This article explores who owns Nvidia and its ownership structure. Nvidia, known for its graphics processing units (GPUs), has revolutionized gaming, AI, and data centers. Understanding who owns this influential company helps clarify the power dynamics behind its innovation and market strategy.
History of Nvidia
Nvidia was founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang, Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem. It began as a small startup in Santa Clara, California, focused on graphics technology for computers. In the late 1990s, Nvidia became a major player in the graphics card market with the launch of its RIVA series. Over the years, Nvidia expanded its portfolio to include cutting-edge technology such as artificial intelligence (AI), self-driving cars, and data centers.
By the early 2000s, the company was well-established, continuously improving its graphics processing units (GPUs). Nvidia’s innovations helped define the gaming and professional graphics markets, leading it to the dominance it enjoys today.
Who Owns Nvidia: Largest Shareholders
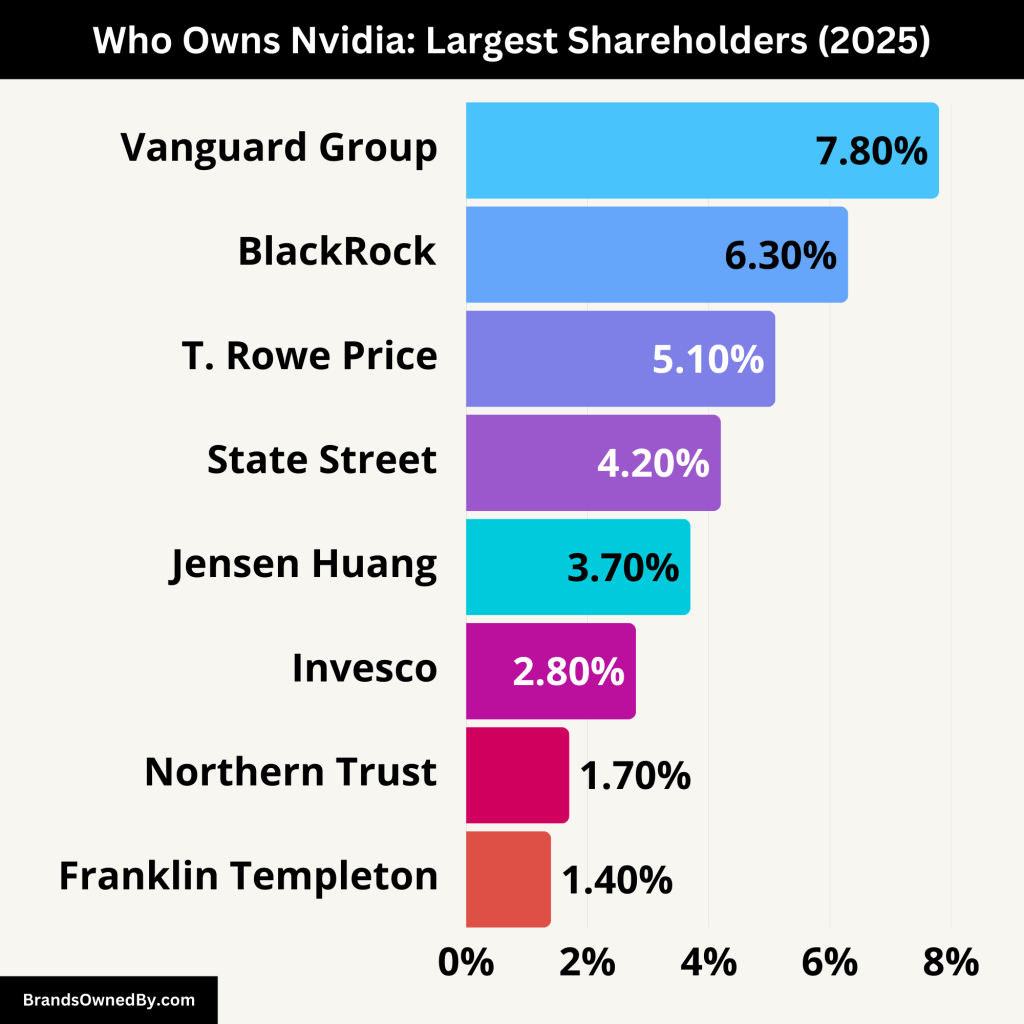
The ownership of Nvidia is divided among a range of institutional investors, retail investors, and key stakeholders. The largest shareholder is typically the company’s CEO and co-founder, Jensen Huang. He has retained a significant portion of the company’s shares since its founding.
Huang owns a substantial number of Nvidia shares, making him one of the wealthiest individuals in the tech industry. Alongside Huang, other institutional investors such as Vanguard Group and BlackRock own large portions of the company.
Below is a list of the major shareholders of Nvidia:
| Shareholder | Percentage of Ownership | Type of Shareholder | Role/Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jensen Huang | 3.7% | Individual | CEO and co-founder, largest individual shareholder, strategic decision-maker. |
| Vanguard Group | 7.8% | Institutional | Major institutional investor, significant influence on corporate governance and decisions. |
| BlackRock | 6.3% | Institutional | Major institutional investor, strong influence on strategic direction and corporate policies. |
| T. Rowe Price Associates | 5.1% | Institutional | Growth-focused institutional investor, plays a role in shaping long-term strategy. |
| State Street Corporation | 4.2% | Institutional | Significant institutional investor with a strong voice in shareholder meetings. |
| Invesco | 2.8% | Institutional | Active investor focused on growth opportunities, contributing to governance decisions. |
| Northern Trust | 1.7% | Institutional | Smaller institutional shareholder, influences corporate policies and strategic matters. |
| Franklin Templeton | 1.4% | Institutional | Institutional investor, brings additional stability and strategic influence. |
| Other Institutional Investors | Varies (smaller shares) | Institutional | Includes firms like Janus Henderson, Wellington Management, Charles Schwab, etc., with a collective influence on governance. |
| Retail Investors | Varies (collective) | Retail | Large base of individual investors with voting power on shareholder matters. |
Jensen Huang
Jensen Huang, co-founder and CEO of Nvidia, is the largest individual shareholder of the company. He owns around 3.7% of Nvidia’s total shares. While Huang’s stake may seem relatively modest compared to institutional investors, his influence over the company’s strategy and vision is immense. He plays a key role in shaping Nvidia’s innovation and future direction.
As CEO, Huang is directly responsible for the company’s day-to-day operations, technological advancements, and long-term strategic goals. His leadership in areas like gaming, AI, and data centers has been critical to Nvidia’s growth.
Vanguard Group
Vanguard Group is one of the leading institutional investors in Nvidia, holding approximately 7.8% of the company’s shares. Vanguard’s role is pivotal, as it is one of the largest asset management firms globally.
The firm’s investment in Nvidia aligns with its long-term strategy of investing in innovative and growth-driven companies. Vanguard has considerable sway in Nvidia’s decision-making process, particularly in shareholder meetings where it helps guide corporate governance and strategic direction. Vanguard’s large stake in Nvidia makes it an important player in determining the future of the company.
BlackRock
BlackRock is another significant institutional investor in Nvidia, owning about 6.3% of the company’s shares. As one of the largest asset management firms in the world, BlackRock’s ownership provides it with significant voting power during shareholder meetings.
BlackRock’s investment reflects confidence in Nvidia’s future potential, especially with the company’s focus on AI, data centers, and gaming technologies. It often has an active role in corporate governance, helping ensure Nvidia’s financial strategies align with shareholder interests.
T. Rowe Price Associates
T. Rowe Price Associates is one of the largest institutional investors in Nvidia, with approximately 5.1% of the company’s shares. T. Rowe Price is known for its expertise in growth investing, and its substantial stake in Nvidia highlights its belief in the company’s long-term prospects.
The firm’s involvement is crucial, as it brings a focus on strategic growth and value creation. T. Rowe Price’s influence ensures that Nvidia remains aligned with investor expectations and market trends, making it a key shareholder in the company.
State Street Corporation
State Street Corporation owns about 4.2% of Nvidia’s shares. As a major player in the financial services industry, State Street’s investment in Nvidia is part of its broader strategy to invest in high-growth technology companies.
Like Vanguard and BlackRock, State Street holds a significant amount of voting power and can influence decisions related to Nvidia’s corporate policies, acquisitions, and other strategic matters. Their investment signals strong confidence in Nvidia’s market position and long-term prospects.
Invesco
Invesco is another important institutional shareholder, holding approximately 2.8% of Nvidia’s shares. As an investment management firm, Invesco focuses on long-term growth opportunities, and Nvidia fits this strategy perfectly. Invesco’s involvement in Nvidia adds further strength to the company’s investor base, providing additional stability and influence during major decisions, such as mergers, acquisitions, or shareholder votes.
Northern Trust
Northern Trust, a global investment management firm, holds about 1.7% of Nvidia’s shares. Although its stake is smaller compared to Vanguard or BlackRock, Northern Trust’s role as a significant institutional investor means it can still exert influence over Nvidia’s corporate governance and financial decisions. Northern Trust’s involvement also signals confidence in Nvidia’s future, particularly as the company continues to innovate in fields like AI, autonomous vehicles, and gaming.
Franklin Templeton
Franklin Templeton is another institutional investor that holds a notable stake in Nvidia. The company owns around 1.4% of Nvidia’s shares. Known for its global reach in asset management, Franklin Templeton’s investment in Nvidia adds to the diverse institutional shareholder base that supports the company’s long-term growth and stability. Their strategic involvement ensures that Nvidia remains aligned with the interests of its investors.
Other Institutional Investors
Several other institutional investors hold smaller but still significant portions of Nvidia’s stock. These include firms like Janus Henderson Group, Wellington Management, and Charles Schwab Investment Management. Collectively, these investors hold additional shares, contributing to Nvidia’s diversified ownership structure.
While their individual stakes may not be as large as the top investors like Vanguard or BlackRock, these institutions still play a role in shaping Nvidia’s financial decisions and corporate governance. Their influence is felt in annual shareholder meetings and key strategic moves the company makes.
Retail Investors
In addition to institutional investors, Nvidia’s stock is also widely held by retail investors. Retail investors typically own smaller amounts of stock, but collectively they make up a significant portion of Nvidia’s total shareholders. These individual investors often drive market movements and contribute to the company’s liquidity. Retail investors benefit from Nvidia’s market performance and innovations in AI, gaming, and other key sectors.
Although retail investors don’t have the same influence on corporate governance as institutional investors, their presence on the shareholder register shows the broad interest in Nvidia and its growth potential. Their votes on major issues can influence decisions in certain scenarios, particularly on shareholder resolutions or executive compensation matters.
Who Controls Nvidia?
Nvidia is a publicly traded company, but its control rests primarily in the hands of its executive team, especially CEO Jensen Huang, and the board of directors. The control of Nvidia extends beyond ownership, as the company is governed by key decision-makers who guide its direction, technological innovations, and business strategy.
CEO Jensen Huang: The Power Behind Nvidia’s Vision
As the co-founder and CEO, Jensen Huang plays an enormous role in controlling Nvidia’s strategic direction. Huang has been with the company since its inception in 1993 and has been integral to its success. His leadership extends far beyond typical CEO duties. Huang’s vision for the company, especially its focus on high-performance GPUs, AI-driven technologies, and future-facing innovations like autonomous driving, has been a driving force behind Nvidia’s market dominance.
Huang’s power and influence come from both his ownership stake (around 3.7%) and his position as CEO. While institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock own significant portions of Nvidia’s stock, Huang’s strategic decision-making and control of day-to-day operations have made him the face and leader of the company. His unique position allows him to guide Nvidia through evolving industries and maintain a competitive edge in the tech world.
Under his leadership, Nvidia has transformed from a graphics card maker into a leader in AI, gaming, data centers, and autonomous vehicle technology. Huang is also actively involved in product development and high-level partnerships, ensuring that Nvidia stays at the forefront of innovation.
Board of Directors
While Huang has significant control over Nvidia, the final corporate decisions are made in conjunction with Nvidia’s board of directors. The board is made up of key executives, industry experts, and experienced professionals who provide strategic guidance to the company. Their role is to oversee Nvidia’s operations, ensuring the company follows the best practices in terms of governance, risk management, and financial performance.
The board of directors has the ultimate authority in making major decisions, such as approving large investments, acquisitions, and changes in corporate policy. However, the CEO (Jensen Huang) typically drives the strategic direction and presents these decisions to the board. While the board can influence decisions, it is Huang’s vision that typically drives Nvidia’s actions.
Key members of Nvidia’s board of directors include:
- Reed Hastings: Co-founder and former CEO of Netflix, who provides valuable experience in scaling and running a high-growth tech company.
- A. Brooke Seawell: A former venture capital partner who brings deep financial expertise to Nvidia’s governance.
- John Dabiri: An expert in bioengineering and technology, contributing technical insights to the board’s decision-making.
Together, these individuals, along with Huang, help maintain Nvidia’s leadership in the tech sector.
Executive Leadership Team
Beyond the board, Nvidia’s executive leadership team, headed by Huang, controls the company’s day-to-day operations. The team includes leaders in finance, engineering, legal affairs, and global operations, all of whom work to ensure Nvidia’s continued growth and success. Some of the key executives on this team include:
- Colette Kress – Executive Vice President and CFO: Kress plays a key role in Nvidia’s financial strategy, overseeing global finances and ensuring profitability.
- Jay Puri – Executive Vice President of Worldwide Field Operations: Puri oversees global sales and marketing efforts, ensuring Nvidia’s products reach the right markets.
- Michael Kagan – Executive Vice President of Engineering: Kagan is in charge of overseeing Nvidia’s engineering teams, including the development of next-generation products and technologies.
The collective expertise of Nvidia’s leadership team is crucial in making the day-to-day operational decisions that help Nvidia thrive in the competitive tech industry.
Institutional Investors and Their Influence
While Jensen Huang and the executive team maintain control over Nvidia’s operations, the company is still subject to the influence of its large institutional investors, such as Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and T. Rowe Price Associates. These investors hold significant shares in Nvidia and often directly influence major corporate decisions.
Although they don’t typically interfere with day-to-day operations, these institutional investors can sway strategic decisions during annual meetings or shareholder votes. Their primary interest lies in maximizing shareholder value, which sometimes aligns with Huang’s vision. For instance, investors have supported Nvidia’s expansion into artificial intelligence and data centers, which has paid off tremendously in terms of financial growth.
During major corporate changes, such as mergers and acquisitions or the introduction of significant new technologies, institutional investors may exert their influence through voting rights at annual meetings or by communicating with the board of directors to express their preferences.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Nvidia
In 2024, Nvidia reported annual revenue of $60.9 billion with a significant portion of this coming from its GPUs and AI-related ventures. The company has seen rapid growth, especially with the increasing demand for AI solutions and gaming technology.
As of April 2025, Nvidia’s market capitalization stands at over $2.8 trillion reflecting its dominance in the tech industry.
Nvidia’s financial success is tied to its leadership in key markets, including AI, gaming, and data centers. As a result, the company has become one of the most valuable tech firms in the world.
Here is a breakdown of Nvidia’s annual revenue and net worth for the last 10 years:
| Year | Revenue (in billion USD) | Net Worth (in billion USD) | Key Drivers of Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 4.68 | 21.72 | Strong gaming revenue and growth in Tegra chips for mobile devices. |
| 2016 | 5.01 | 28.04 | Continued growth in gaming, and early AI and deep learning focus. |
| 2017 | 6.91 | 53.30 | Growth driven by gaming (GeForce) and expansion in data center. |
| 2018 | 9.71 | 85.11 | Surge in gaming and AI, with AI-focused data centers booming. |
| 2019 | 11.72 | 110.85 | Success in data center expansion, AI, and strong gaming sales. |
| 2020 | 10.92 | 320.56 | Gaming and data centers, including COVID-19 pandemic-driven demand. |
| 2021 | 16.68 | 563.20 | Explosive growth in gaming, AI, and data centers. Acquisition of ARM (pending approval). |
| 2022 | 26.91 | 756.03 | Unprecedented demand for GPUs and growth in AI-driven solutions. |
| 2023 | 33.00 | 890.01 | Dominance in AI and deep learning solutions, continued gaming growth. |
| 2024 | 60.9 | 2790.00 | Surge in AI-related revenue, GPUs for AI and generative AI applications. |
Companies Owned by Nvidia
Nvidia has grown significantly through strategic acquisitions, bolstering its position in the semiconductor and AI sectors. The company has acquired several key businesses over the years, each contributing to its diversified portfolio. Below are some of the notable companies Nvidia owns, each contributing to its innovation in gaming, AI, data centers, and other emerging technologies.
Mellanox Technologies
In 2020, Nvidia acquired Mellanox Technologies, a leading supplier of high-performance interconnect solutions for data centers. This acquisition was valued at approximately $6.9 billion. Mellanox is best known for its network switches, adapters, and other interconnect products that enable faster data transfer in data centers.
- Primary Focus: High-performance computing (HPC), data centers, and networking.
- Contribution to Nvidia: Mellanox strengthens Nvidia’s position in the data center market, providing key networking and interconnect technology that complements Nvidia’s GPUs. With this acquisition, Nvidia can offer a more complete solution for data centers, enabling faster and more efficient data processing across industries such as cloud computing, AI, and big data analytics.
Mellanox’s products have become an integral part of Nvidia’s strategy to dominate the data center and AI markets, providing low-latency, high-throughput connectivity essential for AI workloads.
ARM Holdings (Pending Acquisition)
One of Nvidia’s most high-profile acquisitions is the planned purchase of ARM Holdings, which was announced in 2020 for approximately $40 billion. ARM, a British semiconductor and software design company, is renowned for its ARM architecture, which is widely used in mobile devices, IoT (Internet of Things) products, and embedded systems.
- Primary Focus: Chip design for mobile, IoT, embedded systems, and servers.
- Contribution to Nvidia: The acquisition of ARM is seen as a major step for Nvidia to expand beyond its dominance in GPUs and into mobile and server processors. ARM’s energy-efficient architecture powers billions of devices worldwide, and this acquisition will give Nvidia access to a broader market, particularly in the mobile and embedded device sectors. By integrating ARM’s technology with Nvidia’s AI and GPU offerings, Nvidia will have the potential to revolutionize mobile computing, autonomous devices, and network infrastructure.
This acquisition, still pending regulatory approval, has the potential to reshape Nvidia’s product offerings and significantly boost its reach in the global semiconductor market.
High Performance Computing (HPC) Business
While not a separate company, Nvidia’s high-performance computing division, which includes products from companies acquired like Mellanox, is a key part of Nvidia’s growth strategy. The HPC business provides supercomputing solutions, which are used in research, scientific modeling, and large-scale computing projects.
- Primary Focus: Supercomputing, AI, scientific research.
- Contribution to Nvidia: Nvidia’s HPC division combines powerful GPUs and AI tools to accelerate research and innovation in fields like weather modeling, healthcare research, and advanced simulations. This business line has helped Nvidia tap into the growing demand for AI-powered solutions and the rapidly expanding data center market.
Through partnerships and acquisitions, Nvidia has strengthened its HPC division, positioning itself as a leader in providing the computational power needed for cutting-edge scientific research and AI technologies.
The Ice Cream Company (Nvidia’s Venture)
In 2019, Nvidia launched The Ice Cream Company, a new venture that focuses on developing specialized ice cream and frozen dessert technologies, particularly in the AI and machine learning areas. This venture, while in its infancy, is part of Nvidia’s strategy to diversify and expand into other food technologies.
- Primary Focus: AI-powered food innovations.
- Contribution to Nvidia: While still relatively small compared to Nvidia’s core businesses, The Ice Cream Company reflects Nvidia’s commitment to experimenting with AI in various industries, including food production. The project integrates advanced machine learning models to optimize processes like inventory management, product development, and consumer preferences, making it an innovative and unique addition to Nvidia’s broader portfolio.
DeepMind Technologies (Partnership)
Although not a full acquisition, DeepMind Technologies, which was acquired by Google in 2014, has been a close partner of Nvidia, especially in the realm of artificial intelligence. DeepMind, known for its advanced AI research, uses Nvidia’s GPUs to power its groundbreaking work, particularly in reinforcement learning and deep learning.
- Primary Focus: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning.
- Contribution to Nvidia: DeepMind’s partnership with Nvidia is a testament to Nvidia’s GPUs being central to the development of AI models and simulations. DeepMind’s AI breakthroughs, such as the AlphaGo program and advancements in protein folding, rely heavily on Nvidia’s GPUs for computational power. While Nvidia doesn’t own DeepMind, the collaboration between the two companies significantly enhances Nvidia’s presence in the AI research sector.
DGX Systems (Nvidia’s AI Supercomputers)
Nvidia has also developed its own line of advanced AI supercomputers, known as DGX Systems. These systems are designed for high-performance AI and deep learning applications and are not a company acquisition, but a major product line that drives Nvidia’s growth in the AI sector.
- Primary Focus: AI, deep learning, data centers.
- Contribution to Nvidia: DGX systems combine Nvidia’s GPUs with other high-performance computing components, making them ideal for deep learning, data processing, and AI model training. The DGX systems are used by major research institutions, universities, and large enterprises that require top-tier computational power for AI applications.
The success of the DGX systems has further solidified Nvidia’s position as a leading player in the AI and data center industries, offering tailored solutions for businesses and researchers at the forefront of AI technology.
Conclusion
Nvidia is one of the most influential tech companies globally, known for its pioneering work in GPUs and AI technology. Its ownership is primarily split between co-founder Jensen Huang, institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock, and retail investors. Control of the company rests largely with Huang and the executive team, though institutional investors play a key role in major decisions.
With its expanding portfolio, including companies like Mellanox and the potential acquisition of Arm Holdings, Nvidia’s future looks incredibly promising. Its focus on AI, gaming, and autonomous vehicles places it at the forefront of technological innovation.
FAQs
Who is the largest shareholder of Nvidia?
The largest shareholder of Nvidia is Jensen Huang, the co-founder and CEO, who owns a significant percentage of the company’s shares.
Does Nvidia have institutional investors?
Yes, Nvidia has several institutional investors, including Vanguard Group and BlackRock, which hold large portions of the company’s shares and have considerable influence.
What companies does Nvidia own?
Nvidia owns Mellanox Technologies, DeepMap, and is in the process of acquiring Arm Holdings. These acquisitions help Nvidia expand its reach into new markets such as AI, data centers, and autonomous vehicles.
Who founded Nvidia?
Jensen Huang, Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem founded Nvidia in 1993. Huang has served as the CEO since its inception, guiding the company from a startup focused on graphics processors to one of the leading players in AI, gaming, and data centers.
What products does Nvidia make?
Nvidia is primarily known for its graphics processing units (GPUs), including the GeForce and Quadro series for gaming and professional use. However, Nvidia has expanded into several other areas:
- Data center solutions, including the Tesla and DGX systems.
- AI and machine learning technologies, powered by its GPUs and software tools.
- Autonomous driving hardware and software, including the Drive PX platform.
- Gaming hardware, such as the Shield TV and Nintendo Switch chips.
- Software development tools like CUDA for parallel computing.
How much is Nvidia worth?
As of 2025, Nvidia’s market capitalization is valued at approximately $2.79 trillion making it one of the most valuable tech companies globally. This valuation reflects Nvidia’s dominance in GPUs, AI, and its growing presence in other tech sectors.
How did Nvidia become so successful?
Nvidia’s success can be attributed to its strategic focus on high-performance computing, gaming, and AI. By consistently innovating and providing cutting-edge graphics technology, Nvidia captured a significant market share in the gaming industry. The company then expanded into the lucrative data center and AI sectors, establishing itself as a leader in artificial intelligence and deep learning, especially with its CUDA platform.
What is Nvidia’s biggest market?
Nvidia’s largest market is the gaming industry, where its GeForce GPUs are a top choice for gaming enthusiasts and professional gamers. However, Nvidia’s data center business has grown significantly in recent years, driven by the demand for AI, machine learning, and cloud computing services. The company’s increasing focus on autonomous vehicles and AI research also presents growing opportunities.
Does Nvidia own ARM?
Nvidia announced its intention to acquire ARM Holdings in 2020 for around $40 billion, but the deal is still pending regulatory approval. ARM, known for its chip architecture used in mobile devices and IoT products, would significantly expand Nvidia’s reach in the mobile and embedded systems markets.
How does Nvidia contribute to the gaming industry?
Nvidia plays a major role in the gaming industry by providing the GeForce series of graphics cards, which are widely used by both consumers and professional gamers. These GPUs are designed for high-performance gaming, delivering smooth and realistic graphics. Nvidia’s RTX series also introduced ray tracing technology, which significantly enhances visual quality in games. Additionally, Nvidia has developed various gaming technologies, including DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling), to improve performance and image quality.
What are some of Nvidia’s innovations?
Nvidia is known for its continuous innovations, including:
- CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture), is a parallel computing platform that allows developers to leverage Nvidia’s GPUs for general-purpose computing.
- Ray Tracing technology simulates realistic lighting in video games.
- DLSS technology uses AI to upscale lower-resolution images in real-time, improving gaming performance.
- Nvidia Omniverse is a platform for building and simulating 3D virtual worlds for design, gaming, and AI.
Is Nvidia a good investment?
Nvidia is considered a strong investment by many analysts due to its leadership in the GPU market and its expanding role in AI, data centers, and autonomous vehicles. However, like any investment, it carries risks, including competition from companies like AMD and Intel, regulatory scrutiny on the ARM acquisition, and market fluctuations. Potential investors should carefully consider these factors before making an investment decision.

