T-Mobile US has grown into a telecom giant. It began as VoiceStream Wireless and now serves over 130 million subscribers. But who owns T Mobile today? Let’s explore its roots, its owners, and the leaders guiding it.
History of T-Mobile
T-Mobile traces its origins to 1994 when John W. Stanton spun off VoiceStream Wireless from Western Wireless to offer GSM-based personal communications services in western U.S. markets.
In June 2001, Deutsche Telekom AG acquired VoiceStream for $35 billion and Powertel for $24 billion, then rebranded the company as T‑Mobile USA in July 2002.
Growth continued with the 2007 purchase of SunCom Wireless, adding 1.1 million customers and expanding coverage to the Southeast and U.S. territories.
In 2013, a reverse takeover with MetroPCS led to T‑Mobile’s public listing and access to fresh spectrum and capital.
The “Un‑carrier” era began under CEO John Legere in 2013, challenging contracts and simplifying pricing. A landmark merger with Sprint closed in April 2020, solidifying T‑Mobile as the nation’s second‑largest carrier.
Recent acquisitions include Mint Mobile and Ultra Mobile in 2024, marking T‑Mobile’s move into D2C and international calling niches.
Who Owns T-Mobile: Top Shareholders
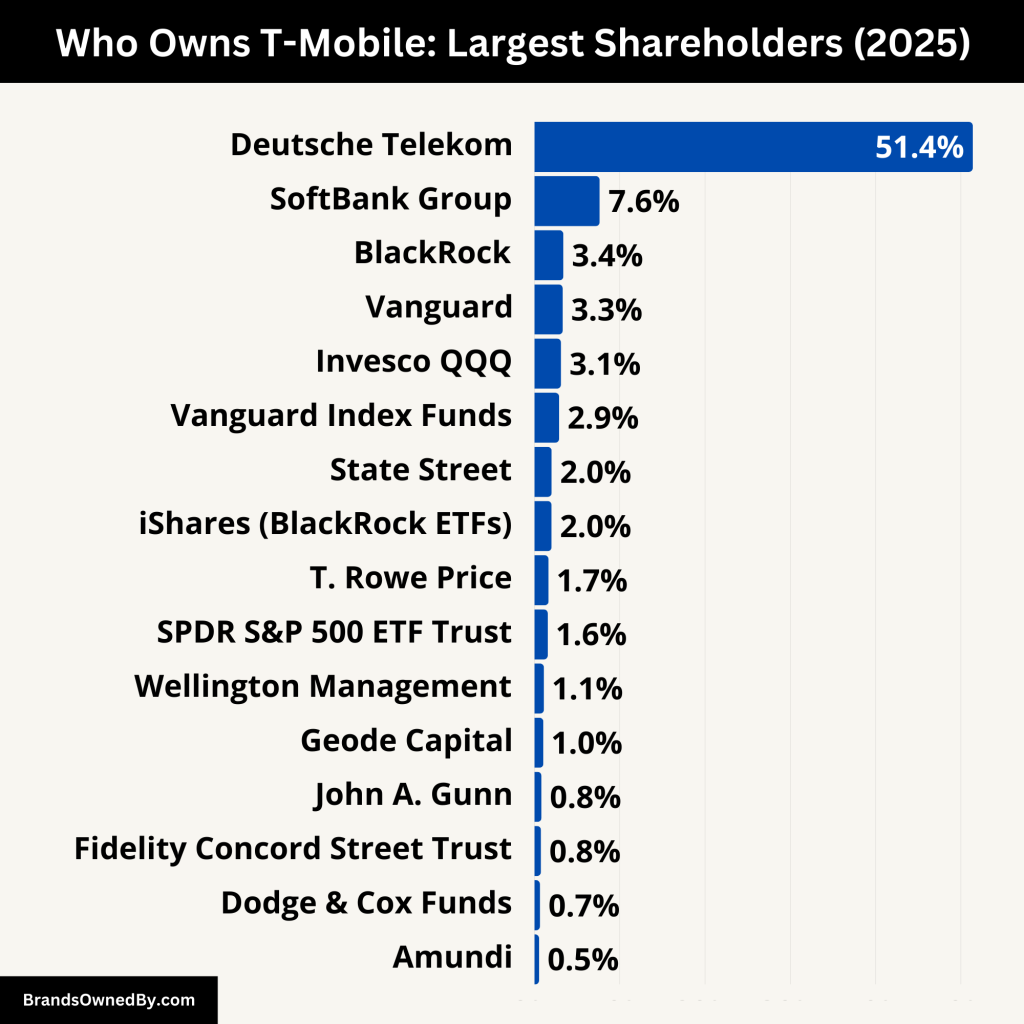
T-Mobile is a public company listed on NASDAQ under TMUS. Its majority owner is Deutsche Telekom AG, the German telecom giant that retains a controlling stake. A diverse group of institutional and strategic investors holds the remainder.
Here’s an overview of the major shareholders of T-Mobile:
| Shareholder | Approx. Ownership | Number of Shares | Type | Role and Influence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deutsche Telekom AG | ≈51.4% | Majority Holder | Strategic Owner | Controls the board and long-term strategy. Most influential shareholder. |
| SoftBank Group Corp | ≈7.64% | ~85.4M | Strategic/Financial | Ex-Sprint owner. Economic influence, no board seat. |
| BlackRock, Inc. | ≈3.39% | ~38.7M | Institutional (Passive) | Votes on ESG, compensation, governance issues. |
| The Vanguard Group | ≈3.31% | ~37.7M | Institutional (Passive) | Large index investor. Active in proxy voting. |
| Invesco QQQ Trust | ≈3.11% | ~35.5M | ETF (Passive) | Tracks Nasdaq-100. No board involvement. |
| Vanguard Index Funds | ≈2.89% | ~33.0M | Index Fund | Passive, votes with governance policies. |
| State Street Global Advisors | ≈2.01% | ~22.9M | Institutional (Passive) | Votes through SPDR ETFs. Advocates board diversity and sustainability. |
| iShares (BlackRock ETFs) | ≈2.00% | ~22.8M | ETF (Passive) | Focuses on ESG and long-term shareholder value. |
| SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust | ≈1.56% | ~17.8M | ETF (Passive) | Reflects T-Mobile’s S&P 500 inclusion. No direct influence. |
| T. Rowe Price Associates | ≈1.65% | ~18.8M | Active Mutual Fund | Conducts research, meets management, votes actively. |
| Wellington Management LLP | ≈1.11% | ~12.6M | Institutional (Active) | Advocates long-term strategy and ESG practices. |
| Geode Capital Management | ≈1.04% | ~11.9M | Institutional (Passive) | Sub-advisor to Vanguard funds. Supports index strategies. |
| John A. Gunn | ≈0.82% | ~9.4M | High-net-worth Investor | Holds a concentrated position. May influence strategic issues. |
| Fidelity Concord Street Trust | ≈0.76% | ~8.7M | Mutual Fund (Active) | Engages with management. Focus on performance and governance. |
| Dodge & Cox Funds | ≈0.65% | ~7.4M | Value Fund (Active) | Long-term investor. Known for deep research and corporate engagement. |
| Amundi | ≈0.54% | ~6.2M | Institutional (Global) | Europe’s top asset manager. Focus on ESG and global governance practices. |
Deutsche Telekom AG (≈51.4%)
Deutsche Telekom is the controlling shareholder of T-Mobile US, owning around 51.4% of the company. Its ownership increased after exercising options to buy additional shares from SoftBank and through T-Mobile’s own share buybacks.
This majority ownership gives Deutsche Telekom significant influence over strategic decisions, corporate policies, and board appointments. The CEO of Deutsche Telekom, Timotheus Höttges, serves as the chairman of T-Mobile US, strengthening the alignment between the parent and subsidiary.
The German company uses its stake to maintain a strong footprint in the U.S. wireless market—T-Mobile being its most valuable international asset.
SoftBank Group Corp (≈7.64%)
SoftBank’s stake in T-Mobile US originated from the 2020 Sprint merger. Following the deal, SoftBank initially held over 24% but gradually sold down its position while retaining a stake of around 7.64% as of early 2025. Though it no longer holds board seats, SoftBank still benefits from its equity interest.
The group is known for investing in telecom and tech, and its T-Mobile stake aligns with its broader vision of backing data-driven and mobile-first industries. Despite reduced involvement in management, SoftBank continues to profit from T-Mobile’s rising stock performance.
The Vanguard Group (≈3.31%)
Vanguard holds approximately 37.7 million shares, translating to about 3.31% ownership. As one of the world’s largest asset managers, Vanguard invests in T-Mobile primarily through its index funds, such as the Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund and Vanguard 500 Index Fund.
It is a passive investor, meaning it doesn’t influence daily operations, but it plays an important role in governance through proxy voting. Vanguard supports shareholder resolutions, executive compensation packages, and board nominations, giving it a subtle but powerful influence on corporate strategy.
Invesco QQQ Trust (≈3.11%)
Invesco QQQ Trust, an ETF that tracks the Nasdaq-100 index, owns around 3.11% of T-Mobile. It provides investors with exposure to major tech and telecom firms. The trust invests passively, with no involvement in management, but its scale makes it an important participant in proxy voting. Its ownership indicates T-Mobile’s strong standing among major tech-related firms and aligns the company with growth-driven investor sentiment.
Vanguard Index Funds (≈2.89%)
Vanguard Index Funds, specifically—distinct from the overarching Vanguard Group—own about 33 million shares. These include various market-wide ETFs and mutual funds, such as the Vanguard Institutional Index Fund.
While the funds are not active managers, they collectively vote on key proposals, often in line with recommendations from corporate governance advisory firms. Their presence shows broad investor confidence in T-Mobile’s long-term growth.
BlackRock, Inc. (≈3.39%)
BlackRock owns roughly 38.7 million shares, or 3.39%, of T-Mobile US. It manages this position across a range of iShares ETFs and mutual funds. As the largest asset manager in the world, BlackRock’s influence is substantial during shareholder meetings.
Although a passive investor, BlackRock often engages with companies on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues. Its voting guidelines support board diversity, sustainability, and transparency—values it may advocate for in T-Mobile’s annual general meetings.
State Street Global Advisors (≈2.01%)
State Street holds about 22.9 million shares of T-Mobile, representing a 2.01% stake. The firm is known for managing ETFs like the SPDR S&P 500 ETF. As a passive investor, State Street doesn’t get involved in corporate management but takes governance seriously.
It regularly evaluates proposals related to executive pay, board composition, and ESG policies. Its ownership reflects broader institutional trust in T-Mobile as a core S&P 500 component.
SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (≈1.56%)
The SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust directly holds about 17.8 million shares (1.56%) in T-Mobile. Managed by State Street, this ETF gives individual and institutional investors exposure to the U.S. stock market’s top companies.
Though it functions passively, its large fund base means it has significant weight in shareholder voting. This adds to the collective voting power of State Street.
iShares (≈2.00%)
iShares, a subsidiary of BlackRock, owns about 22.8 million shares of T-Mobile. This stake is spread across various ETFs such as the iShares Core S&P 500 ETF and the iShares MSCI USA ESG Select ETF.
While it operates on a passive investment model, iShares votes actively on shareholder resolutions, which can influence decisions related to sustainability, diversity, and governance.
T. Rowe Price Associates (≈1.65%)
T. Rowe Price manages approximately 18.8 million shares of T-Mobile through actively managed mutual funds. Unlike passive managers, T. Rowe Price often conducts its own analysis and meets with management teams.
It takes a hands-on approach in proxy voting, potentially influencing decisions on strategic direction and corporate governance. T. Rowe’s position suggests high confidence in T-Mobile’s leadership and future earnings potential.
Wellington Management Group, LLP (≈1.11%)
Wellington Management owns about 12.6 million shares of T-Mobile. The firm manages assets on behalf of global institutional clients, including pension funds and sovereign wealth funds. Wellington engages companies it invests in, often encouraging responsible governance and long-term value creation.
While not as visible in media or activism as some peers, its influence is felt in quiet, behind-the-scenes engagements with corporate boards.
Geode Capital Management LLC (≈1.04%)
Geode manages 11.9 million shares of T-Mobile, often serving as the sub-advisor to Vanguard funds. Its role is more operational than strategic, but it contributes to the broader influence Vanguard has through its indexed products.
As an institutional investor, Geode participates in corporate voting and supports decisions that align with shareholder returns and fiduciary duty.
John A. Gunn (≈0.82%)
John A. Gunn is a high-net-worth individual investor managing around 9.4 million shares of T-Mobile. Though individual, he often invests via institutional structures and long-term strategies.
Gunn is known for maintaining concentrated positions in high-growth companies, suggesting deep conviction in T-Mobile’s trajectory. His voting power, while small compared to giants like BlackRock or Vanguard, still adds to the diversity of shareholder perspectives.
Fidelity Concord Street Trust (≈0.76%)
Fidelity, through its Concord Street Trust, holds about 8.7 million shares. As an active manager, Fidelity assesses companies through rigorous research and often meets with management to evaluate performance and governance.
Its funds are involved in shaping company direction through proxy voting, particularly on issues like board appointments and executive compensation.
Dodge & Cox Funds (≈0.65%)
Dodge & Cox is a long-term value investor with about 7.4 million T-Mobile shares. The firm is known for its thorough analysis and often holds positions it holds for years.
It is a vocal participant in shareholder discussions and may influence T-Mobile’s capital allocation and long-term planning through active dialogue with the company.
Amundi (≈0.54%)
Amundi is Europe’s largest asset manager and owns around 6.2 million shares of T-Mobile. Its investment reflects strong global confidence in T-Mobile’s future. Amundi takes a long-term approach and emphasizes ESG criteria in its investments. It often pushes for greater transparency and environmental responsibility in companies it invests in, including U.S.-based firms like T-Mobile.
Who is the CEO of T-Mobile?
Mike Sievert is the current President and Chief Executive Officer of T-Mobile US. He officially became CEO on April 1, 2020, succeeding long-time chief John Legere. Sievert had served as T-Mobile’s COO and President before his promotion, and played a central role in the company’s transformation, including its merger with Sprint.
He is known for his energetic leadership style and his focus on innovation, 5G expansion, and customer satisfaction. Under Sievert’s leadership, T-Mobile has maintained strong subscriber growth, improved profitability, and become a leader in 5G network coverage in the U.S.
Mike Sievert also sits on the board of directors and works closely with Deutsche Telekom’s leadership. His role as CEO gives him executive authority over company operations, strategic decisions, and long-term planning.
Executive Leadership and Decision-Making
T-Mobile’s executive leadership team includes a President and CEO (Mike Sievert), a CFO (Peter Osvaldik), and other C-level executives overseeing legal, marketing, technology, and operations. These leaders form the Executive Committee, which shapes corporate strategy and oversees business units.
Although the company is publicly traded, it is majority-owned by Deutsche Telekom, which appoints a majority of the board. This gives the parent company major influence on corporate decisions, including CEO selection and compensation.
Past CEOs of T-Mobile US
John Legere (2012–2020)
John Legere is perhaps the most iconic CEO in T-Mobile’s history. Known for his bold, unfiltered personality and customer-first “Un-carrier” strategy, he transformed T-Mobile from the fourth-largest wireless carrier into a major competitor. His marketing tactics and aggressive price wars forced the entire industry to respond. Under his leadership, T-Mobile began a rapid rise in subscribers and revenue.
Legere led the Sprint merger but stepped down shortly after its completion in 2020. He remains one of the most well-known telecom CEOs in recent history.
Jim Alling (Interim CEO, 2012)
Before Legere, Jim Alling briefly served as interim CEO. He was T-Mobile’s COO and held the position during the transitional period after former CEO Philipp Humm’s resignation. Alling helped maintain operations until a permanent CEO was appointed.
Philipp Humm (2010–2012)
Philipp Humm served as CEO during a challenging period for T-Mobile. He aimed to stabilize the company’s performance and improve its market share. His tenure included the failed attempt to merge with AT&T in 2011. After the deal was blocked by U.S. regulators, Humm resigned to return to Europe.
Robert Dotson (2003–2010)
Robert Dotson served as CEO before Humm and helped T-Mobile US grow during the early smartphone era. He was instrumental in building out T-Mobile’s 3G network and expanding its U.S. operations. Dotson’s leadership laid much of the groundwork for the aggressive expansion that followed under Legere.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of T-Mobile
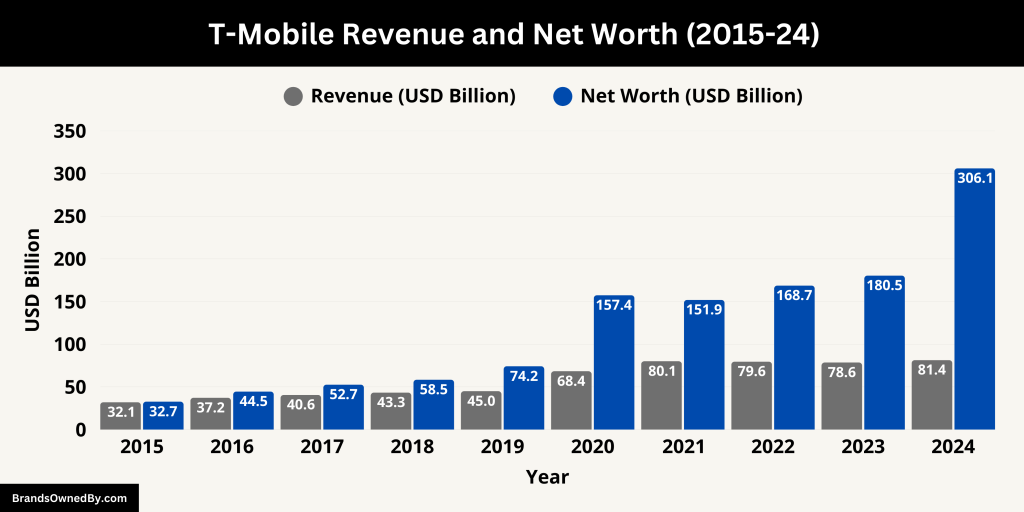
In 2024, T-Mobile reported an annual revenue of $81.4 billion, marking a 3.6% increase from the previous year. This growth was primarily driven by a surge in postpaid service revenues, which rose by 7% to $52.3 billion. The company’s net income for the year reached $11.3 billion, up 36% from 2023, resulting in a profit margin improvement from 11% to 14%.
The fourth quarter of 2024 was particularly strong, with T-Mobile generating $21.87 billion in revenue, surpassing analyst expectations. The company added 903,000 postpaid phone customers and 428,000 net internet customers during this period.
As of April 2025, T-Mobile US’s market capitalization stood at approximately $306.14 billion, reflecting a significant increase from $237.22 billion in September 2024. This growth in market value underscores investor confidence in T-Mobile’s strategic direction and financial performance.
In 2025, T-Mobile announced a $14 billion shareholder return program, highlighting its robust cash flow and commitment to delivering value to its investors.
The table below showcases the annual revenue and net worth of T-Mobile from 2015-24:
| Year | Revenue (USD Billion) | Net Worth (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 81.4 | 306.14 |
| 2023 | 78.56 | 180.45 |
| 2022 | 79.57 | 168.70 |
| 2021 | 80.12 | 151.92 |
| 2020 | 68.40 | 157.44 |
| 2019 | 45.00 | 74.22 |
| 2018 | 43.31 | 58.45 |
| 2017 | 40.60 | 52.66 |
| 2016 | 37.24 | 44.51 |
| 2015 | 32.05 | 32.70 |
Brands and Companies Owned by T-Mobile
Below is a list of the brands and companies owned by T-Mobile:
| Company / Brand | Primary Function or Market Segment |
|---|---|
| T-Mobile (flagship) | Nationwide postpaid wireless and 5G services |
| Metro by T-Mobile | Prepaid wireless services targeting value-conscious consumers |
| Mint Mobile | Online-only prepaid plans with budget pricing |
| Ultra Mobile | International calling and prepaid services |
| Plum | Low-cost prepaid wireless services |
| Assurance Wireless | Government-subsidized Lifeline program provider |
| T-Mobile Home Internet | 5G-based residential broadband service |
| T-Mobile for Business | Enterprise and SMB wireless communication solutions |
| T-Mobile Wholesale | Network access provider for MVNOs and partners |
| Sprint | Legacy brand; merged to expand spectrum and customer base |
| U.S. Cellular (planned) | Rural network expansion through asset and customer acquisition |
| Blis | Location-based and privacy-focused advertising technology |
| iWireless | Regional wireless coverage in Iowa and Midwest (now integrated) |
| SunCom Wireless | Expanded Southeastern U.S. network coverage (acquired in 2008) |
| Omnipoint | Early GSM provider; part of network foundation (acquired in 2000) |
| Aerial Communications | GSM carrier integrated into T-Mobile network (acquired in 2000) |
T-Mobile (Flagship Brand)
T-Mobile is the primary brand of T-Mobile US, offering nationwide postpaid wireless services. Known for its “Un-carrier” initiatives, T-Mobile emphasizes customer-centric policies, such as no annual service contracts and unlimited data plans. The brand has been instrumental in expanding 5G coverage across the United States.
Metro by T-Mobile
Formerly known as MetroPCS, Metro by T-Mobile is T-Mobile’s prepaid wireless brand. It provides affordable, no-contract plans with nationwide coverage. Metro was acquired by T-Mobile in 2013 and rebranded in 2018 to align more closely with its parent company. The brand targets value-conscious consumers seeking flexible mobile solutions.
Mint Mobile
Acquired by T-Mobile in May 2024, Mint Mobile is a mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) that offers budget-friendly prepaid plans. Known for its online-only sales model and multi-month plan structures, Mint Mobile gained popularity for its cost-effective offerings. Actor Ryan Reynolds, a former owner, continues to serve as a spokesperson for the brand.
Ultra Mobile
Also acquired in May 2024, Ultra Mobile is an MVNO specializing in international calling plans. It caters to customers needing affordable international communication options. The brand continues to operate independently under T-Mobile’s ownership, maintaining its focus on serving diverse communities.
Assurance Wireless
Assurance Wireless is a federal Lifeline Assistance program participant, providing free or low-cost phone services to eligible low-income individuals. The brand became part of T-Mobile’s portfolio following the merger with Sprint in 2020. It continues to offer essential communication services to underserved populations.
T-Mobile Home Internet
T-Mobile Home Internet is a wireless broadband service utilizing T-Mobile’s 5G network to deliver high-speed internet to residential customers. Launched to compete with traditional ISPs, it offers a straightforward pricing model without annual contracts or data caps.
T-Mobile for Business
T-Mobile for Business provides wireless communication solutions tailored for businesses of all sizes. Services include mobile plans, device management, and enterprise-level support, leveraging T-Mobile’s extensive network to meet corporate needs.
T-Mobile Wholesale
T-Mobile Wholesale offers network access to other carriers and MVNOs, enabling them to provide services using T-Mobile’s infrastructure. This division supports a variety of partners in delivering wireless solutions to niche markets.
Sprint (Merged Brand)
Sprint Corporation merged with T-Mobile in April 2020, consolidating operations under the T-Mobile brand. The merger expanded T-Mobile’s customer base and spectrum holdings, enhancing its competitiveness in the wireless market.
U.S. Cellular (Pending Acquisition)
In May 2024, T-Mobile announced plans to acquire the majority of U.S. Cellular’s wireless operations for $4.4 billion. The acquisition includes approximately 4 million customers and significant spectrum assets, aiming to bolster T-Mobile’s coverage, particularly in rural areas.
Blis
Acquired by T-Mobile in March 2025 for approximately $175 million, Blis is a UK-based advertising technology company specializing in location-powered and privacy-centric advertising solutions. This acquisition enhances T-Mobile’s advertising capabilities, allowing for more targeted and measurable ad experiences across various digital platforms.
Plum
Plum is a mobile services brand that was part of T-Mobile’s acquisition of Ka’ena Corporation, the parent company of Mint Mobile and Ultra Mobile. While less prominent than its sister brands, Plum contributes to T-Mobile’s portfolio of prepaid and budget-friendly wireless services.
SunCom Wireless
SunCom Wireless was a regional GSM carrier operating in the southeastern United States and parts of the Caribbean. T-Mobile acquired SunCom in 2008 for approximately $2.4 billion, expanding its network coverage in North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Georgia, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
iWireless
iWireless, also known as Iowa Wireless Services, was a regional carrier serving Iowa and parts of Illinois and Nebraska. T-Mobile acquired iWireless in 2018, integrating its operations and transitioning customers to T-Mobile’s network.
Omnipoint and Aerial Communications
In 2000, T-Mobile’s predecessor, VoiceStream Wireless, acquired Omnipoint Corporation and Aerial Communications, two regional GSM carriers. These acquisitions laid the foundation for T-Mobile’s national network expansion in the early 2000s.
Conclusion
T‑Mobile US has evolved from a regional GSM operator into a nationwide 5G leader. Deutsche Telekom’s majority stake ensures strategic alignment with its German parent, while institutional shareholders support its growth.
Under Mike Sievert’s leadership, T‑Mobile continues to expand its brands and spectrum assets. The company’s strong financials and diverse brands position it for continued success.
FAQs
Who is the largest shareholder of T-Mobile US?
Deutsche Telekom AG is the largest shareholder with approximately 51.5% ownership, giving it majority control over corporate decisions.
What percentage of T-Mobile is publicly traded?
About 48.5% of T‑Mobile US shares are held by public and institutional investors, including SoftBank, Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street.
Who is T-Mobile owned by?
T-Mobile US is majority-owned by Deutsche Telekom, the German telecommunications giant. Deutsche Telekom holds around 48% of T-Mobile US’s shares. The remaining shares are publicly traded, with a significant portion held by institutional investors.
Are AT&T and T-Mobile the same company?
No, AT&T and T-Mobile are separate companies. Both are major wireless carriers in the U.S., but they operate independently, offering different services and networks. They are competitors in the telecom industry.
Is T-Mobile owned by Ryan Reynolds?
Ryan Reynolds is not the owner of T-Mobile. However, he previously owned a stake in Mint Mobile, a company acquired by T-Mobile in 2024. While Reynolds was a part-owner of Mint, he did not own T-Mobile.
Who are the main shareholders of T-Mobile?
The largest shareholder of T-Mobile is Deutsche Telekom, which owns about 48% of the company. Other significant shareholders include institutional investors such as Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and T. Rowe Price.
Who runs T-Mobile now?
T-Mobile is currently led by Mike Sievert, who became the CEO in April 2020. He succeeded John Legere, who had been at the helm from 2012 to 2020. Sievert continues to drive T-Mobile’s expansion, particularly focusing on 5G technology and customer-centric services.
Is T-Mobile still a German company?
Yes, T-Mobile US is still primarily owned by Deutsche Telekom, which is a German company. Although it operates as a U.S.-based subsidiary, its ownership structure gives Deutsche Telekom significant control.
What does the T in T-Mobile stand for?
The “T” in T-Mobile originally stood for “Telekom”, reflecting its heritage as part of Deutsche Telekom. It was chosen to align the brand with its parent company and European roots.
Is Ultra Mobile T-Mobile?
No, Ultra Mobile is not the same as T-Mobile, though it is owned by T-Mobile. Ultra Mobile is a Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) that offers international calling and prepaid wireless services. It operates under T-Mobile’s network infrastructure.
Who owns T-Mobile Money?
T-Mobile Money is a mobile banking service provided by T-Mobile US. It is a joint venture between T-Mobile and BankMobile, which is part of Customers Bank.
Is Elon Musk involved with T-Mobile?
Elon Musk is not directly involved in T-Mobile. However, T-Mobile has partnered with SpaceX (Musk’s aerospace company) to provide satellite-based 5G service to remote areas, aiming to extend coverage to rural locations using SpaceX’s Starlink satellites.
How many countries use T-Mobile?
T-Mobile’s brand and services are available in several countries worldwide, with its largest presence in the United States, Germany, Austria, Poland, and the Netherlands. T-Mobile also operates in other countries through subsidiaries and partnerships in Europe and beyond.
Who owns T-Mobile UK?
T-Mobile UK was previously part of T-Mobile’s global operations. However, in 2010, T-Mobile UK merged with Orange UK to form Everything Everywhere. In 2016, Everything Everywhere rebranded as EE, and it is now owned by BT Group.
Did AT&T buy T-Mobile?
AT&T attempted to acquire T-Mobile US in 2011 but was blocked by the U.S. Department of Justice due to antitrust concerns. The deal was valued at $39 billion. As a result, T-Mobile remained an independent company.
Who owns T-Mobile in 2025?
As of 2025, T-Mobile US is still majority-owned by Deutsche Telekom (approximately 48%). The remaining shares are publicly traded, with significant ownership by institutional investors.
T-Mobile is owned by what company?
T-Mobile is owned primarily by Deutsche Telekom, a global telecommunications company based in Germany.
Who owns T-Mobile USA?
T-Mobile US is majority-owned by Deutsche Telekom, with the remaining shares held by public investors.
Who merged with T-Mobile?
In 2020, Sprint merged with T-Mobile US, consolidating its operations and spectrum holdings. This merger helped T-Mobile expand its customer base and 5G coverage.
Who bought out T-Mobile?
T-Mobile US has not been bought out in recent years. However, it has acquired several companies, including MetroPCS, Mint Mobile, and Ultra Mobile. The Sprint merger in 2020 was a major acquisition, but T-Mobile was the acquirer.

