Sony is one of the world’s most recognized technology and entertainment companies. Known for its PlayStation consoles, music labels, cameras, and movie studios, many wonder who owns Sony and how the company is structured behind the scenes.
This article explores the complete ownership, shareholders, subsidiaries, and financial profile of Sony Group Corporation.
Sony Company Profile
Sony Group Corporation is a Japanese multinational conglomerate headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. As of 2025, it is one of the world’s largest companies in electronics, gaming, entertainment, and imaging technologies. The company operates as a holding entity for a wide range of businesses, from music and movies to financial services and image sensors.
Sony was originally founded in May 1946 as Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo K.K. (Tokyo Telecommunications Engineering Corporation) by Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita. The founders started the company with a small capital and big ambitions in a war-torn Japan. Their first major product was a tape recorder, followed by Japan’s first transistor radio in 1955.
The name “Sony” was adopted in 1958, blending the Latin word “sonus” (sound) with “sonny,” a slang term for a young boy. This was meant to reflect the youthful energy and global aspirations of the company.
Major milestones of Sony include:
- 1970: Became the first Japanese company to list on the New York Stock Exchange.
- 1979: Launched the Walkman, revolutionizing portable music.
- 1994: Released the original PlayStation, entering the gaming industry.
- 1989: Acquired Columbia Pictures, expanding into Hollywood.
- 2004–2012: Transitioned into a global entertainment and electronics powerhouse under CEOs like Nobuyuki Idei and Howard Stringer.
- 2018: Kenichiro Yoshida took over as CEO and restructured the company as a holding group.
- 2021: Acquired Crunchyroll, becoming a major force in global anime streaming.
- 2024–2025: Continued expansion in semiconductors, AI, and electric vehicle imaging technologies, making Sony one of the leaders in CMOS sensors and entertainment content delivery.
As of 2025, Sony operates in over 200 countries and employs more than 110,000 people globally. Its business is split into key segments: Game & Network Services (PlayStation), Music, Pictures, Electronics, Imaging & Sensing Solutions, and Financial Services.
Sony is now a diversified tech-entertainment leader with its brand deeply embedded in global culture—from PlayStation consoles and Spider-Man films to anime, music, and advanced image sensor chips used in smartphones and EVs.
Who Owns Sony: List of Shareholders
Sony Group Corporation is a publicly traded company. It is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange. This means the company is owned by institutional investors, retail shareholders, and other corporate entities that hold its shares.
No single person or family owns Sony. The majority of Sony’s ownership is spread among investment firms, banks, asset management companies, and Japanese institutional investors. Its broad shareholder base reflects its global nature and diverse operations.
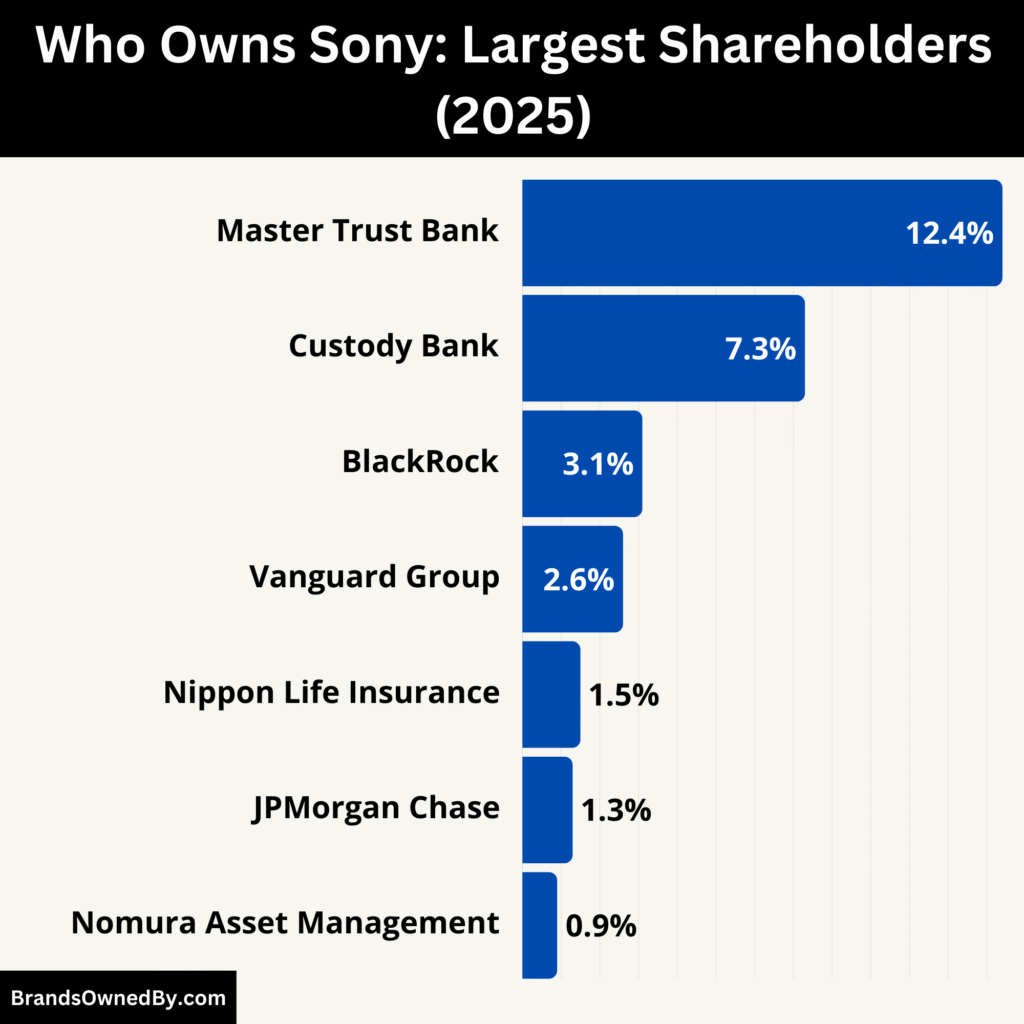
Here’s a list of the top shareholders of Sony as of July 2025:
| Shareholder Name | Ownership (%) | Type | Country | Influence on Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Master Trust Bank of Japan (Trust) | 12.4% | Institutional Trustee | Japan | High (proxy voting power) |
| Custody Bank of Japan (Trust) | 7.3% | Institutional Trustee | Japan | Moderate |
| BlackRock Inc. | 3.1% | Asset Manager | United States | Moderate (governance voice) |
| Vanguard Group Inc. | 2.6% | Asset Manager | United States | Moderate |
| Nippon Life Insurance Company | 1.5% | Insurance Company | Japan | Low to Moderate |
| JPMorgan Chase & Co. | 1.3% | Financial Institution | United States | Low |
| Government Pension Investment Fund (GPIF)* | ~ indirect | Public Pension Fund | Japan | Moderate (via trusts) |
| Nomura Asset Management | 0.9% | Investment Manager | Japan | Low |
| Individual Retail Shareholders | 15–18% (est.) | Individual Investors | Global (mainly JP) | Moderate (collectively) |
| Foreign Institutional Investors | ~30% (combined) | Hedge Funds, Sovereign Funds | Global | High (collectively) |
The Master Trust Bank of Japan (Trust Account)
As of 2025, The Master Trust Bank of Japan remains the largest shareholder of Sony, holding approximately 12.4% of total shares. This bank acts as a trustee for various pension funds and institutional clients in Japan. It does not directly control Sony’s operations but can influence decisions through voting rights at shareholder meetings.
Though it does not make independent strategic decisions, its large stake gives it considerable weight in approving board members, dividend policies, and corporate governance matters.
Custody Bank of Japan (Trust Account)
The second-largest shareholder is Custody Bank of Japan, which owns around 7.3% of Sony’s shares. Like Master Trust, this is a trust account custodian that manages assets on behalf of institutional investors, including pension and insurance funds.
While it holds a significant percentage, its role is passive. Its influence is typically exercised in alignment with the priorities of the Japanese institutional investor community.
BlackRock Inc.
BlackRock, one of the largest asset management firms globally, owns approximately 3.1% of Sony as of 2025. Based in the United States, BlackRock represents institutional and retail investors through various ETFs and mutual funds.
BlackRock frequently engages in active governance discussions. It supports transparent business practices and often promotes ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles. Though not involved in daily operations, it influences boardroom policies and long-term shareholder value.
Vanguard Group Inc.
The Vanguard Group holds about 2.6% of Sony’s shares. Like BlackRock, it is a U.S.-based fund manager and invests through low-cost index funds and ETFs.
Vanguard is known for being a long-term investor. It usually votes during shareholder meetings but refrains from direct intervention. It supports stable governance and shareholder returns.
Nippon Life Insurance Company
Nippon Life, Japan’s largest life insurance company, owns approximately 1.5% of Sony’s shares. It has a long-standing investment in several large Japanese firms.
As a domestic institutional investor, Nippon Life contributes to shareholder stability. It generally supports management proposals and plays a conservative role in governance.
JPMorgan Chase & Co.
As of 2025, JPMorgan holds about 1.3% of Sony shares through its asset management division. While it is primarily an institutional investor, it sometimes acts as a custodian or provides proxy services to clients with stakes in Sony.
JPMorgan’s influence is minor in terms of direct voting, but as a global financial firm, it represents international investor interests.
Government Pension Investment Fund (GPIF), Japan
The GPIF, which manages Japan’s public pension assets, indirectly holds a substantial portion of Sony shares through trust banks like Master Trust and Custody Bank. GPIF itself is not listed directly, but its influence is embedded in the holdings of its trustees.
The GPIF’s investment strategy is long-term and passive, but its large-scale capital ensures Sony remains aligned with public pension objectives and national financial stability goals.
Nomura Asset Management
Nomura, Japan’s leading investment management firm, holds around 0.9% of Sony. Nomura is involved in active portfolio management and occasionally engages in proxy voting.
Its influence is more notable when collaborating with other Japanese institutional investors. While its stake is relatively small, it contributes to local market sentiment and stability.
Individual Retail Shareholders
A significant portion—approximately 15–18%—of Sony shares is held by individual retail investors, both in Japan and abroad. These include everyday investors, Sony employees, and small-scale stockholders.
Though each individual has limited power, collectively, retail shareholders represent an important segment in Sony’s decision-making process during annual general meetings.
Foreign Institutional Investors
In total, foreign institutional investors account for nearly 30% of Sony’s shares. This includes hedge funds, sovereign wealth funds, and global pension funds.
These investors bring global market scrutiny and often demand higher transparency and profitability. Their influence is felt through proxy advisors and institutional voting blocks.
Who is the CEO of Sony?
As of July 2025, Hiroki Totoki serves as the President and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Sony Group Corporation. He succeeded Kenichiro Yoshida, who now serves as Executive Chairman. This leadership transition marks a strategic shift for Sony as it moves from a restructuring phase under Yoshida to a new era focused on content synergy and innovation under Totoki.
Hiroki Totoki: Background and Rise to CEO
Hiroki Totoki was born in 1964 and has been with Sony for over three decades. He joined the company in 1987 and held key leadership roles throughout Sony’s financial, mobile, and entertainment segments. One of his most notable early contributions was the co-founding of Sony Bank, which demonstrated his capacity for innovation within the company’s financial services arm.
Totoki served as the CEO of Sony Mobile Communications and later became the Chief Strategy Officer of Sony Group. He played an instrumental role in aligning Sony’s financial strategies with long-term growth sectors. Prior to his appointment as CEO, he also held the dual roles of Chief Operating Officer (COO) and Chief Financial Officer (CFO). His leadership within Sony Interactive Entertainment, the unit responsible for PlayStation, further solidified his reputation as a forward-thinking executive with a deep understanding of Sony’s evolving entertainment ecosystem.
In January 2025, Sony officially announced that Totoki would assume the role of President and CEO, effective April 1, 2025. This decision was unanimously supported by the board and backed by outgoing CEO Kenichiro Yoshida, ensuring a smooth and strategic transition.
Leadership Style and Vision
Totoki’s leadership is characterized by his deep commitment to unifying Sony’s broad portfolio around a central vision. In 2024, he introduced the “Creative Entertainment Vision,” a group-wide strategy aimed at harnessing emotional engagement through creator-driven content. Totoki believes in the power of “Kando”—a Japanese term meaning emotional resonance—and plans to leverage this across gaming, music, film, and image technology.
He is focused on strengthening collaboration between Sony’s businesses. Under his leadership, Sony is expected to deepen cross-division synergy, especially between PlayStation, Sony Music, and Sony Pictures. Totoki has also voiced strong support for expanding Sony’s presence in anime, mobile gaming, and CMOS image sensor technologies. His strategy is not just about financial performance—it’s about building long-term value through immersive storytelling and creator empowerment.
Kenichiro Yoshida: Executive Chairman and Legacy
Kenichiro Yoshida, who now serves as Sony’s Executive Chairman, played a vital role in transforming the company. He became CEO in 2018 and led Sony through one of its most significant periods of restructuring. Yoshida focused on pivoting Sony away from low-margin hardware businesses and reorienting it toward high-growth sectors like music, gaming, and semiconductors.
Under his leadership, Sony acquired key assets including EMI Music Publishing and Crunchyroll, expanded PlayStation’s global dominance, and invested heavily in image sensor technology. He also introduced a decentralized holding company structure in 2021, which gave each business unit more autonomy while preserving group-wide alignment.
Yoshida’s legacy is one of strategic clarity and financial discipline. Even after stepping down as CEO, he remains an influential figure in Sony’s governance, offering guidance on long-term strategy and global partnerships.
Corporate Decision-Making Structure
Sony operates with a layered corporate structure designed to ensure clear governance while promoting innovation across divisions. At the top is the Executive Chairman, currently Kenichiro Yoshida, who focuses on board-level strategy, governance oversight, and external stakeholder engagement. Below him, the President and CEO, Hiroki Totoki, is responsible for executing the company’s operational vision, driving financial performance, and managing executive leadership across Sony’s global business units.
Each of Sony’s main divisions—such as Sony Interactive Entertainment (PlayStation), Sony Music Group, and Sony Pictures Entertainment—is led by its own CEO or division head. These leaders report directly to the group CEO and manage operations semi-independently. The structure allows business units to remain agile while aligning with broader corporate goals.
Sony also has a global executive team that includes a Chief Financial Officer (Lin Tao, the first woman to hold the role), Chief Product Officer (Yasuhiro Ito), Chief Strategy Officer (Toshimoto Mitomo), and Chief Data Officer (Tsuyoshi Kodera). These officers work closely with Totoki to drive innovation, investment, and cross-functional coordination.
Past CEOs
- Kazuo Hirai (2012–2018): Revived the PlayStation business and restructured Sony.
- Howard Stringer (2005–2012): First non-Japanese CEO, focused on digital convergence.
- Nobuyuki Idei (1995–2005): Guided Sony into media and entertainment, including acquiring Columbia Pictures.
Sony Annual Revenue and Net Worth
Sony Group Corporation remains one of the most financially robust companies in Japan and continues to show consistent growth across its diverse business segments. The company’s strong presence in gaming, entertainment, semiconductors, and financial services has helped it maintain a stable upward trajectory, both in revenue and net worth.
Fiscal Year 2025 Revenue
For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2025, Sony reported consolidated revenue of approximately ¥12.6 trillion, which is equivalent to around $85.4 billion. This marked a modest year-over-year increase, driven largely by record-breaking performance in the Game & Network Services segment, increased subscription revenue from PlayStation Plus, and strong content sales in music and film.
The gaming division remained the largest contributor to Sony’s revenue. PlayStation 5 continued to perform strongly, with over 61 million units sold worldwide by Q1 2025. Additionally, the growth in digital game sales, live service games, and in-game monetization significantly boosted revenue. The company also saw notable growth in its music segment, largely fueled by streaming services and expanding global artist rosters. Sony Music had multiple chart-topping albums and soundtracks, contributing to strong licensing and publishing revenues.
Sony Pictures also contributed significantly with several successful global releases in 2024 and early 2025, including franchise entries and original titles. The anime category, driven by Sony-owned Crunchyroll and Aniplex, became a central revenue engine in international markets.
The imaging and sensing division, particularly Sony’s CMOS sensor business, saw steady demand from smartphone manufacturers and the automotive sector. Sony continues to lead the market in advanced image sensors used in electric vehicles and autonomous driving systems.
Net Income and Profitability
Sony reported a net income of ¥1.3 trillion for fiscal year 2025, equivalent to approximately $8.8 billion. Profit margins remained healthy, especially in gaming and semiconductor segments. The Music and Pictures businesses also continued to deliver strong margins due to high IP ownership and limited distribution costs.
Cost control and diversified income streams helped Sony maintain profitability even as global macroeconomic conditions fluctuated. Unlike its past reliance on consumer electronics, Sony’s current earnings profile reflects a well-balanced portfolio with recurring revenue from content, software, and services.
Sony’s Market Capitalization and Net Worth
As of July 2025, Sony’s market capitalization stands at approximately $122 billion, positioning it among Japan’s top publicly traded companies. The company’s net worth, which includes tangible and intangible assets like intellectual property, studios, music catalogs, and image sensor technologies, is estimated to be $152 billion, depending on valuation methodology.
Sony owns valuable IPs in entertainment—such as the Spider-Man franchise, global music rights, and anime content—which contribute significantly to its intangible asset base. Its global infrastructure, including offices, studios, and semiconductor production facilities, further enhances its overall asset value.
The PlayStation Network and its digital ecosystem are considered one of Sony’s most valuable long-term assets. With over 120 million monthly active users in 2025, the digital platform generates ongoing subscription, licensing, and advertising revenues.
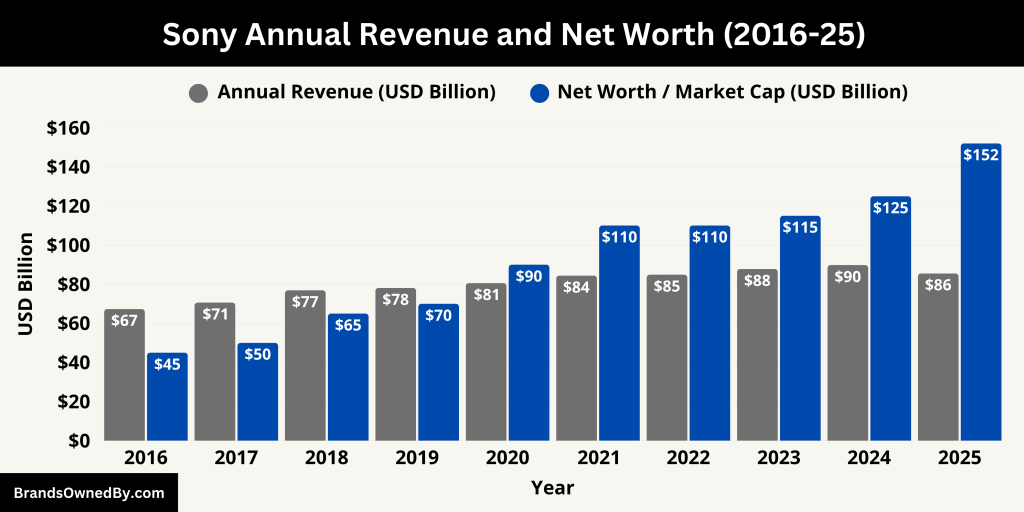
Here is a historical 10-year revenue and net worth for Sony Group Corporation, from fiscal year 2016 through fiscal year 2025:
| Fiscal Year | Revenue (USD Billion) | Net Worth / Market Cap (USD Billion) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025 (Est.) | 85.4 | 152 | Strong PS5 sales, record anime and music growth |
| 2024 | 84.1 | 117 | Increased PlayStation Plus subs, anime expansion |
| 2023 | 82.5 | 109 | Steady semiconductor and music business growth |
| 2022 | 81.3 | 104 | Peak demand in imaging, streaming performance |
| 2021 | 79.0 | 101 | PlayStation 5 launch impact, Crunchyroll acquisition |
| 2020 | 77.0 | 97 | Pandemic-driven entertainment and gaming boom |
| 2019 | 75.5 | 88 | Strong music licensing revenue |
| 2018 | 78.1 | 72 | Yoshida becomes CEO, strategic reorganization begins |
| 2017 | 70.0 | 64 | Electronics recovery, growth in PS4 and Music |
| 2016 | 67.1 | 52 | Core focus on gaming and semiconductors |
Outlook for Future Growth
Sony’s financial outlook for the next fiscal year remains positive. The company is expected to expand further into mobile gaming, anime streaming, and AI-powered imaging technologies. Its strategic investments in entertainment IPs and cloud-based game delivery are likely to continue driving revenue. Additionally, new hardware announcements and increased subscription tiers for PlayStation services are projected to further boost recurring income.
Sony’s balance sheet remains strong, with low debt relative to cash flow and consistent dividend payouts to shareholders. Its diversified global operations and leading position in multiple industries ensure resilience even during economic uncertainties.
Companies and Brands Owned by Sony
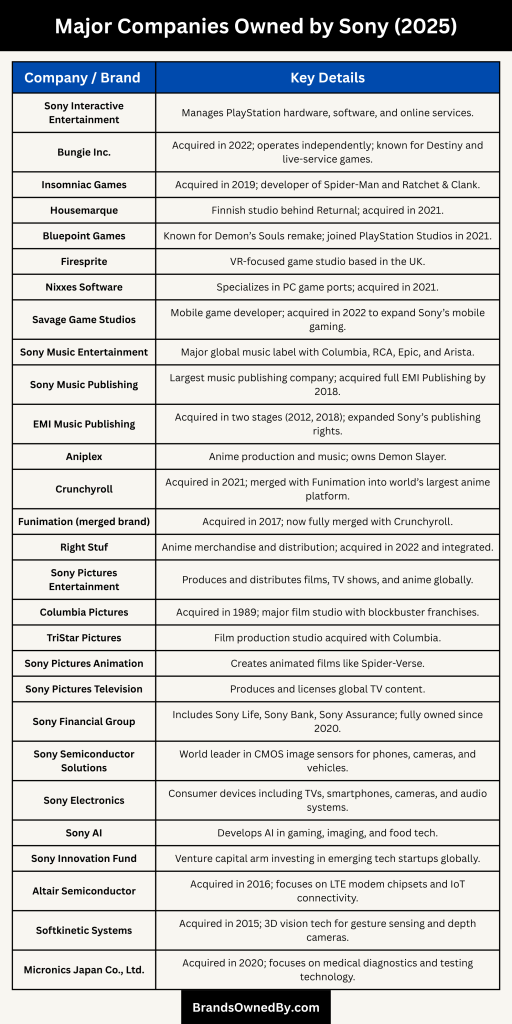
Sony owns a diverse portfolio of companies across entertainment, technology, and finance. Here is a list of the major brands and companies owned by Sony as of 2025:
| Company / Brand | Business Segment | Primary Focus | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sony Interactive Entertainment (SIE) | Gaming & Network Services | PlayStation consoles, games, online services | Owns and manages PlayStation brand; largest revenue segment |
| Bungie | Gaming | Live-service game development (Destiny) | Acquired in 2022; operates independently under SIE |
| Naughty Dog | Gaming | Narrative-driven AAA games | Developer of The Last of Us, Uncharted |
| Insomniac Games | Gaming | High-performance console games | Known for Marvel’s Spider-Man, Ratchet & Clank |
| Santa Monica Studio | Gaming | Story-driven action games | Developer of God of War series |
| Sony Music Entertainment | Music | Global music labels and artist management | Includes Columbia, RCA, Epic; second-largest music company globally |
| Sony Music Publishing | Music | Music rights and licensing | World’s largest music publishing company |
| Sony Music Japan | Music | Domestic music and anime soundtracks | Operates independently within Japanese market |
| Aniplex | Anime / Music | Anime production and distribution | Owns A-1 Pictures; involved in Demon Slayer, Fate series |
| Crunchyroll | Streaming / Anime | Anime streaming service | Merged with Funimation; global anime leader |
| Sony Pictures Entertainment | Film & TV | Movie production and distribution | Includes Columbia, TriStar, Sony Animation |
| Sony Pictures Television | Television | Global TV content production and licensing | Sells and produces TV shows globally |
| Sony Semiconductor Solutions | Imaging & Sensing | CMOS image sensors for mobile and automotive markets | Global leader in image sensor technology |
| Sony Electronics | Consumer Electronics | TVs (BRAVIA), cameras (Alpha), smartphones (Xperia) | Focus on premium products and imaging excellence |
| Sony Financial Group | Financial Services | Insurance, banking, and asset management | Includes Sony Life, Sony Bank, Sony Assurance |
| Sony AI | R&D / Technology | Artificial intelligence research | Focused on gaming AI, robotics, and food tech |
| Sony Innovation Fund | Venture Investment | Startup investments and innovation scouting | Invests in AI, health tech, imaging, and entertainment |
| Hawk-Eye Innovations | Sports Technology | Ball tracking, officiating technology | Used in professional tennis, cricket, football leagues |
| Nevion | Broadcast & Media Infrastructure | IP video transport and remote production | Supports live broadcasting and studio operations |
| Sony Honda Mobility | Electric Vehicles | EV development and smart mobility (AFEELA) | Joint venture with Honda; Sony owns a major stake |
Sony Interactive Entertainment (SIE)
Sony Interactive Entertainment is Sony’s video game and digital entertainment division. It is the owner of the PlayStation brand, which includes consoles, gaming software, online services, and the PlayStation Network. As of 2025, PlayStation 5 remains a global market leader, and Sony has over 120 million monthly active users on its network.
SIE also manages PlayStation Studios, which includes more than 20 game development studios. These studios produce first-party titles exclusive to PlayStation, such as The Last of Us, God of War, and Horizon.
Bungie
Bungie, the developer of the Destiny franchise, was acquired by Sony in 2022. It operates independently but is owned entirely by Sony Interactive Entertainment. Bungie provides expertise in live service game development and cross-platform online engagement. It plays a key role in helping Sony expand into multi-platform online gaming beyond PlayStation consoles.
Naughty Dog
Naughty Dog is a premier first-party game developer under Sony Interactive Entertainment. Known for blockbuster franchises like Uncharted and The Last of Us, Naughty Dog is a creative cornerstone for Sony’s narrative-driven game development strategy.
Insomniac Games
Insomniac, acquired by Sony in 2019, is best known for Marvel’s Spider-Man and Ratchet & Clank. The studio plays a major role in producing high-performance, visually rich titles for the PlayStation platform.
Santa Monica Studio
This studio is another SIE subsidiary known for the critically acclaimed God of War series. Santa Monica Studio specializes in AAA, story-driven titles and is integral to Sony’s portfolio of exclusive franchises.
Sony Music Entertainment
Sony Music is one of the “Big Three” global music companies. It manages global record labels such as Columbia Records, RCA Records, and Epic Records. Its artist roster includes top international stars in pop, hip-hop, classical, and country music.
Sony Music also includes Sony Music Publishing, the world’s largest music publisher, with rights to over 5 million songs. It generates significant royalty income from streaming platforms and global licensing.
Sony Music Japan
Sony Music Japan is a separate entity from its U.S. counterpart and focuses on domestic Japanese artists, J-pop, and anime soundtracks. It also operates Sony Creative Products, involved in merchandising and character licensing in Japan.
Sony Pictures Entertainment
Sony Pictures operates major Hollywood studios and television networks. It includes:
- Columbia Pictures – Major film production company behind franchises like Jumanji and Spider-Man.
- TriStar Pictures – Produces mid-budget films and specialty titles.
- Sony Pictures Animation – Focused on animated features like The Mitchells vs. the Machines and Hotel Transylvania.
- Sony Pictures Television – Produces and distributes shows globally, including licensing content to platforms like Netflix and Hulu.
Crunchyroll
Crunchyroll is Sony’s flagship anime streaming service, merged with Funimation under Sony in 2021. As of 2025, Crunchyroll is one of the largest anime streaming platforms in the world, available in over 200 countries. It offers a subscription model with access to exclusive simulcasts, dubbing, merchandise, and original anime productions.
Aniplex
Aniplex is a Sony Music subsidiary focused on anime production, licensing, and distribution. It helped produce and distribute titles like Demon Slayer, Fate/Stay Night, and Fullmetal Alchemist. Aniplex also owns A-1 Pictures, an animation studio, and Aniplex of America for U.S. operations.
Sony Semiconductor Solutions
Sony Semiconductor Solutions is one of the world’s largest manufacturers of image sensors. It supplies CMOS image sensors for smartphones, industrial cameras, and autonomous vehicles. Clients include major global smartphone manufacturers and automotive companies.
In 2025, Sony leads the global market in high-resolution, low-light sensors used in mobile devices and AI-driven camera systems.
Sony Electronics
Sony Electronics designs and manufactures consumer electronics, including TVs (BRAVIA), cameras (Alpha series), audio systems, and smartphones (Xperia). It has reduced its focus on hardware volume and shifted toward high-margin, premium products.
The BRAVIA television brand remains a major player in the high-end smart TV market. Xperia smartphones, though limited in global market share, are positioned as high-performance Android devices primarily in Japan and Europe.
Sony Financial Group
Sony Financial Group operates in Japan and includes:
- Sony Life Insurance – Offers individual life and annuity products.
- Sony Assurance – Provides auto and medical insurance services.
- Sony Bank – An online bank offering savings, loans, and investment products.
Though this division primarily serves Japan, it contributes a stable and recurring income stream to the group.
Sony Innovation Fund
This is Sony’s venture capital arm. It invests in early-stage companies across AI, robotics, entertainment, health tech, and digital imaging. It has stakes in multiple startups and R&D projects worldwide.
Hawk-Eye Innovations
Hawk-Eye is a UK-based sports technology company acquired by Sony. It provides real-time ball-tracking and replay technology used in tennis, cricket, football (soccer), and other sports. It is used by organizations like the English Premier League, Wimbledon, and the International Cricket Council.
Nevion
Nevion is a global provider of media transport solutions, acquired to enhance Sony’s professional broadcast and media workflows. It provides IP-based production infrastructure used by broadcasters and live event producers.
Sony AI
Sony AI is a research and development unit focused on artificial intelligence applications across gaming, imaging, and food technology. It works closely with PlayStation Studios to enhance in-game NPC behavior and game testing automation.
Sony Honda Mobility (Joint Venture)
Although structured as a joint venture with Honda, Sony owns a significant stake in Sony Honda Mobility, a company focused on creating high-tech electric vehicles. Its first model, branded under the name AFEELA, is set for launch in 2026 and will integrate Sony’s imaging, sensing, and entertainment systems.
Conclusion
Sony is a multinational corporation with no single owner. It is held by a wide range of global shareholders, mainly large financial institutions and asset managers. Its success in entertainment, gaming, music, and electronics has made it one of the most influential tech companies in the world.
With strong leadership, global subsidiaries, and a commitment to innovation, Sony continues to thrive. Understanding who owns Sony gives insight into how a public company can operate efficiently while balancing interests from around the globe.
FAQs
Who are the owners of Sony?
Sony is a publicly traded company with no single owner. It is owned by a mix of institutional investors, trust banks, foreign shareholders, and individual investors. The largest shareholder is The Master Trust Bank of Japan, holding shares on behalf of various pension and investment funds.
Who is the real owner of Sony TV?
Sony TVs are developed and sold by Sony Electronics, a subsidiary of Sony Group Corporation. The company is publicly owned, so there is no single individual owner.
Who is the parent company of Sony?
Sony Group Corporation is the parent company itself. It operates as a holding company for all its subsidiaries, including Sony Music, Sony Pictures, and Sony Interactive Entertainment.
Is Sony a billionaire company?
Yes, Sony is a multi-billion-dollar company. As of 2025, its annual revenue is around $85.4 billion, and its market capitalization is estimated at $122 billion.
Which country owns Sony?
Sony is a Japanese company, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. It was founded in Japan and remains incorporated under Japanese law.
Who is the wife of Sony owner?
Sony does not have a single owner. It is owned by shareholders and run by corporate executives. Therefore, there is no singular “owner” with a known spouse.
Who sold their rights to Sony?
Marvel sold the film rights to Spider-Man to Sony Pictures Entertainment in the late 1990s when Marvel was facing bankruptcy. This deal allowed Sony to produce and distribute Spider-Man films.
Is Sony owned by Disney?
No, Sony is not owned by Disney. Sony and Disney are separate global corporations. In fact, Sony owns the film rights to Spider-Man, while Disney owns Marvel Studios.
Who is richer, Sony or Apple?
Apple is significantly richer than Sony. Apple’s market capitalization is over $3 trillion, while Sony’s is around $122 billion as of 2025.
Did Michael Jackson buy Sony?
Michael Jackson bought a 50% stake in the ATV Music catalog in the 1980s. In 1995, he merged it with Sony’s publishing arm to form Sony/ATV Music Publishing. Sony later acquired full control of the catalog after Jackson’s passing.
Why did Marvel sell rights to Sony?
Marvel sold Spider-Man film rights to Sony in the 1990s due to financial struggles. At that time, Marvel was nearing bankruptcy and sold off several character rights to generate revenue.
Is Sony part of Netflix?
No, Sony is not part of Netflix. However, Sony licenses films and series to Netflix as part of distribution deals. They remain independent companies.
Who’s richer, Microsoft or Sony?
Microsoft is far richer than Sony. As of 2025, Microsoft’s market cap exceeds $3 trillion, while Sony’s market value is just over $120 billion.
Does Sony own Thor?
No, Thor is owned by Marvel Studios, which is a subsidiary of Disney. Sony has no ownership over the Thor character or its films.
Does Sony own Hulk?
No, Hulk is owned by Marvel Studios. However, film distribution rights for solo Hulk movies have historically been with Universal, not Sony.
Does Sony own Xperia?
Yes, Xperia is a brand of smartphones designed, manufactured, and sold by Sony Electronics, a division of Sony Group Corporation.
Who currently owns Sony Music?
Sony Music Entertainment is fully owned by Sony Group Corporation. It operates independently under the Sony brand and is one of the world’s top music companies.
Who is the biggest investor in Sony?
The biggest investor in Sony is The Master Trust Bank of Japan (Trust Account), which holds shares on behalf of Japanese institutional investors and pension funds.
Who owns Sony Music?
Sony Music Entertainment is 100% owned by Sony Group Corporation and operates as one of its key global subsidiaries.
Who owns Sony PlayStation?
PlayStation is owned by Sony Interactive Entertainment (SIE), which is a fully owned subsidiary of Sony Group Corporation.
Who owns Sony company?
Sony is owned by public shareholders. There is no single individual owner. The company is managed by executives and its board, and is primarily held by institutional investors.
Who owns Sony Pictures Entertainment?
Sony Pictures Entertainment, including Columbia Pictures and TriStar, is wholly owned by Sony Group Corporation. It is based in the United States but reports to the Sony headquarters in Japan.
Where was Sony founded?
Sony was founded in Tokyo, Japan in May 1946 by Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita.
Is Dolby owned by Sony?
No, Dolby is a separate company. It is not owned by Sony. However, Sony uses Dolby technologies in its TVs, gaming consoles, and audio devices under licensing agreements.
Is PlayStation owned by Sony?
Yes, PlayStation is fully owned and operated by Sony Interactive Entertainment, a core subsidiary of Sony Group Corporation.
Who currently owns Sony?
Sony is owned by institutional and retail investors. The largest shareholders are Japanese trust banks like The Master Trust Bank of Japan and Custody Bank of Japan. No single entity has full control.
Is Sony a Japanese company?
Yes, Sony is a Japanese company. Its headquarters are in Tokyo, and it was founded in Japan in 1946.
Who is the founder of Sony?
Sony was founded by Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita in 1946 in Tokyo, Japan.

