General Mills is one of the most recognized names in the global food industry. With a wide range of brands and household staples, many people ask: Who owns General Mills?
This article dives into the company’s ownership structure, revenue, leadership, and more.
General Mills Company Profile
General Mills is a major American multinational food manufacturer. It is known for producing popular consumer food products that are sold in more than 100 countries. The company has a strong presence in categories like cereals, baking goods, snacks, yogurt, and pet food. It is one of the largest food companies in the world and is headquartered in Golden Valley, Minnesota.
Company Details
- Full Name: General Mills, Inc.
- Founded: 1928
- Headquarters: Golden Valley, Minnesota, USA
- Stock Ticker: GIS (listed on the New York Stock Exchange)
- Industry: Packaged Foods and Consumer Goods
- Employees: Over 35,000 globally
- Product Categories: Breakfast cereals, snacks, baking mixes, refrigerated dough, frozen foods, yogurt, pet food.
General Mills operates in four main geographic regions: North America Retail, North America Foodservice, Europe and Australia, and Asia and Latin America.
Founders
While General Mills as a corporate entity was founded in 1928, its origins date back to the Washburn-Crosby Company, which was one of its primary predecessors.
- Cadwallader C. Washburn was one of the earliest founders of the milling business that later evolved into General Mills.
- He established the Washburn “B” Mill in Minneapolis in 1866.
- Later, through mergers and acquisitions, his company grew and merged with others to form General Mills in 1928.
Major Milestones
1866: Cadwallader Washburn establishes the original flour mill in Minneapolis.
1877: Formation of the Washburn-Crosby Company, which becomes a leading flour milling firm.
1921: Betty Crocker is created as a fictional character for marketing purposes.
1928: General Mills is officially formed through the merger of several regional milling companies.
1940s: Enters the breakfast cereal business with brands like Cheerios, originally called “Cheerioats.”
1950s–60s: Expands into convenience foods and household brands, including cake mixes and snacks.
1985: Enters the toy industry briefly after acquiring Kenner and Parker Brothers (later sold).
2001: Acquires Pillsbury’s U.S. operations from Diageo, significantly expanding its baking and refrigerated food portfolio.
2011: Acquires a controlling interest in Yoplait, strengthening its yogurt segment.
2014: Acquires Annie’s, a leading organic and natural food brand.
2018: Enters the pet food industry with the acquisition of Blue Buffalo for $8 billion.
2021–2023: Sells some non-core businesses and focuses on core food brands and global expansion, particularly in health and wellness.
Who Owns General Mills: Largest Shareholders in 2025
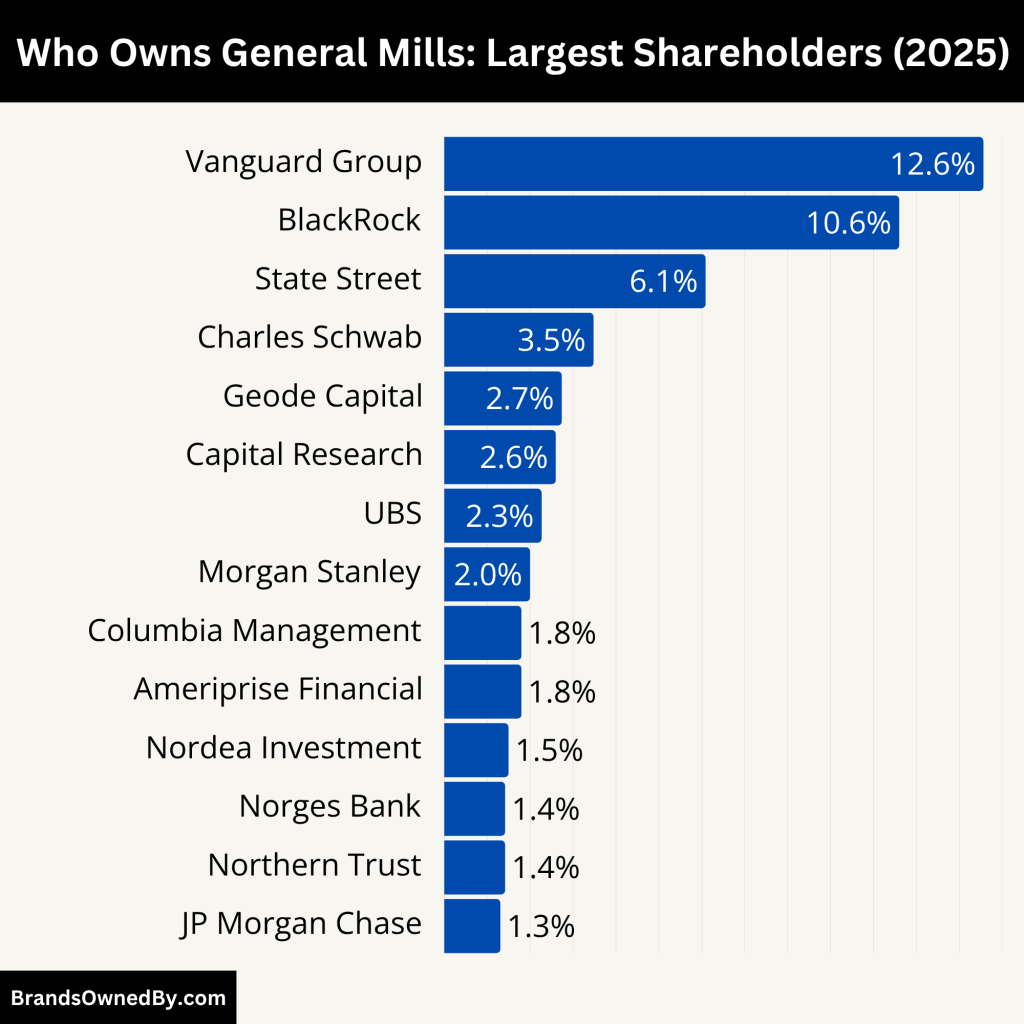
General Mills is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol GIS. It is not owned by a single entity or individual. Instead, it is primarily owned by a combination of institutional investors and public shareholders.
No single entity holds a controlling stake. However, the top three—Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street—together own around 29%. This bloc steers voting on board composition, strategy approvals, and executive remuneration. Despite their clout, the board retains full decision-making power, though now often in alignment with institutional preferences. Insiders have limited voting weight, while retail investors have minimal direct control.
Here’s a list of the major shareholders of General Mills as of June 2025:
| Shareholder | Ownership % | Approximate Shares Owned | Type | Influence/Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group | 12.56% | ~68.8 million | Institutional (Mutual Funds/ETFs) | Largest shareholder; strong voting power |
| BlackRock, Inc. | 10.60% | ~58 million | Institutional (Asset Manager) | High influence in governance and policy decisions |
| State Street Global Advisors | 6.09% | ~33.3 million | Institutional (Index Funds) | Exercises proxy votes; third-largest shareholder |
| Charles Schwab Investment Management | 3.48% | ~19 million | Institutional (Retail/Advisory) | Moderate voting influence |
| Geode Capital Management | 2.74% | ~15 million | Institutional (Quantitative) | Passive influence, supports governance norms |
| Capital Research & Management | 2.60% | ~14.2 million | Institutional (Active Manager) | Participates in strategic votes |
| UBS Asset Management | 2.27% | ~12.4 million | Institutional (Bank-Owned) | Moderate influence in proxy matters |
| Columbia Management Investment Advisers | 1.80% | ~9.9 million | Institutional (Asset Manager) | Participates in executive and governance votes |
| Morgan Stanley | 2.00% | ~10.9 million | Institutional (Brokerage) | Mid-sized voting power |
| Ameriprise Financial | 1.80% | ~9.9 million | Institutional (Financial Services) | Similar influence to Morgan Stanley |
| Nordea Investment Management | 1.50% | ~8.2 million | Institutional (European Asset Manager) | Adds international investor presence |
| Norges Bank Investment Management | 1.42% | ~7.8 million | Institutional (Sovereign Fund) | Long-term sustainability-focused investor |
| Northern Trust | 1.42% | ~7.8 million | Institutional (Custodian Bank) | Passive investor; supports major initiatives |
| JP Morgan Chase | 1.31% | ~7.2 million | Institutional (Bank) | Participates in broader financial governance |
| Other Institutional Investors (combined) | ~17% | ~93 million | Various | Collectively influence board decisions |
| Retail/Public Shareholders | ~13–16% | ~71–88 million | Individual Investors | Limited influence; affects market value |
| Company Insiders | ~1.6% | ~8.8 million | Executives & Board Members | Minimal control; advisory or symbolic voting role |
The Vanguard Group
As of June 2025, Vanguard is General Mills’ largest shareholder. It owns about 12.56% of all shares, which translates to roughly 68.8 million shares. Vanguard manages vast mutual funds and ETFs that include General Mills in their portfolios. While this doesn’t give Vanguard direct control over daily operations, its significant stake gives it strong voting power at annual meetings and during board elections. Its decisions as a top investor carry substantial weight in corporate governance.
BlackRock, Inc.
BlackRock ranks as the second-largest shareholder with approximately 10.60% ownership, equating to about 58 million shares as of June 2025.
This stake allows BlackRock to exert considerable influence over strategic decisions, including executive appointments and compensation policies. As one of the “Big Three” asset managers, BlackRock’s voice is powerful in shaping the company’s direction.
State Street Global Advisors
State Street holds the third-largest institutional stake at around 6.09%, or 33.3 million shares. Known for managing index and passive funds, State Street exercises shareholder influence mainly through proxy votes. Its ownership adds another institutional layer to company governance.
Charles Schwab Investment Management
Charles Schwab owns about 3.48% of the company (roughly 19 million shares) as of March 31, 2025. This reflects Schwab’s retail and institutional client holdings. Its share size allows it to support or oppose proposals at shareholder votes, albeit with less influence than the larger institutions.
Geode Capital Management
Geode holds roughly 2.74% (~15 million shares). As a quant-focused asset manager, Geode’s stake is often included in funds like Fidelity and Schwab. It engages in voting on governance matters, though it doesn’t lead any initiatives.
Capital Research & Management
Capital Research owns 2.60%, or 14.2 million shares, as of March 2025. As a large active fund manager, it uses its stake to influence key proposals. Though smaller than the top three, it remains a respected voice in corporate oversight.
UBS Asset Management
UBS controls around 2.27% of General Mills’ shares (~12.4 million). This places UBS among the top ten investors. Its influence is moderate, generally supporting governance aligned with other large institutions.
Columbia Management Investment Advisers
Owning approximately 1.80% (about 9.9 million shares), Columbia Management also participates in key shareholder votes on executive and policy matters.
Nordea Investment Management
Nordea, based in Denmark, holds roughly 1.50% (~8.2 million shares). It represents a major European institutional owner, adding global diversity to the shareholder base.
Norges Bank Investment Management
The Norwegian sovereign wealth fund holds around 1.42%, or 7.8 million shares. This long-term investor typically supports sustainable governance and adds stability to ownership.
Morgan Stanley & Ameriprise Financial
Morgan Stanley holds roughly 2.0% (~10.9 million shares) and Ameriprise about 1.80% (~9.9 million shares) as of early 2025. These mid-sized holdings grant influence in proposals and board elections.
Other Notable Institutional Investors
Other investors like Northern Trust (~1.42%), JP Morgan Chase (~1.31%), and UBS Group (~1.32%) each hold between 1–1.5% of shares. Multiple smaller institutions like Dimensional Fund Advisors, Invesco, Diamond Hill Capital, and Capital World Investors hold 0.5–1%.
Ownership Breakdown
- Institutional investors collectively control around 82% of General Mills shares.
- Public retail shareholders own roughly 13–16%.
- Company insiders, such as executives and board members, hold about 1.6%.
Who is the CEO of General Mills?
Jeff Harmening is the current architect of General Mills’ strategic and operational direction. With over 30 years at the company, robust academic credentials, and a compensation package tied closely to performance, he embodies the leadership standards of large public food companies today. His predecessors laid the groundwork for the brand and strategic transformations that Harmening continues to build upon in 2025.
Current CEO: Jeffrey L. Harmening
Jeff Harmening has been the CEO since June 1, 2017, and also serves as chairman of the board since January 1, 2018. He joined General Mills in 1994 and has risen through leadership roles across North America and Europe.
Professional Background and Education
- Earned a bachelor’s degree from DePauw University in 1989.
- Completed an MBA at Harvard Business School in 1994.
- Began his career as a financial analyst at Eli Lilly before joining General Mills.
- Before becoming CEO, he served as COO (July 2016–May 2017) and led U.S. Retail and Cereal Partners Worldwide.
Leadership Style and Strategy
- Harmening is known for blending purpose with performance. He emphasizes environmental stewardship, employee culture, and long‑term profitability.
- He launched the “Accelerate” strategy, focusing on strong brands, innovation, digital transformation, and sustainability. Over 30% of the portfolio has been reshaped since 2018.
Compensation and Personal Stake
- In 2023, his total compensation was approximately $16 million, including a base salary of $1 million and significant equity awards.
- As of May 2025, he personally owns around 353,346 shares, worth about $19 million, and receives an annual salary of $5.21 million.
Governance and Decision‑Making
- As CEO and chairman, Harmening leads General Mills’ board. He chairs its sustainability council.
- He operates within a strong governance framework, with board committees reviewing strategy and compensation.
- Major decisions require board approval, though institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock also influence key votes.
Notable Past CEOs of General Mills
- Ken Powell (2007–2017): Guided the company through global expansion, launched the Partners in Food Solutions nonprofit, and emphasized corporate responsibility.
- Stephen W. Sanger (1995–2007): Oversaw steady growth, the blockbuster Pillsbury merger in 2001, and refocused the company on food.
- Earlier leaders include Cadwallader C. Washburn, James Ford Bell, Donald D. Davis, and others who shaped the foundation and diversification of General Mills.
General Mills Annual Revenue and Net Worth
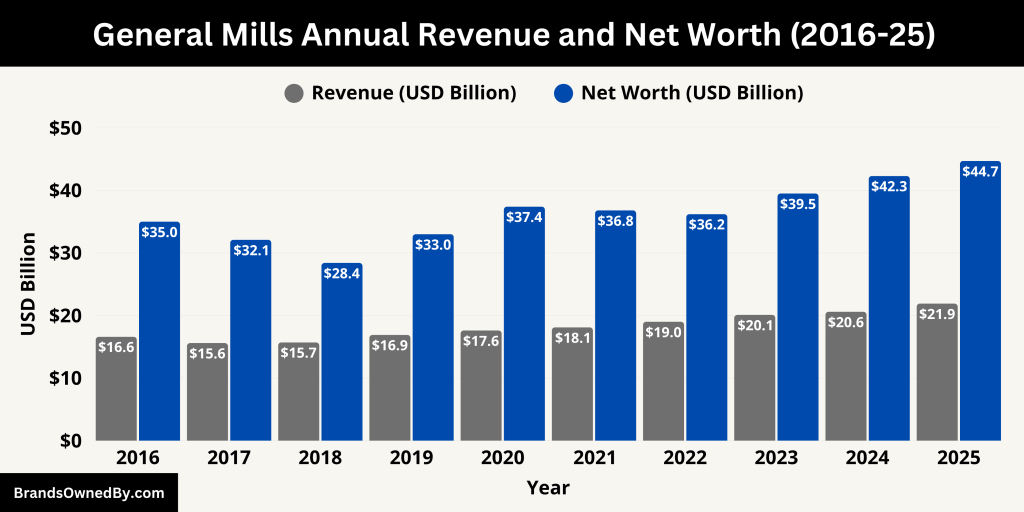
General Mills continues to maintain a strong financial position in 2025, backed by its diverse brand portfolio and growing international presence. The company remains resilient despite global inflation, supply chain pressures, and changing consumer habits.
General Mills Revenue in 2025
As of the fiscal year ending in May 2025, General Mills reported annual revenue of approximately $21.9 billion. This marks a modest increase from the previous year, reflecting stable demand for its core brands and expansion in the pet food and natural snack categories.
Key contributors to 2025 revenue growth:
- Pet food sales (especially through Blue Buffalo) continued to perform strongly in North America.
- International operations showed growth in Latin America and parts of Asia, despite currency headwinds.
- Snacks and convenience meals experienced higher sales, driven by consumer demand for quick, affordable meals.
- E-commerce and direct-to-consumer sales also helped offset weaker retail volumes in some segments.
The company’s focus on value, efficiency, and innovation helped protect margins and maintain a competitive edge. Despite rising ingredient and logistics costs, General Mills achieved improved operating efficiency through automation and supply chain optimization.
General Mills Net Worth in 2025
The estimated net worth (market capitalization) of General Mills in 2025 stands at approximately $44.7 billion. This is based on its current share price and total outstanding shares. The company’s stock has remained relatively stable, offering consistent returns to shareholders through dividends and buybacks.
Factors influencing net worth in 2025:
- Steady dividend payouts increased investor confidence.
- Continued brand strength in core categories like cereal, yogurt, and snacks.
- Expansion into health-conscious and organic product lines through acquisitions and internal product development.
- Investor optimism in the long-term growth of pet nutrition and global food demand.
Earnings and Profitability
General Mills reported net income of approximately $2.9 billion in fiscal 2025. This strong profitability was supported by:
- Strategic cost reductions across supply chains.
- Higher-margin products in the pet and organic food segments.
- Strong brand loyalty in North America and Europe.
Earnings per share (EPS) for 2025 stood around $4.94, which met analysts’ expectations and signaled healthy performance in a mixed economic environment.
Financial Position and Outlook
General Mills maintains a healthy debt-to-equity ratio and continues to prioritize cash flow stability. The company also holds strong free cash flow, which supports reinvestment into innovation, marketing, and global expansion.
Looking forward, General Mills aims for mid-single-digit revenue growth through:
- Global market penetration
- Sustainable food initiatives
- Strengthening e-commerce channels
The company’s balanced approach to profitability and long-term investment makes it a reliable player in the global food industry.
Here is an overview of General Mills’ historical revenue and net worth (market capitalization) over the past 10 fiscal years (2016–2025):
| Fiscal Year | Revenue (USD Billion) | Net Worth / Market Cap (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | 21.9 | 44.7 |
| 2024 | 20.6 | 42.3 |
| 2023 | 20.1 | 39.5 |
| 2022 | 19.0 | 36.2 |
| 2021 | 18.1 | 36.8 |
| 2020 | 17.6 | 37.4 |
| 2019 | 16.9 | 33.0 |
| 2018 | 15.7 | 28.4 |
| 2017 | 15.6 | 32.1 |
| 2016 | 16.6 | 35.0 |
Companies Owned by General Mills
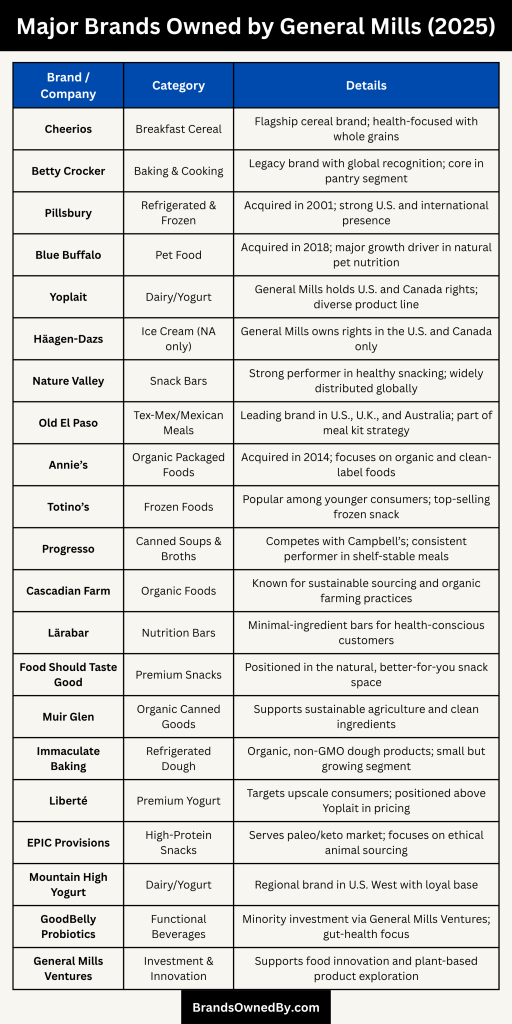
As of 2025, General Mills owns and operates a diverse collection of food and wellness brands. From legacy names like Cheerios and Pillsbury to fast-growing new-age brands like Blue Buffalo and Annie’s, the company continues to expand its global reach while staying relevant to evolving consumer needs. Each brand under the General Mills umbrella serves a specific audience, helping the company maintain its leadership in multiple food categories across retail, convenience, and pet care.
Here is a detailed overview of major companies, brands, acquisitions, and entities owned and operated by General Mills as of 2025:
| Brand/Company | Category | Key Products | Notable Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cheerios | Breakfast Cereal | Original, Honey Nut, Multi-Grain, Apple Cinnamon | Flagship cereal brand; health-focused with whole grains |
| Betty Crocker | Baking & Cooking | Cake mixes, frostings, cookbooks | Legacy brand with global recognition; core in pantry segment |
| Pillsbury | Refrigerated & Frozen | Dough, cookies, pie crusts, biscuits | Acquired in 2001; strong U.S. and international presence |
| Blue Buffalo | Pet Food | Dog food, cat food, treats | Acquired in 2018; major growth driver in natural pet nutrition |
| Yoplait | Dairy/Yogurt | Original, Go-GURT, Whips!, Oui | General Mills holds U.S. and Canada rights; diverse product line |
| Häagen-Dazs | Ice Cream (NA only) | Pints, bars, frozen desserts | General Mills owns rights in the U.S. and Canada only |
| Nature Valley | Snack Bars | Granola bars, protein bars, nut-based snacks | Strong performer in healthy snacking; widely distributed globally |
| Old El Paso | Tex-Mex/Mexican Meals | Tacos, tortillas, salsas, seasoning kits | Leading brand in U.S., U.K., and Australia; part of meal kit strategy |
| Annie’s | Organic Packaged Foods | Mac & cheese, snacks, dressings | Acquired in 2014; focuses on organic and clean-label foods |
| Totino’s | Frozen Foods | Pizza rolls, party pizzas | Popular among younger consumers; top-selling frozen snack |
| Progresso | Canned Soups & Broths | Hearty and traditional soups | Competes with Campbell’s; consistent performer in shelf-stable meals |
| Cascadian Farm | Organic Foods | Cereal, granola, frozen fruits/vegetables | Known for sustainable sourcing and organic farming practices |
| Lärabar | Nutrition Bars | Fruit and nut bars, protein bars | Minimal-ingredient bars for health-conscious customers |
| Food Should Taste Good | Premium Snacks | Chips made with flaxseed, black beans, sweet potatoes | Positioned in the natural, better-for-you snack space |
| Muir Glen | Organic Canned Goods | Tomatoes, pasta sauces, salsas | Supports sustainable agriculture and clean ingredients |
| Immaculate Baking | Refrigerated Dough | Cookies, rolls, pastries | Organic, non-GMO dough products; small but growing segment |
| Liberté | Premium Yogurt | Rich, globally inspired yogurt flavors | Targets upscale consumers; positioned above Yoplait in pricing |
| EPIC Provisions | High-Protein Snacks | Meat bars, jerky, trail mixes | Serves paleo/keto market; focuses on ethical animal sourcing |
| Mountain High Yogurt | Dairy/Yogurt | Plain, creamy yogurt | Regional brand in U.S. West with loyal base |
| GoodBelly Probiotics | Functional Beverages | Probiotic juice shots and drinks | Minority investment via General Mills Ventures; gut-health focus |
| General Mills Ventures | Investment & Innovation | Stakes in Kite Hill, Urban Remedy, etc. | Supports food innovation and plant-based product exploration |
Cheerios
Cheerios is one of General Mills’ most iconic cereal brands. Launched in 1941, it remains a household staple. Variants like Honey Nut Cheerios, Multi-Grain Cheerios, and Apple Cinnamon Cheerios have helped the brand dominate the breakfast cereal market. It continues to lead in North America with a strong health-oriented image.
Betty Crocker
Betty Crocker is a legendary brand for baking mixes, cake mixes, frostings, and cooking aids. The brand also offers cookbooks and digital recipes. It is central to General Mills’ baking segment and contributes significantly to its pantry products category.
Pillsbury
Pillsbury is one of General Mills’ most valuable acquisitions. It offers refrigerated dough products like crescent rolls, biscuits, pie crusts, and ready-to-bake cookies. Pillsbury also includes frozen baked goods and international baking mixes in some markets. General Mills acquired Pillsbury in 2001.
Blue Buffalo
Acquired in 2018 for around $8 billion, Blue Buffalo is General Mills’ largest entry into the pet food industry. It offers natural dog and cat food, and its sub-brands include BLUE Life Protection Formula, BLUE Wilderness, and BLUE Basics. Blue Buffalo has become a growth engine, expanding into both U.S. and Asian markets.
Yoplait
Yoplait is General Mills’ flagship yogurt brand. It includes varieties such as Original, Whips!, Go-GURT (for kids), and Oui (a French-style yogurt). General Mills holds licensing rights to Yoplait in the U.S. and Canada, having acquired a majority stake in the brand in 2011.
Häagen-Dazs (U.S. and Canada only)
General Mills owns the Häagen-Dazs brand in the U.S. and Canada. The premium ice cream line includes pints, bars, and specialty desserts. International rights to the brand were sold, but in North America, General Mills continues to manage and market the brand successfully.
Nature Valley
Nature Valley is a leading granola and snack bar brand, known for its crunchy bars, protein bars, and fruit-based snacks. It plays a key role in the company’s snacks segment and is popular among health-conscious consumers worldwide.
Old El Paso
Old El Paso offers Tex-Mex products like taco shells, salsa, refried beans, and seasoning mixes. The brand is a leader in the U.S., U.K., and Australia, and it plays a vital role in General Mills’ global meal kits category.
Annie’s
Acquired in 2014 for $820 million, Annie’s focuses on organic and natural packaged foods. The brand offers macaroni & cheese, snacks, cereals, and dressings. It appeals to younger, health-conscious families and continues to grow through clean-label innovation.
Totino’s
Totino’s is a frozen food brand offering pizza rolls and party pizzas. It targets the quick-meal and snack segment and is especially popular among younger demographics in the U.S.
Progresso
Progresso is General Mills’ canned soup and broth brand. Known for hearty soups and classic recipes, Progresso is a steady performer in the shelf-stable meal segment. It faces competition from Campbell’s but retains strong brand loyalty.
Cascadian Farm
Cascadian Farm focuses on organic cereals, granola, frozen fruits, and vegetables. It promotes sustainable agriculture and environmental stewardship and is often used as a platform for General Mills’ regenerative agriculture messaging.
Lärabar
Lärabar produces energy and nutrition bars made from minimal ingredients. Its clean-label approach, including gluten-free and vegan products, appeals to wellness-focused consumers.
Food Should Taste Good
This brand specializes in premium chips and snacks made from real ingredients like black beans, sweet potatoes, and flaxseed. It fits into the better-for-you snacks category.
Muir Glen
Muir Glen offers organic canned tomatoes, pasta sauces, and salsas. Known for farm-to-table principles and environmentally responsible practices, the brand complements the company’s clean-eating product line.
Immaculate Baking
Immaculate Baking focuses on organic and non-GMO refrigerated doughs, cookies, and pastries. It supports General Mills’ expansion into healthier baking products.
Liberté
Liberté is a premium yogurt brand known for its rich, indulgent texture and globally inspired flavors. It helps General Mills target upscale and adult-focused dairy categories.
EPIC Provisions
EPIC specializes in meat-based protein bars, jerky, and snacks made from high-quality, sustainably raised animals. It serves the paleo, keto, and high-protein diet segments.
Mountain High Yogurt
A regional brand, Mountain High offers plain, creamy-style yogurt products. It’s known for its simplicity and loyal consumer base in the western U.S.
GoodBelly Probiotics
General Mills has a strategic investment stake in GoodBelly through its venture arm. The brand sells probiotic juice drinks and supplements focused on gut health and wellness.
General Mills Ventures
This is the company’s corporate venture capital arm. It has invested in early-stage food and beverage startups like Kite Hill (plant-based dairy), Urban Remedy, and Beyond Meat (earlier rounds). These investments reflect General Mills’ commitment to the future of food innovation.
Final Thoughts
General Mills remains a powerful force in the global food industry. It is not owned by one person or company but by a mix of institutional and public shareholders. With an experienced CEO and a diverse portfolio of brands, General Mills continues to adapt and grow in a competitive market.
FAQs
Who owns the majority of General Mills?
The majority of General Mills shares are publicly traded and owned by institutional investors. As of 2025, The Vanguard Group is the largest shareholder with around 8.6% of the company. Other major shareholders include BlackRock, State Street, and Wellington Management. No single entity has complete control, making it a widely held public company.
Is General Mills owned by Nestlé?
No, General Mills is not owned by Nestlé. However, the two companies were once partners in a joint venture called Cereal Partners Worldwide (CPW) to market cereals outside North America. They remain separate and independent corporations.
Who bought General Mills?
No one has bought General Mills. It remains an independent, publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol GIS.
Is General Mills owned by anyone?
General Mills is owned by its shareholders, primarily large institutional investors such as Vanguard and BlackRock. It is not owned by a parent company or single individual.
Who is the CEO of General Mills?
As of 2025, the CEO and Chairman of General Mills is Jeffrey L. Harmening. He has held the CEO position since 2017 and leads the company’s strategic and operational direction.
Is Kellogg’s owned by General Mills?
No, Kellogg’s is not owned by General Mills. They are direct competitors in the global breakfast cereal and snacks markets. Kellogg’s (now called Kellanova for its snacks business after a corporate split) is a completely separate entity.
What is General Mills’ full name?
The full legal name of the company is General Mills, Inc. It is commonly referred to simply as General Mills.
Did General Mills pay $300 million to investors?
Yes, in recent fiscal years, General Mills has returned significant capital to shareholders through dividends and share buybacks. In 2024 and 2025 combined, the company paid over $300 million in dividends to investors, reflecting strong cash flow and a commitment to shareholder returns.
Is General Mills a Nestlé company?
No, General Mills is not a Nestlé company. The two are independent food giants. They collaborate only in a joint venture (CPW) for cereal sales outside the U.S., but they are not financially or structurally tied.
Who is General Mills’ biggest competitor?
General Mills’ top competitors include:
- Kellogg’s/Kellanova – in cereals and snacks
- Post Holdings – in cereals and refrigerated foods
- Nestlé – in global food products and dairy
- Mondelez – in snack foods
- Unilever and Campbell’s – in soups, sauces, and pantry products
Is General Mills associated with Nestlé?
Yes, but only in a limited capacity. General Mills and Nestlé operate a joint venture called Cereal Partners Worldwide, which markets breakfast cereals outside of North America. Beyond this, they are separate companies.
Why boycott General Mills 2025?
Some boycott calls in 2025 have stemmed from concerns over:
- GMO usage in products
- Political donations and lobbying
- Environmental concerns tied to supply chain sourcing
However, these campaigns are typically limited in scale and have not significantly affected the company’s consumer base.
Is General Mills owned by Kellogg?
No, General Mills is not owned by Kellogg, and never has been. Both companies are competitors and operate independently in the global food industry.
Who founded General Mills?
General Mills was founded in 1928 following a merger of several milling companies. Its roots trace back to Cadwallader C. Washburn, who opened the Washburn-Crosby Company, a key predecessor to General Mills. James Ford Bell was instrumental in its formal creation.
What cereals are owned by General Mills?
General Mills owns a wide portfolio of cereal brands, including:
- Cheerios (Original, Honey Nut, Multi-Grain, etc.)
- Lucky Charms
- Cinnamon Toast Crunch
- Trix
- Wheaties
- Golden Grahams
- Reese’s Puffs
- Cocoa Puffs
- Kix
- Total
- Count Chocula, Boo Berry, and other seasonal cereals
These cereals are among the most popular in North America and make up a significant share of General Mills’ U.S. retail revenue.
Is General Mills privately owned?
No, General Mills is a publicly traded company listed on the NYSE under the symbol GIS.
What companies does General Mills own?
General Mills owns brands such as Cheerios, Betty Crocker, Pillsbury (U.S./Canada), Yoplait (U.S.), Blue Buffalo, Nature Valley, Annie’s, Old El Paso, and controls Haagen-Dazs outside North America.
How much is General Mills worth?
As of June 2025, the company’s market value is estimated to be $40 billion.
Where is General Mills based?
General Mills is headquartered in Golden Valley, Minnesota, USA.

