The Hershey Company is one of the most iconic chocolate manufacturers in the world. Known for its delicious candies and sweets, the brand has been a household name for over a century. But many people wonder — who owns Hershey Company, and how is it controlled today? Let’s dive into the ownership, leadership, and financials of this legendary American confectionery brand.
Key Takeaways
- The Hershey Trust Company is the controlling shareholder, owning around 28% of Hershey’s total equity but holding over 80% of the voting power through special Class B shares. This structure gives the Trust full strategic control while directing company profits toward funding the Milton Hershey School.
- Institutional investors collectively own most of Hershey’s common stock, including The Vanguard Group (9.3%), BlackRock (6%), Capital Group (5.3%), State Street (3.5%), and Charles Schwab (2.5%).
- Retail and insider shareholders hold the remaining 40% of outstanding shares, providing market liquidity and reflecting broad investor confidence, though with minimal influence over corporate decisions.
- Hershey’s dual-class ownership structure ensures long-term mission alignment — combining the philanthropic leadership of the Hershey Trust with the financial backing of global institutional investors to maintain both stability and shareholder value.
The Hershey Company Overview
The Hershey Company is a leading American confectionery and snacking business. Headquartered in Hershey, Pennsylvania, it has grown from a chocolate-maker to a diversified snack company with global reach. The firm is widely recognized for iconic brands and its deep ties to community and legacy. While the core remains confectionery, it increasingly emphasises broader snacking categories and innovation.
The Hershey Company was originally founded in 1894 by Milton S. Hershey in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, as the Hershey Chocolate Company (a subsidiary of his Lancaster Caramel Company).
The business later relocated operations to what is now Hershey, Pennsylvania. It trades on the New York Stock Exchange under ticker symbol HSY and serves markets around the world.
The company emphasises manufacturing, marketing and distribution of chocolate and non-chocolate confectionery, as well as salty snacks and other categories.
Its governance is unusual in that though it is a public company, a trust founded by Milton Hershey retains controlling voting power.
Founder
Milton S. Hershey (born September 13, 1857, died October 13, 1945) is the visionary behind the company.
He grew up on a farm near Derry Township and had limited formal schooling (about fourth grade) as his family moved frequently and his father’s ventures repeatedly failed.
After apprenticing with a local confectioner, he attempted several candy-business ventures (in Philadelphia, Chicago and New York) which failed.
In 1883 (or 1886 depending on source) he founded the Lancaster Caramel Company in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, which achieved success by making caramels with fresh milk.
Inspired by machinery he saw at the 1893 Chicago World’s Exposition, he decided to pivot into chocolate.
In 1894 he established the Hershey Chocolate Company as a subsidiary of Lancaster Caramel.
Over time, his ambition extended beyond confectionery: he built a model town (Hershey, Pennsylvania), invested in community infrastructure, and in 1909 he and his wife Catherine founded the Hershey Industrial School (later the Milton Hershey School) for underprivileged children.
His philanthropic commitment was such that in 1918 he placed a large portion of his fortune and his company stock into a trust to support that school.
Major Milestones
- 1883 (or 1886): Milton Hershey founds the Lancaster Caramel Company in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, marking his first major entrepreneurial success.
- 1893: After visiting the World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago, Hershey is inspired by chocolate-making equipment, leading him to shift his focus toward chocolate production.
- 1894: The Hershey Chocolate Company is officially established as a subsidiary of the Lancaster Caramel Company.
- 1900: The first Hershey’s Milk Chocolate Bar is introduced, making affordable chocolate available to the masses.
- 1903: Construction begins on a massive chocolate factory in Derry Township, Pennsylvania — the future town of Hershey.
- 1905: The Hershey factory opens, and the surrounding community of Hershey, Pennsylvania, is founded as a model town for workers.
- 1906: Hersheypark opens as a recreational venue for employees and local residents, highlighting the company’s community-first approach.
- 1907: Hershey’s Kisses are launched and become one of the brand’s most iconic products.
- 1915: The company introduces the Hershey’s Chocolate Syrup line, expanding its product offerings beyond bars.
- 1918: Milton Hershey transfers the majority of his company shares to the Hershey Trust, ensuring profits would fund the Milton Hershey School for disadvantaged children.
- 1927: The Hershey Chocolate Corporation is incorporated as a separate public entity following the sale of the caramel business.
- 1939: During World War II, Hershey develops the “D Ration Bar” for U.S. soldiers, becoming a key military supplier.
- 1956: Hershey expands into international markets, establishing operations in Canada and Mexico.
- 1963: The H.B. Reese Candy Company is acquired, adding the hugely successful Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups to the product portfolio.
- 1970: The company introduces Hershey’s Miniatures — an assortment of small chocolate bars that quickly become a best-seller.
- 1977: Hershey acquires Y&S Candies, adding the Twizzlers licorice brand.
- 1988: Hershey gains the U.S. distribution rights for Kit Kat and Rolo from Nestlé, strengthening its presence in global chocolate.
- 1996: The company officially changes its name from Hershey Foods Corporation to The Hershey Company, reflecting a broader focus.
- 2005: Hershey celebrates its 100th anniversary of chocolate production and invests heavily in product innovation.
- 2012: Hershey opens its new global headquarters expansion in Hershey, Pennsylvania, emphasizing sustainable design and innovation.
- 2017: The company acquires Amplify Snack Brands, the parent company of SkinnyPop, marking its move into the healthy snacking sector.
- 2019: Hershey acquires ONE Brands, adding protein bars to its growing better-for-you product line.
- 2020: Hershey introduces its first plant-based chocolate line in response to consumer demand for alternative and sustainable ingredients.
- 2022: Hershey expands production capacity in Mexico and the U.S. to meet increasing global demand for snacks and chocolate.
- 2024: The company signs a long-term cocoa sustainability initiative, ensuring ethical sourcing and improved farmer livelihoods.
- 2025: Hershey opens a fully integrated digital manufacturing plant at its Reese’s facility and invests in AI-driven production systems to enhance efficiency and product quality.
Who Owns Hershey Company: Largest Shareholders
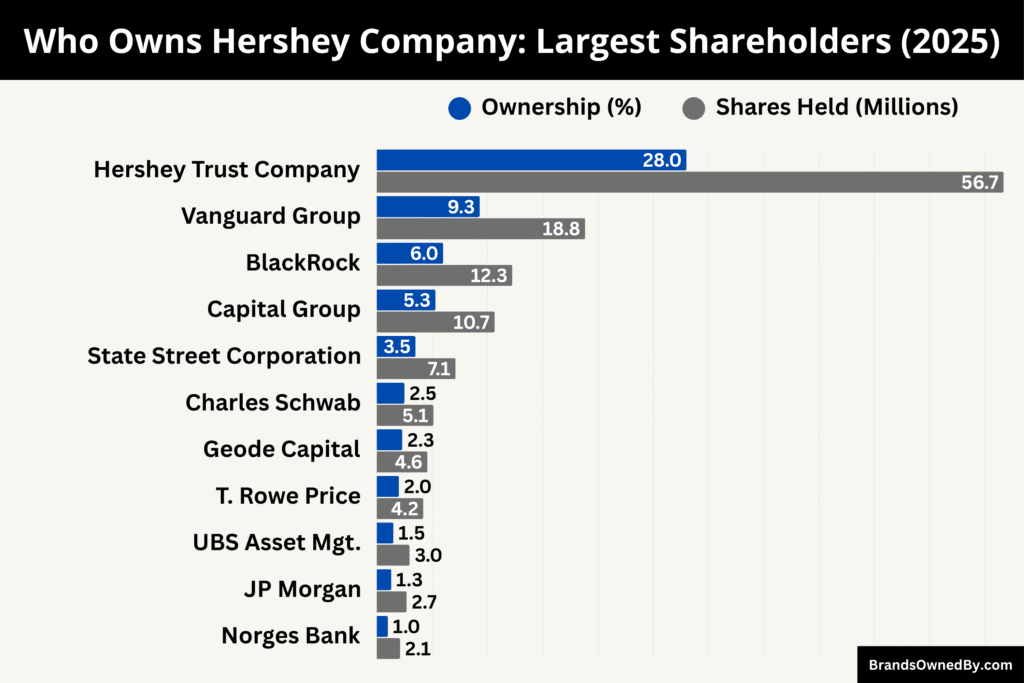
The Hershey Company is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol HSY. However, the true controlling power lies with the Hershey Trust Company, which acts as the trustee for the Milton Hershey School Trust. This trust is the largest shareholder and ultimate controlling entity of Hershey.
The Hershey Trust Company was established by Milton Hershey himself to fund and manage the Milton Hershey School — a philanthropic institution for underprivileged children. This structure ensures that while Hershey operates as a for-profit corporation, its profits indirectly support education and social welfare programs.
The trust holds special Class B shares that carry much greater voting power than ordinary shares. That gives the trust effective control over corporate decisions.
As of October 2025, Hershey has around 202.7 million outstanding shares, divided between common and Class B shares. The Trust holds the majority of Class B shares, giving it more than 80% of voting control, while large financial institutions such as Vanguard, BlackRock, and Capital Group hold significant economic stakes through common stock.
Below is a list of the top shareholders of the Hershey Company as of October 2025:
| Shareholder / Entity | Type | Approx. Shares Held | % Ownership of Total Equity | Voting Power / Control | Key Role / Influence | Notable Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hershey Trust Company / Milton Hershey School Trust | Philanthropic Trust (Controlling Owner) | ~56.68 million | ~28% | Over 80% voting control via Class B shares | Effective controlling shareholder | Ensures profits benefit the Milton Hershey School; long-term mission and board control |
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | Institutional (Passive) | ~18.84 million | ~9.3% | Limited | Largest institutional holder | Holds shares through ETFs and mutual funds; long-term governance engagement |
| BlackRock, Inc. | Institutional (Passive & Active) | ~12.25 million | ~6% | Limited | Second-largest institutional investor | Engages on ESG and sustainability; major influence through proxy voting |
| Capital Research & Management Co. (Capital Group) | Institutional (Active) | ~10.66 million | ~5.3% | Limited | Long-term active shareholder | Focuses on sustainable value creation and diversification strategy |
| State Street Corporation | Institutional (Passive) | ~7.12 million | ~3.5% | Limited | Major index fund manager | Supports governance best practices and corporate transparency |
| Charles Schwab Investment Management | Institutional (Passive) | ~5.12 million | ~2.5% | Limited | Aggregated fund holder | Represents retail and institutional investors; steady economic holder |
| Geode Capital Management, LLC | Institutional (Quant / Passive) | ~4.57 million | ~2.3% | Limited | Index manager | Manages Fidelity’s index assets; contributes to market stability |
| T. Rowe Price Group, Inc. | Institutional (Active) | ~4.2 million | ~2.0% | Limited | Active investment manager | Focused on consistent earnings and global expansion strategy |
| JP Morgan Asset Management | Institutional (Active) | ~2.7 million | ~1.3% | Limited | Global asset manager | Views Hershey as a stable, defensive investment with long-term growth |
| UBS Asset Management | Institutional (Active / Global) | ~2.96 million | ~1.5% | Limited | ESG-focused investor | Supports transparency and sustainability; holds through global equity funds |
| Norges Bank Investment Management (NBIM) | Sovereign Wealth Fund | ~2.1 million | ~1.0% | Limited | Long-term institutional investor | Prioritizes ethical sourcing and sustainability practices |
| Retail & Insider Shareholders | Mixed (Public & Executives) | ~81.4 million (estimated combined float) | ~40% | Minimal | Broad retail base + executives | Provides liquidity and market confidence; insiders hold < 2% individually |
Hershey Trust Company / Milton Hershey School Trust
The Hershey Trust Company, serving as the trustee for the Milton Hershey School Trust, is the true controlling shareholder of The Hershey Company. It owns about 56.68 million shares, representing roughly 28% of total equity but controlling over 80% of total voting power through its Class B shares.
This control enables the Trust to influence Hershey’s corporate strategy, board appointments, and long-term goals. The Trust’s primary mission is to fund the Milton Hershey School, which provides free education and housing to children from disadvantaged backgrounds. This philanthropic ownership structure ensures that a significant portion of Hershey’s profits benefit social causes rather than private shareholders.
The Trust’s voting power gives it the final say in any major decision, ensuring Hershey remains aligned with its founding values of community, education, and ethical business practices.
The Vanguard Group, Inc.
Vanguard is Hershey’s largest institutional investor, owning approximately 18.84 million shares, or around 9.3% of outstanding stock as of October 2025. As a leading global asset manager, Vanguard’s stake is held across multiple index funds and ETFs, representing millions of individual investors.
While Vanguard does not hold the special voting rights of the Class B shares, its influence lies in its scale and stewardship. The firm regularly engages with Hershey’s management on governance issues, including sustainability, executive pay, and board diversity.
Vanguard’s investment reflects confidence in Hershey’s consistent performance, brand strength, and dividend reliability — qualities that align with its long-term investment philosophy.
BlackRock, Inc.
BlackRock is the second-largest institutional holder of Hershey’s common stock, with around 12.25 million shares, equating to about 6% of total equity. The company’s interest in Hershey is primarily through its iShares ETFs and actively managed mutual funds.
BlackRock’s investment strategy centers on long-term value creation, and it often supports management teams that demonstrate responsible governance and sustainable growth.
Although it lacks control over corporate decisions, BlackRock’s voting influence is significant in shareholder resolutions and proxy votes. The firm’s analysts also monitor Hershey’s expansion into global snacking and its sustainability commitments, reinforcing investor trust in the company’s long-term direction.
Capital Research & Management Company
Capital Group, through its International Investors and American Funds, holds an estimated 10.66 million shares, or roughly 5.3% of Hershey’s total equity. Unlike passive investors, Capital Group takes an active approach by engaging with company executives and boards to drive shareholder value.
It supports Hershey’s strategy of diversifying into snacks and healthier product lines while maintaining strong margins in core chocolate segments.
Capital’s long-term investment approach aligns well with Hershey’s steady, dividend-paying business model. Although it does not exert direct control, its active participation in proxy votes and governance discussions gives it meaningful influence among institutional peers.
State Street Corporation
State Street Global Advisors, a major institutional investor and one of the “Big Three” asset managers, owns approximately 7.12 million shares, representing 3.5% of outstanding shares. Its position is primarily through index and ETF holdings.
While State Street’s investment style is passive, the firm exercises its proxy voting rights in alignment with corporate governance best practices. It has supported Hershey’s efforts to maintain high ethical sourcing standards, transparent governance, and diversity initiatives. Hershey’s stable cash flow and strong market position make it a valuable holding within State Street’s index portfolios.
Charles Schwab Investment Management
Charles Schwab Investment Management owns about 5.12 million shares, equal to roughly 2.5% of Hershey’s total stock. Its position reflects the aggregated holdings of Schwab-managed funds and retail investor accounts.
Although not an activist investor, Schwab’s collective vote can influence corporate policies in combination with other institutional shareholders. Schwab’s inclusion of Hershey across diversified portfolios highlights the company’s reputation for reliability, consistent growth, and robust brand equity.
Geode Capital Management, LLC
Geode Capital Management, known for managing index fund assets primarily associated with Fidelity Investments, holds approximately 4.57 million shares, about 2.3% of Hershey’s shares outstanding.
As a quantitative and passive manager, Geode does not seek direct involvement in governance but contributes to the overall stability and liquidity of Hershey’s shareholder base. Its long-term, data-driven investment approach complements Hershey’s profile as a dependable, high-performing consumer staples company.
T. Rowe Price Group, Inc.
T. Rowe Price holds an estimated 4.2 million shares, or roughly 2% of Hershey’s total shares. The firm’s active investment management focuses on companies with consistent earnings, strong management, and durable competitive advantages — traits that fit Hershey perfectly. T. Rowe analysts frequently highlight Hershey’s global expansion strategy and disciplined capital management as reasons for maintaining their stake.
While T. Rowe has limited governance control, its votes often align with other large institutions on issues such as executive compensation and sustainability disclosure.
JP Morgan Asset Management
JP Morgan Asset Management owns around 2.7 million shares, or approximately 1.3% of Hershey’s stock.
As a global asset manager, JP Morgan’s position spans both institutional and retail funds. The firm views Hershey as a stable, defensive investment in the consumer goods sector, offering steady returns through dividends and growth in premium confectionery markets.
JP Morgan also supports Hershey’s digital transformation initiatives, which aim to modernize production and supply chain operations.
Norges Bank Investment Management
Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, Norges Bank Investment Management (NBIM), holds roughly 2.1 million shares, or around 1% of Hershey’s equity. NBIM’s investment in Hershey reflects its strategy of maintaining exposure to global consumer brands with sustainable and ethical business practices.
The fund values Hershey’s commitment to responsible cocoa sourcing and its social-impact-driven governance model. Though small in size, NBIM’s reputation as a long-term investor adds prestige and international credibility to Hershey’s shareholder roster.
UBS Asset Management
UBS Asset Management holds approximately 2.96 million shares, about 1.5% of Hershey’s outstanding stock. Its investment spans global equity funds that target stable, dividend-paying companies. UBS’s analysts view Hershey as a model for balancing profitability with corporate responsibility. UBS also participates in governance votes through proxy engagements that prioritize transparency and ESG alignment.
Retail and Insider Shareholders
The remainder of Hershey’s shares — roughly 40% of total equity — is distributed among retail investors, small funds, and company insiders. Insiders, including executives and board members, collectively own less than 2% of outstanding shares but remain incentivized through equity compensation plans. Retail investors play an important role in liquidity and brand loyalty, given Hershey’s strong consumer recognition.
The dispersed nature of these holdings reflects broad public confidence in Hershey’s long-term success and the stability of its governance model.
Who is the CEO of the Hershey Company?
As of October 2025, Kirk Tanner serves as the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of The Hershey Company. He succeeded Michele G. Buck, who led the company from 2017 to mid-2025. Tanner’s appointment marked the beginning of a new era for the iconic chocolate and snack manufacturer, as Hershey continues to expand globally and diversify into new product categories beyond confectionery.
Background and Career of Kirk Tanner
Kirk Tanner is a seasoned executive with more than three decades of experience in the food and beverage industry.
Before joining Hershey, he served as CEO and President of The Wendy’s Company, where he successfully oversaw global operations and implemented digital and menu innovations.
Prior to Wendy’s, Tanner spent over 30 years at PepsiCo, where he held numerous leadership roles, including CEO of PepsiCo Beverages North America.
Tanner is known for his operational expertise, focus on brand performance, and ability to modernize legacy companies through technology and strategic innovation. His leadership style is collaborative and results-driven, emphasizing brand growth, efficiency, and culture. His extensive experience in global food and beverage operations makes him an ideal choice to lead Hershey’s evolving portfolio of snacks, chocolates, and better-for-you brands.
Leadership Style and Strategic Focus
As CEO, Tanner’s leadership is centered on innovation, sustainability, and disciplined expansion. He has prioritized expanding Hershey’s global footprint, investing in digital supply chain technologies, and maintaining strong relationships with cocoa suppliers to ensure ethical sourcing.
Under his early tenure, Hershey has continued to strengthen its snack portfolio, focusing on brands such as SkinnyPop, Pirate’s Booty, and ONE Brands.
Tanner also aims to enhance Hershey’s market share in the United States while growing in emerging international markets. His management approach combines financial discipline with brand creativity, emphasizing consumer data analytics and marketing innovation to sustain Hershey’s competitive edge.
Relationship with the Board and Governance Structure
Kirk Tanner reports to the Board of Directors, which is heavily influenced by the Hershey Trust Company — the controlling shareholder of Hershey. The Trust’s long-term mission to fund the Milton Hershey School aligns with Tanner’s focus on sustainable and ethical business practices. While Hershey’s institutional investors provide economic input, the Trust retains governance authority, ensuring that the company remains rooted in its founding values.
Tanner’s role involves balancing corporate growth with the Trust’s philanthropic objectives. His background in leading global operations within structured governance environments has positioned him well to navigate this unique ownership model.
CEO Salary and Total Compensation
Kirk Tanner’s compensation package for 2025 reflects Hershey’s recognition of his leadership experience and the competitive nature of executive recruitment in the global food sector. His base salary is approximately $1.25 million per year, complemented by annual performance bonuses, long-term stock incentives, and one-time signing awards.
In total, his expected annual compensation for 2025 is valued at around $17 million, which includes stock grants and performance-based equity incentives tied to company performance, shareholder value, and sustainability targets. Tanner’s compensation aligns him with both short-term profitability goals and long-term corporate growth.
Net Worth
As of October 2025, Kirk Tanner’s estimated net worth is approximately $45–50 million.
This figure reflects his long career at PepsiCo and Wendy’s, where he accumulated substantial stock holdings, along with his signing bonuses and equity awards from Hershey. His wealth primarily consists of long-term stock options and performance shares that vest over time, emphasizing his commitment to Hershey’s long-term success.
Former CEO Michele G. Buck
Michele Buck, who led Hershey from 2017 until mid-2025, remains a significant figure in the company’s modern history. She was Hershey’s first female CEO and successfully guided the company through a period of transformation and expansion. During her tenure, Hershey acquired several snack brands, modernized operations, and grew into a diversified food company. Buck continues to serve as an advisor and board member during the leadership transition, ensuring continuity and strategic alignment.
Hershey Annual Revenue and Net Worth
As of October 2025, The Hershey Company (HSY) reports a trailing-twelve-month revenue of approximately $11.29 billion and a market capitalization (net worth) of about $38.35 billion. These figures reflect the company’s scale in the global confectionery and snack industry and provide a basis for assessing its financial strength and investor valuation.
Annual Revenue
Hershey’s revenue has grown modestly in recent years. For example, the fiscal year 2024 revenue stood at about $11.20 billion, and the latest trailing-12-months figure of roughly $11.29 billion shows incremental growth of around 0.8%. The revenue figure encompasses all of Hershey’s major business segments, including North America confectionery, salty snacks, and international operations.
Despite macroeconomic headwinds such as cocoa cost inflation and supply chain disruptions, Hershey has maintained stable top-line performance. Growth variances by segment are worth noting — while some segments experienced flat or modest declines, others (notably salty snacks and international) contributed to offsetting pressures.
Net Worth
Hershey’s net worth, as measured by its market capitalization, reached approximately $38.35 billion in October 2025. This valuation is derived from the share price multiplied by shares outstanding and reflects investor expectations of future cash flows, brand strength, and competitive position.
The company’s market cap has fluctuated over time — for example, about $37.25 billion earlier in 2025 — indicating market sensitivity to commodity costs, currency movements, and global growth prospects. The net-worth figure places Hershey among the large-cap consumer goods companies.
Interpretations and Implications
The combination of moderate revenue growth and a strong market valuation suggests that investors view Hershey as a relatively stable asset in consumer staples. The company’s heritage brands, global footprint, and diversified snack portfolio contribute to its value.
However, the modest growth in revenue also signals that the market is not expecting explosive expansion; rather, it rewards Hershey for consistency, brand equity, and margin preservation.
The net-worth figure, being more than three times annual revenue, implies a price-to-sales ratio near 3.4x — showing that Hershey trades at a premium compared with many peers, likely due to its perceived defensiveness and strong dividend profile.
Risks and Context
Despite the positive metrics, Hershey faces headwinds that may influence future revenue and market-worth outcomes. Key risks include rising input costs (especially cocoa), volatile foreign exchange rates for international operations, and shifting consumer trends in snacking and confectionery.
Additionally, a slower growth rate in revenue relative to historical averages may limit upside in the market valuation unless Hershey can unlock higher growth through new products, markets, or operational efficiencies. Investors should also note that the net-worth figure is market‐driven and can fluctuate, even if operational performance remains steady.
Outlook
Looking ahead, if Hershey can accelerate growth in its salty snacks and international segments, improve margin performance via supply-chain optimization, and manage commodity cost pressures, its revenue base could expand beyond the current ~11.3 billion level.
That could support an upward revision of its market valuation. On the flip side, stagnation in core segments or margin compression could dampen investor sentiment and reduce net worth.
Overall, the 2025 figures reflect a mature company with a strong base and valuable brand portfolio — though growth ambitions and margin improvements will be key to unlocking further value.
Historical Revenue and Net Worth
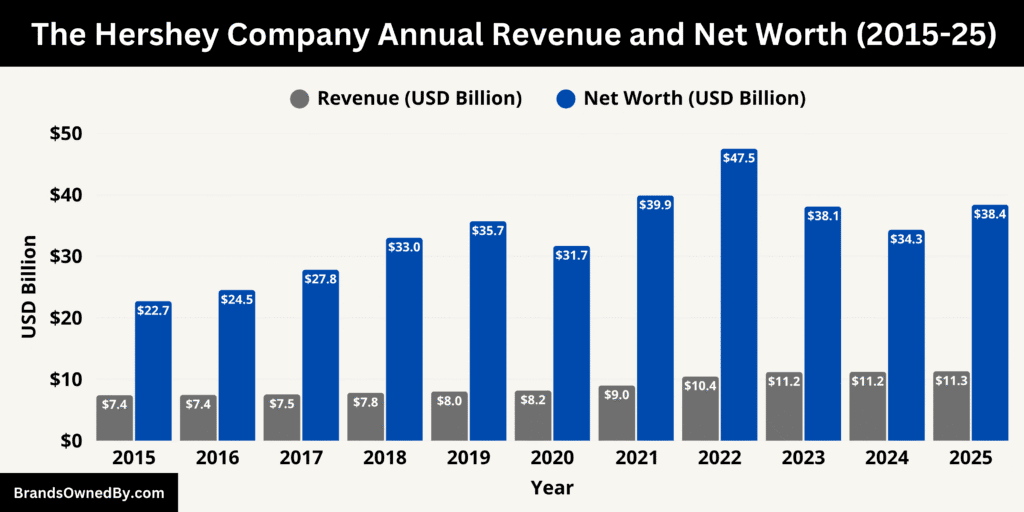
Over the past decade, The Hershey Company has demonstrated steady and resilient growth, evolving from a primarily chocolate-focused manufacturer into a diversified global snacking powerhouse.
Revenue has climbed from around $7.4 billion in 2015 to roughly $11.3 billion in 2025 — an increase of more than 50 percent over ten years. This consistent upward trend highlights Hershey’s ability to expand its product mix, strengthen its brands, and successfully navigate shifting consumer preferences.
The company’s market value has also followed a generally positive trajectory, rising from the low-$20 billion range in 2015 to nearly $38 billion in 2025. While there have been modest dips during economic slowdowns or periods of commodity cost volatility, Hershey’s long-term stability and strong brand loyalty have maintained investor confidence.
The data underscores Hershey’s balanced approach — blending heritage and innovation. Its steady revenue growth reflects strong performance in North America and increased contributions from its international and snack segments. Meanwhile, its high valuation shows how investors view Hershey not just as a confectionery leader but as a durable, cash-generating company with a strong dividend profile and reliable long-term outlook.
Overall, Hershey’s decade-long financial record paints the picture of a company that has modernized its business model while preserving the brand trust that has made it a household name for over a century.
Companies Owned by Hershey
As of 2025, The Hershey Company owns and operates a diverse portfolio of confectionery, snack, and better-for-you brands that extend far beyond its iconic chocolate bars.
Below is a list of the major brands and companies owned by The Hershey Company as of 2025:
| Brand / Company / Entity | Category | Acquisition / Founding Year | Description and Role within Hershey |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Hershey Company | Corporate / Parent Entity | Founded 1894 | The main operating company managing Hershey’s entire global portfolio of chocolate, candy, and snack brands. Oversees production, marketing, R&D, and distribution. |
| Reese’s | Confectionery / Chocolate | Acquired 1963 (H.B. Reese Candy Company) | Flagship peanut butter and chocolate brand. One of Hershey’s highest revenue drivers with wide global recognition and seasonal product success. |
| Hershey’s | Chocolate / Core Brand | Founded 1894 | The original brand representing Hershey’s identity. Includes bars, syrups, baking products, and cocoa. Central to Hershey’s product range and marketing. |
| Hershey’s Kisses | Chocolate / Bite-Sized | Introduced 1907 | Iconic foil-wrapped chocolates symbolizing Hershey’s heritage. Strong performer in gifting and seasonal markets. |
| Kit Kat (U.S. Rights) | Chocolate / Wafer | Licensed (since mid-20th century) | Hershey holds exclusive U.S. rights to manufacture and market Kit Kat, a globally recognized wafer-based chocolate bar. |
| Jolly Rancher | Non-Chocolate Confectionery | Acquired 1996 | Fruit-flavored candy brand producing hard candies, chews, and gummies. Strengthens Hershey’s non-chocolate portfolio. |
| Twizzlers (Y&S Candies) | Non-Chocolate / Licorice | Acquired 1977 | One of the oldest chewy candy brands. Adds variety to Hershey’s candy lineup and maintains strong seasonal demand. |
| York Peppermint Pattie | Chocolate / Mint | Acquired 1988 | Popular mint-filled chocolate brand. Provides diversity in Hershey’s chocolate offerings. |
| Rolo | Chocolate / Caramel | Licensed (U.S. rights) | A caramel-filled chocolate candy adding to Hershey’s variety of core confectionery items. |
| Almond Joy & Mounds | Chocolate / Coconut | Acquired 1988 | Classic coconut-based chocolate bars that complement Hershey’s legacy brands. |
| Brookside | Premium Chocolate / Fruit | Acquired 2011 | Premium chocolate brand offering fruit-infused chocolate pieces, expanding Hershey into the premium segment. |
| barkTHINS | Premium Snacking Chocolate | Acquired 2016 | Snacking chocolate brand targeting health-conscious consumers seeking small-portion indulgence. |
| Lily’s | Low-Sugar / Better-for-You Chocolate | Acquired 2021 | Specializes in low- and no-sugar chocolate products, aligning Hershey with health-conscious trends. |
| Amplify Snack Brands | Salty Snacks / Portfolio Company | Acquired 2017 | Brought Hershey into the salty-snack market, including SkinnyPop, Paqui, Tyrrells, and Oatmega. |
| SkinnyPop | Salty Snack / Popcorn | Acquired 2017 (via Amplify) | A leading popcorn brand emphasizing simple, clean ingredients and strong growth in health-focused snacking. |
| Paqui | Salty Snack / Spicy Chips | Acquired 2017 (via Amplify) | Known for bold flavors and viral marketing (“One Chip Challenge”), appealing to younger consumers. |
| Tyrrells | Salty Snack / Premium Chips | Acquired 2017 (via Amplify) | Premium kettle-cooked chip brand extending Hershey’s salty-snack reach into global markets. |
| Oatmega | Nutrition / Protein Bars | Acquired 2017 (via Amplify) | Protein bar brand targeting active and fitness consumers. Enhances Hershey’s presence in nutrition categories. |
| Pirate Brands (Pirate’s Booty, Smart Puffs, Original Tings) | Salty Snacks / Puffed Snacks | Acquired 2018 | Expands Hershey’s footprint in family-friendly, natural snack categories with puffed corn and cheese snacks. |
| Dot’s Homestyle Pretzels | Salty Snacks / Pretzels | Acquired 2021 | Fast-growing seasoned pretzel brand, strengthening Hershey’s pretzel and snack category leadership. |
| Pretzels, Inc. | Manufacturing / Salty Snacks | Acquired 2021 | Provides pretzel production capacity and supports Hershey’s snack operations across multiple brands. |
| One Brands | Nutrition / Protein Bars | Acquired 2019 | Specializes in low-sugar, high-protein bars, positioning Hershey in the performance and nutrition segment. |
| LesserEvil | Organic / Better-for-You Snacks | Acquired 2025 | Produces organic popcorn, paleo puffs, and grain-free snacks. Supports Hershey’s strategic pivot toward cleaner-label snacking. |
| Oatmega | Nutrition / Protein Bars | Acquired 2017 | Protein snack brand focused on high-quality, omega-3-rich ingredients. Complements Hershey’s nutrition portfolio. |
| Fulfil | Protein / Snack Bars | Acquired 2020 | Vitamin-enriched protein bar brand distributed in convenience and retail stores, strengthening Hershey’s global bar business. |
| Miscellaneous Licenses and Regional Entities | Manufacturing / Distribution | Ongoing | Includes U.S. Kit Kat licensing, international distribution rights, and joint ventures supporting Hershey’s operations globally. |
The Hershey Company
The Hershey Company itself is the corporate umbrella that designs, manufactures and markets a wide range of confectionery and snack products. It operates large manufacturing campuses in the United States and runs global sales, marketing and R&D functions. The corporate brand manages flagship product development, global licensing and the company’s pivot into salty and better-for-you snacks. It is both a manufacturer and an integrator of acquired brands, folding them into Hershey’s distribution and retail relationships.
Reese’s
Reese’s is one of Hershey’s most valuable and recognizable brands. Centered on the peanut-butter-and-chocolate cup, Reese’s has expanded into seasonal, snack-size and innovation lines. Hershey acquired the H.B. Reese business decades ago and has since grown Reese’s into a global powerhouse through marketing, limited-edition launches and product line extensions that reach beyond traditional confectionery aisles.
HERSHEY’S
The HERSHEY’S flagship brand covers classic milk chocolate bars, baking ingredients, syrups and seasonal products. This brand remains the heart of the company’s identity. It supports large-scale manufacturing and seasonal promotions. Hershey’s core chocolate business supplies key retail channels and anchors the company’s heritage while funding longer-term investments in innovation and portfolio diversification.
HERSHEY’S KISSES
Hershey’s Kisses are bite-sized, foil-wrapped chocolates that have been a signature product for the company for over a century. The brand is driven by strong seasonal programs, licensing and multipack formats. Kisses are a high-margin, high-awareness product that supports Hershey’s confectionery leadership and global brand recognition.
Kit Kat
Hershey owns the rights to manufacture, market and sell Kit Kat in the United States under a long-standing license arrangement. Outside the U.S., Kit Kat is owned by another company. The U.S. license is strategically important because Kit Kat is a globally known candy bar that expands Hershey’s portfolio into wafer-based chocolate and taps into global trends while leveraging Hershey’s U.S. manufacturing and retail reach.
Jolly Rancher
Jolly Rancher is Hershey’s hard candy and fruity-candy franchise. The brand includes hard candies, gummies and chews. Jolly Rancher helps Hershey compete in non-chocolate confectionery categories and provides year-round SKU depth in impulse and checkout zones.
Twizzlers (Y&S Brands)
Twizzlers is Hershey’s long-standing licorice and chewy candy brand, acquired through earlier deals that brought Y&S Candies into Hershey’s family. Twizzlers are a core non-chocolate item sold across grocery, convenience and seasonal channels. The brand also serves as an entry point for cross-promotions and novelty items.
York, Rolo, Almond Joy, and Mounds
Hershey manages a portfolio of legacy chocolate names such as York Peppermint Pattie, Rolo, Almond Joy and Mounds. These brands give Hershey broad shelf presence across classic chocolate formats — mint, caramel and nut-based offerings — and help the company address diverse consumer tastes without relying on a single product line.
Brookside and barkTHINS
Brookside and barkTHINS represent Hershey’s play in premium, indulgent and better-for-you chocolate snacks. Brookside focuses on chocolate-covered fruit centers, while barkTHINS positions Hershey in the snacking chocolate segment with a bark-style product marketed to more health- and ingredient-conscious consumers. These acquired brands extend Hershey’s reach into specialty aisles and natural foods channels.
LILY’S
Lily’s is Hershey’s major low-sugar and no-added-sugar chocolate brand. Acquired to accelerate growth in the better-for-you confectionery market, Lily’s offers sugar-free bars, baking chips, and snacking products that target consumers looking for lower sugar alternatives without sacrificing chocolate taste.
Amplify Snack Brands
Amplify was a transformational acquisition that brought SkinnyPop popcorn, Paqui chips, Tyrrells (regional kettle chips), and Oatmega protein bars into Hershey’s portfolio. SkinnyPop became Hershey’s flagship salty-snack success story. Paqui and Tyrrells added spicy and premium chip offerings. Oatmega and similar bar lines provided nutrition-bar credibility. Together, these brands allowed Hershey to expand beyond confectionery into the larger snacking aisle.
SKINNYPOP
SkinnyPop is Hershey’s leading popcorn brand and one of the company’s primary growth vectors in salty snacks. Known for simple ingredient lists and multiple flavors, SkinnyPop helped Hershey enter health-oriented snacking and capture incremental retail shelf space outside traditional candy sections.
Pirate Brands
Pirate Brands were acquired to round out Hershey’s better-for-you snack portfolio. Pirate’s Booty and related snacks offer cheese puffs, puffed corn snacks, and other savory options. These brands bring scale to the value and club channels and complement SkinnyPop’s popcorn business.
Dot’s Homestyle Pretzels and Pretzels, Inc.
Dot’s Homestyle Pretzels and its co-manufacturer were added to Hershey’s salty-snack capabilities through a major 2021 acquisition. Dot’s is known for a distinctive seasoned pretzel that sells strongly in snack aisles. Bringing Dot’s and Pretzels, Inc. in-house created manufacturing scale, capacity, and a foothold in seasoned pretzels — a high-growth segment for Hershey.
ONE Brands
ONE Brands produces low-sugar, high-protein nutrition bars aimed at fitness and on-the-go consumers. Hershey purchased ONE to bolster its snack-bar presence and to accelerate entry into growing nutrition and protein categories. ONE complements Oatmega and other bar lines, giving Hershey a cross-channel bar platform.
PAQUI
Paqui is a spicy and flavor-forward tortilla chip brand that tends to attract younger, trend-driven consumers. Paqui’s product innovation and social-media visibility provide Hershey with a creative, edgy brand that contrasts with older, heritage chocolate names. It helps Hershey appeal to taste seekers and expand into bold flavor segments.
LesserEvil and Emerging Healthier Snack Brands
In 2025 Hershey continued to buy health-and-better-for-you snack franchises. The company announced deals to add niche organic and better-for-you snack brands, including a high-profile agreement to bring LesserEvil into the portfolio. These moves deepen Hershey’s presence in organic, clean-ingredient and premium snack categories and add manufacturing or sourcing capabilities to meet consumer demand.
Oatmega and Fulfil
Oatmega and Fulfil are part of Hershey’s strategy to own nutrition-forward bars and protein snacks. Oatmega arrived through Amplify acquisitions and Fulfil represents branded bar offerings targeting convenience and grocery channels. These products let Hershey market to active consumers seeking protein and convenience in bar form.
Miscellaneous Licenses and Regional Entities
Hershey also operates regional or licensed businesses and manufacturing agreements. The company holds U.S. manufacturing and distribution licenses for certain global brands and runs regional operations (for example, specific rights for Kit Kat in the U.S.). Hershey manages joint ventures, co-packing arrangements and contract manufacturing through these entities to maximize shelf presence and distribution efficiency.
Final Words
The Hershey Company remains one of the world’s most iconic and trusted chocolate and snack manufacturers. Guided by the Hershey Trust Company, which owns and controls the business to fund the Milton Hershey School, the company blends purpose with profitability. Its diverse portfolio — from classic Hershey’s chocolates and Reese’s to modern brands like SkinnyPop and Dot’s Pretzels — reflects a balance of tradition and innovation. As of 2025, Hershey continues to grow globally while staying true to its founding mission, making the question “who owns Hershey Company” a story of enduring legacy, responsibility, and success.
FAQs
Who is Hershey’s owned by?
Hershey is primarily owned and controlled by the Hershey Trust Company, which acts as the trustee for the Milton Hershey School Trust. The Trust owns about 28% of the company’s stock but controls over 80% of its voting power, giving it effective control over corporate strategy and board decisions.
Is Hershey owned by Nestlé?
No, Hershey is not owned by Nestlé. The Hershey Company is an independent, U.S.-based corporation headquartered in Hershey, Pennsylvania. Although Hershey holds the U.S. rights to manufacture and sell Kit Kat, which is owned by Nestlé globally, the two companies are separate and not affiliated by ownership.
Who owns Hershey Company?
The Hershey Company is owned by a mix of the Hershey Trust Company and public shareholders. The Trust holds controlling voting power, while institutional investors such as Vanguard, BlackRock, and Capital Group collectively own significant portions of the company’s common stock.
Who bought Hershey Company?
No single entity “bought” The Hershey Company. It remains an independent corporation. However, since its founding, it has been majority-controlled by the Hershey Trust Company, which Milton Hershey established in 1909 to fund and sustain the Milton Hershey School.
Who are the largest shareholders of Hershey’s?
As of 2025, the largest shareholders include:
- Hershey Trust Company – owns about 28% of shares and controls over 80% of votes
- The Vanguard Group – approximately 9.3%
- BlackRock, Inc. – approximately 6%
- Capital Group – approximately 5.3%
- State Street Corporation – approximately 3.5%
The remaining shares are held by institutional funds, retail investors, and company insiders.
Is Cadbury owned by Hershey?
Not entirely. Cadbury is owned globally by Mondelez International, but Hershey holds the U.S. licensing rights to produce and sell Cadbury products within the United States. This long-standing licensing agreement allows Hershey to sell Cadbury chocolates in U.S. stores while Mondelez manages Cadbury’s international markets.
Why did Hershey sue Cadbury?
Hershey sued Cadbury (Mondelez International) in 2015 over allegations that the company imported and sold unauthorized Cadbury products made outside the U.S., violating Hershey’s exclusive licensing rights. The lawsuit resulted in a settlement that restricted the import of non-U.S. Cadbury chocolate into American markets.
Does Hershey own Kit Kat?
Hershey owns the U.S. rights to Kit Kat, but not the global brand. Nestlé owns Kit Kat worldwide, except in the U.S., where Hershey manufactures and markets it under a long-term licensing agreement.
Does Hershey own Oreo?
No, Oreo is owned by Mondelez International, not Hershey. However, Hershey and Oreo have collaborated on co-branded products such as Hershey’s Cookies ‘n’ Creme and Oreo-flavored candy bars, which are produced under licensing partnerships.
How many brands does Hershey own?
As of 2025, Hershey owns and operates over 80 brands across chocolate, candy, and snack categories. Major brands include Hershey’s, Reese’s, Kit Kat (U.S. rights), Jolly Rancher, Twizzlers, York, Ice Breakers, SkinnyPop, Dot’s Pretzels, Paqui, Lily’s, Brookside, barkTHINS, and ONE Brands.
Where did Milton Hershey live?
Milton S. Hershey lived in Hershey, Pennsylvania, the town he founded for his employees and their families. The community was designed as a model industrial town featuring affordable housing, schools, and amenities. Today, Hershey, Pennsylvania remains home to The Hershey Company headquarters, the Milton Hershey School, and Hersheypark, the amusement park he built for residents and workers.

