General Motors is one of the largest automakers in the world, and the question of who owns General Motors is one that many investors and car enthusiasts often ask. As a publicly traded company, its ownership is shared among many shareholders. This article explores its history, leadership, shareholders, revenue, and subsidiaries.
General Motors Company Profile
General Motors, commonly known as GM, is one of the most iconic and influential automobile manufacturers in the world. It was established in 1908 in Flint, Michigan, by William C. Durant, a visionary entrepreneur who saw the potential in consolidating multiple auto companies under one corporate structure. Over time, GM evolved into a major industrial conglomerate and a global automotive leader.
Overview and Company Details
General Motors is a multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The company designs, manufactures, markets, and distributes vehicles and vehicle parts across more than 100 countries. GM operates under several well-known brand names including Chevrolet, GMC, Cadillac, Buick, and newer ventures like BrightDrop and Cruise.
GM is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker symbol GM. It employs over 160,000 people worldwide and has dozens of manufacturing facilities in North America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
The company’s core areas now include electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous vehicle technology, and mobility services. GM aims to lead the transition to a zero-emission, all-electric future through its Ultium battery platform.
Founders of General Motors
General Motors was founded by William C. Durant on September 16, 1908. Durant was a leading figure in the early automotive industry and initially built a fortune in the carriage business. After gaining control of the Buick Motor Company, he formed GM as a holding company to acquire and manage other carmakers.
Some of the key individuals associated with GM’s early growth include:
- Charles Stewart Mott, a businessman and one of the early investors in GM.
- Louis Chevrolet, co-founder of the Chevrolet Motor Car Company, which became part of GM in 1918.
- Alfred P. Sloan, who later became president and then chairman of GM, introducing the concept of decentralized management and brand segmentation.
Major Milestones
- 1908: General Motors is incorporated in Flint, Michigan.
- 1910: Durant loses control of GM due to financial overreach.
- 1916: GM acquires Chevrolet, created by Durant and Louis Chevrolet, and Durant regains control of GM.
- 1923–1946: Under Alfred P. Sloan, GM introduces innovative business practices and overtakes Ford in auto sales.
- 1955: GM becomes the first American corporation to earn over $1 billion in a single year.
- 1980s–1990s: GM expands globally but struggles with rising competition and quality issues.
- 2000: GM creates OnStar, a pioneering in-car safety and communication system.
- 2009: Files for Chapter 11 bankruptcy and undergoes government-backed restructuring during the financial crisis.
- 2010: Returns to public trading with a successful IPO, one of the largest in U.S. history.
- 2016: Launches Maven, a car-sharing service, and invests in Cruise, an autonomous vehicle startup.
- 2020: Announces commitment to an all-electric future with plans to phase out internal combustion engines.
- 2021–2025: Launches Ultium battery platform and begins production of new EVs like the Hummer EV and Chevy Silverado EV.
- 2025: Continues global leadership in EV and autonomous technology while maintaining strong traditional vehicle sales.
General Motors’ journey from a group of small auto companies to a leading global automotive force has been defined by innovation, resilience, and transformation. It continues to play a major role in shaping the future of mobility.
Who Owns General Motors: Top Shareholders
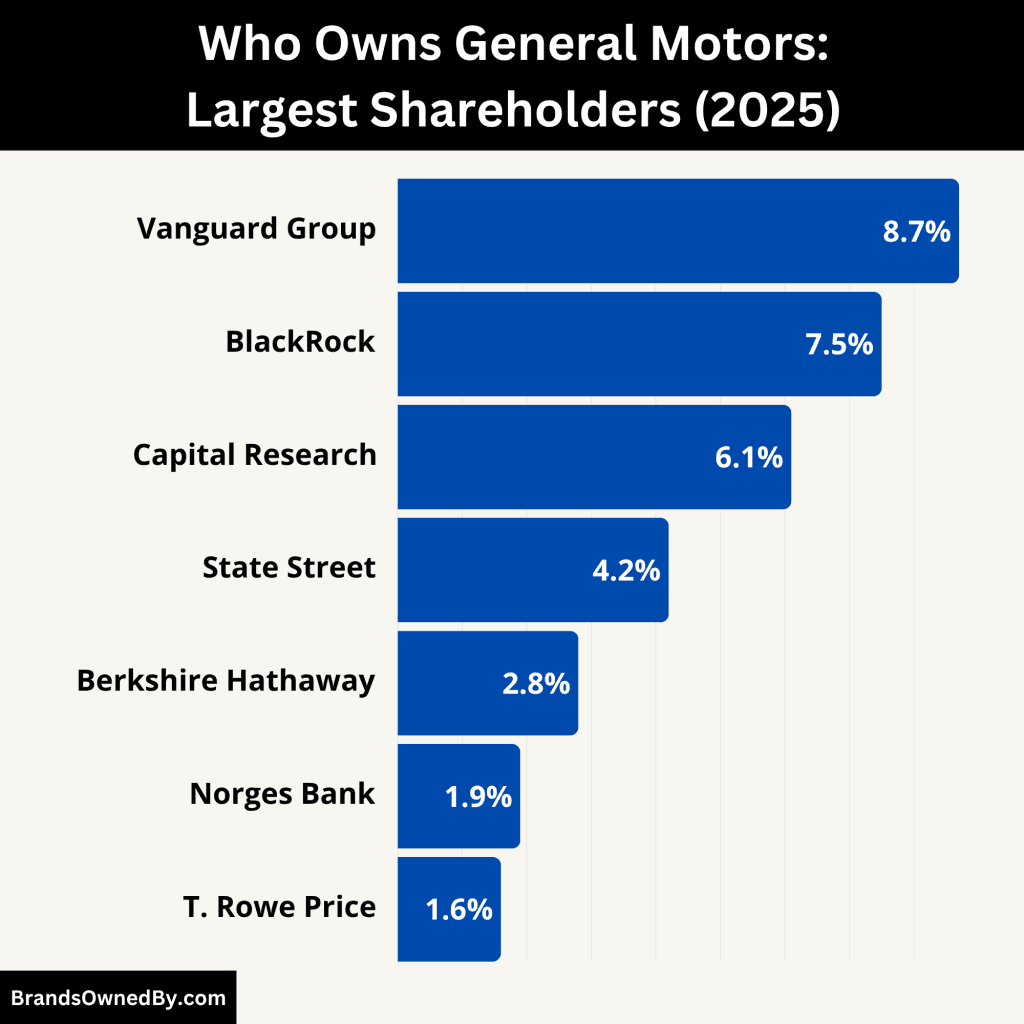
General Motors is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker symbol GM. The company has a diverse shareholder base consisting of institutional investors, mutual funds, retail investors, and company insiders. There is no single controlling shareholder, but some institutional investors hold significant influence due to their large ownership stakes and voting power.
Here’s a list of the major shareholders of General Motors (GM) as of June 2025:
| Shareholder | Ownership % | Type | Control/Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group | ~8.7% | Institutional (Passive) | High voting influence via proxy |
| BlackRock Inc. | ~7.5% | Institutional (Passive) | Strong ESG advocacy and voting power |
| Capital Research & Management | ~6.1% | Institutional (Active) | Long-term investor, strategic voice |
| State Street Global Advisors | ~4.2% | Institutional (Passive) | Proxy voting, governance engagement |
| Berkshire Hathaway | ~2.8% | Institutional (Strategic) | Passive support, high investor trust |
| Norges Bank Investment Management | ~1.9% | Sovereign Wealth Fund | Governance-focused investor |
| T. Rowe Price | ~1.6% | Institutional (Active) | Active portfolio management |
| GM Executives & Directors | <1% | Insiders | Operational decision-making authority |
| Retail Investors | ~15–20% | Individual Shareholders | Vote collectively in annual meetings |
| Other Institutions & Mutual Funds | ~40% | Diversified Ownership | Combined minority influence |
The Vanguard Group – Approx. 8.7%
As of 2025, The Vanguard Group remains the largest institutional shareholder of General Motors. Vanguard owns approximately 8.7% of GM’s outstanding shares. The firm manages a wide range of mutual funds and index funds, and invests on behalf of millions of clients.
While Vanguard does not actively participate in GM’s operations, it holds voting rights proportional to its stake. This allows it to influence major corporate decisions such as board appointments, executive pay, and strategic direction through proxy votes. Vanguard is known for its long-term investment philosophy, which supports stability and sustainability in the companies it invests in.
BlackRock Inc. – Approx. 7.5%
BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, holds about 7.5% of General Motors’ shares in 2025. Like Vanguard, BlackRock is a passive investor, but its size gives it significant voting influence over shareholder resolutions and governance matters.
BlackRock’s investments are typically held through its iShares ETF platform. It often advocates for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices, which align with GM’s recent shift toward electric vehicles and sustainability goals.
Capital Research & Management – Approx. 6.1%
Capital Research and Management Company, part of the Capital Group, holds approximately 6.1% of GM’s shares. It is known for active portfolio management and long-term investment strategies.
Capital Group’s stake reflects its confidence in GM’s future, particularly its electric vehicle and autonomous driving ventures. While not a controlling stakeholder, it may engage with GM management on strategy and financial performance.
State Street Global Advisors – Approx. 4.2%
State Street Corporation, through its investment arm State Street Global Advisors (SSGA), owns around 4.2% of General Motors stock. State Street is a major passive investor and holds voting rights in proportion to its ownership.
The firm often supports corporate governance reforms and transparency. Its influence is mainly exercised through proxy voting and engagement with company boards.
Berkshire Hathaway – Approx. 2.8%
Berkshire Hathaway, the conglomerate led by Warren Buffett, holds an estimated 2.8% stake in GM as of 2025. Although the firm had reduced its stake in earlier years, it has maintained a steady interest in the automotive sector.
Berkshire’s investment is strategic rather than controlling. It does not actively intervene in operations but lends credibility and long-term investor confidence to GM.
Norges Bank Investment Management – Approx. 1.9%
Norges Bank, which manages Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, owns around 1.9% of General Motors. It is one of the largest international institutional shareholders and focuses heavily on ESG standards.
Norges Bank often participates in shareholder meetings and votes on governance issues. Though its stake is smaller, it represents one of the most prominent foreign investors in GM.
T. Rowe Price – Approx. 1.6%
T. Rowe Price Associates holds nearly 1.6% of GM’s stock. The investment management firm is known for active investment strategies and closely monitors corporate financial performance.
Its voting rights allow it to influence decisions, especially in matters of executive compensation and board appointments.
General Motors Executives and Directors – Combined <1%
Company insiders, including CEO Mary Barra, CFO Paul Jacobson, and other executives, own less than 1% combined of the outstanding shares. These holdings are usually part of compensation packages, stock options, and performance-based awards.
Although their individual ownership is small, executives hold operational control of the company and are responsible for its day-to-day decisions. Their influence stems from leadership roles rather than equity control.
Retail and Individual Shareholders – Approx. 15–20%
General Motors has a broad base of retail investors, which includes everyday shareholders who own stock through brokerage accounts, retirement plans, or direct investment. These individuals collectively hold 15% to 20% of GM’s equity.
While no single retail investor holds a controlling interest, their combined votes matter during annual shareholder meetings, especially in close decisions.
Other Institutional Investors and Mutual Funds
Numerous other investment firms, pension funds, insurance companies, and index funds own small percentages of GM stock. Some notable examples include Fidelity Investments, Invesco, and JP Morgan Asset Management. Each owns less than 1% individually, but collectively contributes to the company’s diversified shareholder base.
Who is the CEO of General Motors?
Mary Teresa Barra is the Chairperson and Chief Executive Officer of General Motors as of 2025. She has held the CEO role since January 2014 and was appointed Chair in December 2016. She is the first woman to lead a major global automaker.
Leadership Style and Strategic Focus
Barra leads with a customer-centric and innovation-driven approach. She is known for her bold decisions, including:
- Shifting GM’s long-term strategy toward electric vehicles (EVs) and sustainable mobility.
- Steering investment in autonomous driving through Cruise.
- Driving efficiency via cost optimization and restructuring efforts.
- Championing diversity, inclusion, and workforce development across GM.
Major Achievements under Barra
Under her leadership since 2014, GM has:
- Recovered from the 2009 bankruptcy and returned to consistent profitability.
- Launched the Ultium battery platform, powering multiple EV models.
- Introduced EVs like the Hummer EV, Chevy Silverado EV, and Cadillac Lyriq.
- Expanded autonomous vehicle testing and services with Cruise in U.S. cities.
- Committed to carbon neutrality and sustainability across global operations by 2035.
CEO Appointment and Board Role
The GM Board of Directors oversees CEO performance. Mary Barra reports directly to the Board as both CEO and Board Chair, granting her a central role in governance and strategy execution.
Executive Decision‑Making Structure
Reporting to Mary Barra is a robust executive leadership team, including:
- CFO: Paul Jacobson – responsible for financial reporting and capital allocation.
- CTO: Michael Simcoe – oversees vehicle design and technology innovation.
- EV Group President: Doug Parks – leads EV and software development strategies.
- Heads of Global Markets, Customer Experience, Supply Chain, Legal, and other key functions.
These leaders collaborate to execute GM’s transformation across electrification, autonomy, and emerging mobility services.
Past CEOs Leading to Barra
General Motors has seen several leaders in the decade preceding Barra:
- Dan Akerson (2010–2014): Guided GM’s post-bankruptcy turnaround and IPO in 2010.
- Ed Whitacre Jr. (2009–2010): Temporarily assumed leadership as a retired AT&T executive, helping stabilize GM after bankruptcy.
- Fritz Henderson (2009): Served briefly during the restructuring period and Chapter 11 emergence.
Their contributions set the foundation for Barra’s long-term vision and ambitious strategic trajectory.
General Motors Annual Revenue and Net Worth
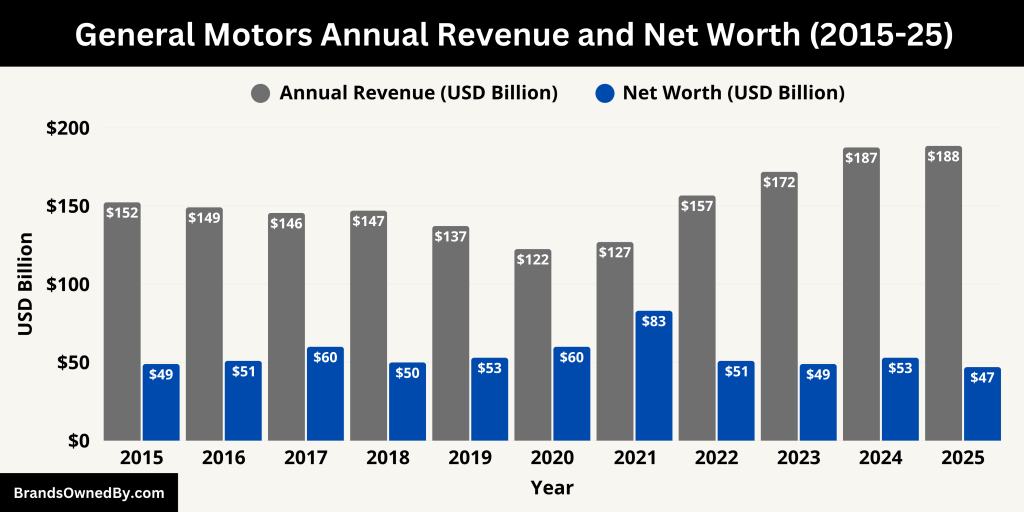
As of 2025, General Motors continues to demonstrate strong financial performance. In the first quarter of 2025 alone, the company generated approximately $44.02 billion in revenue, showing a 2.3% increase compared to the same period in 2024. Over the trailing twelve months ending March 31, 2025,
GM’s total revenue reached around $188.45 billion, reflecting nearly an 8% year-over-year growth. This upward trend is consistent with its recent performance. For the full calendar year 2024, GM reported $187.44 billion in revenue, up from $171.84 billion in 2023 and $156.74 billion in 2022.
These figures highlight the automaker’s recovery momentum and the growing contribution of electric vehicles, autonomous technology, and global market demand.
Net Worth and Market Capitalization in 2025
General Motors’ market capitalization in mid-2025 is estimated to be between $46.8 billion and $47.4 billion. This represents a moderate decline from 2024, when the company was valued at approximately $53–58 billion. The decline is attributed to broader market corrections, cost pressures, and global supply chain adjustments, despite consistent growth in revenue. GM’s market value continues to fluctuate based on investor sentiment, regulatory developments, and competition in the electric vehicle market.
Profitability and Net Income Forecast
GM reported a net income of about $6 billion for the fiscal year 2024. Looking ahead, the company’s 2025 forecast anticipates net earnings in the range of $11.2 billion to $12.5 billion, supported by rising electric vehicle sales, strong North American performance, and restructuring benefits. Adjusted EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes) is projected between $13.7 billion and $15.7 billion. This outlook reflects GM’s renewed focus on profitability and operating efficiency, particularly in the face of changing automotive industry dynamics.
Automotive Cash Flow and Capital Allocation
General Motors maintains a healthy cash flow position. In 2024, the company reported automotive operating cash flow of $23.9 billion, with $14 billion in free cash flow. For 2025, GM expects to generate between $21 billion and $24 billion in operating cash flow, and $11 billion to $13 billion in free cash flow. These figures underscore GM’s strong liquidity and ability to invest in technology, repay debt, and return value to shareholders.
Dividends and Share Buyback Strategy
In early 2025, General Motors increased its quarterly dividend by 25%, raising it to 15 cents per share, yielding roughly 1.2% annually. The company also approved a new $6 billion share repurchase program, in addition to more than $22 billion already returned to shareholders through buybacks since 2023. This capital return strategy signals GM’s confidence in its long-term financial position and its commitment to shareholder value, even as it invests aggressively in electric and autonomous vehicle development.
Overall Financial Health
General Motors remains one of the top revenue-generating automotive companies in the world. With nearly $188 billion in annual revenue and a market cap near $47 billion, GM is leveraging its scale, innovation pipeline, and strong North American presence to maintain its competitive edge. Despite market fluctuations, the company’s robust earnings forecast, capital efficiency, and steady cash generation position it well for sustained growth through 2025 and beyond.
Here’s an overview of the annual revenue and net worth of General Motors for the last 10 years:
| Year | Annual Revenue (USD) | Market Cap / Net Worth (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | $188.45 billion (est.) | $47 billion (mid-2025) |
| 2024 | $187.44 billion | $53–58 billion |
| 2023 | $171.84 billion | $49–52 billion |
| 2022 | $156.74 billion | $51–53 billion |
| 2021 | $127.00 billion | $83–85 billion |
| 2020 | $122.48 billion | $60–62 billion |
| 2019 | $137.24 billion | $53–55 billion |
| 2018 | $147.05 billion | $50–52 billion |
| 2017 | $145.59 billion | $60–63 billion |
| 2016 | $149.18 billion | $51–54 billion |
| 2015 | $152.36 billion | $49–51 billion |
Companies Owned by General Motors
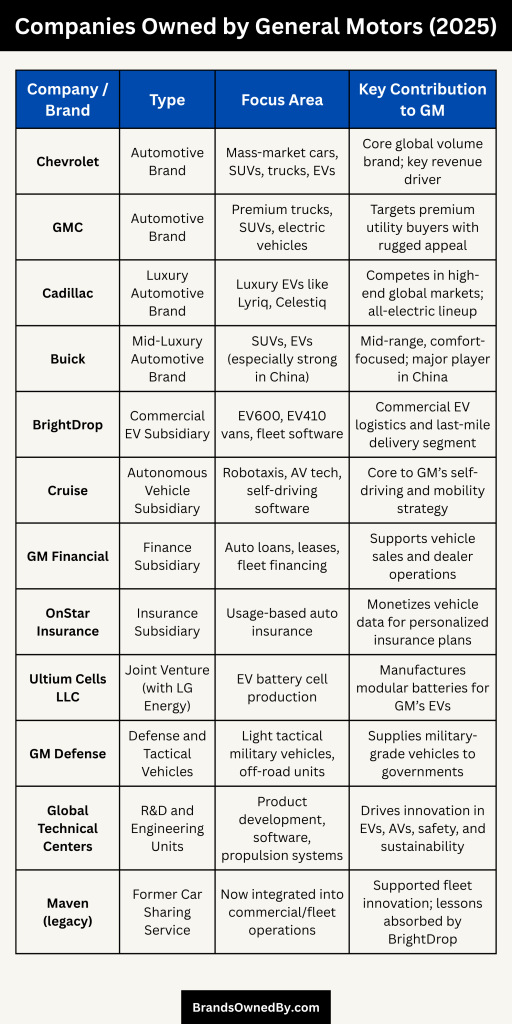
As of 2025, General Motors owns and operates a range of brands and business units. These are directly under GM’s control—not through any parent company. Here’s a detailed overview of the top companies and brands owned by General Motors:
| Company/Brand Name | Type | Focus Area/Products | Key Contribution to GM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chevrolet | Automotive Brand | Mass-market cars, SUVs, trucks, EVs | Core global volume brand; key revenue driver |
| GMC | Automotive Brand | Premium trucks, SUVs, electric vehicles | Targets premium utility buyers with rugged appeal |
| Cadillac | Luxury Automotive Brand | Luxury EVs like Lyriq, Celestiq | Competes in high-end global markets; all-electric lineup |
| Buick | Mid-Luxury Automotive Brand | SUVs, EVs (especially strong in China) | Mid-range, comfort-focused; major player in China |
| BrightDrop | Commercial EV Subsidiary | EV600, EV410 vans, fleet software | Commercial EV logistics and last-mile delivery segment |
| Cruise | Autonomous Vehicle Subsidiary | Robotaxis, AV tech, self-driving software | Core to GM’s self-driving and mobility strategy |
| GM Financial | Finance Subsidiary | Auto loans, leases, fleet financing | Supports vehicle sales and dealer operations |
| OnStar Insurance | Insurance Subsidiary | Usage-based auto insurance | Monetizes vehicle data for personalized insurance plans |
| Ultium Cells LLC | Joint Venture (with LG Energy) | EV battery cell production | Manufactures modular batteries for GM’s EVs |
| GM Defense | Defense and Tactical Vehicles | Light tactical military vehicles, off-road units | Supplies military-grade vehicles to governments |
| Global Technical Centers | R&D and Engineering Units | Product development, software, propulsion systems | Drives innovation in EVs, AVs, safety, and sustainability |
| Maven (legacy) | Former Car Sharing Service | Now integrated into commercial/fleet operations | Supported fleet innovation; lessons absorbed by BrightDrop |
Chevrolet
Chevrolet is GM’s flagship mass-market brand. It spans a wide vehicle lineup including compact cars (Cruze), sedans (Malibu), SUVs (Equinox, Traverse), pickup trucks (Silverado), and electric vehicles (Bolt EV, Silverado EV).
Chevrolet is known for blending affordability with performance. Its SUVs and trucks are core to GM’s revenue in North America. Strong brand loyalty, extensive dealer network, and investments in new EV models like the Blazer EV and Equinox EV keep Chevrolet at the front of GM’s portfolio.
GMC
GMC focuses on rugged, premium trucks and SUVs. Its notable models include the Sierra pickup, Yukon SUV, and the reintroduced Hummer EV. GMC positions itself as a step above Chevrolet in terms of luxury and capability. With an emphasis on rough-terrain readiness and sleek design, GMC appeals to both commercial and affluent personal buyers. Its EV rollout via Hummer EV and upcoming Denali EV models highlights GM’s electric strategy within GMC.
Cadillac
Cadillac is GM’s luxury brand, competing with international premium players. By 2025, Cadillac has fully embraced electrification. The Lyriq SUV and Celestiq flagship sedan showcase GM’s technological and EV capabilities. Cadillac emphasizes design, advanced connectivity, and premium craftsmanship. Its North American showrooms and marketing focus on delivering luxury fused with cutting-edge innovation.
Buick
Buick serves the mid-luxury crossover and sedan market. It remains highly popular in China, where it outsells many competitors. Current offerings include the Enclave and Encore crossovers, along with the Electra EV series. Buick emphasizes comfort, quiet rides, and refined interiors. Its EV portfolio caters to both U.S. and Chinese markets, making it a bridge between mainstream appeal and luxury performance.
BrightDrop
BrightDrop is GM’s electric commercial vehicle and fleet solutions division. It designs and delivers zero-emission delivery vans (EV600 and EV410) to major logistics clients. BrightDrop also offers telematics and fleet management software. By 2025, it has signed contracts with large delivery companies and government fleets. BrightDrop is central to GM’s strategy to electrify urban and commercial transportation.
Cruise
Cruise is GM’s subsidiary dedicated to autonomous vehicle (AV) development. It builds and deploys self-driving ride-hailing shuttles in U.S. cities. Backed by investments from GM, Honda, and Microsoft, Cruise operates a growing autonomous fleet. In 2025, it began limited commercial AV services in cities including San Francisco. The company focuses on safety, software, and regulatory compliance to scale AV mobility.
GM Financial
GM Financial is GM’s captive financing arm. It provides retail and commercial auto loans and leases. GM Financial supports dealership financing programs globally. With growing electric and autonomous vehicle sales, it has introduced EV-specific financing offers. It also services and securitizes vehicle loans, contributing a steady earnings stream for GM’s overall financial stability.
OnStar Insurance
OnStar Insurance is a newer venture that offers usage-based auto insurance, leveraging vehicle telematics and data to tailor personalized insurance policies. This service is integrated with the OnStar connectivity platform and GM’s broader data ecosystem.
Ultium Cells LLC
Ultium Cells is a joint battery manufacturing venture formed by GM and LG Energy Solution. By 2025, Ultium operates multiple gigafactories in North America. It produces modular battery packs for GM’s electric vehicle lineup and may also supply battery cells to external partners.
Maven (Legacy)
Though Maven’s consumer-focused car-sharing service was wound down earlier in the decade, its technology and fleet expertise were absorbed into GM’s urban mobility and fleet rental operations. Components of its platform help support BrightDrop and fleet subscription services.
GM Cruise Origin (Discontinued)
Originally developed within Cruise, the Cruise Origin was a purpose-built driverless shuttle. The program has since been discontinued, though its R&D insights continue to inform Cruise’s vehicle and software development efforts.
GM Defense
GM Defense is a division that designs and manufactures light tactical vehicles for the U.S. armed forces and allied militaries. Its armored vehicles and support platforms combine standard GM vehicle components with defense-grade systems for government procurement.
AeroVironment (Joint Projects)
While GM does not own AeroVironment, it partners with the company on drone-based delivery trials linked to BrightDrop. These collaborative projects support integrated urban logistics, though GM does not hold equity in AeroVironment.
Global Technical Center and R&D Labs
GM’s global technical centers—located in Michigan, Germany, China, and other innovation hubs—drive advanced engineering work. These include research on next-gen propulsion, autonomous systems, software integration, and materials science. These internal entities underpin new vehicle programs and technology roadmaps.
Conclusion
General Motors is a publicly traded automotive giant with diversified ownership. The question of who owns General Motors does not have a single answer. Its shares are held by a mix of institutional investors, individuals, and company insiders. The company continues to evolve under Mary Barra’s leadership and is investing heavily in electric and autonomous technologies. With a rich history and a forward-looking strategy, GM remains a key player in the global auto market.
FAQs
Who is the current owner of General Motors?
General Motors is a publicly traded company. It does not have a single owner. Its ownership is divided among institutional investors, individual shareholders, and insiders. The largest shareholder is currently The Vanguard Group, followed by BlackRock, and State Street. These are large asset management firms that hold shares on behalf of their clients.
Is GM still an American company?
Yes, General Motors is still an American company. It is headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, and is incorporated in the United States. While it operates globally and has international shareholders, its management, strategic decisions, and core operations are all U.S.-based.
Who owns most of GM?
As of 2025, the largest shareholders in GM are institutional investors. The Vanguard Group owns the most shares, holding over 9% of GM’s total outstanding stock. BlackRock and State Street also hold significant stakes, each owning around 6–8%. No single individual or company owns a controlling share of GM.
Is General Motors American or German?
General Motors is American, not German. It was founded in Michigan, USA, and has remained a U.S.-based company throughout its history. German automakers like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Volkswagen are separate entities and not affiliated with GM.
What country owns General Motors?
No country owns General Motors. It is owned by public shareholders worldwide. However, it is legally and operationally an American company, with its incorporation, headquarters, and board of directors based in the United States.
Who founded General Motors?
General Motors was founded by William C. Durant in 1908. Durant was a leading figure in the early American automotive industry and played a key role in assembling multiple car manufacturers under one corporate structure, which eventually became GM.
Is GM Chinese-owned?
No, General Motors is not Chinese owned. While it operates in China through joint ventures (such as SAIC-GM), the company itself is not owned by any Chinese firm or government. Its majority shareholders are U.S.-based institutional investors.
Does the US government still own GM?
No, the U.S. government sold its remaining GM shares in 2013 after the bailout during the 2009 financial crisis.
Is General Motors a private or public company?
GM is a public company listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker GM.
What happened to Pontiac and Saturn?
These brands were discontinued during GM’s restructuring in 2009 to focus on core operations.
Does GM still own Opel and Vauxhall?
No, GM sold both Opel and Vauxhall to the PSA Group (now part of Stellantis) in 2017.
What brands does General Motors own in 2025?
As of 2025, GM owns Chevrolet, Cadillac, GMC, Buick, BrightDrop, Cruise, and GM Financial.
Who is the largest shareholder of General Motors?
The Vanguard Group is the largest single shareholder, owning about 8.7% of the company.
How much revenue does GM make annually?
General Motors generates around $168 billion in annual revenue as of 2025.

