PayPal is one of the most recognized digital payment platforms in the world. Millions use it daily to send and receive money securely. But many still ask, who owns PayPal? The answer is layered and involves public ownership, large institutional investors, and a long corporate history.
History of PayPal
PayPal started in 1998 as Confinity, a software security company founded by Max Levchin, Peter Thiel, and Luke Nosek.
Early Foundations: Confinity and X.com
PayPal was born from two separate startups. In December 1998, Max Levchin, Peter Thiel, and Luke Nosek founded Confinity. It started as a company focused on cryptography and security software for handheld devices. Soon, it shifted toward digital payments, allowing users to beam money between PalmPilots and later via email.
Around the same time, Elon Musk launched X.com in 1999. It was an ambitious online banking platform. Musk saw potential in offering financial services entirely online, without brick-and-mortar branches.
The Merger That Created PayPal
In March 2000, Confinity and X.com merged. This move was driven by competition and a shared vision of digital finance. Elon Musk initially led the combined entity. However, there were internal conflicts over technical decisions, particularly over the platform’s code base. Musk favored Microsoft-based technology, while the Confinity team preferred Unix-based systems.
By late 2000, Musk was replaced by Peter Thiel as CEO. The company soon rebranded as PayPal, focusing solely on online payments rather than broader financial services.
PayPal Goes Public
PayPal’s business grew rapidly by partnering with eBay sellers. It became the dominant payment method on eBay, outpacing rivals like Billpoint. In February 2002, PayPal held its initial public offering (IPO) and traded under the ticker symbol PYPL. The IPO was a success, raising over $60 million and valuing the company at around $1.2 billion.
Acquisition by eBay
Only a few months after the IPO, eBay acquired PayPal in July 2002 for $1.5 billion in stock. PayPal became the default payment method for eBay transactions, replacing its own system, Billpoint. This partnership helped PayPal grow rapidly, especially in peer-to-peer and small business transactions.
Spinning Off into Independence
In 2015, after more than a decade as a subsidiary, eBay spun off PayPal into a separate public company. The split allowed both companies to pursue independent strategies. PayPal could now expand into broader areas of e-commerce, mobile payments, and international markets without being tied to eBay.
PayPal resumed trading on NASDAQ under the original ticker PYPL. Dan Schulman became the CEO, leading PayPal into a new era of acquisitions, product innovation, and digital finance leadership.
A Fintech Powerhouse
Since its independence, PayPal has acquired key companies like Braintree, Venmo, Xoom, Honey, and Paidy. These moves helped PayPal expand into peer-to-peer payments, international remittances, mobile commerce, and “buy now, pay later” services.
Today, PayPal serves over 430 million active accounts across more than 200 markets. Its rise from a startup to a global payment network is one of the most influential stories in tech and finance.
PayPal Company Profile
PayPal Holdings, Inc. is a global digital payments platform that enables consumers and merchants to send, receive, and hold funds securely. Headquartered in San Jose, California, PayPal operates in over 200 markets and supports payments in more than 25 currencies. As of 2025, it serves over 430 million active accounts, including both individuals and merchants.
PayPal’s business model is built around online payment processing, peer-to-peer transfers, mobile payments, and financial services for small to medium-sized businesses. It also offers credit solutions, fraud management, and checkout services that are integrated into e-commerce websites and mobile apps.
Founders and Early History
PayPal began as a merger of two startups: Confinity, founded by Max Levchin, Peter Thiel, and Luke Nosek in December 1998, and X.com, an online financial services company started by Elon Musk in 1999. The companies merged in 2000 and eventually adopted the PayPal name.
In 2002, PayPal went public through an IPO, raising over $60 million. Just a few months later, eBay acquired PayPal for $1.5 billion, making it the primary payment service on its platform.
Major Milestones
- 1998: Confinity is founded by Levchin, Thiel, and Nosek.
- 1999: Elon Musk launches X.com, an online financial services company.
- 2000: X.com and Confinity merge; Musk is briefly CEO.
- 2001: PayPal brand is introduced; company shifts focus solely to payments.
- 2002: PayPal IPO and acquisition by eBay.
- 2013: PayPal acquires Braintree, including Venmo.
- 2015: PayPal spins off from eBay, becoming an independent public company.
- 2018: Acquires iZettle to expand point-of-sale and hardware offerings.
- 2020: Acquires Honey Science to enter the shopping deals and coupon space.
- 2021: Expands into cryptocurrency, allowing users to buy, hold, and sell crypto.
- 2022: Launches PayPal Zettle in the U.S. for in-person payments.
- 2023: Alex Chriss becomes CEO, focusing on product-led growth and AI.
- 2024: Introduces advanced AI fraud detection tools and a unified merchant platform.
- 2025: PayPal strengthens its global merchant services and launches real-time cross-border payment tools to compete with emerging fintech platforms.
Who Owns PayPal: Largest Shareholders
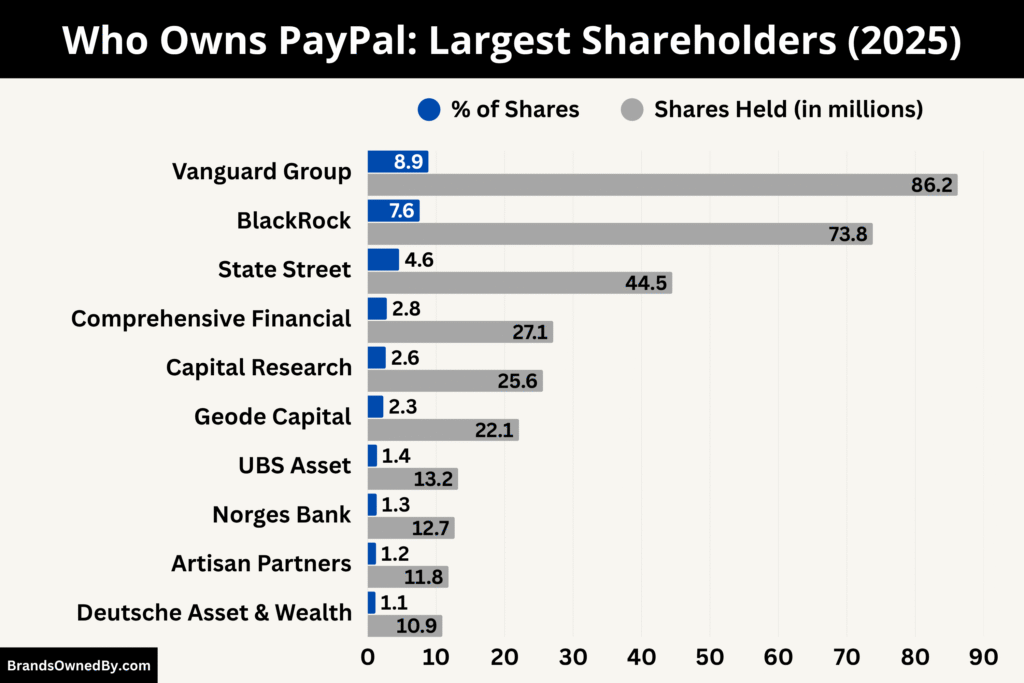
PayPal Holdings, Inc. is a publicly traded company listed on the NASDAQ under the ticker symbol PYPL. It is not owned by a single person or entity. Instead, ownership is spread among institutional investors, mutual funds, and retail shareholders.
The largest shareholders include major asset management firms that hold significant stakes due to their broad investment strategies.
Below is a list of the major PayPal shareholders and entities that own PayPal today:
| Shareholder | Ownership (%) | Type | Role / Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vanguard Group | ~8.87% | Institutional | Largest shareholder; passive investor with strong voting power |
| BlackRock Inc. | ~7.59% | Institutional | Major passive investor; active in ESG and corporate governance |
| State Street Corporation | ~4.58% | Institutional | Index fund manager; participates in proxy voting and governance |
| Capital Research & Management | ~2.63% | Institutional (Active) | Actively managed; long-term investment based on fundamentals |
| T. Rowe Price Associates | ~2.6% | Institutional | Long-term mutual fund investor; active in shareholder meetings |
| Geode Capital Management | ~2.28% | Institutional | Sub-advisor to Vanguard; passive role with voting influence |
| Norges Bank Investment Management | ~1.31% | Sovereign Wealth Fund | Ethical investor; supports sustainability and corporate transparency |
| Retail Investors | ~7–8% (combined) | Individual Investors | Buy shares via brokers; participate in shareholder votes |
| Insider Ownership | ~1.5–2% | Executives/Directors | Small stake; includes RSUs and options held by leadership for alignment |
Vanguard Group – Approx. 8.87%
Vanguard is the largest shareholder of PayPal. As of early 2025, it holds approximately 9.3% of PayPal’s outstanding shares. Vanguard is known for its passive investing strategy, where it holds long-term positions across thousands of public companies through index and ETF products.
Despite not being directly involved in management, Vanguard’s large stake gives it significant voting power in key shareholder decisions. Vanguard often advocates for corporate governance standards and long-term value creation, and its votes can influence board elections and compensation packages.
BlackRock Inc. – Approx. 7.59%
BlackRock holds around 7.2% of PayPal shares. It manages over $10 trillion in global assets, and its stake in PayPal is part of its diversified holdings across tech, finance, and consumer sectors.
BlackRock, like Vanguard, is a passive investor but often engages with companies on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) topics. It has a dedicated stewardship team that interacts with management to ensure companies act in the interest of long-term shareholders.
State Street Corporation – Approx. 4.58%
State Street is another major institutional investor, holding about 4.1% of PayPal. It provides asset management services primarily through index funds and ETFs. While State Street generally follows a passive investment model, it is active in proxy voting and corporate governance discussions.
The firm’s ownership in PayPal is part of its broader strategy to maintain diversified exposure to high-performing tech and fintech stocks.
Capital Research and Management – Approx. 2.63%
Capital Research and Management Company, a division of Capital Group, owns roughly 3.7% of PayPal. Unlike other index-focused firms, Capital Research follows a more active investment strategy. Its analysts and portfolio managers evaluate companies individually, often holding positions based on long-term fundamentals and growth potential.
Capital Group’s presence as a shareholder reflects confidence in PayPal’s business model, management, and growth opportunities.
T. Rowe Price Associates – Approx. 2.6%
T. Rowe Price is another significant shareholder, with around 2.6% ownership. The firm manages mutual funds and retirement accounts and is known for its disciplined investment approach.
T. Rowe Price typically holds long-term positions in companies that demonstrate strong financials and leadership. It participates in key votes during shareholder meetings and monitors strategic decisions made by company leadership.
Geode Capital Management – Approx. 2.28%
Geode Capital Management, a lesser-known but highly influential firm, owns around 1.8% of PayPal. It manages assets for institutional clients and operates as a sub-advisor for several of Vanguard’s index funds. Geode’s position in PayPal reflects the broader tech allocation of its portfolios.
Though Geode does not engage directly with management like Vanguard or BlackRock, its stake contributes to the overall institutional control of the company.
Norges Bank Investment Management – Approx. 1.31%
Norges Bank, which manages Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, owns about 1.3% of PayPal. The fund is one of the largest in the world and takes long-term positions in global companies. Norges Bank is known for its focus on sustainability, transparency, and ethical investing.
It frequently votes on shareholder proposals and engages in discussions on executive pay, climate policies, and board diversity.
Retail Investors and Insider Ownership – Combined ~10%
In addition to institutional shareholders, retail investors also own a portion of PayPal’s stock, estimated at 7–8%. These include individual shareholders who buy stock through brokerage accounts.
Insider ownership, including shares held by PayPal’s executives, board members, and senior management, is relatively small—about 1.5–2% combined. This low level of insider ownership is common in large public companies. Still, executives may own restricted stock units (RSUs) or options that align their incentives with long-term shareholder value.
Who is the CEO of PayPal?
As of 2025, Alex Chriss is the president and chief executive officer of PayPal. He assumed the role on September 27, 2023. Chriss was recruited from Intuit, where he led the Small Business and Self-Employed Group. He was instrumental in expanding that division and played a central part in the $12 billion acquisition of Mailchimp. His appointment came after a formal search and followed Dan Schulman’s planned transition off the CEO role while remaining on the board for a time.
Background of Alex Chriss
Alex Chriss has nearly two decades of experience in financial software and platform businesses. At Intuit, he oversaw products used by millions of small businesses, focusing on simplifying complex financial workflows and integrating services. He is known for a product-led mindset, data-driven decision making, and operational rigor. His leadership style emphasizes engineering excellence, user experience, and aligning product development tightly with merchant and consumer needs.
Strategic Priorities under Chriss
Since taking over, Chriss has pushed PayPal to go “beyond payments.” He has focused on reviving growth in core checkout products, improving margin performance, and accelerating innovation in cross-border real-time payments. There is a renewed emphasis on unifying merchant tools, enhancing fraud detection with AI, and making PayPal more indispensable for small and medium businesses. Chriss has also steered the company toward tighter integration of its ecosystem—including digital wallets, loyalty mechanics, and embedded finance—while managing cost efficiency and investor expectations.
Previous CEO: Dan Schulman
Dan Schulman served as PayPal’s CEO from 2014 until 2023. He oversaw the spin-off from eBay and led the company through a period of rapid expansion. Under his tenure, PayPal’s revenue grew substantially, and its total payment volume scaled dramatically. Schulman pushed a mission-driven narrative around financial inclusion, expanded global reach, and made several strategic acquisitions, including Venmo (via Braintree), Xoom, iZettle, and Honey. His vision included a “super app” and digital wallet ambitions, some of which faced execution challenges. His departure came amid pressure from activist investors and stagnating account growth after earlier pandemic-driven surges.
Decision-Making and Governance Structure
The CEO of PayPal operates within a layered governance framework. The board of directors provides oversight and sets broad strategic direction. Key board committees—such as audit, compensation, nominating and governance, and risk—work in tandem with the CEO and the executive leadership team. Day-to-day decisions are driven by the CEO alongside functional heads in product, engineering, finance, legal, operations, and global markets. Strategic initiatives typically flow from the executive leadership team, get debated with the board, and are evaluated against performance metrics and risk thresholds.
PayPal uses a formal succession planning process. This includes internal development of potential leaders, bench strength evaluation, and, when needed, external searches to fill gaps. The CEO’s compensation and incentives are tied to long-term shareholder value, including stock-based awards, performance metrics, and qualitative strategic goals.
Recent Leadership Transition
The transition from Dan Schulman to Alex Chriss was structured to provide continuity. Schulman remained engaged with the company through the board for a period, helping to smooth strategic handoffs. The new leadership under Chriss has balanced honoring prior investments in brand and inclusion while recalibrating execution to meet current growth and profitability targets.
Board of Directors
PayPal’s board of directors plays a central role in corporate governance. It provides oversight of the executive team, approves strategic initiatives, and represents shareholder interests. The board includes members with expertise in finance, technology, cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and global commerce.
Some notable board members as of 2025 include:
- John Donahoe – Former CEO of eBay and current CEO of Nike, brings experience in e-commerce and global brand building.
- Deborah Messemer – Former KPMG executive, known for her audit and accounting expertise.
- Belinda Johnson – Former Chief Operating Officer at Airbnb, offers insight into digital platforms and operations.
- Jonathan Christodoro – Investor and former board member of several major companies.
The board is chaired by an independent director, ensuring that oversight remains separate from executive management. This helps maintain checks and balances in decision-making.
Shareholder Influence and Governance
While the board and CEO handle corporate leadership, institutional shareholders like Vanguard and BlackRock can indirectly influence control. They do this through:
- Proxy voting on key matters such as board elections, executive pay, and corporate strategy.
- Engagement with the board or management on ESG practices, performance, and long-term planning.
- Shareholder proposals that can be raised during annual meetings.
Although these investors don’t manage operations, their collective influence plays a significant role in shaping PayPal’s strategic direction.
Regulatory Oversight
PayPal also operates under the scrutiny of financial regulators across multiple countries. It is subject to:
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) standards
- Anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) laws globally
These agencies influence corporate behavior and internal controls, especially given PayPal’s involvement in cross-border and peer-to-peer transactions.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of PayPal
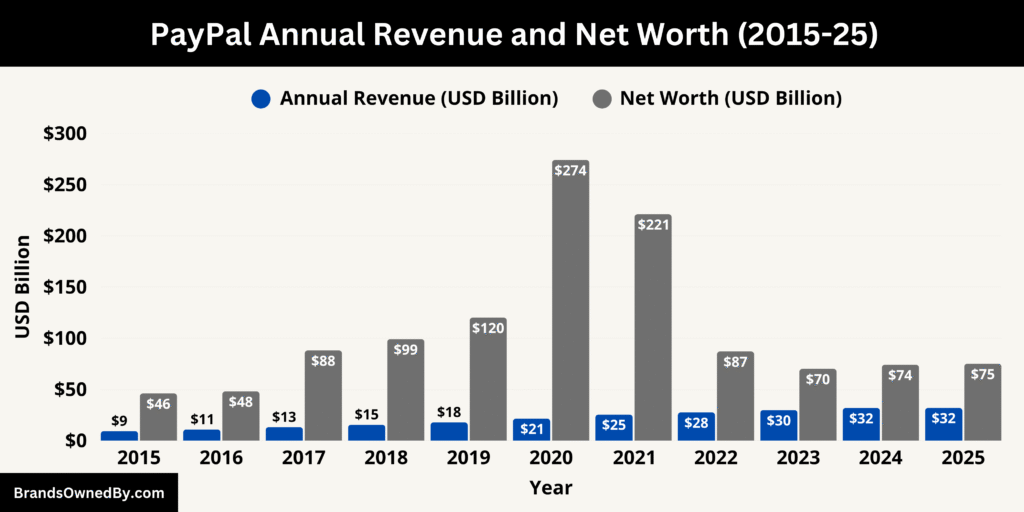
PayPal’s annual revenue for fiscal year 2025 reached approximately $31.89 billion. This figure underscores strong growth despite softening consumer spending and increased competition in digital payments. Growth was fueled by international expansion of merchant services, elevated use of branded checkout experiences, and robust adoption of PayPal Zettle and Braintree across new regions.
Venmo continued to contribute meaningfully, both through peer‑to‑peer activity and its growing business profile ecosystem. Expanded offerings such as working capital, merchant analytics, and AI‑driven fraud prevention helped drive up average revenue per active account.
Net Worth and Market Capitalization
As of August 2025, PayPal’s market capitalization (often referred to in casual terms as its net worth) is estimated to be around $75 billion. While slightly below the levels of some peers, this valuation reflects investor confidence in PayPal’s earnings stability and future prospects.
PayPal has maintained solid profitability—reporting net income of nearly $4.5 billion—while managing cost structure and returning capital to shareholders through buybacks. Its balance sheet remains healthy, with substantial cash reserves, limited long‑term debt, and financial flexibility to invest in growth or acquisitions.
The table below summarizes PayPal’s annual revenue and net worth from 2016 to 2025:
| Year | Annual Revenue (USD) | Net Worth / Market Cap (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | $31.89 billion | $75 billion |
| 2024 | $29.6 billion | $70 billion |
| 2023 | $27.5 billion | $84 billion |
| 2022 | $27.52 billion | $88 billion |
| 2021 | $25.37 billion | $221 billion |
| 2020 | $21.45 billion | $274 billion |
| 2019 | $17.77 billion | $125 billion |
| 2018 | $15.45 billion | $102 billion |
| 2017 | $13.09 billion | $89 billion |
| 2016 | $10.84 billion | $45 billion |
Strategic Financial Position
The gap between revenue and market capitalization suggests that investors emphasize sustainable profit margins, competitive moat, and execution discipline more than just top‑line scale. Under current leadership, PayPal has focused on optimizing high‑value payment flows, reducing exposure to low‑margin transactions, and investing in product integration across platforms. These actions aim to deliver predictable financial performance and reinforce sustainable growth for the years ahead.
Companies Owned by PayPal
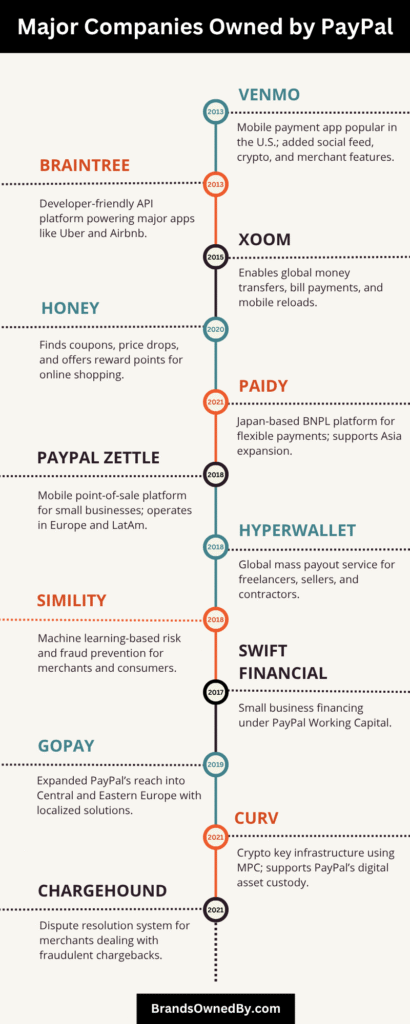
Over the years, PayPal has acquired several companies to expand its reach and capabilities in the digital payment space.
Here’s a list of the brands and companies owned by PayPal:
Venmo
Venmo is one of PayPal’s most well-known brands, especially in the United States. Acquired through PayPal’s purchase of Braintree in 2013, Venmo has become a dominant peer-to-peer (P2P) payment app among younger users.
Venmo allows users to send money to friends, split bills, and pay for services using a social-media-like feed. As of 2025, Venmo processes over $250 billion annually and has also rolled out features like Venmo debit cards, crypto trading, and business payments. It’s a core part of PayPal’s mobile-first and consumer-focused strategy.
Xoom
Xoom is a digital remittance company that PayPal acquired in 2015 for $890 million. It allows users in the U.S. and other countries to send money abroad, pay utility bills, or reload phones in over 160 countries.
Xoom is a major player in the cross-border money transfer market, competing with services like Western Union and Wise. Its integration with PayPal has made it easier for users to fund transfers using their PayPal balance or linked accounts.
Braintree
Braintree is a global payment gateway that PayPal acquired in 2013 for $800 million. It provides tools for businesses to accept payments online and via mobile apps.
What makes Braintree unique is its support for multiple payment methods, including credit cards, digital wallets, and PayPal itself. It powers transactions for some of the world’s biggest platforms including Airbnb and Uber. Through Braintree, PayPal strengthened its role as a merchant services provider.
Hyperwallet
Hyperwallet was acquired by PayPal in 2018 for $400 million. It is designed to manage mass payouts for companies that need to send money to a large number of recipients across the globe—such as freelancers, gig workers, or affiliate partners.
Hyperwallet offers a customizable payout platform with local compliance, tax documentation, and multi-currency support. It’s especially useful for marketplaces and platforms with a global footprint.
iZettle (now Zettle by PayPal)
iZettle, now rebranded as Zettle by PayPal, was a Swedish fintech company acquired in 2018 for $2.2 billion. It offers point-of-sale (POS) solutions including card readers, registers, and inventory management tools for small and medium-sized businesses.
Zettle helps PayPal serve in-person retail environments, especially in Europe and Latin America. It’s considered PayPal’s answer to Square (now Block Inc.) and adds physical commerce capabilities to its otherwise online-focused ecosystem.
Paidy (Japan)
Paidy is a Japanese buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) platform acquired by PayPal in 2021 for approximately $2.7 billion. It allows consumers to shop online and pay later without a credit card, using installment options or monthly bills.
This acquisition gave PayPal a strong presence in Japan’s e-commerce market, one of the largest in Asia. Paidy complements PayPal’s global BNPL offerings and helps it compete with services like Klarna and Afterpay.
Simility
Simility is a fraud detection and risk management platform acquired in 2018 for $120 million. It uses machine learning and behavioral analytics to help merchants prevent fraud, monitor transactions, and ensure compliance.
By integrating Simility into its ecosystem, PayPal improved its risk management capabilities, which is critical given the rise in digital fraud and regulatory scrutiny.
Jetlore (Defunct / Integrated)
Jetlore was a predictive retail platform acquired in 2018. It offered AI-powered personalization tools for retailers, helping them recommend products and personalize email campaigns based on customer behavior.
Jetlore was eventually absorbed into PayPal’s broader merchant services, with its technology helping build smarter tools for business customers. It is no longer marketed as a standalone brand.
Honey Science Corporation
Honey is a browser extension and app for deal-finding and coupon codes, acquired in 2020 for $4 billion. Honey automatically finds the best promo codes at checkout and offers cashback and rewards through its Honey Gold program.
TIO Networks
TIO Networks was acquired by PayPal in 2017 for approximately $238 million. The company specialized in bill payment solutions, allowing consumers to pay for utilities, credit cards, and other services. TIO Networks integrated its services into PayPal’s broader payment network, allowing PayPal users to easily manage payments for bills and other essential services in North America.
This acquisition allowed PayPal to expand its reach into bill pay and cash-based payment processing.
PayPal Credit (formerly Bill Me Later)
PayPal Credit, previously known as Bill Me Later, was acquired by PayPal in 2008. The platform offers consumers a credit line for online purchases, providing a pay later option with flexible financing terms. This service is a significant part of PayPal’s buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) strategy. PayPal Credit is integrated into the checkout process and is widely used across millions of e-commerce merchants.
Zong
Acquired by PayPal in 2011, Zong was a mobile payment provider that allowed users to make purchases via their mobile phone carrier billing. This acquisition helped PayPal enter the mobile payments space and expand its ability to process carrier billing transactions globally.
Zong was primarily focused on allowing digital goods and services to be bought using mobile phone numbers, bypassing traditional bank accounts or credit cards. Eventually, Zong’s platform was integrated into PayPal, enhancing the company’s mobile payment capabilities.
Tala (Minority Stake)
PayPal acquired a minority stake in Tala in 2019. Tala is a micro-lending platform that leverages mobile data to offer small loans to underserved populations in emerging markets such as Kenya, the Philippines, and India. Tala uses smartphones and mobile data to assess creditworthiness and provide instant credit to people without formal banking access.
PayPal’s investment in Tala helps expand its reach in the microfinance and lending space, aligning with PayPal’s strategy to provide financial inclusion in developing markets.
Pine Labs (Minority Stake)
In 2021, PayPal made a minority investment in Pine Labs, a merchant payment solutions provider based in India. Pine Labs offers POS systems, merchant financing, and digital payment tools for businesses.
This acquisition allows PayPal to deepen its merchant services offerings in Asia, especially in India, where digital payments have seen tremendous growth. PayPal’s stake in Pine Labs allows it to expand its footprint in one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing e-commerce markets.
Final Words
PayPal is not owned by any single entity. Instead, it is controlled by a mix of large institutional shareholders, guided by its board of directors, and operated by a skilled executive team.
The largest shareholders like Vanguard and BlackRock hold significant influence but do not manage daily operations. With a global footprint, steady revenue, and a suite of powerful brands, PayPal remains a dominant force in the fintech industry.
FAQs
Is PayPal owned by Musk?
No, Elon Musk does not own PayPal. While he was one of the early founders of X.com, which merged with Confinity to become PayPal, he sold his stake after eBay acquired the company in 2002. He has not been involved with PayPal since then.
Does Peter Thiel still own PayPal?
No, Peter Thiel no longer owns PayPal. He was one of the original co-founders and its first CEO, but he sold his shares after PayPal’s acquisition by eBay in 2002. He has since moved on to other ventures, including Palantir and various venture capital investments.
Who started PayPal?
PayPal was founded by two companies that merged: Confinity, started in 1998 by Peter Thiel, Max Levchin, and Luke Nosek, and X.com, an online banking platform launched in 1999 by Elon Musk. The merger led to the creation of PayPal as we know it.
Who owns PayPal Credit?
PayPal Credit is operated by PayPal but is issued by Synchrony Bank. PayPal acts as the platform, while Synchrony manages the credit line, billing, and underwriting. PayPal itself does not directly issue the credit—it partners with the bank to offer the service.
Who runs PayPal?
As of 2025, PayPal is run by CEO Alex Chriss, who took over leadership in 2023. He is responsible for the strategic direction and day-to-day operations of the company, working with the board of directors and executive leadership team.
Who is PayPal owned by?
PayPal is a publicly traded company, so it is owned by its shareholders. These include large institutional investors like The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, FMR (Fidelity), and State Street, as well as millions of retail investors. No single individual or entity has complete ownership.
Who bought PayPal?
eBay acquired PayPal in 2002 for $1.5 billion. However, PayPal was spun off from eBay in 2015 and is now an independent company. Since then, it has operated separately and is traded on the NASDAQ under the ticker symbol PYPL.
When was PayPal founded?
PayPal’s foundation traces back to December 1998, when Confinity was created. It later merged with X.com in 2000, and the unified brand PayPal launched in 2001. It went public in 2002.
Is PayPal owned by eBay?
No, PayPal is no longer owned by eBay. eBay owned PayPal from 2002 until 2015. That year, the two companies separated, and PayPal became a standalone publicly traded firm.
Who is the major shareholder of PayPal?
As of 2025, The Vanguard Group is PayPal’s largest shareholder, holding approximately 8.4% of the company’s stock. Other major shareholders include BlackRock (6.7%), FMR LLC (3.3%), and State Street (3.2%).
Why did Elon Musk leave PayPal?
Elon Musk left PayPal after it was acquired by eBay in 2002. He had been removed as CEO before the acquisition but still held equity. Once the sale was complete, he cashed out his shares and used the funds to launch SpaceX and later invest in Tesla, shifting his focus entirely to new ventures.
Which bank owns PayPal?
No bank owns PayPal. It is an independent, publicly traded company. However, PayPal partners with banks like Synchrony Bank (for PayPal Credit) and others globally to offer various financial services.
Who owns Venmo?
Venmo is owned by PayPal. It became part of PayPal’s portfolio in 2013 through the acquisition of Braintree, which had previously acquired Venmo. Today, Venmo operates as a subsidiary under the PayPal umbrella.

