Porsche, a legendary name in the automotive industry, is known for its luxurious sports cars and high-performance vehicles. If you’ve ever wondered, “who owns Porsche?”, this article will provide detailed insights into the ownership, financials, and key figures behind the iconic brand.
History of Porsche

Porsche’s history is rich with innovation and a focus on precision engineering, evolving from a small design office to one of the most iconic names in the automotive world. The company’s journey can be broken down into significant milestones year by year.
1931 – The Beginning
Porsche was founded in 1931 by Ferdinand Porsche in Stuttgart, Germany. The company was initially a design and consulting firm, known as Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche GmbH. The firm’s first major project was to design the “Volkswagen” (the people’s car), which was commissioned by Adolf Hitler, laying the groundwork for the future relationship between Porsche and Volkswagen.
1948 – The First Porsche Car
After World War II, Porsche’s son, Ferry Porsche, set out to create a car under the Porsche name. The result was the Porsche 356, the first car designed and built by the company. The 356 became an immediate success, marking the start of Porsche’s journey as a manufacturer of high-performance cars. It was initially built by an Austrian company, Reutter Karosserie, before being moved to Zuffenhausen, Germany, where Porsche’s headquarters is located.
1951 – Entry into Motorsports
Porsche’s involvement in motorsport began with the Porsche 356’s success in various races, solidifying the brand’s reputation for high-performance engineering. This was a pivotal move for Porsche, as motorsport became an integral part of its identity.
1963 – Introduction of the Iconic Porsche 911
One of the most significant moments in Porsche’s history came with the launch of the Porsche 911 in 1963. Designed by Ferdinand “Butzi” Porsche, the 911 became synonymous with Porsche’s brand identity. Its unique design and engineering innovations, including its rear-engine layout, helped make it a performance icon. The 911 is still in production today, continuously evolving while retaining the core features that made it a legend.
1972 – Establishment of Porsche AG
In 1972, Porsche became Porsche AG, a public company listed on the German stock exchange. The company had grown significantly by this time, and the shift to a public company allowed for broader investment and expansion. This was also the year Porsche introduced its first production sports car with a turbocharged engine, the Porsche 911 Turbo.
1984 – The Porsche 911 Carrera 3.2
Porsche continued to refine the 911 with the release of the 911 Carrera 3.2 in 1984. This model introduced a more powerful 3.2-liter engine and several performance improvements that solidified the 911’s reputation as a true driver’s car. Porsche’s focus on quality and engineering excellence was now more apparent than ever.
1990s – Expansion and New Models
During the 1990s, Porsche introduced a series of new models. In 1995, Porsche released the Porsche Boxster, a mid-engine sports car that became an instant success. The Boxster’s success helped Porsche navigate through a financially turbulent period. Additionally, the Porsche 911 underwent several redesigns to keep the car relevant to the changing demands of the luxury sports car market.
2002 – The Launch of Porsche Cayenne
In 2002, Porsche made its foray into the luxury SUV market with the introduction of the Porsche Cayenne. Initially met with skepticism by purists, the Cayenne became a massive success and significantly boosted Porsche’s financial performance. The SUV, built in collaboration with Volkswagen, showcased Porsche’s ability to innovate beyond sports cars and tap into new market segments.
2009 – Financial Crisis and Porsche’s Takeover of Volkswagen
Amid the global financial crisis, Porsche faced significant financial struggles. However, the company made a bold move by attempting to take over Volkswagen, a process that ultimately reversed roles. By 2009, Volkswagen became the majority shareholder in Porsche, after Porsche’s failed attempt to acquire a controlling interest in Volkswagen. The merger led to a closer relationship between the two companies.
2012 – Launch of Porsche 918 Spyder
Porsche unveiled the 918 Spyder in 2012, a hybrid supercar that combined cutting-edge technology with Porsche’s high-performance standards. The 918 Spyder was notable for its hybrid powertrain, blending electric motors with a V8 engine to achieve incredible acceleration while maintaining fuel efficiency. This model also highlighted Porsche’s future direction towards sustainable mobility.
2015 – Introduction of the Porsche Mission E
In 2015, Porsche announced its entry into the electric vehicle market with the Mission E concept, which would later become the Porsche Taycan. This marked Porsche’s commitment to sustainability while preserving its high-performance DNA. The Mission E concept indicated the company’s focus on electric mobility as a key component of its future.
2019 – The Launch of the Porsche Taycan
The Porsche Taycan, the first fully electric sports car from Porsche, was launched in 2019. The Taycan was a major milestone for the company, proving that a brand built on high-performance, internal combustion engines could transition to electric vehicles without compromising on performance. The Taycan has been praised for its acceleration, handling, and luxury features, further cementing Porsche’s position in the electric vehicle market.
2021 – Porsche’s IPO Plans
In 2021, Porsche’s parent company, Volkswagen Group, revealed plans to list Porsche on the stock exchange through an initial public offering (IPO). This potential IPO would further separate the two companies but would still maintain close ties between Porsche and Volkswagen, with both benefiting from the shared technological expertise and global reach.
2022 – Porsche’s Shift to Electric and Sustainable Mobility
Porsche began focusing even more on sustainability and electric mobility, increasing its investments in electric vehicles and sustainable production methods. The launch of the Taycan marked the start of a new era, but by 2022, Porsche had committed to making its entire lineup electric by 2030. This move aligns with global trends towards sustainability, positioning Porsche as a future-forward brand in a rapidly changing automotive landscape.
2023 – Continued Success and Growth
As of 2023, Porsche continues to thrive in the luxury sports car market, maintaining its reputation for producing high-performance vehicles while expanding its electric vehicle offerings. The company is committed to becoming a leader in sustainable automotive innovation, blending high-performance with ecological responsibility.
Who Owns Porsche: Major Shareholders
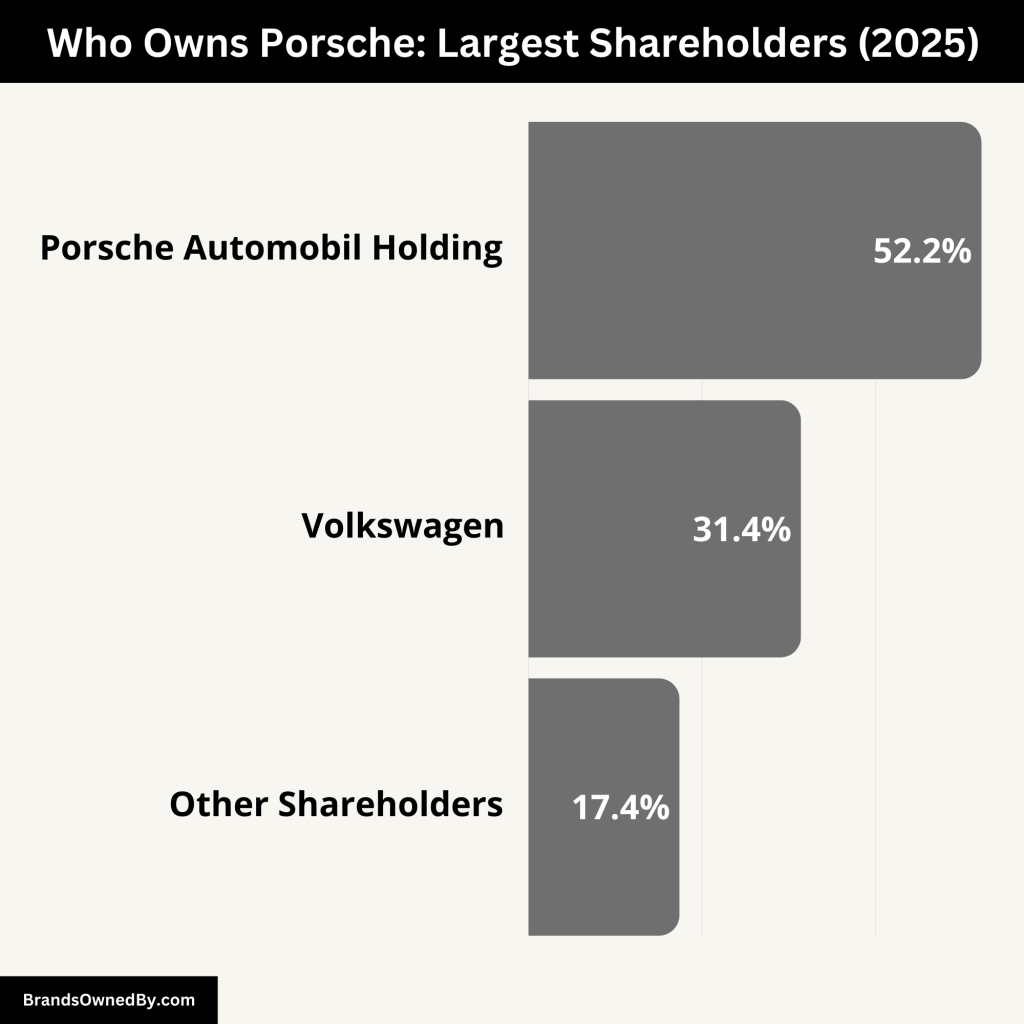
Porsche’s ownership structure is a unique blend of family-controlled entities, institutional investors, and public shareholders. Each shareholder plays a significant role in shaping the company’s strategy and governance. Here’s an in-depth look at the major shareholders, their ownership percentages, and their influence on Porsche’s operations.
Here’s an overview of the major shareholders of Porsche:
| Shareholder | Ownership % | Type | Role & Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porsche Automobil Holding SE | 52.2% (voting rights) | Family-controlled entity | Largest shareholder; controlled by Porsche and Piëch families; full voting control. |
| Volkswagen AG | 31.4% (common shares) | Automotive group | Significant shareholder; financial partner; no controlling rights. |
| Porsche & Piëch Families | Indirect via Porsche SE | Founding families | Ultimate controllers of Porsche through Porsche SE; strong influence on governance. |
| Institutional & Public Shareholders | 17.4% (common shares) | Institutional & retail | Includes mutual funds, pension funds, asset managers, etc.; provide capital and voting on financial matters; no operational control. |
| Government Entities | Small % indirectly | Public investment funds | Passive ownership through pension and sovereign wealth funds; no management role. |
| Porsche Employees | Very small % | Internal shareholders | Own shares via stock options; symbolic ownership; limited influence. |
Porsche Automobil Holding SE (52.2% of voting shares)
Porsche Automobil Holding SE is the largest shareholder of Porsche AG, holding 52.2% of the voting shares. This holding company is controlled by the Porsche and Piëch families, who are descendants of Ferdinand Porsche, the founder of the company.
The Porsche family controls the majority of voting rights through this holding company, enabling them to influence key decisions at Porsche AG. With this significant voting power, the family can determine the company’s direction and governance, ensuring that Porsche remains aligned with their values and objectives. Despite Porsche Automobil Holding SE being a separate entity, it provides the Porsche family with a firm grip on Porsche’s operations and future strategies.
Volkswagen Group (31.4% of common shares)
Volkswagen Group holds 31.4% of Porsche’s common shares, making it the second-largest shareholder. While Volkswagen’s stake is substantial, it does not provide the group with majority control, as the Porsche family retains the majority of voting rights through Porsche Automobil Holding SE.
Volkswagen’s significant shareholding creates a close strategic and financial relationship between the two companies, and their shared technological innovations, manufacturing partnerships, and market synergies benefit both parties. However, Volkswagen’s role is more focused on financial influence, rather than direct control over Porsche’s operations.
The Porsche and Piëch Families
Although the precise breakdown of the Porsche and Piëch families’ direct shares in Porsche Automobil Holding SE is not public, they control the majority of the voting shares within Porsche Automobil Holding SE. As a result, the families exert substantial influence over Porsche’s operations. The Porsche and Piëch families have maintained control over the company since its inception, and they continue to shape its strategic direction through their ownership of Porsche SE.
Their influence extends not only to Porsche AG but also to the broader Volkswagen Group, where they hold a significant position in corporate governance. The families have played an integral role in shaping Porsche’s legacy, ensuring the company’s focus on performance, luxury, and innovation remains intact.
Institutional Investors and Public Shareholders (17.4% of shares)
Institutional investors and public shareholders own the remaining 17.4% of Porsche’s stock. These include large institutional investors such as mutual funds, pension funds, and hedge funds. Though their stakes are smaller, their collective ownership can still have a financial impact on the company, particularly in terms of stock prices and market sentiment.
While these shareholders do not hold voting power over major corporate decisions, their influence is mostly limited to financial matters, such as shareholder meetings, stock price fluctuations, and capital raising efforts. Institutional investors may also play a role in influencing corporate governance indirectly through shareholder proposals or public activism, although they have minimal control over day-to-day operations.
Government Entities
Though Porsche is primarily owned by private shareholders, some government-related entities may hold small portions of Porsche stock through various investment vehicles. These holdings are usually indirect and do not significantly influence the company’s operations. Public investment funds or government pension funds from Germany and abroad might own shares as part of their broader portfolio.
However, government entities do not have any direct control over Porsche’s decisions. Their role is purely as passive investors, with no involvement in the management or strategy of the company.
Porsche Employees (via Stock Options and Employee Shares)
Porsche also offers stock options and employee share programs, allowing employees to purchase shares or receive them as part of their compensation. These shares, however, make up a very small portion of the overall ownership structure and do not grant employees any meaningful control over the company’s decisions.
Employee shareholders benefit from Porsche’s financial success, but they don’t influence major corporate actions or governance. Their stake in the company aligns them with the brand’s success, although their ownership is more symbolic than impactful in the larger shareholder structure.
Who Controls Porsche?
While Porsche AG is a publicly traded company, control over its strategic direction and key decisions lies primarily with the Porsche and Piëch families, through Porsche Automobil Holding SE. Operational control, however, is exercised by Porsche’s executive leadership team, led by its CEO. Below is a detailed breakdown of how control is distributed across the company.
Control Through Porsche Automobil Holding SE
Porsche Automobil Holding SE holds 52.2% of Porsche AG’s voting rights, making it the most powerful entity in the company’s governance structure. This holding company is itself controlled by the Porsche and Piëch families, who are direct descendants of Ferdinand Porsche, the company’s founder.
Even though Porsche AG is listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange, the majority of voting power rests with Porsche SE. This means that the families behind Porsche SE have the final say in all major decisions, such as the appointment of board members, corporate strategy, long-term investments, and acquisitions. Their influence ensures that Porsche maintains its brand heritage, core identity, and long-term vision without external pressure from short-term investors.
The Porsche and Piëch families exercise their control by holding the majority of voting shares in Porsche SE, allowing them to appoint representatives to Porsche AG’s supervisory board and shape executive leadership decisions.
Supervisory Board Oversight
Porsche AG follows the dual-board structure typical in German corporations. This includes a Supervisory Board and an Executive Board.
The Supervisory Board monitors the Executive Board and makes high-level decisions, such as approving major business plans and strategic changes. A majority of the Supervisory Board members are aligned with the Porsche and Piëch families, either directly or indirectly through Porsche SE. Other members include representatives from labor unions and shareholders like Volkswagen.
This board plays a crucial role in appointing or removing the CEO and other executive members. Thus, while Porsche AG operates independently, its top-level strategy is shaped by the Supervisory Board under strong family influence.
Executive Board and CEO
Day-to-day control of Porsche AG is handled by the Executive Board, which is responsible for operations, product development, global strategy, finance, and marketing.
CEO: Oliver Blume
As of 2025, Oliver Blume serves as the Chairman of the Executive Board (CEO) of Porsche AG. He was appointed CEO in 2015 and continues to lead the company through its transformation into an electric and digitally advanced luxury car brand.
Blume is known for his engineering background and his clear vision of blending Porsche’s sports car legacy with modern sustainability. Under his leadership, Porsche has made major investments in electrification, including the launch of the Taycan and the upcoming electric Macan.
He is also the CEO of Volkswagen Group, a rare dual role that further ties the strategic directions of both automotive giants. His unique position allows for synergies in technology, supply chain, and innovation between the Porsche and Volkswagen brands.
Labor Representation
Porsche’s Supervisory Board also includes labor representatives, which is a legal requirement in Germany under the co-determination model (Mitbestimmung). These representatives protect the interests of employees and ensure decisions align with workforce welfare and long-term employment stability.
Though they don’t hold majority control, labor representatives influence decisions related to working conditions, factory expansions, and corporate social responsibility.
Shareholder Voting Rights
While institutional and public shareholders own 17.4% of Porsche’s common shares, they have limited control. Their influence is primarily exercised through shareholder meetings and voting on resolutions. However, due to the controlling interest held by Porsche SE, their impact is minimal when it comes to strategic or governance decisions.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Porsche
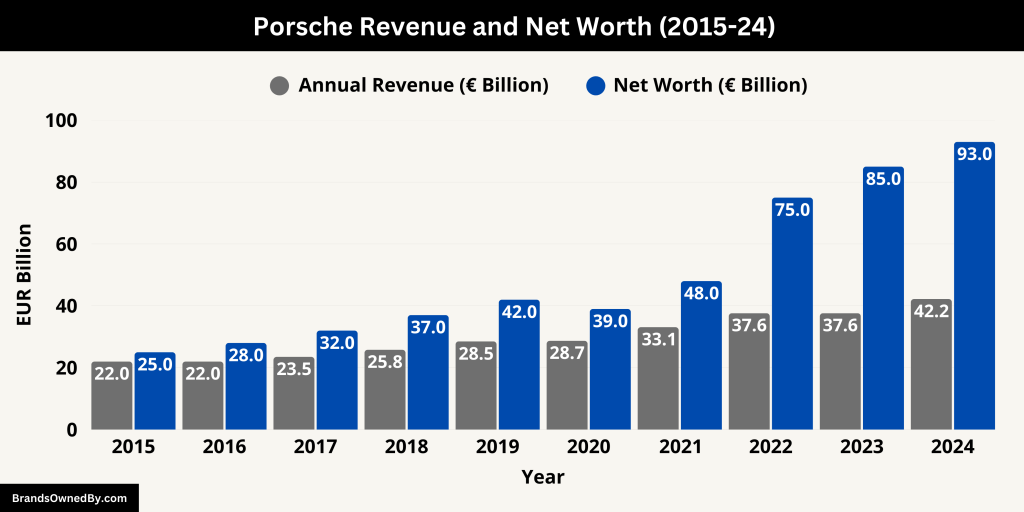
In the fiscal year 2024, Porsche AG reported record-breaking revenue of €42.2 billion, up from €37.6 billion in 2023. This growth was driven by strong global demand for the Porsche 911, Cayenne, and the fully electric Taycan. The company’s expansion into electric mobility, along with a premium pricing strategy and strong sales in the U.S. and China, contributed significantly to its top-line growth.
In 2024, Porsche also expanded its production capacity and introduced digital services linked to vehicle software, which created new recurring revenue streams. Despite inflationary pressures and supply chain issues, Porsche maintained an impressive operating return on sales of 18%, one of the highest margins in the automotive sector.
As of April 2025, Porsche AG’s market capitalization (net worth) is estimated at around €98 billion. This valuation places it among the most valuable car manufacturers in the world, ahead of some traditional giants, and behind only a few high-growth companies in the electric vehicle space, like Tesla.
The net worth reflects strong investor confidence, driven by Porsche’s luxury positioning, successful transition into EVs, and its independence as a listed entity since its IPO in 2022. Analysts continue to view Porsche as a premium stock with long-term growth potential due to its strategic focus on electrification, innovation, and brand loyalty.
The historical revenue and net worth of Porsche are covered below:
| Year | Annual Revenue (€ Billion) | Estimated Net Worth (€ Billion) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 21.5 | 25.0 | Strong sales of Cayenne and Macan. |
| 2016 | 22.3 | 28.0 | Growth driven by China and U.S. markets. |
| 2017 | 23.5 | 32.0 | Stable growth; increasing SUV demand. |
| 2018 | 25.8 | 37.0 | Continued SUV growth; early EV R&D. |
| 2019 | 28.5 | 42.0 | Launch of Porsche Taycan (EV). |
| 2020 | 28.7 | 39.0 | COVID-19 impact balanced by luxury demand. |
| 2021 | 33.1 | 48.0 | Strong post-pandemic recovery. |
| 2022 | 37.6 | 75.0 | Porsche AG IPO boosts valuation. |
| 2023 | 37.6 | 85.0 | Consistent financials; growing EV adoption. |
| 2024 | 42.2 | 93.0 | Record revenue; expansion in EV and digital tech. |
Brands and Companies Owned by Porsche
Porsche AG owns and operates several subsidiaries, brands, and joint ventures across automotive production, engineering, motorsports, and digital services. These companies support its innovation, technology development, and global expansion.
Below is a detailed look at each major entity owned or controlled by Porsche AG:
| Company / Division | Porsche AG Ownership | Function / Description |
|---|---|---|
| Porsche Engineering Group GmbH | 100% | Engineering services, vehicle development, powertrain and autonomous systems. |
| Porsche Design Group (Lifestyle) | 100% | Luxury lifestyle brand for fashion, watches, eyewear, and electronics. |
| MHP – A Porsche Company | ~81.8% | Management and IT consulting, especially for the automotive and manufacturing sectors. |
| Porsche Digital GmbH | 100% | Digital innovation, software development, mobility platforms, and startup incubation. |
| Porsche eBike Performance GmbH | 100% | Electric bike systems and performance eBike manufacturing. |
| Porsche Motorsport Division | Internal Division | Motorsport operations including Formula E and endurance racing. |
| Porsche Financial Services GmbH | 100% | Vehicle financing, leasing, and insurance services. |
| Porsche Ventures | 100% | Venture capital arm investing in future mobility and tech startups. |
| Fazua GmbH (via eBike division) | ~100% | High-end eBike drive system manufacturer, acquired by Porsche. |
| Rimac Group | ~20.4% | Minority stake; EV hypercar and battery tech company; strategic partner. |
| Bugatti Rimac (via Rimac Group) | Indirect Influence | Porsche indirectly influences Bugatti Rimac through its stake in Rimac Group. |
Porsche Engineering Group GmbH
Porsche Engineering is a fully owned subsidiary of Porsche AG. It provides engineering services to automotive and industrial clients worldwide. Originally founded in 1931 by Ferdinand Porsche, the group was restructured under Porsche AG and now works on:
- Vehicle development
- Software integration
- Powertrain and chassis systems
- Autonomous driving technologies
It has facilities in Germany, Italy, the Czech Republic, and China, helping other brands (including Volkswagen Group) innovate while maintaining Porsche’s engineering excellence.
Porsche Design Group (Porsche Lifestyle GmbH & Co. KG)
Porsche Design is the luxury lifestyle and accessories brand of Porsche AG. It was established in 1972 by Ferdinand Alexander Porsche, the designer of the original 911. The company offers:
- High-end watches, eyewear, and fashion
- Travel gear and electronics
- Collaborations with brands like Huawei, Adidas, and LaCie
Although independent in branding, it is wholly owned by Porsche AG and reinforces Porsche’s image in the premium consumer space.
MHP – A Porsche Company
MHP (Management- und IT-Beratung GmbH) is a management and IT consulting firm that is majority-owned by Porsche AG. It specializes in digital transformation within the automotive and manufacturing industries. With more than 4,000 employees globally, MHP plays a key role in Porsche’s internal operations, optimizing:
- IT architecture
- Supply chain systems
- Smart manufacturing and AI integration
- Digital customer platforms
MHP’s services also extend to Volkswagen brands and other external clients.
Porsche Digital GmbH
Porsche Digital is Porsche AG’s innovation and venture arm, focused on building the future of mobility and customer experience through digital platforms. It develops:
- Connected car services
- In-car software ecosystems
- Subscription-based digital services
- Smart mobility solutions
It also invests in startups and tech ventures, making Porsche a player in the digital and mobility-as-a-service space.
Porsche eBike Performance GmbH
As part of Porsche’s sustainability and mobility strategy, this subsidiary focuses on electric bicycle technology and production. It includes:
- Drive systems for eBikes
- High-performance eBike models under the Porsche brand
- Partnerships with companies like Fazua (in which Porsche holds a majority stake)
The eBike division is growing fast, targeting both urban commuters and premium biking enthusiasts.
Porsche Motorsport
Although not a separate company, Porsche Motorsport is a dedicated division that handles all of Porsche’s racing activities. This includes:
- Formula E team operations
- FIA WEC (World Endurance Championship) and Le Mans participation
- Customer racing programs for GT3 and GT4 series
- Development of track-only hypercars like the 911 GT2 RS Clubsport
Porsche Motorsport serves as a testing ground for high-performance technology that often trickles down to consumer vehicles.
Porsche Financial Services
Porsche AG also operates its own financial arm through Porsche Financial Services GmbH, offering:
- Vehicle financing and leasing
- Insurance and fleet services
- Customer loyalty programs
This division ensures that customers receive a seamless Porsche ownership experience from purchase to after-sales.
Porsche Ventures
Porsche Ventures is Porsche’s venture capital arm. It invests in innovative startups and mobility companies that align with Porsche’s future direction. Portfolio companies include:
- Rimac Automobili (electric hypercars)
- Urgently (mobility and roadside assistance tech)
- Holoride (in-car VR entertainment)
- Glydways (urban micromobility infrastructure)
Porsche Ventures strengthens the company’s ecosystem and keeps it aligned with future mobility trends.
Stake in Rimac Group
Porsche owns a significant minority stake (over 20%) in Rimac Group, a Croatian electric vehicle and battery technology firm. Rimac is best known for the Rimac Nevera, a fully electric hypercar. Porsche’s partnership with Rimac allows access to high-performance battery systems and powertrain innovations.
Rimac has also taken over Bugatti through the Bugatti Rimac joint venture (Porsche holds indirect influence via its Rimac stake and Volkswagen ties).
Conclusion
Porsche’s ownership structure is dominated by the Porsche and Piëch families through Porsche Automobil Holding SE. While Volkswagen Group holds a significant share, the Porsche family retains control over key decisions, maintaining the brand’s legacy and ensuring its strategic direction. Porsche’s financial success and control over several key brands solidify its status as one of the world’s most respected and valuable automotive companies.
FAQs
Who owns Porsche today?
Porsche is primarily owned by Porsche Automobil Holding SE, which is controlled by the Porsche and Piëch families. Volkswagen Group also holds a significant stake in the company.
Does Volkswagen own Porsche?
Yes, Volkswagen owns a substantial portion of Porsche, but it is the Porsche family through Porsche SE that maintains control over the brand.
Is Porsche a family-owned company?
Yes, Porsche is largely family-owned, with the Porsche and Piëch families controlling Porsche Automobil Holding SE, which holds a majority of voting shares in the company.
Who is the real owner of Porsche?
The real owner of Porsche AG is Porsche Automobil Holding SE, which holds 52.2% of Porsche AG’s voting rights. Porsche SE is controlled by the Porsche and Piëch families, descendants of company founder Ferdinand Porsche.
Does VW own 100% of Porsche?
No, Volkswagen does not own 100% of Porsche AG. It owns 75% of the non-voting preferred shares (equal to a 31.9% equity stake). The majority of voting control lies with Porsche SE, not Volkswagen.
Who is the major shareholder of Porsche?
The major shareholder of Porsche AG is Porsche Automobil Holding SE, owning 52.2% of voting shares, giving it majority control of the company.
Who is the CEO of Porsche?
As of 2025, the CEO of Porsche AG is Oliver Blume. He also serves as CEO of Volkswagen Group, making him one of the most influential executives in the automotive industry.
How rich is the Porsche family?
The Porsche and Piëch families have a combined net worth of over $40 billion, primarily through their controlling stake in Porsche SE and investments in Volkswagen Group. They are among the wealthiest families in Europe.
Is Porsche bigger than Volkswagen?
No, Volkswagen Group is much larger than Porsche AG. VW owns multiple brands, including Audi, Lamborghini, Bentley, and Skoda. Porsche is one of VW Group’s most profitable brands, but not larger in size or revenue.
Who invented Porsche?
Ferdinand Porsche, an Austrian engineer, invented the first car under the Porsche name in 1931 and later developed the iconic Volkswagen Beetle and Porsche 356.
Does Bill Gates own Porsche?
No, Bill Gates does not own Porsche. However, he has reportedly owned Porsche cars, including a rare Porsche 959, but he has no business or investment stake in the company.
Porsche is owned by which country?
Porsche is a German company. It was founded in Germany and is headquartered in Stuttgart, operating under German corporate laws.
Does Porsche own Volkswagen?
No, Porsche does not own Volkswagen. In fact, Volkswagen Group owns a large portion of Porsche’s non-voting shares, and the two companies are closely linked through their shared history and family ownership.
What celebrities own Porsche?
Many celebrities own Porsche cars, including:
- Jerry Seinfeld – owns over 40 Porsche models
- Ellen DeGeneres – owns a Porsche 911
- Patrick Dempsey – races Porsches professionally
- Kendall Jenner – owns a classic Porsche 356
- LeBron James – reportedly owns a Porsche 911 Turbo S
Where was Porsche founded?
Porsche was founded in Stuttgart, Germany in 1931 by Ferdinand Porsche as an engineering consultancy.
Who manufactures Porsche cars?
Porsche cars are manufactured by Porsche AG, with main production facilities in Zuffenhausen (Stuttgart) and Leipzig, Germany.
Who owns Porsche Piëch family?
The Piëch family, together with the Porsche family, owns 100% of Porsche Automobil Holding SE, which controls a majority of voting shares in Porsche AG. They are indirect owners of the company through this holding structure.
Where did Porsche originate?
Porsche originated in Germany. It began as a design and engineering consultancy in Stuttgart before producing its own cars in the late 1940s.
When did Volkswagen buy Porsche?
Volkswagen began acquiring Porsche in stages starting in 2009, and by 2012, it acquired 100% of Porsche’s automotive business. However, after Porsche AG’s IPO in 2022, ownership shifted, and now Porsche SE (not VW) holds majority control.
What is the net worth of Porsche?
As of 2025, Porsche AG has an estimated net worth (market capitalization) of €98 billion, placing it among the most valuable automotive brands in the world.

