When thinking of automotive excellence and innovation, Toyota is undoubtedly one of the first names that come to mind. This Japanese automotive giant has conquered the global market with its reliable vehicles, cutting-edge technology, and commitment to sustainability.
But who owns Toyota? Is it a single individual, a group of investors, or something more complex?
In this comprehensive article, we unpack Toyota’s ownership structure, spotlight its top shareholders, and explore its market dominance, rivalries, and brands under its umbrella. If you’ve ever wondered who calls the shots at Toyota, keep reading to learn more.
Toyota History
Toyota Motor Corporation was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda in 1937 as a spinoff from the family company, Toyoda Automatic Loom Works. With humble beginnings in Japan, Toyota grew rapidly, becoming a global automotive leader known for its quality and innovation.
Toyota pioneered mass production strategies, introducing the Toyota Production System (TPS), which emphasizes efficiency and just-in-time manufacturing. By the 1970s, Toyota had achieved international recognition, especially in the North American market, and continued to expand its reach globally. Today, Toyota stands as one of the leading automakers worldwide, producing sedans, trucks, electric cars, and hybrids like the iconic Toyota Prius.
Who Owns Toyota: Top Shareholders
Toyota is a publicly traded company listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange, which means its ownership is divided among millions of shareholders globally. No single individual or organization has complete ownership of the company.
The largest shareholder of Toyota is the Toyota Motor Corporation itself, through treasury stock (shares the company holds in its name). Beyond that, institutional investors and other shareholders own significant stakes.
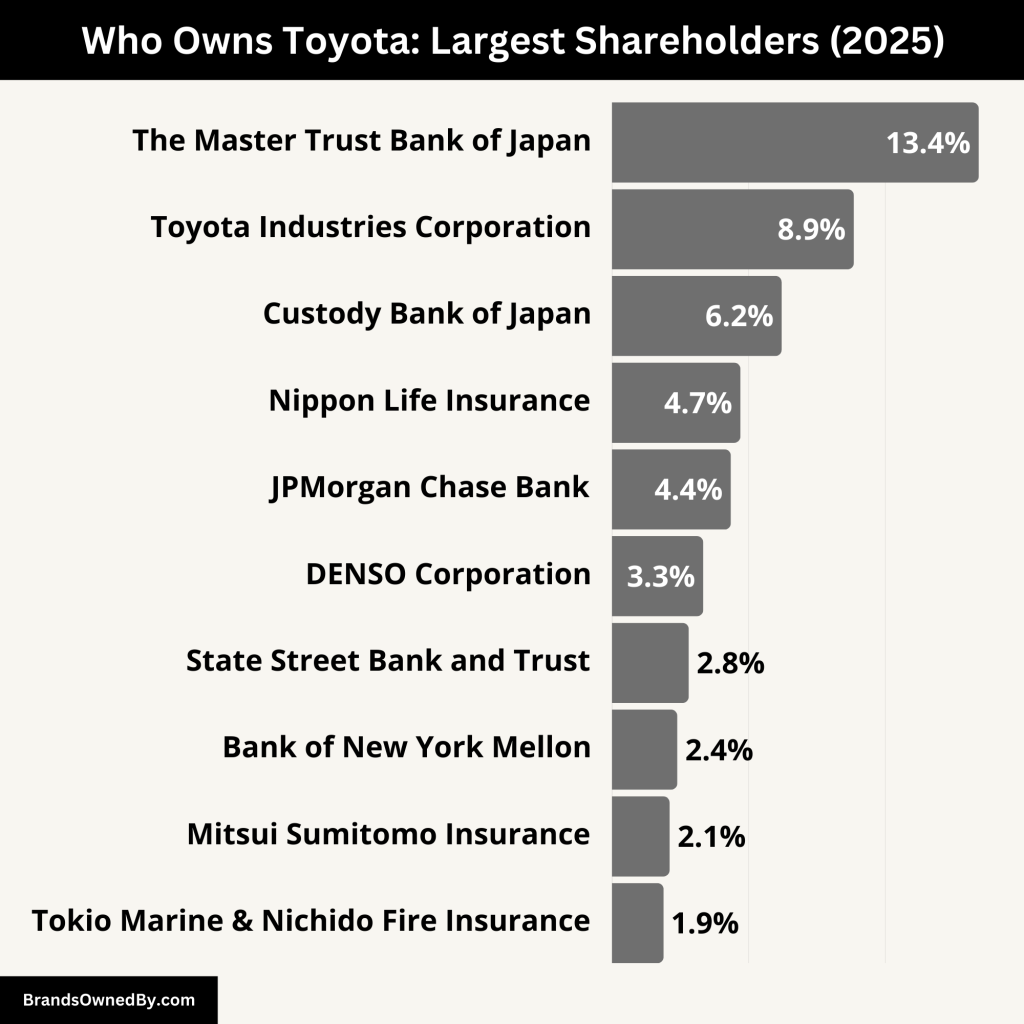
Below is an overview of the top shareholders of Toyota:
| Shareholder | Shares Held (Thousands) | Ownership Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd. | 1,808,404,000 | 13.42% |
| Toyota Industries Corporation | 1,192,331,000 | 8.85% |
| Custody Bank of Japan, Ltd. | 836,489,000 | 6.21% |
| Nippon Life Insurance Company | 633,230,000 | 4.70% |
| JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. | 585,585,000 | 4.35% |
| DENSO Corporation | 449,576,000 | 3.34% |
| State Street Bank and Trust Company | 378,847,000 | 2.81% |
| The Bank of New York Mellon (ADR Holders) | 321,674,000 | 2.39% |
| Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance Company, Limited | 284,072,000 | 2.11% |
| Tokio Marine & Nichido Fire Insurance Co., Ltd. | 255,324,000 | 1.89% |
The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd.
The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd. holds 1,808,404,000 shares of Toyota, representing 13.42% of the company’s outstanding shares. As Japan’s largest trust bank, TMTBJ acts as trustee for pension funds and other institutional investors. Its holdings represent pooled assets from multiple clients, granting it significant influence over Toyota’s shareholder decisions and voting at Annual General Meetings (AGMs).
Toyota Industries Corporation
Toyota Industries Corporation owns 1,192,331,000 shares of Toyota, which equates to 8.85% of the total outstanding shares. A founding member of the Toyota Group, Toyota Industries manufactures textile machinery, materials handling equipment, and automotive components. This cross‑shareholding arrangement ensures alignment between Toyota Industries and Toyota, fostering cooperation on technology sharing and group strategies.
Custody Bank of Japan, Ltd.
Custody Bank of Japan, Ltd. holds 836,489,000 shares of Toyota, amounting to 6.21% of the company’s outstanding shares. Serving as a central custodian and trustee bank, CBJ holds these shares on behalf of domestic institutional investors, offering settlement and asset‑management services. This role solidifies Toyota’s deep institutional investor base and enhances its corporate governance structure.
Nippon Life Insurance Company
Nippon Life Insurance Company holds 633,230,000 shares of Toyota, which represents 4.70% of the company’s outstanding shares. As one of Japan’s largest life insurers, Nippon Life invests policyholders’ premiums in high‑quality equities like Toyota. Its ownership reflects the insurer’s long‑term investment strategy, which seeks stable returns and helps support its ongoing financial obligations to policyholders.
JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A.
JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. holds 585,585,000 shares of Toyota, representing 4.35% of the company’s outstanding shares. The shares are held as American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) for U.S. investors. JPMorgan uses Mizuho Bank, Ltd. as a proxy for settlement and clearing in Japan. The bank’s substantial holdings reflect the significant interest from U.S. investors in Toyota’s stock.
DENSO Corporation
DENSO Corporation holds 449,576,000 shares of Toyota, or 3.34% of the company’s outstanding shares. As a key affiliate and global auto‑parts supplier for Toyota, DENSO’s stake underscores the strategic partnership between the two entities. This collaboration is crucial in fields like powertrain, electrification, and electronics development, ensuring Toyota’s competitive edge in the global automotive market.
State Street Bank and Trust Company
State Street Bank and Trust Company holds 378,847,000 shares of Toyota, which represents 2.81% of the total outstanding shares. A major global custodian, State Street holds these shares on behalf of institutional clients through its proxy Mizuho Bank. The bank’s investment in Toyota reflects the interest of numerous institutional investors seeking stable returns from a prominent global automaker.
The Bank of New York Mellon as Depositary Bank for ADR Holders
The Bank of New York Mellon holds 321,674,000 shares of Toyota, or 2.39% of the company’s outstanding shares. BNY Mellon issues American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) for foreign investors, representing Toyota shares held in trust. Its role as the depositary bank makes it a key player in enabling U.S. investors to hold Toyota stock while facilitating liquidity and corporate governance.
Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance Company, Limited
Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance Company holds 284,072,000 shares of Toyota, representing 2.11% of the company’s outstanding shares. As part of MS&AD Insurance Group, the company holds Toyota stock as part of its investment portfolio, balancing risk and achieving stable returns. This cross‑shareholding enhances ties between the Toyota Group and major Japanese insurers, contributing to long‑term investment stability.
Tokio Marine & Nichido Fire Insurance Co., Ltd.
Tokio Marine & Nichido Fire Insurance Co., Ltd. owns 255,324,000 shares of Toyota, or 1.89% of the company’s outstanding shares. As the largest property‑casualty insurer in Japan, Tokio Marine invests its policyholders’ premiums in high-quality equities like Toyota. This investment strategy allows the company to secure stable returns while fostering a close relationship with the Toyota Group.
Who Controls Toyota?
Toyota’s ownership structure is characterized by stable, long‑term investors—many of whom are core members of the Toyota Group itself. The top ten shareholders collectively control roughly 48% of the company’s outstanding shares, with The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd. alone owning 13.42% and Toyota Industries Corporation holding 8.85%.
This cross‑shareholding framework—in which affiliates like DENSO and Toyota Industries each maintain significant stakes—helps prevent hostile takeovers and ensures management continuity.
Institutional investors, such as Nippon Life Insurance and major custodial banks (e.g., Custody Bank of Japan, State Street, BNY Mellon), round out the roster, providing Toyota with a deep, diversified base of long‑term capital.
Board of Directors
Toyota’s Board of Directors consists of a blend of internal executives and independent outside directors.
- Inside Directors (e.g., President & CEO, Executive Vice Presidents) oversee day‑to‑day strategy and operations.
- Outside Directors bring external perspectives on governance, compliance, and global trends.
- Committees for Audit, Nomination, and Compensation ensure checks and balances, with outside directors holding a majority on the Audit Committee to strengthen oversight.
Executive Leadership
CEO: Koji Sato
Koji Sato took over as President and Chief Executive Officer on April 1, 2023, succeeding Akio Toyoda. A mechanical engineer by training, Sato graduated from Waseda University in 1992 and joined Toyota the same year. He led the Lexus brand from 2016, was appointed Chief Branding Officer in 2021, and became an Operating Officer and President in April 2023.
His elevation to CEO reflects Toyota’s push toward carbon neutrality and the expansion of “mobility” beyond cars, emphasizing electrification, software‑defined vehicles, and connected services.
Chairman: Akio Toyoda
Akio Toyoda, grandson of the company’s founder, served as President from 2009 until April 2023, when he transitioned to Chairman of the Board. Under his presidency, Toyota became the world’s largest automaker and pioneered the hybrid‑electric market with the Prius.
As Chairman, Toyoda retains significant influence over long‑term strategy and governance, guiding the board and supporting the new executive team.
Other Key Executives
- Executive Vice Presidents oversee major functions such as Research & Development, Manufacturing & Engineering, and Regional Operations.
- CFO (Chief Financial Officer) manages capital allocation, investor relations, and risk oversight.
- Supervisory Board Members (Audit & Supervisory Board) provide independent auditing and compliance checks, with the majority drawn from outside the company to reinforce accountability.
Toyota Revenue and Net Worth
Toyota Revenue
In the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Toyota Motor Corporation reported:
- Revenue: ¥45 trillion (approximately $290 billion), marking a 21% increase from the previous year.
- Net Income: ¥4.9 trillion (around $31.9 billion), a significant rise from ¥2.65 trillion in FY2023.
This growth was driven by strong global vehicle sales, favorable exchange rates, and strategic investments in electrification and technology.
For the first nine months of FY2025 (April–December 2024), Toyota’s financial performance included:
- Sales Revenue: ¥35.67 trillion, up 4.9% year-over-year.
- Net Income Attributable to Toyota Motor Corporation: ¥3.95 trillion, reflecting a 13.2% decrease compared to the same period in FY2024.
Despite the decline in net income, Toyota maintains a strong financial position, with a robust balance sheet and continued investments in future mobility solutions.
Toyota Net Worth
As of April 2025, Toyota Motor Corporation’s net worth, commonly referred to as its market capitalization, is approximately $230.8 billion. This valuation places Toyota among the top 50 most valuable companies globally, reflecting its strong position in the automotive industry.
In the first three quarters of fiscal year 2025 (April–December 2024), Toyota reported:
- Net Revenues: ¥35.67 trillion (approximately $233.2 billion), marking a 4.9% increase year-over-year.
- Operating Income: ¥3.68 trillion (about $24.0 billion), a decrease from ¥4.24 trillion in the previous year.
- Income Before Income Taxes: ¥5.43 trillion (around $35.5 billion) .
Despite a slight decline in operating income, Toyota’s robust revenue growth indicates resilience in its business operations.
As of December 2024, Toyota’s net assets, which represent the difference between total assets and total liabilities, stood at $234.76 billion. This figure underscores the company’s strong financial foundation and capacity to invest in future growth initiatives.
In addition to its financial metrics, Toyota’s brand value has seen significant growth. According to Brand Finance, Toyota’s brand value surged by 23% to $64.7 billion in 2025, reclaiming its position as the world’s most valuable automotive brand.
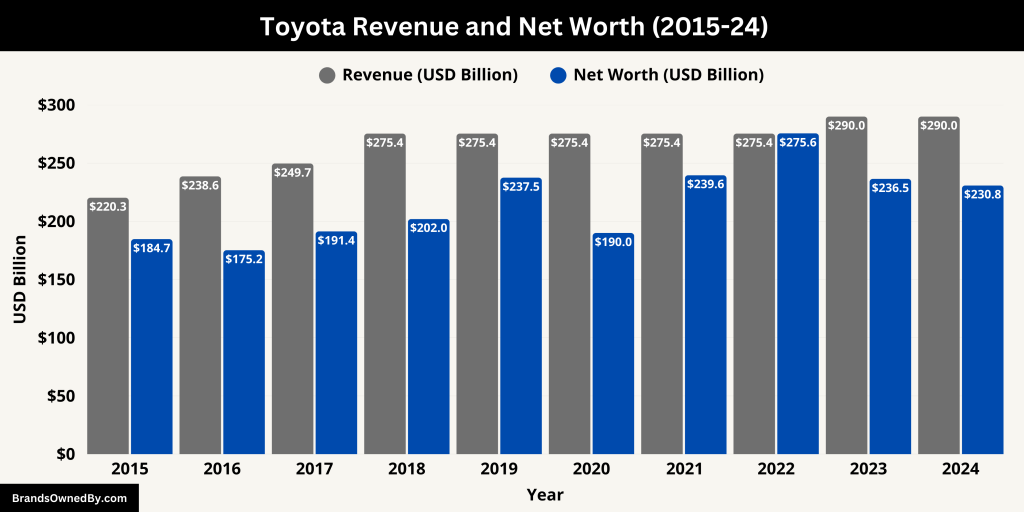
Here’s a table of the historical revenue and net worth of Toyota:
| Year | Revenue (USD Billion) | Net Worth (Market Cap, USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 220.3 | 184.7 |
| 2016 | 238.6 | 175.2 |
| 2017 | 249.7 | 191.4 |
| 2018 | 275.4 | 202.0 |
| 2019 | 275.4 | 237.5 |
| 2020 | 275.4 | 190.0 |
| 2021 | 275.4 | 239.6 |
| 2022 | 275.4 | 275.6 |
| 2023 | 290.0 | 236.5 |
| 2024 | 290.0 | 230.8 |
Toyota Market Share and Competitors
Toyota is the #1 automaker in terms of global sales volume, often competing closely with Volkswagen Group. Here’s an overview of its market performance:
Global Market Share (2023): Toyota commands roughly 10.4% of the global automotive market.
Key Competitors:
- Volkswagen Group (9.7%) – Known for its iconic brands like VW, Audi, and Porsche.
- General Motors (7.6%) – Stronghold in the North American market.
- Ford Motor Company (6.3%) – Dominant in pickup trucks and SUVs.
- Hyundai-Kia Group (8.9%) – Known for affordable and reliable vehicles.
- Tesla (3.4%) – Rapidly growing due to its focus on electric vehicles.
While newer competitors like Tesla are thriving in the EV space, Toyota’s hybrid dominance and conventional vehicle production ensure it retains a significant edge.
Brands Owned by Toyota
Beyond the Toyota brand, the company owns several automotive and non-automotive brands. Here’s a snapshot of its key subsidiaries:
| Company | Established | Key Role and Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Toyota Industries Corporation | 1926 | Manufactures automotive parts, materials handling equipment, and air-conditioning systems; involved in logistics and industrial machinery. |
| DENSO Corporation | 1949 | Supplies automotive technology and components like powertrain systems, thermal systems, and safety systems; leads in electrification and autonomous driving technology. |
| Lexus | 1989 | Toyota’s luxury vehicle division, known for combining dependability with high-end features, innovation, and luxury; pioneers in hybrid luxury vehicles. |
| Hino Motors, Ltd. | 1942 | Manufactures commercial vehicles such as trucks and buses; key player in Toyota’s global commercial vehicle market and developments in electric and hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles. |
| Toyota Financial Services | 1989 | Provides financing, leasing, and insurance services for Toyota customers and dealers; essential for customer and dealer relationships. |
| Toyota Boshoku Corporation | 1918 | Specializes in manufacturing automotive interiors and parts such as seats, door trims, air filters, and environmental solutions for vehicle interiors. |
| Aisin Seiki Co., Ltd. | 1949 | Manufactures automotive components including transmissions, drivetrains, brakes, and climate control systems; involved in electric and autonomous vehicle technologies. |
| Toyota Tsusho Corporation | 1948 | Engages in trading, logistics, and global supply chain management; invests in various industries including energy, chemicals, and infrastructure. |
| Toyota Auto Body Co., Ltd. | 1945 | Specializes in manufacturing vehicle bodies for a wide range of vehicles, focusing on durability, safety, and lightweight materials for Toyota’s lineup. |
| Daihatsu Motor Co., Ltd. | 1907 | Specializes in manufacturing small cars, particularly kei cars; plays a key role in Toyota’s strategy in emerging markets and contributes to sustainable mobility solutions. |
DENSO Corporation
DENSO Corporation, a key player in the Toyota Group, is a global leader in automotive technology. Founded in 1949 as a subsidiary of Toyota, DENSO primarily focuses on the development of automotive components such as powertrain systems, thermal systems, and electronic control systems. The company’s products range from air-conditioning units to advanced safety systems, playing a vital role in Toyota’s quest to develop safe, fuel-efficient, and environmentally friendly vehicles.
DENSO also leads efforts in electrification, autonomous driving technology, and artificial intelligence to support the future of mobility. With operations in more than 35 countries, DENSO has become a major supplier not only to Toyota but also to other automakers, reflecting its significant impact on the global automotive industry.
Lexus
Lexus, Toyota’s luxury vehicle division, was launched in 1989 and has since become synonymous with high-end vehicles known for their reliability, luxury, and innovation. Lexus vehicles are designed to combine Toyota’s hallmark dependability with refined aesthetics, advanced technology, and superior driving performance. Lexus was the first brand to introduce hybrid luxury cars with the RX400h in 2005, and it continues to expand its hybrid and electric vehicle offerings.
Lexus has a significant presence in North America, Europe, and Asia, competing with other luxury brands like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Audi. The brand’s reputation for quality has earned it numerous industry awards and a loyal customer base. It is also at the forefront of Toyota’s push into sustainable luxury, with plans to expand its electric vehicle lineup.
Hino Motors, Ltd.
Hino Motors, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Toyota, is Japan’s largest manufacturer of commercial vehicles and diesel engines. Founded in 1942, Hino specializes in the production of trucks, buses, and engines used in commercial transportation. Hino’s vehicles are known for their durability, efficiency, and environmental performance.
Hino plays a crucial role in Toyota’s strategy for expanding its presence in the global commercial vehicle market. The company has made significant strides in electric and hydrogen fuel-cell technology for commercial vehicles, aligning with Toyota’s vision of a zero-emissions future. Hino’s products are widely used for logistics, public transportation, and infrastructure development across the globe.
Toyota Financial Services
Toyota Financial Services (TFS) is the financial arm of Toyota, providing a range of services including financing, leasing, and insurance products. It was established to support Toyota customers and dealers, offering convenient financing solutions for the purchase of vehicles. TFS operates in numerous markets worldwide, serving both individual consumers and commercial clients.
Through Toyota Financial Services, the company strengthens its relationship with customers by making vehicle ownership more accessible. Additionally, TFS provides financial services to dealerships, helping them maintain inventory and manage operations. The division contributes significantly to Toyota’s overall revenue and is an essential part of Toyota’s strategy to build long-term customer loyalty.
Toyota Boshoku Corporation
Toyota Boshoku Corporation, a leading manufacturer of automotive interior components, is another important subsidiary of Toyota. Established in 1918, Toyota Boshoku designs and manufactures automotive seats, door trims, and interior panels, as well as air filters and other components critical to vehicle performance and comfort.
The company is also involved in the development of environmentally friendly products, including bio-based materials for automotive interiors. Toyota Boshoku is actively working on innovations to reduce the environmental impact of vehicle interiors while improving overall safety and comfort.
Aisin Seiki Co., Ltd.
Aisin Seiki, founded in 1949, is a key supplier of automotive components and systems to Toyota and other automakers. Aisin manufactures a wide range of products, including transmissions, braking systems, drivetrains, and climate control systems. The company is integral to Toyota’s production of fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles.
Aisin is also involved in the development of advanced technologies such as electric vehicle components and autonomous driving systems. Its research and development efforts focus on providing Toyota with the latest innovations in mobility solutions, contributing to the company’s global competitiveness.
Toyota Tsusho Corporation
Toyota Tsusho Corporation, a trading and investment arm of Toyota, plays a significant role in Toyota’s global supply chain. The company engages in the import and export of raw materials, automotive parts, and finished products. It also invests in various industries, including energy, chemicals, and infrastructure, contributing to Toyota’s business diversification.
Toyota Tsusho is involved in global procurement and logistics, ensuring that Toyota’s manufacturing plants around the world are supplied with the necessary materials and components. The company is also active in emerging markets, helping Toyota expand its presence in regions such as Africa and South America.
Toyota Auto Body Co., Ltd.
Toyota Auto Body, founded in 1945, specializes in the manufacturing of vehicle bodies and assembly. The company produces a wide range of vehicles, including commercial vehicles, SUVs, and minivans, with a focus on durability and safety. Toyota Auto Body’s vehicles are an essential part of Toyota’s global lineup, particularly in the markets for utility vehicles and specialized transportation solutions.
The company is a leader in lightweight vehicle body manufacturing and has pioneered efforts to integrate sustainable materials into its production processes. It also contributes to Toyota’s electrification goals, with plans to produce electric vehicle bodies that support the company’s environmental objectives.
Daihatsu Motor Co., Ltd.
Daihatsu, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Toyota, is one of Japan’s leading manufacturers of small cars, particularly kei cars (miniature cars designed to meet Japanese tax regulations). Founded in 1907, Daihatsu is known for producing affordable, fuel-efficient vehicles, which have become extremely popular in Japan and other Asian markets.
Daihatsu has a key role in Toyota’s global strategy, particularly in the emerging markets of Southeast Asia, where its compact and cost-effective vehicles are well-suited. The company also contributes to Toyota’s commitment to sustainable mobility with plans to develop electric vehicles and other environmentally friendly transportation options.
Final Words
Toyota Motor Corporation remains a proudly Japanese-owned company with a complex yet transparent ownership structure. Its largest shareholder is Toyota Industries Corporation, reinforcing strong internal group ties within the Toyota Group. Alongside it, prominent institutional investors such as The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Custody Bank of Japan, and international firms like JPMorgan Chase & Co. and Vanguard Group hold significant stakes.
Despite its global operations and investor base, Toyota’s control remains deeply rooted in Japan through its founding group companies and leadership, preserving the company’s legacy while driving forward its innovation and global expansion.
FAQs
Does the Toyoda family still own Toyota?
The Toyoda family no longer directly owns Toyota but remains influential, particularly through governance roles like Akio Toyoda’s chairmanship.
Is Toyota owned by Japan?
Toyota is a publicly traded company. While it originated in Japan, its shares are owned by investors globally, including large foreign stakeholders.
What is Toyota’s largest brand?
The Toyota brand itself is the largest, but Lexus is its flagship luxury brand.
Who is the largest shareholder of Toyota?
Toyota Industries Corporation is the largest shareholder of Toyota, holding 8.28% of the total shares.
Are Toyota and Honda owned by the same company?
No, Toyota and Honda are independent, publicly traded companies and not owned by the same entity.
Who is the CEO of Toyota?
The current President and CEO of Toyota is Koji Sato, appointed in April 2023.
Who is the original owner of Toyota?
Toyota was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda in 1937, who is considered the original owner and creator of the company.
Is Toyota still Japanese-owned?
Yes, Toyota is still a Japanese-owned company, headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi Prefecture, Japan.
Where are Toyota engines made?
Toyota engines are manufactured in multiple countries, including Japan, the United States, the UK, Thailand, and China, among others.
What is the full name of Toyota?
The full name is Toyota Motor Corporation.
Who is the largest Toyota distributor?
Gulf States Toyota is one of the largest private Toyota distributors in the world, covering five U.S. states. Globally, Toyota Tsusho Corporation handles major distribution and trade.
How much is the CEO of Toyota worth?
Koji Sato’s net worth is not publicly disclosed as he is a salaried executive. However, his annual compensation is estimated to be in the range of $1–2 million USD, excluding bonuses or stock options.
In which country is Toyota sold the most?
The United States is Toyota’s largest market by vehicle sales, followed by Japan and China.
Is Hyundai owned by Toyota?
No, Hyundai is an independent South Korean automotive company and is not owned by Toyota.
Who makes Toyota cars and vehicles?
Toyota vehicles are made by Toyota Motor Corporation, which operates manufacturing plants worldwide, including in Japan, the U.S., the UK, Thailand, Canada, and others.
Is Nissan owned by Toyota?
No, Nissan is a separate Japanese automaker and is not owned by Toyota.
Is Toyota Japanese or Chinese?
Toyota is a Japanese company, founded and headquartered in Japan.

