Applebee’s is one of the most recognized names in American casual dining. If you’ve ever wondered who owns Applebee’s and what companies operate under its parent brand, this article covers all of that in detail.
From ownership to revenues and subsidiary brands, here’s everything you need to know.
Applebee’s Company Profile
Applebee’s Neighborhood Grill + Bar is one of the most popular casual dining chains in the United States. Known for its approachable American fare and welcoming, family-friendly atmosphere, Applebee’s offers a wide selection of menu items, including burgers, ribs, pasta, and cocktails. Its restaurants are often located in suburban neighborhoods, consistent with its branding as a neighborhood grill.
Company Details
Applebee’s operates under Dine Brands Global, Inc., which is based in Glendale, California. Applebee’s is a franchised brand, with the majority of its restaurants operated by third-party owners under long-term agreements. The brand serves millions of customers every year across the United States and several international markets.
As of 2025, there are over 1,500 Applebee’s restaurants in operation globally. The company emphasizes affordability, comfort, and convenience, with a growing focus on online ordering, takeout, and delivery. Its marketing efforts frequently highlight limited-time deals and seasonal promotions.
Applebee’s menu includes a mix of hearty main courses, shareable appetizers, and signature beverages. The chain is especially known for its late-night happy hours, two-for-$20 deals, and half-price appetizers.
Founders
Applebee’s was founded in 1980 by Bill Palmer and TJ Palmer, a husband-and-wife duo. The first location, named T.J. Applebee’s Rx for Edibles & Elixirs, opened in Decatur, Georgia.
Bill Palmer later became one of the brand’s first franchisees. Under his direction, the franchise model grew rapidly during the 1980s and 1990s. Palmer remained a key figure in expanding the chain’s concept and solidifying its presence in American suburbia.
Major Milestones
1980 – Applebee’s is founded in Decatur, Georgia, by Bill and TJ Palmer.
1983 – Bill Palmer sells the company but becomes an active franchisee and continues growing the brand.
1988 – The chain is renamed Applebee’s Neighborhood Grill & Bar to reflect its community-centric branding.
1989 – Applebee’s opens its 100th location, marking significant national expansion.
1991 – The company goes public, trading on NASDAQ under the ticker APPB.
1998 – Applebee’s reaches 1,000 locations, becoming the largest sit-down dining chain in the U.S. by restaurant count.
2007 – Applebee’s is acquired by IHOP Corporation for $2.1 billion. IHOP later forms DineEquity, now known as Dine Brands Global, Inc.
2010s – Applebee’s introduces digital ordering, revamps its menu, and launches the 2-for-$20 meal deal, which becomes a customer favorite.
2020 – During the COVID-19 pandemic, Applebee’s expands its off-premise dining services and integrates with food delivery apps.
2023–2025 – Applebee’s focuses on modernization, testing smaller store formats, mobile ordering tech, and sustainability initiatives while continuing to dominate the casual dining segment.
Who Owns Applebee’s?
Applebee’s is owned by Dine Brands Global, Inc., a leading operator and franchisor in the casual dining sector. Dine Brands is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker DIN. Applebee’s operates primarily under a franchise-based model, meaning that most of its restaurants are owned and run by independent franchisees rather than by the company itself.
Approximately 95% of Applebee’s restaurants are franchised, with the remaining being company-operated. This business model helps Dine Brands reduce operating costs while generating consistent revenue through royalties, franchise fees, and marketing contributions.
Applebee’s is one of two flagship brands under Dine Brands, the other being IHOP (International House of Pancakes). Both brands operate with independent leadership under the broader strategic framework set by Dine Brands Global.
Parent Company: Dine Brands Global, Inc.
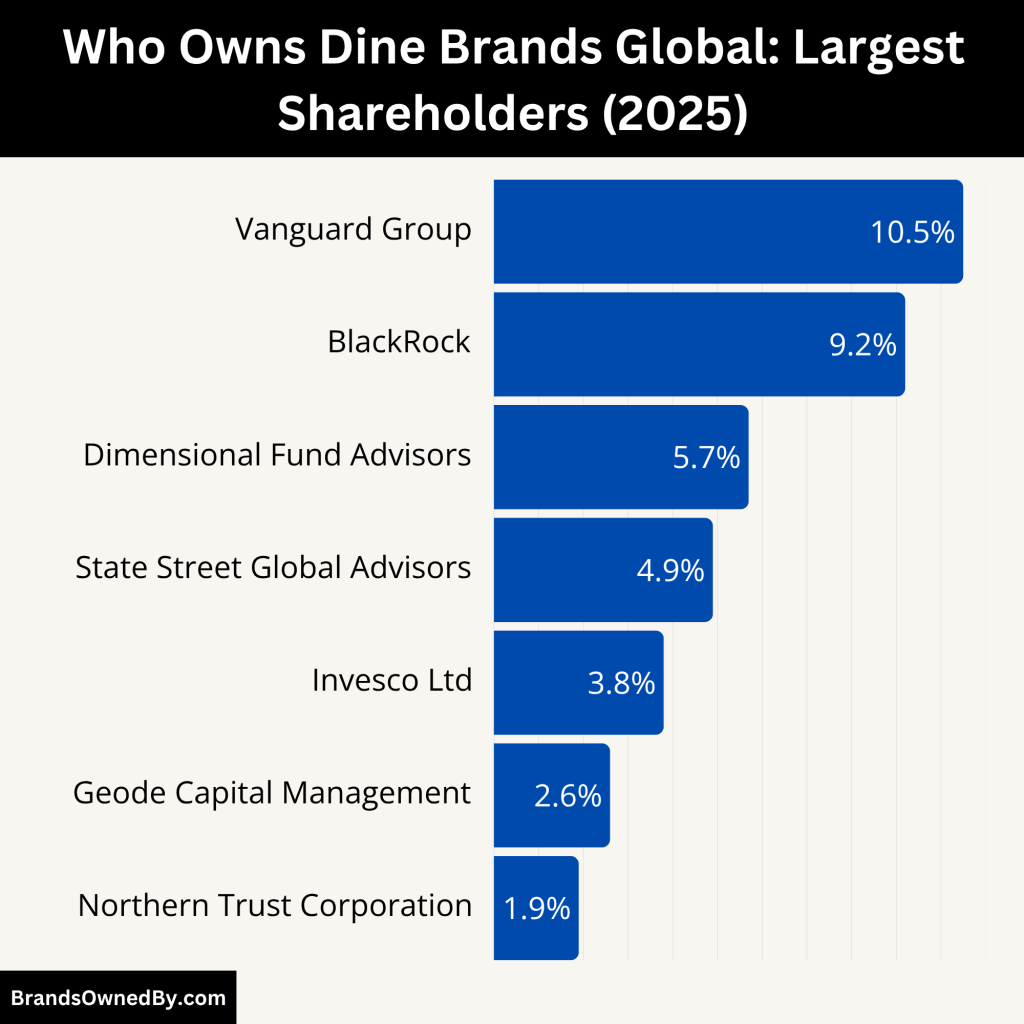
Dine Brands Global is the parent company of Applebee’s. The company was originally known as IHOP Corporation before it acquired Applebee’s in 2007. Following the acquisition, it rebranded as DineEquity, Inc., and later changed its name to Dine Brands Global, Inc. in 2018 to reflect its broader portfolio and global ambitions.
Dine Brands is headquartered in Glendale, California, and focuses exclusively on the casual dining segment. Its primary revenue sources come from franchise royalties, licensing fees, and development agreements. The corporation maintains a lean operation, with franchisees managing most day-to-day restaurant activities.
Dine Brands oversees two global restaurant chains:
- Applebee’s Neighborhood Grill + Bar
- IHOP (International House of Pancakes)
These brands collectively operate over 3,500 restaurants worldwide.
Acquisition Insights and Key Details
The most significant ownership change in Applebee’s history occurred in 2007, when it was acquired by IHOP Corporation in a $2.1 billion deal. This acquisition was a major event in the restaurant industry, forming one of the largest full-service restaurant companies in the world.
Key Details of the Acquisition:
- The deal was announced in July 2007 and finalized later that year.
- IHOP purchased Applebee’s for $25.50 per share in cash, totaling approximately $2.1 billion.
- The acquisition was funded through a combination of debt and cash, with IHOP taking on significant leverage to complete the purchase.
- Following the deal, IHOP became the parent company and rebranded as DineEquity.
- The strategy behind the acquisition was to consolidate operations, improve profitability, and expand global reach through a strong franchising model.
The acquisition resulted in a major shift in Applebee’s business approach. Dine Brands began refranchising company-owned Applebee’s restaurants, eventually selling off most locations to franchisees. This helped streamline the business and improve cash flow.
Other Relevant Ownership Insights
Franchising and Global Strategy
Under Dine Brands, Applebee’s has aggressively expanded through franchising in both domestic and international markets. Franchise partners are responsible for building, staffing, and operating each location. In return, they pay ongoing royalties and contribute to a joint advertising fund managed by the parent company.
This franchising model allows for scalable global growth without incurring the full cost of restaurant development.
Investor and Shareholder Control
Since Dine Brands is a public company, ownership of Applebee’s is indirectly held by its shareholders. Major institutional investors include BlackRock, Vanguard, State Street, and Dimensional Fund Advisors. These investors hold voting power and influence corporate decisions through the Dine Brands board of directors.
Brand Autonomy
Though Applebee’s is fully owned by Dine Brands, it maintains operational autonomy. Applebee’s has its own executive team, marketing department, and restaurant strategy. However, high-level decisions—such as financial planning, strategic partnerships, and global expansion—are approved at the Dine Brands Global level.
This hybrid approach allows Applebee’s to retain brand identity while benefiting from the scale and resources of its parent company.
Who is the CEO of Applebee’s?
John Peyton has served as CEO of Dine Brands Global—the parent company of Applebee’s, IHOP, and Fuzzy’s Taco Shop—since January 2021. Before joining Dine Brands, Peyton was President and CEO at Realogy Franchise Group, overseeing major real estate franchises, and spent 17 years in senior leadership at Starwood Hotels & Resorts.
Peyton is responsible for the strategic direction and operational oversight of all Dine Brands’ restaurants, including Applebee’s. He brings extensive experience in global branding and franchise operations.
Here’s a summary of ownership and CEO details:
| Role | Person | Date Appointed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CEO, Dine Brands Global | John Peyton | Jan 2021 | Oversees all brands; interim Applebee’s President as of Mar 2025 |
| President, Applebee’s | Tony Moralejo | Jan 2023–Mar 2025 | Focused on value and menu innovation; advisory until June 2025 |
| Interim President, Applebee’s | John Peyton | Mar 2025–present | Ensuring stability and continuity during CEO role overlap |
Interim President of Applebee’s (as of March 2025)
In early 2023, Tony Moralejo stepped into the role of Applebee’s President, coming from leading international development for Dine Brands. He brought deep experience from roles at Burger King, Church’s Chicken, and Texas Chicken.
However, Moralejo stepped down on March 4, 2025, transitioning to an advisory position through June 4, 2025. His tenure saw a renewed focus on value-driven promotions and menu innovation amid a challenging consumer landscape.
Meanwhile, John Peyton assumed the interim President duties for Applebee’s, combining brand leadership with his CEO responsibilities. The board prioritized continuity during the search for a permanent president.
Key Responsibilities and Leadership Role
Under this leadership structure:
- John Peyton oversees brand strategy, finances, and operational performance for Applebee’s while also guiding the entire Dine Brands portfolio.
- The hiring of a new Applebee’s President remains ongoing, with Peyton bridging the role to maintain momentum and stability.
Historical Context: Previous Leadership of Applebee’s
- Tony Moralejo (Jan 2023–Mar 2025): Spearheaded menu updates, value deals, and digital expansion initiativesBefore Moralejo, Applebee’s leaders included brand heads working under Dine Brands’ shared executive structure, though specific names are less publicly highlighted. Under Peyton’s interim leadership, the brand remains in trusted hands while a permanent successor is selected.
Applebee’s Annual Revenue and Net Worth
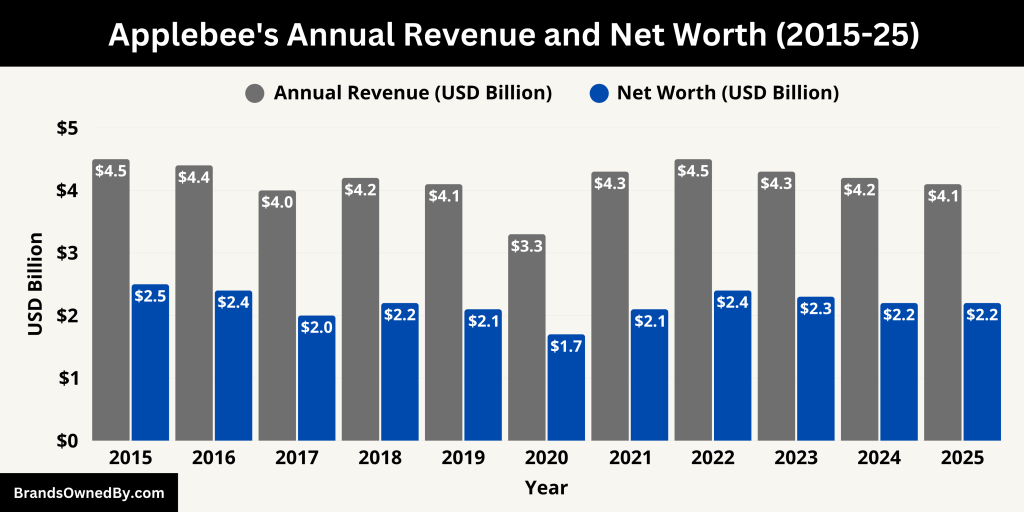
Applebee’s generated an estimated $4.1 billion in systemwide sales in 2025. These figures represent the total gross sales across all franchised and company-owned Applebee’s restaurants globally. While Dine Brands Global only reports consolidated revenue, Applebee’s is consistently the largest contributor to the company’s system sales.
Approximately 58–60% of Dine Brands’ total revenue is attributed to Applebee’s. The restaurant chain earns its revenue through a mix of:
- Franchise royalties (typically 4–5% of gross restaurant sales)
- Company-owned restaurant sales
- Marketing fund contributions
- Licensing fees and promotional partnerships
In 2025, Applebee’s system sales declined slightly by about 2.2% year-over-year, largely due to reduced same-restaurant traffic. However, this was offset by modest gains in check averages and the acquisition of several previously franchised locations, boosting direct revenue contribution.
Applebee’s also benefited from growth in off-premise channels, including delivery, takeout, and curbside pickup, which made up 23.5% of total sales in Q1 2025 alone.
Applebee’s Net Worth in 2025
While Applebee’s does not publish standalone balance sheets as a private brand under Dine Brands Global, its estimated brand valuation in 2025 ranges from $1.8 billion to $2.2 billion. This is based on:
- Systemwide sales performance
- Franchise network size (1,500+ global units)
- Long-term revenue-generating franchise contracts
- Brand equity and recognition
- Comparable valuations of similar restaurant chains
This valuation is significantly higher than Dine Brands Global’s market capitalization because Applebee’s contributes the majority of operating income and brand value within the portfolio. Its network of over 1,500 restaurants, with an average annual unit volume (AUV) of $2.7–$2.8 million, supports its multi-billion-dollar valuation.
Additionally, Applebee’s controls major assets through its brand trademarks, exclusive franchise territories, and robust loyalty program, which further bolster its net worth.
Here’s a detailed overview of Applebee’s systemwide revenue and estimated brand net worth from 2015 to 2025:
| Year | Systemwide Revenue (USD) | Estimated Net Worth (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025 | $4.1 billion | $1.8 – $2.2 billion | Decline in same-store traffic offset by off-premise growth |
| 2024 | $4.2 billion | $2.2 billion | Boost from value menu promotions and delivery expansion |
| 2023 | $4.3 billion | $2.3 billion | Recovery after inflation-driven slowdown |
| 2022 | $4.5 billion | $2.4 billion | High check averages; pandemic rebound year |
| 2021 | $4.3 billion | $2.1 billion | Continued recovery; off-premise orders strong |
| 2020 | $3.3 billion | $1.7 billion | COVID-19 impact; dine-in traffic heavily reduced |
| 2019 | $4.1 billion | $2.1 billion | Menu revamp and marketing repositioning |
| 2018 | $4.2 billion | $2.2 billion | Strong franchise growth; traffic growth stabilizes |
| 2017 | $4.0 billion | $2.0 billion | Store closures began; refocus on core offerings |
| 2016 | $4.4 billion | $2.4 billion | Peak system sales before strategic pullback |
| 2015 | $4.5 billion | $2.5 billion | Brand near peak footprint with strong market penetration |
Factors Affecting Applebee’s 2025 Financials
- Traffic softness: Customer visits declined slightly, especially in mid-tier markets.
- Check growth: Higher menu prices and promotions improved per-visit spending.
- Franchisee performance: While some franchisees underperformed, others expanded aggressively, balancing overall results.
- International operations: Non-U.S. units contributed a smaller share but remain strategic for long-term growth.
Brands Owned by Applebee’s
Applebee’s in 2025 is more than a restaurant chain—it’s a multi-platform brand encompassing physical, digital, and virtual entities. While it does not own other external companies, it has expanded internally through diversified business models like ghost kitchens, virtual brands, and off-premise channels.
Here’s a detailed expansion of companies, brands, acquisitions, and entities directly owned and operated by Applebee’s as of 2025:
| Name / Division | Type | Description | Operational Scope | Purpose / Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applebee’s Neighborhood Grill + Bar | Core Brand | Main dine-in restaurant brand offering American casual dining | 1,500+ global locations | Core business and brand identity |
| Applebee’s To Go | Off-Premise Division | Takeout, curbside, and delivery-focused operations | U.S. nationwide | Capture off-premise revenue and digital sales |
| Applebee’s Ghost Kitchens | Delivery-Only Kitchens | No-dine-in kitchens serving high-volume online orders | Select U.S. urban markets | Low-cost expansion and delivery efficiency |
| Cosmic Wings | Virtual Brand | Online-exclusive wing brand with bold, Cheetos-inspired flavors | Operates from Applebee’s kitchens | Competes in delivery-first chicken wing segment |
| Neighborhood Nachos (pilot) | Virtual Brand | Digital brand for nachos, dips, and Tex-Mex platters | Limited cities (pilot phase) | Targets group orders and sports-viewing occasions |
| Applebee’s Branded Merchandise | Retail Extension | Branded apparel, glassware, sauces, and novelty items | Online and select in-store locations | Brand loyalty and secondary revenue stream |
| Applebee’s Global Franchise Network | Franchise Partnerships | Independent operators licensed by Applebee’s to run international locations | Mexico, MENA, Caribbean, Latin America | Brand expansion in non-U.S. territories |
| In-House Training & Culinary Division | Internal Operations Unit | Oversees staff training, menu development, and quality control | Global (all locations) | Ensures brand consistency and operational standards |
| Applebee’s Loyalty Program | Digital Customer Program | App-based program for points, personalized deals, and engagement | U.S. (integrated with app & web) | Enhances customer retention and spending |
Applebee’s Neighborhood Grill + Bar
This is the core brand and the foundation of Applebee’s business model. As of 2025, Applebee’s operates over 1,500 restaurants worldwide, with more than 95% of them franchised. Each restaurant offers casual dining experiences with a focus on American favorites—burgers, steaks, ribs, salads, and cocktails.
The brand operates under a uniform menu and service model, but local franchisees often adapt certain elements to regional tastes. Applebee’s also promotes limited-time offers, happy hour deals, and family meal bundles to attract diverse customers.
Applebee’s To Go (Off-Premise Dining Division)
Launched as a strategic extension of the main brand, Applebee’s To Go focuses on carryout, curbside pickup, and third-party delivery. This business division expanded rapidly during and after the COVID-19 pandemic, and by 2025, it accounts for over 23% of all Applebee’s revenue.
While not a separate legal entity, Applebee’s To Go operates as a major internal unit responsible for:
- Online ordering platform and mobile app integration
- Partnerships with delivery aggregators like Uber Eats and DoorDash
- Packaging and kitchen optimization for takeout efficiency
This division is critical for increasing sales from younger demographics and busy professionals.
Applebee’s Ghost Kitchen Program
Applebee’s operates a ghost kitchen network in select urban markets. These kitchens are delivery-only facilities without a storefront, designed to handle high-volume online orders.
By 2025, Applebee’s had over a dozen ghost kitchen operations across the U.S., either independently or through partnerships with virtual kitchen providers. The ghost kitchen program helps:
- Enter dense metro areas without the cost of full-service restaurants
- Test new menu items
- Expand delivery reach without altering dine-in operations
This strategy enhances Applebee’s digital presence and allows for flexible brand scaling.
Applebee’s Virtual Brand Extensions
Applebee’s has tested and operated virtual-only sub-brands to cater to specific food niches under its umbrella. These brands are fulfilled from Applebee’s kitchens but marketed separately through delivery apps.
Notable examples include:
- Cosmic Wings: A virtual chicken wing brand originally launched in collaboration with Cheetos-branded flavoring. It offers bold, youth-oriented flavors and is available exclusively online.
- Neighborhood Nachos (Pilot phase): A virtual brand specializing in party platters and Tex-Mex items. Targeted at group orders and sporting events.
These virtual brands allow Applebee’s to enter competitive delivery categories without diluting its core brand identity.
Applebee’s Branded Merchandise (Limited Retail)
In recent years, Applebee’s began selling branded merchandise, including:
- Apparel (T-shirts, hats, hoodies)
- Glassware and novelty items (beer mugs, shot glasses)
- Limited edition sauces and seasoning mixes
Although still a niche business, this merchandise is sold online and occasionally in-store, helping reinforce brand loyalty and generate auxiliary revenue.
Applebee’s Global Franchise Network
While not separate companies, Applebee’s international franchisees operate under exclusive territorial licensing agreements. As of 2025, Applebee’s maintains franchise operations in:
- Mexico
- Qatar
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- Guam
- Panama
- Dominican Republic
Each regional partner adapts Applebee’s menu and service to local customs while maintaining brand standards. The international unit is a key growth area, with more focus on Middle East and Latin America in recent years.
Applebee’s In-House Training & Culinary Division
Applebee’s operates an internal training and culinary development division, which oversees:
- Franchisee onboarding and certification
- Menu innovation and testing
- Operational compliance audits
- Kitchen staff training programs
While not branded as a separate company, this division is crucial in ensuring operational consistency across all locations worldwide.
Applebee’s Loyalty Program (Integrated Tech Asset)
Applebee’s runs a digital loyalty and rewards program integrated with its mobile app. While part of the brand’s tech infrastructure, it operates as a semi-independent unit managing:
- Customer engagement and segmentation
- Personalized promotions
- Rewards point tracking and redemption
This program is integrated with both dine-in and delivery orders and is pivotal to driving repeat visits and increasing check sizes.
Final Thoughts
Understanding who owns Applebee’s reveals a larger picture about corporate ownership in the food industry. Applebee’s is more than a restaurant chain; it is part of a strategic portfolio operated by Dine Brands Global.
With a heavy reliance on franchising and strong institutional backing, Applebee’s continues to be a leading name in casual dining both in the U.S. and globally.
FAQs
Which country owns Applebee’s?
Applebee’s is owned by a U.S.-based corporation, Dine Brands Global, Inc., headquartered in Glendale, California.
Are Panera and Applebee’s owned by the same company?
No, Panera Bread and Applebee’s are not owned by the same company. Panera is owned by JAB Holding Company, while Applebee’s is owned by Dine Brands Global.
Who is the sister company of Applebee’s?
The sister company of Applebee’s is IHOP (International House of Pancakes). Both are owned by Dine Brands Global.
How many Applebee’s are in the US?
As of 2025, there are approximately 1,300 Applebee’s locations in the United States.
Who is the owner of Applebee’s Qatar?
Applebee’s Qatar is operated by a local franchisee under a licensing agreement with Applebee’s International, Inc. The franchise rights are held by a regional hospitality group, but the brand ownership remains with Dine Brands Global in the U.S.
Is Applebee’s a private company?
No, Applebee’s is not a private company. It is a wholly owned brand of Dine Brands Global, Inc., which is a publicly traded company on the New York Stock Exchange (Ticker: DIN).
Who did Applebee’s merge with?
Applebee’s did not merge directly with another restaurant chain. However, it was acquired by IHOP Corporation in 2007, and the combined company was renamed DineEquity, now known as Dine Brands Global.
Who owns Applebee’s and Chili’s?
Applebee’s is owned by Dine Brands Global, while Chili’s is owned by Brinker International. They are not owned by the same company.
What is the major list of Applebee’s franchise owners?
Major Applebee’s franchise operators in the U.S. and internationally include:
- Flynn Restaurant Group (largest U.S. franchisee)
- The Rose Group
- RMH Franchise
- Apple Investors Group
- Neighborhood Restaurant Partners
- Various regional operators in the Middle East, Latin America, and the Caribbean.
Where was the first Applebee’s located?
The first Applebee’s restaurant was opened in Decatur, Georgia, in 1980 by Bill and T.J. Palmer.
How many Applebee’s are there in the world?
As of 2025, there are approximately 1,500 Applebee’s locations globally, including the U.S. and international markets such as Mexico, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Panama, and the Dominican Republic.
Who owns Applebee’s brand?
The Applebee’s brand is owned by Dine Brands Global, Inc., a public restaurant holding company based in the United States.
Who owns Applebee’s restaurant?
Each individual Applebee’s restaurant is either franchise-owned or company-operated, but the overall brand is owned and controlled by Dine Brands Global.
When did IHOP buy Applebee’s?
IHOP Corporation acquired Applebee’s in November 2007 in a $2.1 billion deal. The combined company was rebranded as DineEquity, now known as Dine Brands Global.
What corporation owns Applebee’s?
Applebee’s is owned by Dine Brands Global, Inc., a publicly listed restaurant company on the New York Stock Exchange.
Does IHOP own Applebee’s?
IHOP does not directly own Applebee’s. Both brands are owned by their mutual parent company, Dine Brands Global, Inc.
Who owns IHOP and Applebee’s?
Both IHOP and Applebee’s are owned by Dine Brands Global, Inc., a U.S.-based corporation focused on full-service restaurant brands.
Who owns the Applebee’s restaurant chain?
Applebee’s is owned by Dine Brands Global, Inc., which also owns IHOP. It purchased the brand in 2007.
Is Applebee’s still a franchise?
Yes. Over 95% of Applebee’s locations are franchised, operated by independent restaurant owners under licensing agreements.

