officially launched in San Francisco with just a few black cars.
- 2011: Rebranded to Uber and expanded to New York, Paris, and other cities.
- 2014: Introduced UberX, a low-cost version using everyday drivers and vehicles.
- 2015: Launched UberPOOL, allowing passengers to share rides with others going in the same direction.
- 2015: Entered the food delivery market with Uber Eats.
- 2016: Began testing self-driving cars in Pittsburgh and acquired Otto, a self-driving truck company.
- 2017: Travis Kalanick resigned as CEO amid controversies. Dara Khosrowshahi was appointed CEO.
- 2019: Uber went public in one of the largest tech IPOs in U.S. history, listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol UBER.
- 2020: Acquired Postmates and Careem, strengthening its position in food delivery and the Middle East ride-hailing market.
- 2021–2023: Focused on cost-cutting, profitability, and integrating acquired services.
- 2024: Reached consistent profitability and reported annual revenue exceeding $37 billion.
Who Owns Uber: Top Shareholders
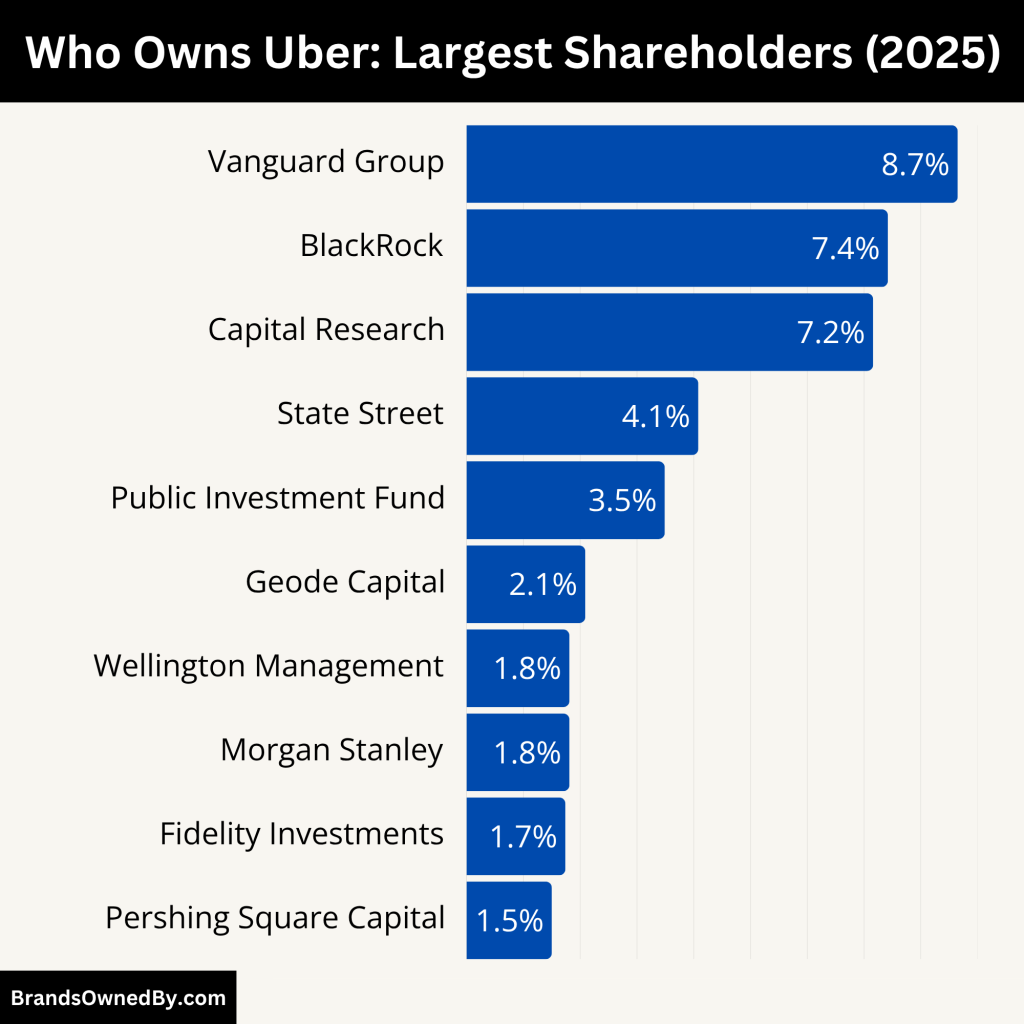
Uber is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol UBER. Ownership of Uber is distributed among institutional investors, mutual funds, company insiders, and public shareholders. The largest shareholders are major investment firms that hold significant influence through voting rights.
Here’s an overview of the major shareholders of Uber as of June 2025:
| Shareholder | Ownership% (2025) | Investor Type | Role and Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | 8.65% | Institutional (Passive) | Largest shareholder, strong voting power, influences governance decisions. |
| BlackRock, Inc. | 7.42% | Institutional (Passive) | Promotes ESG, votes in shareholder meetings, adds market credibility. |
| Capital Research and Management | 7.16% | Institutional (Active) | Long-term active investor, involved in strategic alignment and company oversight. |
| State Street Global Advisors | 4.08% | Institutional (Passive) | Passive index investor, influences governance through proxy voting. |
| Public Investment Fund (Saudi Arabia) | 3.49% | Sovereign Wealth Fund | Strategic international investor, supported Uber’s expansion into the Middle East. |
| Geode Capital Management | 2.09% | Institutional (Quantitative) | Index-based investor, reflects algorithmic and risk-adjusted interest in Uber. |
| Wellington Management Group LLP | 1.81% | Institutional (Active) | Veteran investor, involved in strategic and governance matters. |
| Morgan Stanley | 1.81% | Institutional/Advisor | Former IPO underwriter, financial advisor, investor with strategic insight. |
| FMR LLC (Fidelity Investments) | 1.74% | Institutional (Active) | Diversified growth investor, active in governance and company dialogue. |
| Pershing Square Capital Management | ~1.5% | Hedge Fund (Activist) | Recently acquired, likely to support or push for strategic and financial optimization. |
The Vanguard Group, Inc. – Uber’s Largest Shareholder (8.65%)
The Vanguard Group is the largest institutional shareholder in Uber, holding approximately 8.65% of the outstanding shares. As one of the world’s biggest asset managers, Vanguard represents millions of retail and institutional investors through its mutual funds and ETFs.
Although Vanguard does not participate directly in day-to-day operations, it exercises voting rights at shareholder meetings and influences board-level decisions. The firm typically votes on issues such as executive compensation, corporate governance, and sustainability policies. Its long-term passive investment strategy reflects confidence in Uber’s growth and stability.
BlackRock, Inc. – A Strategic Institutional Stakeholder (7.42%)
BlackRock holds around 7.42% of Uber’s shares, making it the second-largest shareholder. As another global investment powerhouse, BlackRock’s influence is considerable. It manages assets through iShares ETFs and various institutional funds.
The firm is known for advocating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards across its portfolio. In Uber’s case, BlackRock’s presence adds institutional credibility and supports Uber’s image among long-term investors. The company votes actively in shareholder meetings and engages in dialogue with corporate boards.
Capital Research and Management Company – Long-Term Investment Partner (7.16%)
Capital Research, part of the Capital Group, owns 7.16% of Uber. Known for its active investment style, Capital Research takes a hands-on approach to portfolio companies. Unlike passive investors, it often works closely with companies to ensure strong governance and strategic direction.
Its significant stake in Uber signals high confidence in the company’s fundamentals, profitability roadmap, and leadership. Capital Group’s investments are typically long-term, which aligns well with Uber’s shift toward sustainable earnings and global expansion.
State Street Global Advisors – Passive but Powerful (4.08%)
State Street Global Advisors holds about 4.08% of Uber. Though known for its passive investment strategy, State Street has a history of engaging with its portfolio companies on corporate governance issues.
Its large position gives it a voice in proxy voting on matters like board composition and strategic direction. While it doesn’t directly influence operations, its presence strengthens Uber’s shareholder base and enhances its standing on Wall Street.
Public Investment Fund (Saudi Arabia) – Strategic International Backer (3.49%)
The Public Investment Fund (PIF) of Saudi Arabia owns 3.49% of Uber, positioning it as one of the few sovereign wealth funds with a direct stake in the company. PIF initially invested in Uber back in 2016 and played a major role in Uber’s international expansion, particularly in the Middle East.
Uber’s 2020 acquisition of Careem, a Dubai-based ride-hailing firm, aligned with PIF’s vision of global technology partnerships. The fund’s strategic interest supports Uber’s footprint in high-growth regions, and although it holds a smaller stake now, it remains a significant investor with global insights.
Geode Capital Management – Quantitative Confidence (2.09%)
Geode Capital Management, which manages assets for Fidelity’s index funds, holds 2.09% of Uber. As a quantitative investment firm, Geode’s holdings reflect algorithmic and data-driven confidence in Uber’s performance.
It does not actively engage with the company but adds to the institutional investor base that supports Uber’s public valuation and market confidence. Geode’s role is primarily financial, focusing on index replication and risk-adjusted returns.
Wellington Management Group LLP – Veteran Active Investor (1.81%)
Wellington Management owns 1.81% of Uber. Known for its rigorous research and active portfolio management, Wellington invests across both public and private markets. Its Uber stake represents a belief in the company’s core business and growth into adjacent verticals like logistics and delivery. Wellington often engages with companies it invests in, providing strategic input and supporting long-term innovation.
Morgan Stanley – From Underwriter to Shareholder (1.81%)
Morgan Stanley has a longstanding relationship with Uber. It served as one of the lead underwriters during Uber’s 2019 IPO and continues to hold a 1.81% stake in the company. The firm’s continued interest suggests it still sees value in Uber’s business model. Morgan Stanley also provides financial advisory services and has helped Uber navigate major acquisitions and partnerships. Its dual role as an investor and advisor adds strategic depth to Uber’s financial backbone.
FMR LLC (Fidelity Investments) – Diversified Growth Holder (1.74%)
FMR LLC, the parent company of Fidelity Investments, holds a 1.74% stake in Uber. Fidelity is known for its diversified approach, investing in both stable and high-growth companies.
Fidelity’s stake in Uber is part of its growth-focused portfolio, reflecting optimism in the company’s delivery services, international expansion, and evolving profitability. Fidelity participates in proxy voting and may also engage with company executives on governance matters.
Pershing Square Capital Management – Activist Confidence (Approx. 1.5%)
In early 2025, Pershing Square Capital Management, led by activist investor Bill Ackman, acquired a substantial stake in Uber, reportedly over 30 million shares, equivalent to about 1.5%. Ackman described Uber as “undervalued with world-class leadership.”
His fund tends to invest in companies where it sees potential for long-term transformation and improved profitability. While Pershing’s stake is smaller than the big institutional players, its activist approach may add pressure or support for strategic changes if needed. The entry of Pershing Square signals that Uber is seen not only as a tech giant but also as an undervalued asset in capital markets.
Who is the CEO of Uber?
As of 2025, Dara Khosrowshahi serves as the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Uber Technologies Inc. He has held this position since September 2017, leading the company through significant transformations and steering it toward sustained profitability.
Background and Career
Born on May 28, 1969, in Tehran, Iran, Dara Khosrowshahi immigrated to the United States during his childhood. He earned a Bachelor of Science degree in Electrical and Electronics Engineering from Brown University. Khosrowshahi began his professional journey as an analyst at Allen & Company, later working under Barry Diller at USA Networks. He served as the Chief Financial Officer of IAC before becoming the CEO of Expedia in 2005. During his tenure at Expedia, he expanded the company’s global presence and oversaw acquisitions such as Travelocity, Orbitz, and HomeAway.
Leadership at Uber
Khosrowshahi took over as CEO of Uber in 2017, succeeding co-founder Travis Kalanick. Under his leadership, Uber has achieved several milestones:
- Profitability: Uber reported its first annual operating profit in 2023, with continued growth in subsequent years.
- Diversification: The company expanded beyond ride-hailing into areas like food delivery, freight, and micromobility.
- Strategic Partnerships: Khosrowshahi has emphasized collaborations, such as integrating autonomous vehicle services into Uber’s platform.
- Corporate Culture: He has worked to reshape Uber’s corporate culture, focusing on ethical practices and employee engagement.
Decision-Making Structure
Uber’s governance includes a Board of Directors and an Executive Leadership Team. The Board oversees strategic decisions and corporate policies, while the Executive Team manages daily operations. Khosrowshahi, as CEO, plays a pivotal role in both strategic planning and operational execution.
Past CEOs of Uber
- Ryan Graves (2010): Uber’s first CEO, who helped launch the company’s early operations.
- Travis Kalanick (2010–2017): Co-founder who led Uber through rapid global expansion but resigned amid controversies.
Who Controls Uber?
Uber is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol UBER. Control is distributed among shareholders, the Board of Directors, and the Executive Leadership Team.
- Shareholders: Major institutional investors include The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and Capital Research, among others.
- Board of Directors: Comprises experienced professionals from various industries, providing oversight and strategic guidance.
- Executive Leadership Team: Led by CEO Dara Khosrowshahi, responsible for implementing strategies and managing day-to-day operations.
This structure ensures a balance between investor interests, strategic oversight, and operational efficiency.
Uber Annual Revenue and Net Worth
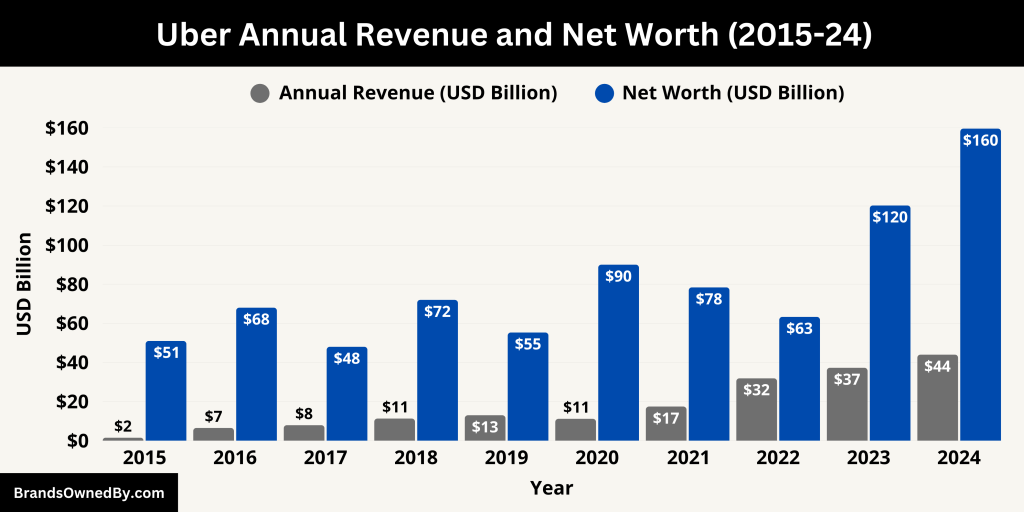
In the fiscal year ending December 31, 2024, Uber reported a total revenue of $43.98 billion, marking an 18% increase from the previous year’s $37.28 billion.
Revenue Breakdown by Segment:
- Mobility: $25.1 billion (57.0% of total revenue)
- Delivery: $13.8 billion (31.3%)
- Freight: $5.1 billion (11.7%)
Revenue Breakdown by Region:
- United States and Canada: $23.6 billion (53.7%)
- Europe, Middle East, and Africa: $12.5 billion (28.5%)
- Asia-Pacific: $5.0 billion (11.5%)
- Latin America: $2.8 billion (6.4%)
This growth is attributed to increased demand across all segments, particularly in the Mobility and Delivery services.
Uber achieved a net income of $9.86 billion for 2024, a substantial rise from $1.89 billion in 2023. This increase includes a $6.4 billion benefit from the release of a valuation allowance on certain U.S. federal and state deferred tax assets.
Market Capitalization
As of June 2025, Uber’s market capitalization stands at approximately $159.64 billion, reflecting investor confidence and the company’s robust financial performance.
Operational Highlights
- Trips: Uber facilitated 11.27 billion trips in 2024, a 19% increase from 9.45 billion in 2023.
- Gross Bookings: Totaled $162.77 billion in 2024, up 18% from the previous year.
- Adjusted EBITDA: Reported at $6.48 billion, a 60% increase year-over-year.
- Free Cash Flow: Reached $6.89 billion, doubling from $3.36 billion in 2023.
These figures underscore Uber’s successful strategies in expanding its services and optimizing operations, leading to enhanced profitability and shareholder value.
Here’s an overview of the annual revenue and net worth of Uber from 2015 to 2024:
| Year | Annual Revenue (USD) | Market Cap / Net Worth (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | $43.98 billion | ~$159.6 billion | Record revenue; major profit jump due to tax benefit. |
| 2023 | $37.28 billion | ~$120.3 billion | First full-year net profit; strong Mobility and Delivery performance. |
| 2022 | $31.88 billion | ~$63.3 billion | Significant growth post-pandemic; focus on profitability. |
| 2021 | $17.45 billion | ~$78.4 billion | Recovery year; strong bounce-back in ride-hailing demand. |
| 2020 | $11.14 billion | ~$90.0 billion | Impact of COVID-19; Delivery grew while Mobility declined. |
| 2019 | $13.00 billion | ~$55.3 billion (post-IPO) | IPO year (May 2019); raised $8.1 billion. |
| 2018 | $11.27 billion | ~$72.0 billion (private est.) | Final year before IPO; major global expansion. |
| 2017 | $7.93 billion | ~$48.0 billion (private est.) | Dara Khosrowshahi appointed as CEO. |
| 2016 | $6.50 billion (est.) | ~$68.0 billion (private est.) | Massive private funding from investors like SoftBank and PIF. |
| 2015 | $1.50 billion (est.) | ~$51.0 billion (private est.) | Early growth driven by global ride-hailing adoption. |
Brands and Companies Owned by Uber
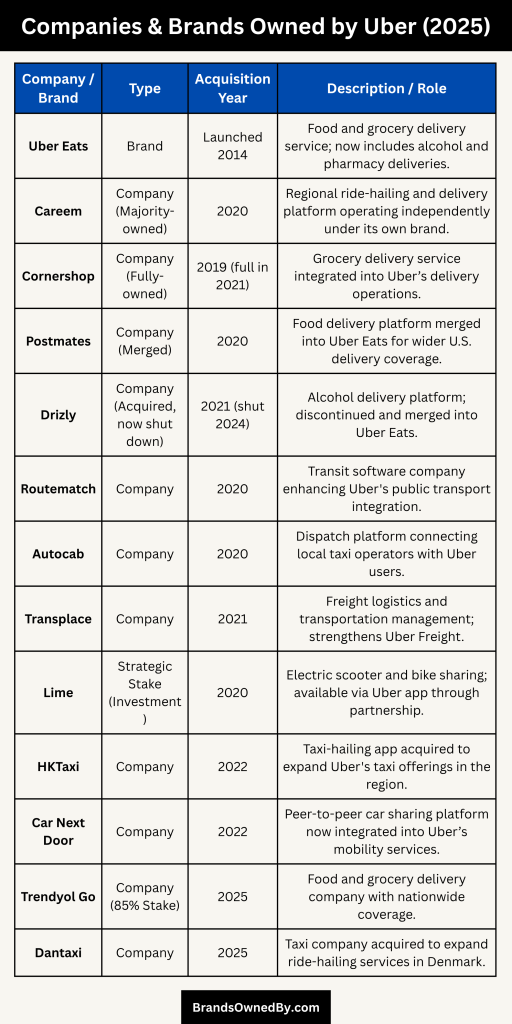
As of 2025, Uber Technologies Inc. has expanded its global footprint through strategic acquisitions and partnerships, enhancing its services across ride-hailing, food delivery, freight, and micromobility sectors.
Below is an overview of the key companies and brands owned by Uber:
| Company/Brand | Type | Acquisition Year | Region of Focus | Description / Role |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uber Eats | Brand | Launched 2014 | Global | Food and grocery delivery service; now includes alcohol and pharmacy deliveries. |
| Careem | Company (Majority-owned) | 2020 | Middle East, North Africa, South Asia | Regional ride-hailing and delivery platform operating independently under its own brand. |
| Cornershop | Company (Fully-owned) | 2019 (full in 2021) | Latin America, U.S. | Grocery delivery service integrated into Uber’s delivery operations. |
| Postmates | Company (Merged) | 2020 | United States | Food delivery platform merged into Uber Eats for wider U.S. delivery coverage. |
| Drizly | Company (Acquired, now shut down) | 2021 (shut 2024) | U.S. | Alcohol delivery platform; discontinued and merged into Uber Eats. |
| Routematch | Company | 2020 | U.S. | Transit software company enhancing Uber’s public transport integration. |
| Autocab | Company | 2020 | United Kingdom | Dispatch platform connecting local taxi operators with Uber users. |
| Transplace | Company | 2021 | North America | Freight logistics and transportation management; strengthens Uber Freight. |
| Lime | Strategic Stake (Investment) | 2020 | Global | Electric scooter and bike sharing; available via Uber app through partnership. |
| HKTaxi | Company | 2022 | Hong Kong | Taxi-hailing app acquired to expand Uber’s taxi offerings in the region. |
| Car Next Door | Company | 2022 | Australia | Peer-to-peer car sharing platform now integrated into Uber’s mobility services. |
| Trendyol Go | Company (85% Stake) | 2025 | Turkey | Food and grocery delivery company with nationwide coverage. |
| Dantaxi | Company | 2025 | Denmark | Taxi company acquired to expand ride-hailing services in Denmark. |
Uber Eats
Launched in 2014, Uber Eats is Uber’s food delivery platform, operating in numerous countries worldwide. It offers a wide range of cuisines and has integrated various services, including grocery and alcohol delivery. In 2024, Uber consolidated its delivery services by shutting down Drizly and integrating its features into Uber Eats. The platform continues to innovate with autonomous delivery pilots and partnerships with major retailers.
Careem
Acquired by Uber in 2020 for $3.1 billion, Careem is a leading ride-hailing service in the Middle East, North Africa, and South Asia. Despite the acquisition, Careem operates independently, maintaining its brand and app. The acquisition strengthened Uber’s presence in emerging markets and allowed it to compete effectively against regional players.
Cornershop
Uber acquired a majority stake in Cornershop, a grocery delivery service primarily operating in Latin America, in 2019 and completed the acquisition in 2021. Cornershop has been integrated into Uber’s platform, expanding its grocery delivery capabilities and enhancing its presence in the Latin American market.
Postmates
In December 2020, Uber acquired Postmates, a U.S.-based food delivery service, for $2.65 billion. The acquisition aimed to consolidate Uber’s position in the food delivery market, particularly in the United States. Postmates’ operations have been integrated into Uber Eats, streamlining services and expanding customer reach.
Drizly
Uber acquired Drizly, an alcohol delivery service, in 2021 for $1.1 billion. However, in early 2024, Uber shut down Drizly to consolidate its delivery services under Uber Eats. The move aimed to streamline operations and provide a unified platform for various delivery services, including alcohol.
Routematch
Routematch, a software company providing transit solutions, was acquired by Uber in 2020. The acquisition aimed to enhance Uber’s public transportation offerings by integrating Routematch’s software into its platform. This move supports Uber’s goal to become a comprehensive mobility platform, offering various transportation options.
Autocab
In 2020, Uber acquired Autocab, a UK-based technology company that connects riders with local taxi operators. The acquisition allows Uber to offer its services in areas where it doesn’t operate directly, expanding its reach and providing more transportation options to users.
Transplace
Uber Freight acquired Transplace, a logistics technology and transportation management services company, in 2021 for $2.25 billion. The acquisition aimed to enhance Uber Freight’s capabilities, providing shippers with a comprehensive suite of logistics solutions and expanding Uber’s presence in the freight industry.
Lime (Stake)
Uber holds a significant stake in Lime, a micromobility company offering electric scooters and bikes. The partnership allows Uber to integrate Lime’s services into its app, providing users with more transportation options for short-distance travel. This collaboration supports Uber’s commitment to sustainable and diversified mobility solutions.
HKTaxi
Uber acquired HKTaxi, a Hong Kong-based taxi-hailing app, to strengthen its presence in the region. The acquisition allows Uber to offer taxi services in Hong Kong, integrating HKTaxi’s network into its platform and expanding its service offerings in the city.
Car Next Door
In 2022, Uber acquired Car Next Door, an Australian peer-to-peer car-sharing platform. The acquisition enables Uber to offer car-sharing services, allowing users to rent vehicles from private owners. This move diversifies Uber’s mobility offerings and caters to users seeking flexible transportation options.
Trendyol Go
In 2025, Uber announced plans to acquire an 85% controlling stake in Trendyol Go, a Turkish food and grocery delivery platform, for $700 million. The acquisition aims to expand Uber’s footprint in emerging markets and enhance its delivery services in Turkey. Trendyol Go operates nationwide, partnering with thousands of restaurants and markets.
Dantaxi
Uber acquired Dantaxi, a Danish taxi company, to strengthen its presence in Denmark. The acquisition allows Uber to integrate Dantaxi’s network into its platform, offering users access to a broader range of transportation options and expanding its services in the region.
Final Thoughts
Uber is owned by a diverse group of institutional investors, mutual funds, and public shareholders. While no single entity holds majority control, firms like Vanguard, Morgan Stanley, and Fidelity have a strong influence.
Under Dara Khosrowshahi’s leadership, Uber has transitioned into a more stable, diversified, and profitable company. Its portfolio includes global ride-sharing, food delivery, freight, and more. Uber’s growth and structure reflect the future of mobility and on-demand services.
FAQs
Who founded Uber?
Uber was founded in 2009 by Garrett Camp and Travis Kalanick.
When did Uber go public?
Uber went public in May 2019 on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol UBER.
Who is Uber’s CEO in 2025?
As of 2025, Dara Khosrowshahi is the CEO of Uber.
What percentage of Uber does Vanguard own?
Vanguard owns approximately 8.65% of Uber shares as of June 2025 making it the largest single shareholder.
Does Uber still own Drizly?
No, Uber shut down Drizly in 2023 and integrated its features into Uber Eats.
What companies does Uber own?
Uber owns Uber Eats, Uber Freight, Careem, and Postmates.
Who currently runs Uber?
Uber is currently led by CEO Dara Khosrowshahi, who has been in charge since 2017. He oversees the company’s strategic direction and daily operations.
Who is behind Uber?
Uber was founded by Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp in 2009. While Kalanick was the original CEO, the company today is driven by its executive leadership team, with Dara Khosrowshahi as the key figure.
What is the net worth of Uber?
As of 2025, Uber’s market capitalization, often referred to as its net worth, is approximately $160 billion.
What is the real name of Uber?
The full and official name of the company is Uber Technologies Inc.
Which country is the owner of Uber?
Uber Technologies Inc. is an American company headquartered in San Francisco, California, USA.
How much does the Uber CEO make?
Dara Khosrowshahi’s total compensation in recent years has been estimated to be around $25 million annually, including salary, bonuses, and stock options.
Who is Uber’s biggest competitor?
Uber’s biggest competitors vary by sector but include Lyft in ride-hailing (mainly U.S.), DoorDash and Grubhub in food delivery, and Didi Chuxing in China’s ride-hailing market.
Who owns Uber Eats?
Uber Eats is wholly owned and operated by Uber Technologies Inc.
Who invested in Uber?
Uber has received investments from major entities such as SoftBank Vision Fund, Benchmark Capital, Toyota, Alphabet (Google), Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund, and many institutional investors.
Who owns Uber stock today?
Uber stock is publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). Major shareholders include institutional investors like Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and SoftBank, alongside retail investors.
Who owns Uber in Australia?
Uber operates directly in Australia as Uber Technologies Inc., but it also owns the Australian car-sharing company Car Next Door. Local investors and shareholders hold Uber stock, but Uber as a company controls operations in Australia.

