Virgin Mobile is a global mobile network brand recognized for its affordability, innovation, and customer-first approach. Originally founded by Richard Branson’s Virgin Group, the company changed the telecom landscape by introducing flexible mobile services without owning physical network infrastructure. Over time, who owns Virgin Mobile has varied across countries, as the brand expanded through partnerships and licensing agreements with major telecom operators worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- Virgin Mobile is not owned by a single company — ownership varies by country. The brand operates under different telecom partners, licensing agreements, and joint ventures across regions.
- Virgin Group, founded by Sir Richard Branson, no longer holds full ownership in most Virgin Mobile operations. It primarily acts as a brand licensor, allowing other telecom companies to use the Virgin name.
- In major markets, control lies with regional operators — such as Liberty Global and Telefónica (Virgin Media O2) in the UK, Beyond ONE in Latin America and the Middle East, and Bell Canada in Canada.
- As of 2025, Virgin Mobile functions globally as a licensed telecom brand rather than a single corporate entity, with each market managed independently under long-term partnerships with the Virgin Group.
Virgin Mobile Overview
Virgin Mobile is a brand used for mobile services under the mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) model. It does not generally build its own network but leases capacity from established carriers.
The brand allows flexibility, lower capital commitments, and a focus on customer experience and innovation. Over time, Virgin Mobile has appeared in multiple countries, each operating under different corporate arrangements. Its identity is tied closely to the Virgin Group and the entrepreneurial spirit of its founder, Sir Richard Branson.
Company Details
Virgin Mobile’s structure, offerings, and footprint differ by region. In markets where it still operates, it offers prepaid and postpaid voice and data plans, messaging services, bundles, roaming, and devices. In many cases, Virgin Mobile functions under a licensing or joint venture agreement with a major telecom operator that supplies network infrastructure.
For example, in South Africa, Virgin Mobile (before its closure) operated as an MVNO on the Cell C network.
In the Middle East & Africa region, Virgin Mobile is headquartered in Dubai, servicing several markets under a regional brand management structure.
In the United Kingdom, Virgin Mobile UK ceased operating as its own brand in 2023 after migrating customers to O2 under the combined Virgin Media O2 group.
Because Virgin Mobile is not a singular global corporation, details such as employee count, revenue, and corporate headquarters depend on local subsidiaries or licensees.
Founders
The Virgin brand was originally founded by Sir Richard Branson and Nik Powell in 1970.
The expansion into mobile telephony began later. Virgin Mobile, as a mobile venture, traces back to the late 1990s when the Virgin Group decided to enter the telecom landscape.
In the UK, Virgin Mobile launched in 1999 in partnership with a carrier network.
In the United States, Virgin Mobile USA was founded as a joint venture in 2001 between Virgin Group and Sprint Corporation, and operations began in 2002 using Sprint’s infrastructure.
Another name often associated with the early operational side in the U.S. is Amol Sarva. He was among the early team members who helped negotiate the joint venture, define the MVNO model, and build the early management structure.
Major Milestones
- 1970 – Virgin Group is founded by Sir Richard Branson and Nik Powell as a mail-order record business, later expanding into music stores, airlines, and multiple industries.
- 1999 – Virgin Mobile is launched in the United Kingdom as the world’s first mobile virtual network operator (MVNO), operating on the One2One network. This marks Virgin’s entry into the telecom industry.
- 2001 – Virgin Mobile USA is formed as a joint venture between Virgin Group and Sprint Corporation.
- 2002 – Virgin Mobile officially begins operations in the United States, offering prepaid mobile services using Sprint’s infrastructure.
- 2003 – Virgin Mobile Australia launches through a partnership with Optus, becoming one of the region’s leading MVNOs.
- 2004 – Virgin Mobile Canada begins operations on Bell Mobility’s network, bringing the brand to North America’s second-largest telecom market.
- 2005 – Virgin Mobile USA goes public on NASDAQ, becoming one of the first MVNOs to list on a major stock exchange.
- 2006 – NTL:Telewest acquires Virgin Mobile UK, merging it into Virgin Media to create the UK’s first fully integrated media and communications company.
- 2007 – Virgin Mobile South Africa launches as the brand’s first venture into Africa.
- 2008 – Virgin Mobile India begins operations in collaboration with Tata Teleservices, introducing the Virgin brand to South Asia.
- 2009 – Sprint Nextel acquires full ownership of Virgin Mobile USA, turning it into a wholly owned subsidiary.
- 2010 – Virgin Mobile Chile launches, marking Virgin’s debut in Latin America under Virgin Mobile Latin America (VMLA).
- 2011 – Virgin Mobile expands further in the region, establishing operations in Peru and announcing plans for Colombia.
- 2012 – Virgin Mobile Colombia officially launches and quickly gains traction with young mobile users through flexible prepaid plans.
- 2015 – Virgin Mobile France ceases operations after being acquired by SFR, ending the brand’s presence in the French market.
- 2016 – Virgin Mobile Mexico launches, continuing expansion across Latin America.
- 2017 – Virgin Mobile Canada becomes fully owned by Bell Mobility but retains the Virgin brand name and identity.
- 2018 – Virgin Mobile Middle East & Africa (VMMEA) strengthens its presence in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Oman, offering fully digital mobile experiences.
- 2020 – Virgin Mobile USA shuts down following the T-Mobile and Sprint merger, with customers migrated to Boost Mobile.
- 2021 – Virgin Media merges with O2 to form Virgin Media O2 in the UK, bringing mobile, broadband, and media services under one joint venture.
- 2023 – Virgin Mobile UK brand is retired as all remaining customers are transferred to O2 under Virgin Media O2.
- 2024 – Virgin Mobile continues to operate successfully in the Middle East and Latin America, adapting to digital-first strategies and app-based services.
- 2025 – Virgin Mobile Latin America (covering Mexico, Chile, and Colombia) operates under Beyond ONE, maintaining the Virgin brand through licensing agreements and ongoing innovation.
Who Owns Virgin Mobile in 2025?
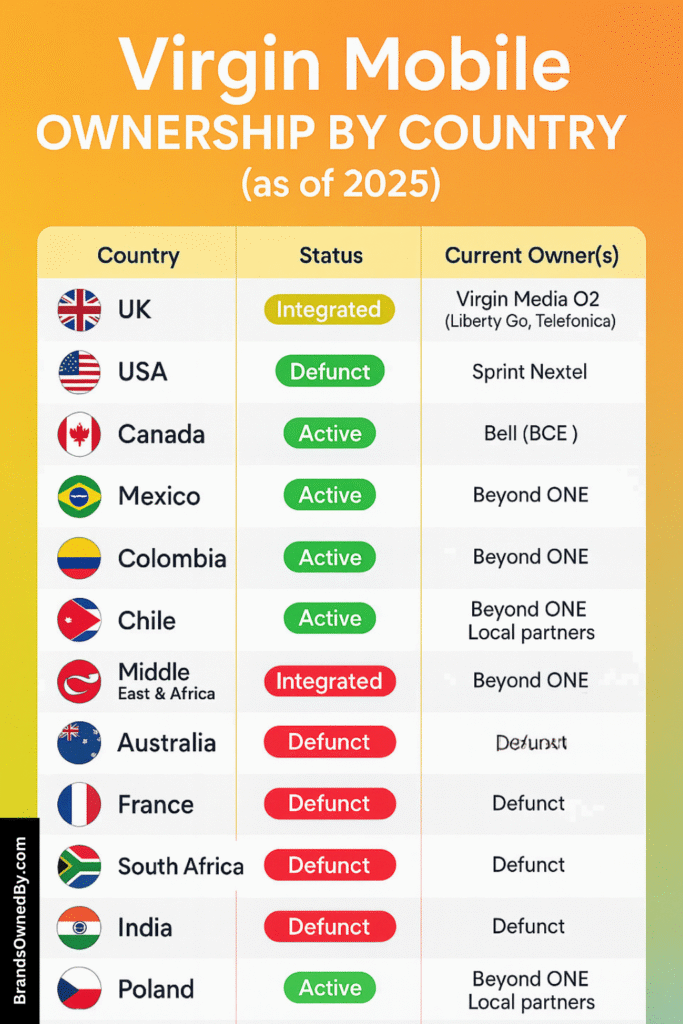
Virgin Mobile is rarely a wholly independent company. Rather, it often exists as a brand under joint ventures, licensing agreements, or acquisitions. The ownership in any given region depends on local telecom partners, investment firms, and the Virgin Group’s stake (or brand-licensing role).
Virgin has moved from being a majority owner in many operations to a minority, licensing, or partner role in several markets.
Below is an overview of the regional ownership of Virgin Mobile as of October 2025:
| Country / Region | Status (as of 2025) | Current Owner(s) | Ownership & Control Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Retired as a separate brand; integrated | Virgin Media O2 (50% Liberty Global / 50% Telefónica) | Virgin Mobile UK was merged into Virgin Media and later absorbed into Virgin Media O2. The mobile business is now operated under Virgin Media O2, jointly owned and controlled by Liberty Global and Telefónica. |
| United States | Retired; customers migrated | Sprint (acquired 2009) → now part of T-Mobile | Sprint fully acquired Virgin Mobile USA in 2009. Following the Sprint–T-Mobile merger, the Virgin Mobile brand was discontinued in 2020, and customers were moved to Boost Mobile under T-Mobile’s network. |
| Canada | Active (rebranded as Virgin Plus) | Bell Mobility | Virgin Mobile Canada is operated and fully owned by Bell Mobility. The Virgin Group no longer holds an equity stake but licenses the Virgin brand name to Bell. |
| Mexico | Active | Beyond ONE (Virgin Mobile Latin America) | Virgin Mobile Mexico operates as part of Virgin Mobile Latin America (VMLA). Beyond ONE acquired VMLA in 2023 and now owns and manages its operations, while Virgin Group retains a minority brand licensing arrangement. |
| Colombia | Active | Beyond ONE (Virgin Mobile Latin America) | Virgin Mobile Colombia is managed by Beyond ONE under the Virgin Mobile Latin America umbrella. Beyond ONE controls operations, while Virgin Group maintains a licensing partnership. |
| Chile | Active | Beyond ONE (Virgin Mobile Latin America) | Virgin Mobile Chile operates as part of Beyond ONE’s Latin American portfolio. The group oversees strategy, while network services are leased from local telecom operators under MVNO agreements. |
| Middle East & Africa (regional) | Active in UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman | Beyond ONE / Local Telecom Partners | Virgin Mobile operations across the Middle East and Africa are managed by Beyond ONE in partnership with national telecom operators. Beyond ONE holds majority ownership and operational control, while Virgin Group provides brand licensing. |
| Australia | Former (market exit) | Optus (former partner) | Virgin Mobile Australia operated under a joint venture with Optus. The brand was discontinued after being phased out and integrated into Optus’ services. |
| France | Former (brand phased out) | SFR | Virgin Mobile France was acquired by SFR and eventually rebranded. Virgin Group no longer holds ownership or brand presence in the French market. |
| South Africa | Former (operation closed) | Joint Venture with Cell C (defunct) | Virgin Mobile South Africa operated as a 50–50 joint venture with Cell C. The business ceased operations and no longer exists under the Virgin brand. |
| India | Former (market exit) | Tata Teleservices (former partner) | Virgin Mobile India launched through a partnership with Tata Teleservices but was later discontinued following regulatory changes and market consolidation. |
| Poland | Active | Play Communications (P4 Sp. z o.o.) | Virgin Mobile Poland operates under Play Communications, which acquired the business and continues to use the Virgin brand under license. |
| Kuwait | Active | Local Licensee (Virgin Mobile Kuwait) | Operates as an MVNO using a local network operator’s infrastructure under a license from Virgin Group. |
| Saudi Arabia | Active | Virgin Mobile Saudi Consortium / Beyond ONE | Operates under Virgin Mobile Middle East & Africa (VMMEA). Beyond ONE and local investors control the venture, with a Virgin Group brand license. |
| United Arab Emirates | Active | Beyond ONE / Virgin Mobile UAE | Operates under Beyond ONE, offering app-based digital mobile services. Virgin Group licenses the brand while Beyond ONE runs full operations. |
| Oman | Active | Beyond ONE / Local Telecom Partner | Operates under Virgin Mobile MEA, run by Beyond ONE through partnerships with local telecom providers. |
Virgin Group / Branson Family
In many Virgin Mobile operations, the Virgin Group retains a stake or the rights to use the Virgin brand. The group often acts as a strategic minority shareholder, licensor, or brand guardian rather than a full owner in recent years.
- Virgin Group was originally the founder of Virgin Mobile in various markets.
- As markets matured or telecom partners acquired control, Virgin’s share was diluted or fully sold in several countries.
- Virgin often stays on as a brand licensor or retains a small equity share in deals, especially in markets where it retains influence or brand value.
- For new markets, Virgin may negotiate minority equity roles so as to limit capital risk and leverage partner capabilities.
Major Telecom Operator Partners
These are telecom companies that either fully control the local Virgin Mobile operation or hold a strong controlling stake. Their role is pivotal because they provide network infrastructure and operational support.
- In the U.S., Sprint (later merged with T-Mobile) fully acquired Virgin Mobile USA, eliminating Virgin’s ownership interest.
- In the UK, Virgin Mobile UK was subsumed under Virgin Media, and later into Virgin Media O2 (a joint venture between Liberty Global and Telefónica). There, the telecom side (O2) holds operational control.
- In many markets, the telecom partner holds majority operational control and decision-making power over network, billing, and infrastructure, while Virgin’s role is more on branding and customer experience.
Investment & Private Equity Investors
Some operations of Virgin Mobile, particularly in Latin America or newer markets, attract external investors, growth capital firms, and venture capital groups. These firms may take minority or significant stakes, influencing strategic direction.
- In 2025, Virgin Mobile Latin America (VMLA) is owned by Beyond ONE, a digital services investment platform, which acquired VMLA in 2023. In that acquisition, Virgin Group retained a minority role, and a long-term brand licensing agreement remains.
- Beyond ONE is backed by equity funding via Priora Management Holding and related institutional investors.
- Virgin Mobile Latin America’s investor base also includes growth partners and capital firms such as Archimedia, Hermes Growth Partners, HighMark Capital Management, and Latin American Partners.
- In the Middle East and Africa region, Virgin retains some minority stake in Virgin Mobile MEA (VMMEA) via brand partnership agreements with Beyond ONE, though control lies primarily with Beyond ONE in operations.
Recent and Region-Specific Shareholders
Because ownership is local, these are some updated examples by country or region as of 2025:
Virgin Mobile Latin America (VMLA)
As of 2025, Beyond ONE is the primary owner of VMLA, having acquired it in 2023. Virgin Group remains a minority stakeholder or brand partner under licensing terms.
Investors such as Archimedia, Hermes Growth Partners, HighMark Capital Management, and Latin American Partners are among its shareholder base.
Beyond ONE leads operational decisions, capital deployment, and brand strategy in Latin America.
Virgin Mobile UK
Virgin Mobile UK no longer operates as an independent brand. Its parent structure is Virgin Media O2, a joint venture between Liberty Global and Telefónica. Virgin Mobile was fully absorbed; the parent telecom entities govern the mobile business and brand sunset.
In that setup, Virgin Group has no direct operational share, but may hold residual brand or legacy rights via licensing within the joint venture.
Virgin Mobile USA
Virgin Mobile USA ceased operations in 2020, and its assets were fully taken over by Boost Mobile under the broader T-Mobile / Sprint merger. In 2009, Sprint had already acquired Virgin’s stake and became the sole owner.
Other Markets (Past or Reduced Presence)
- In South Africa, Virgin Mobile was a joint venture between Virgin Group and Cell C, each holding roughly 50% at one point. That venture is now closed.
- In France, the joint venture behind Virgin Mobile was bought by SFR, and Virgin no longer retains share control.
- In Canada, Bell Mobility acquired full ownership of Virgin Mobile Canada, eliminating external shareholders.
Who Owns Virgin Mobile Canada?

Virgin Mobile Canada launched on March 1, 2005, as a joint venture between Virgin Group and Bell Canada (BCE). Its idea was to offer a youth-oriented wireless brand using Bell’s network.
Over time, Bell acquired full ownership. As of 2009, Bell Canada (through Bell Mobility) owns Virgin Mobile Canada outright. It operates today under the name Virgin Plus, a broader brand offering wireless, internet, and TV services.
Joint Venture Origins (2005 – 2009)
Virgin Mobile Canada was launched on March 1, 2005, as a joint venture between Virgin Group and Bell Canada / BCE Inc. The model was that Virgin would contribute the brand, marketing strategy, and customer-facing functions, while Bell would supply network access (as Bell Mobility) and infrastructure. At inception, Bell and Virgin each held approximately 50 % equity stake in the Canadian operation.
During this period, Virgin Mobile Canada operated as an MVNO on Bell’s network. It marketed as a youthful, value-oriented alternative to the major carriers. It had its own branding, retail outlets, or partnerships, and customer programs, though network and technical operations relied fully on Bell.
Acquisition of the Remaining Stake (2009)
On July 1, 2009, Bell Mobility (a subsidiary of Bell Canada / BCE) purchased the remaining 50 % stake in Virgin Mobile Canada for CAD 142 million. This acquisition gave Bell 100 % ownership of the operation. The deal included a long-term licensing agreement for use of the “Virgin” brand in Canada. In effect, Virgin Group transitioned from being a co-owner to a brand licensor.
Upon acquiring full control, Bell integrated Virgin Mobile Canada more closely with its overall mobile business. But Bell committed to allow the Virgin brand to retain operational distinctions: separate distribution channels, marketing autonomy, and target demographics.
Bell also expanded Virgin’s retail presence via The Source stores (owned by Bell), integrating Virgin mobile products into The Source’s network of kiosks and retail locations.
Current Ownership and Control (Post-2009 to Present)
Bell Canada / BCE Inc.
Since 2009, Virgin Plus (formerly Virgin Mobile Canada) has been a wholly owned subsidiary of Bell Canada, via its parent company BCE Inc. In corporate terms, the Canadian Virgin operation is a full internal brand under Bell’s wireless division. Bell Mobility acts as the network provider and operational backbone.
Although Bell has full equity control, the Virgin brand continues under a licensing agreement with Virgin Group. That means Bell pays for the rights to use the “Virgin” name, trademarks, and brand identity in Canada. Virgin Group no longer holds equity but retains influence through brand and licensing oversight.
Under Bell’s ownership, Virgin Plus uses Bell’s entire wireless infrastructure — from 3G, LTE, to 5G — and benefits from Bell’s scale, spectrum holdings, and network investments.
Brand Autonomy, Rebranding & Strategic Position
On July 19, 2021, Virgin Mobile Canada officially rebranded to Virgin Plus. The rebrand reflected its evolution from purely mobile services to offering home Internet and TV in certain regions. Though fully owned by Bell, Virgin Plus maintains a distinct identity, marketing, and “Member Benefits” program to differentiate from Bell’s flagship brand.
Bell’s approach is to maintain multiple brands in the wireless market: Bell itself, Virgin Plus, and lower-cost sub-brands. Virgin Plus occupies a middle tier with youth and value appeal while leveraging Bell’s assets.
Autonomy Within Bell
While Bell controls all decisions on network, capital, spectrum, and operational investments, Virgin Plus retains internal autonomy in:
- Marketing strategy and promotions
- Product/plan structuring
- Retail branding and channel design
- Customer experience and perks programs.
Bell focuses on maximizing synergies between its core and sub-brands, reducing cost duplication, and leveraging scale. Virgin Plus acts more like a differentiated product line than an independent company.
Virgin Mobile Canada Ownership Timeline
Below is an overview of the Virgin Mobile Canada ownership timeline from 2004 to 2025:
| Period | Bell’s Stake | Virgin Group’s Stake | Structure / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005–2009 | 50% | 50% | Joint venture; Virgin handles branding, Bell handles network |
| 2009–Present | 100% | 0% (licensing only) | Full Bell ownership; Virgin retains brand license |
| 2021–Present | 100% (Bell) | Brand rights (Virgin) | Rebranded as Virgin Plus; Bell runs operations, Virgin licenses name |
2004–2005: Formation and Launch
- Parties involved: Virgin Group (UK) and Bell Canada (BCE Inc.)
- Ownership split: 50% Virgin Group / 50% Bell Canada
- Virgin Mobile Canada is officially incorporated and launches in March 2005.
- Operates as a mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) using Bell’s infrastructure.
- Targets youth and budget-conscious customers with prepaid plans and flexible pricing.
2006–2008: Expansion Under Joint Venture
- Virgin Mobile Canada grows rapidly in prepaid subscriptions.
- Expands into postpaid services, competing with Fido and Koodo.
- Maintains brand independence in marketing, but depends on Bell’s network and wholesale agreements.
- Bell and Virgin jointly fund marketing and retail distribution.
2009: Bell Acquires Full Ownership
- Bell Mobility acquires the remaining 50% stake from Virgin Group for approximately CAD 142 million.
- After the acquisition, Bell becomes the sole owner (100%) of Virgin Mobile Canada.
- Virgin Group exits as an equity partner but remains a brand licensor under a long-term agreement.
- Bell integrates Virgin Mobile Canada into its wireless portfolio alongside Bell Mobility and Solo Mobile.
2010–2014: Growth Under Bell Control
- Virgin Mobile continues to operate as a separate brand within Bell’s structure.
- Launches new smartphones, plans, and loyalty programs under Bell’s network.
- Introduces the “Member Benefits” program to distinguish itself from Bell Mobility.
- Bell expands retail presence for Virgin through The Source and mall kiosks.
2015–2019: Digital and 4G Expansion
- Virgin Mobile Canada adopts LTE and later 4G+ through Bell’s network.
- The company expands into bundled services, including phone + internet deals.
- The brand begins positioning itself as a mid-tier carrier: below Bell, above discount carriers like Lucky Mobile.
- Bell continues to invest in Virgin’s marketing but keeps corporate operations fully centralized.
2020: Transition to 5G and Brand Modernization
- Virgin Mobile gains access to Bell’s nationwide 5G network for compatible plans.
- Focus shifts toward digital-first services and app-based management.
- Internal restructuring begins to align Virgin Mobile with Bell’s long-term digital transformation strategy.
2021: Rebrand to Virgin Plus
- On July 19, 2021, Virgin Mobile Canada officially rebrands to Virgin Plus.
- The rebrand reflects the brand’s expansion beyond mobile into home Internet and TV services.
- The move positions Virgin Plus as a lifestyle and entertainment brand, not just a telecom provider.
- Ownership remains 100% Bell (BCE Inc.), with Virgin Group continuing its brand licensing partnership.
2022–2025: Virgin Plus Under Bell’s Full Integration
- Virgin Plus operates as one of Bell’s key consumer brands, offering 5G, Internet, and TV bundles.
- Virgin Group continues to collect licensing fees but holds no equity stake.
- Bell Mobility manages all technical, financial, and operational aspects.
- Virgin Plus maintains a distinct identity, advertising style, and “Member Perks” loyalty ecosystem.
- As of 2025, Virgin Plus is a wholly owned Bell brand with its own customer base, marketing strategy, and separate brand positioning in the Canadian telecom market.
Final Words
Virgin Mobile remains one of the most iconic names in the global telecom industry. Although who owns Virgin Mobile varies by region, the brand continues to represent the spirit of innovation and customer care that Richard Branson’s Virgin Group is known for. Through strategic partnerships and licensing agreements, Virgin Mobile continues to operate successfully around the world, maintaining its position as a trusted and forward-thinking mobile service provider.
FAQs
Who owns Virgin Mobile Canada?
Virgin Mobile Canada, now known as Virgin Plus, is 100% owned and operated by Bell Canada (BCE Inc.). Bell acquired the remaining 50% stake from the Virgin Group in 2009 for CAD 142 million. The Virgin Group no longer has an equity stake but continues to license the “Virgin” name and branding to Bell under a long-term agreement.
Who owns Virgin Group?
The Virgin Group is privately owned by Sir Richard Branson through his investment company, Virgin Group Holdings Ltd., based in the British Virgin Islands. Branson remains the founder, majority shareholder, and ultimate controller of the Virgin brand and its global licensing network.
Who owns Virgin Mobile USA?
Virgin Mobile USA was originally a joint venture between the Virgin Group and Sprint. In 2009, Sprint Nextel acquired the Virgin Group’s remaining stake, becoming the sole owner. After Sprint’s merger with T-Mobile in 2020, Virgin Mobile USA was shut down, and all customers were migrated to Boost Mobile under T-Mobile’s network.
Where is Virgin Mobile located?
Virgin Mobile does not have one global headquarters because it operates through regional companies. The Virgin Group’s global headquarters is in London, England, while active Virgin Mobile operations are headquartered regionally — for example, Virgin Mobile Canada is managed from Toronto, and Virgin Mobile Middle East & Africa is based in Dubai, UAE.
Who owns Virgin Atlantic Airlines?
As of 2025, Virgin Atlantic Airways is jointly owned by Virgin Group (51%) and Delta Air Lines (49%). Richard Branson’s Virgin Group retains majority control, while Delta holds a significant strategic and financial stake.
Who bought Virgin Mobile TV?
Virgin Mobile TV, a short-lived mobile television service launched in the UK, was integrated into Virgin Media after the 2006 merger of NTL:Telewest and Virgin Mobile UK. Today, all Virgin-branded TV and broadband services in the UK fall under Virgin Media O2, jointly owned by Liberty Global and Telefónica.
Is Virgin owned by Rogers or Bell?
Virgin is owned by Bell in Canada, not Rogers. Bell (BCE Inc.) fully owns and operates Virgin Plus under a licensing agreement with the Virgin Group. Rogers Communications has no ownership or control over Virgin-branded services.
Does Virgin Mobile use Bell Towers?
Yes. Virgin Plus (formerly Virgin Mobile Canada) uses Bell Mobility’s cell towers and network infrastructure. Since Bell owns Virgin Plus, both brands operate on the same network, offering identical coverage and speeds across Canada.
Is Virgin British owned?
Yes. The Virgin brand is British-owned through the Virgin Group, founded by Sir Richard Branson in the United Kingdom. Although many Virgin companies are now joint ventures or licensees, the brand’s ownership and headquarters remain British.
Did Virgin buy O2?
No. Virgin did not buy O2. In 2021, Virgin Media and O2 merged to form Virgin Media O2, a joint venture between Liberty Global (Virgin Media’s parent company) and Telefónica (O2’s parent). Each company owns 50% of the joint venture.
Does Virgin use the Vodafone network?
In most countries, Virgin Mobile does not use Vodafone’s network. It typically partners with other telecom operators. For instance, in the UK, it used EE’s network before moving to O2; in Canada, it uses Bell’s network; and in the Middle East, it partners with local carriers under Beyond ONE.
Why did Virgin Mobile shut down?
Virgin Mobile has shut down in some markets due to mergers, brand consolidation, or strategic rebranding. For example, in the U.S., it was discontinued after the Sprint–T-Mobile merger, and in the U.K., customers were migrated to O2 under Virgin Media O2 in 2023. The shutdowns were part of efforts to unify operations and reduce overlapping brands.
Are Bell and Virgin affiliated?
Yes. Bell and Virgin are directly affiliated in Canada. Bell owns 100% of Virgin Plus and manages all of its operations, networks, and services under a long-term brand licensing deal with the Virgin Group.
Which company owns Virgin Media?
Virgin Media is owned by Virgin Media O2, a 50–50 joint venture between Liberty Global and Telefónica. Virgin Group licenses the Virgin name but does not hold any ownership stake in Virgin Media O2.
Is Virgin Radio owned by Bell?
Yes. In Canada, Virgin Radio is operated by Bell Media, which owns the broadcast rights to the Virgin Radio brand under a licensing agreement with the Virgin Group. Bell Media runs multiple Virgin Radio stations across major Canadian cities, including Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.

