- CVS Pharmacy is owned by CVS Health, which is publicly traded. Ownership is spread across institutional and public shareholders, with no single controlling owner.
- The two largest shareholders are The Vanguard Group and BlackRock, each holding approximately 9%–10% of CVS Health’s outstanding shares, giving them the strongest voting influence in corporate governance.
- Other major shareholders include Capital Research and Management Company with about 8%–9%, Dodge & Cox with roughly 5%–6%, and State Street Global Advisors with around 4%–5% ownership.
- Collectively, the top five institutional shareholders control over one-third of total shares, meaning CVS is institutionally owned, board-governed, and operated by professional management rather than a founder or parent conglomerate.
CVS is one of the largest retail pharmacy chains in the United States. It operates as a core business segment of CVS Health. The brand focuses on prescription dispensing, consumer health products, preventative care access, and everyday retail essentials.
The company plays a frontline role in U.S. healthcare delivery. CVS Pharmacy stores often serve as the first point of contact for patients seeking medications, vaccinations, and basic health guidance. Over time, the brand has evolved from a traditional drugstore into a healthcare access hub closely connected with clinics, insurance services, and pharmacy benefit programs.
As of 2025, CVS Pharmacy continues to adapt its store formats. The company is emphasizing pharmacy-led locations, expanded health services, and digital prescription management to meet changing patient needs.
Founders of CVS
CVS was founded in 1963 in Lowell, Massachusetts, under the original name Consumer Value Stores. The company was created by brothers Stanley P. Goldstein and Sidney Goldstein, alongside their business partner Ralph P. Hoagland III.
Stanley and Sidney Goldstein had a clear vision. They wanted to build a retail business focused on everyday health, beauty, and personal care products at affordable prices. Their approach emphasized convenience, neighborhood accessibility, and consistent customer experience. This strategy helped the brand scale quickly in its early years.
Ralph P. Hoagland III played a crucial operational role. He helped structure the company’s early expansion and later served in executive leadership positions as the business grew. His retail expertise supported CVS’s transition from a small regional chain into a nationally recognized brand.
Notably, the first CVS stores did not include prescription pharmacies. The founders initially positioned CVS as a value-driven retail concept. The decision to add pharmacy services a few years later proved transformational and permanently reshaped the company’s identity.
Major Milestones
- 1963: Consumer Value Stores is founded in Lowell, Massachusetts. This marks the origin of CVS as a health and beauty retail concept rather than a pharmacy business.
- 1964: CVS expands rapidly within its first year, opening multiple stores across Massachusetts and establishing its value-driven retail model.
- 1967: CVS introduces full-service pharmacy counters. This decision fundamentally shifts the company toward prescription-based healthcare retail.
- 1969: CVS is acquired by Melville Corporation. The acquisition accelerates geographic expansion and strengthens pharmacy operations across new markets.
- 1972: CVS officially adopts the abbreviated name “CVS,” helping standardize branding as the chain expands nationally.
- 1980: CVS surpasses 400 stores nationwide, reflecting its growing dominance in neighborhood pharmacy retail.
- 1990: CVS acquires Peoples Drug, a major regional pharmacy chain, significantly expanding its footprint along the U.S. East Coast.
- 1996: CVS is spun off from Melville Corporation and becomes an independent, publicly traded company. This marks a major shift in ownership structure and strategic control.
- 2000: CVS launches its online pharmacy platform, an early move into digital prescription services.
- 2007: CVS merges with Caremark Rx. The merger creates a combined retail pharmacy and pharmacy benefits management business, reshaping how CVS operates and is owned.
- 2010: CVS introduces expanded in-store health services, strengthening its role in preventative and routine care.
- 2014: The company rebrands as CVS Health. In the same year, CVS removes tobacco products from all stores, reinforcing its healthcare-first identity.
- 2015: CVS expands MinuteClinic services nationwide, increasing access to walk-in clinical care inside CVS locations.
- 2018: CVS Health completes the acquisition of Aetna, integrating insurance, pharmacy benefits, and retail pharmacy under one corporate structure.
- 2020: CVS plays a central role in COVID-19 testing and vaccination efforts across the United States, expanding its public health presence.
- 2022: CVS increases its focus on primary care and home health integration within its retail ecosystem.
- 2023: CVS begins piloting smaller, pharmacy-focused store formats designed around healthcare services rather than general retail.
- 2024: CVS continues streamlining underperforming retail locations while investing in digital prescription management and virtual care tools.
- 2025: CVS operates as a key pillar of CVS Health, emphasizing pharmacy-led care, insurance integration, and community-based healthcare access.
Who Owns CVS: Largest Shareholders
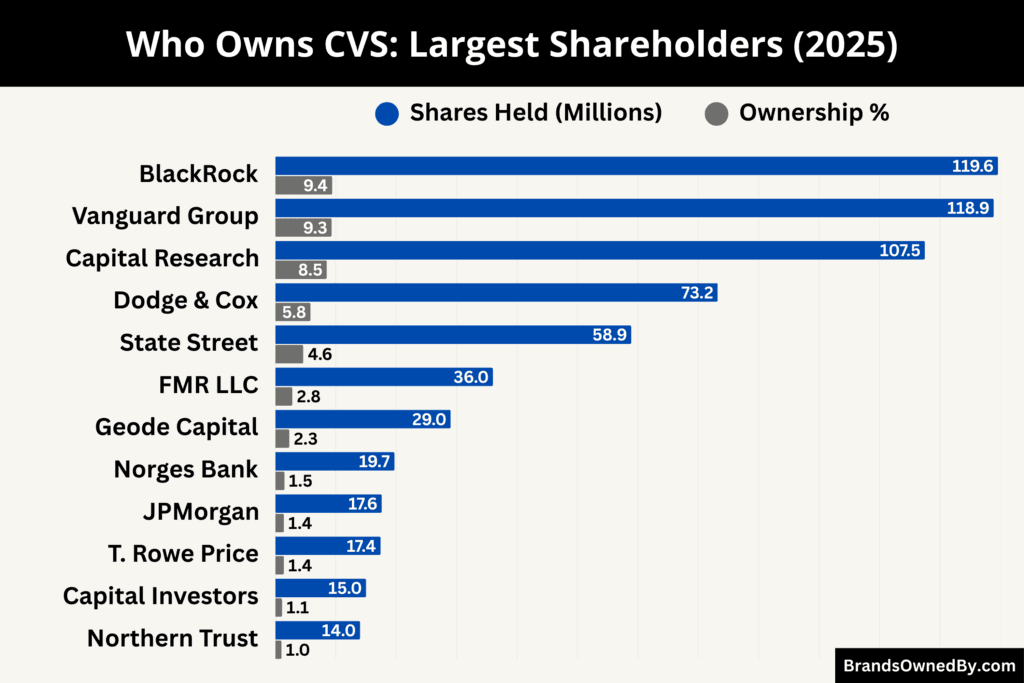
CVS Pharmacy is owned by CVS Health Corporation, a publicly traded healthcare company. CVS Health’s shares are listed on the New York Stock Exchange and are held by a wide range of investors including institutional funds, mutual funds, retail shareholders, and company insiders.
The company’s shareholder base is dominated by asset management firms. The largest shareholders are The Vanguard Group and BlackRock, each holding roughly 9% to 10% of outstanding shares. Capital Research and Management Company follows with a stake of around 8% to 9%. Dodge & Cox owns close to 6%, while State Street Global Advisors controls approximately 4% to 5%.
Collectively, the top five institutional shareholders own more than one-third of CVS Health’s total outstanding shares. This concentration gives institutional investors significant influence over corporate governance, board appointments, and executive compensation, while day-to-day operations remain under the control of company management and the board of directors.
Below is a list of the top shareholders of CVS Health (the parent company of CVS Pharmacy) as of December 2025:
The Vanguard Group
The Vanguard Group is the largest institutional shareholder of CVS Health. It owns approximately 118.9 million shares of CVS Health stock, representing around 9.3% of the company’s total shares outstanding. Vanguard holds these shares primarily through its index and mutual funds.
It is a passive investor by mandate, meaning it typically does not push for operational changes, but it exercises voting rights on key corporate governance matters such as board elections, executive compensation, and shareholder proposals. Vanguard’s significant stake gives it considerable weight in governance outcomes, especially on issues where other institutional holders align with its positions.
BlackRock, Inc.
BlackRock, Inc. is another top shareholder with approximately 119.6 million shares, equivalent to about 9.4% of CVS Health’s outstanding shares.
This makes BlackRock one of the largest single holders alongside Vanguard. BlackRock invests through a range of funds and managed accounts. Its influence arises from both the size of its position and its active governance approach, which often includes engagement with corporate leadership on strategy, risk oversight, and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) priorities.
BlackRock’s voting power is frequently observed in alignment with other large institutional investors on governance matters.
Capital Research and Management Company
Capital Research and Management Company (often through its Capital World Investors unit) holds roughly 107.5 million shares, or about 8.5% of the company. This investor is known for long-term, research-driven investment strategies.
Its stake is significant and places it among the top three largest institutional owners. Capital’s approach typically includes active evaluation of corporate strategy and performance metrics, and it uses its voting rights to hold leadership accountable for long-term value creation.
Dodge & Cox
Dodge & Cox owns approximately 73.2 million shares, representing about 5.8% of CVS Health. As a value-oriented investment management firm, it tends to hold positions for extended periods based on fundamental valuation and management quality. Dodge & Cox’s ownership stake is large enough to influence governance outcomes and provides continuity in shareholder engagement, particularly on capital allocation and operational performance.
State Street Global Advisors
State Street Global Advisors holds close to 58.9 million shares, which is about 4.6% of the company’s shares outstanding. State Street participates in governance through proxy voting and often supports initiatives that enhance transparency, shareholder rights, and accountability. Its stake, while smaller than the top three holders, remains material in collective governance decisions.
Fidelity Management & Research Company (FMR LLC)
Fidelity Management & Research Company (FMR LLC) owns around 36.0 million shares, roughly 2.8% of CVS Health’s total shares. Fidelity’s holdings are typically spread across multiple mutual funds and retirement accounts. While not among the very largest holders, Fidelity’s participation in annual meetings and voting on shareholder proposals contributes to overall governance dynamics.
Geode Capital Management, LLC
Geode Capital Management, LLC holds approximately 29.0 million shares, accounting for about 2.3% of the company. Geode’s position is smaller relative to the largest institutional holders, but it still represents a substantial investment. The firm tends to hold shares across index-oriented strategies, and its voting participation adds to the collective voice of institutional investors during key votes.
JPMorgan Asset Management
JPMorgan Asset Management holds approximately 17.6 million shares of CVS Health, representing about 1.4% ownership.
The firm manages assets on behalf of pension funds, sovereign institutions, and private investors. Its CVS stake is spread across actively managed and indexed strategies. JPMorgan’s role is governance-focused. It evaluates board effectiveness, capital allocation discipline, and executive compensation alignment. While not an activist investor, its voting power contributes meaningfully in close shareholder resolutions.
Norges Bank Investment Management
Norges Bank Investment Management owns roughly 19.7 million shares of CVS Health, equating to about 1.5% of outstanding shares.
This entity manages Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, one of the largest institutional investors globally. Its investment in CVS reflects a long-term, rules-based approach. Norges Bank is known for strong positions on corporate governance, transparency, and shareholder rights. Although it does not intervene in operations, its voting policies often influence governance standards, especially on board independence and executive accountability.
T. Rowe Price Group
T. Rowe Price Group holds approximately 17.4 million shares, accounting for around 1.4% ownership in CVS Health.
The firm is an active manager with a research-driven investment philosophy. Its CVS holdings are typically concentrated in long-term equity funds. T. Rowe Price engages with company leadership on strategic execution, competitive positioning, and long-term growth initiatives. Its ownership reflects confidence in CVS Health’s integrated healthcare model rather than short-term market movements.
Capital International Investors
Capital International Investors, an affiliate of Capital Group, holds a meaningful but non-controlling stake estimated at over 15 million shares, representing slightly above 1% ownership.
This investor focuses on fundamental analysis and long holding periods. Its involvement adds stability to CVS Health’s shareholder base and supports continuity in strategic oversight. Capital International typically uses proxy voting and management engagement to influence governance rather than public activism.
Northern Trust Asset Management
Northern Trust Asset Management holds an estimated 12–14 million shares of CVS Health, amounting to roughly 1% ownership.
The firm primarily manages institutional and retirement assets. Its CVS stake is largely passive but governance-aware. Northern Trust emphasizes fiduciary responsibility, risk management, and board accountability. While its ownership is smaller than the largest institutional holders, it contributes to the overall institutional voting bloc.
Insider and Retail Ownership
Insiders — including company executives and directors — collectively own a small fraction of the company, generally under 1–1.5% of outstanding shares. Retail investors and smaller public investors hold the remaining portion of shares. While their individual votes carry less influence than large institutional holders, their combined participation can still impact close governance decisions at shareholder meetings.
Who is the CEO of CVS?
The CEO of CVS Health is J. David Joyner. He was appointed as president and chief executive officer in October 2024 and also serves on the board of directors. His leadership spans the entire CVS Health enterprise, including retail pharmacy operations, insurance services through Aetna, and pharmacy benefits management under CVS Caremark.
Joyner brings over 35 years of experience in healthcare and has held multiple senior roles within CVS Health prior to becoming CEO. His tenure reflects a focus on operational efficiency, strategic realignment, and integration across the company’s major business segments.
In late 2025, he was also named Chair of the Board of Directors, combining governance leadership with executive oversight in a consolidated leadership structure.
Professional Background and Experience
David Joyner brings more than three decades of healthcare and operational leadership experience. Before becoming CEO, he held multiple senior roles within CVS Health, giving him deep institutional knowledge of the company’s structure and challenges.
He previously served as President of CVS Caremark, where he oversaw pharmacy benefits management operations serving employers, insurers, and government programs.
Earlier in his career, he led large-scale healthcare operations, focusing on efficiency, cost control, and patient access. His background is heavily operational rather than promotional, which aligns with CVS Health’s current emphasis on execution, margin discipline, and integrated care delivery.
Joyner’s appointment signaled a shift toward operational rigor and internal execution rather than transformational acquisitions.
Decision-Making Structure and Authority
As CEO, Joyner leads the enterprise executive committee, which includes heads of retail pharmacy, insurance, medical services, finance, and legal functions. Strategic decisions flow through this leadership group before being reviewed or approved by the board of directors.
The board maintains oversight authority, particularly on capital allocation, executive compensation, and long-term strategy. However, day-to-day operational decisions, restructuring initiatives, and integration efforts are directed by the CEO and his leadership team.
Joyner also plays a central role in investor communications, regulatory engagement, and long-term planning, particularly as CVS Health balances pharmacy retail pressures with insurance and care delivery growth.
CEO Salary and Net Worth
David Joyner’s compensation reflects the scale and complexity of CVS Health. His total annual compensation package is estimated at approximately $17–18 million.
This package includes a base salary of roughly $1.1 million, supplemented by annual cash incentives and long-term equity awards. The majority of his compensation is performance-based and tied to multi-year operational, strategic, and shareholder return targets. Equity awards are structured to vest over time, aligning his financial incentives with long-term company performance rather than short-term stock movements.
Such a compensation structure is consistent with large publicly traded healthcare companies of similar size and scope.
As of December 2025, David Joyner’s estimated net worth is approximately 20 million. This figure is primarily derived from accumulated stock awards, vested equity, and long-term incentive compensation earned during his tenure in senior executive roles.
Unlike founders or controlling shareholders, Joyner does not hold a large ownership stake in CVS Health. His wealth is tied to executive compensation rather than equity control, reinforcing the separation between ownership and management at CVS Health.
Past CEOs of CVS Health
Understanding CVS Health’s leadership evolution provides context for the current CEO’s role:
- Karen S. Lynch served as CEO from 2021 until October 2024. She led major healthcare expansion initiatives and guided the company through strategic shifts.
- Before her, leadership included Larry Merlo, who oversaw the integration of Aetna and other healthcare assets.
- Earlier CEOs such as Thomas M. Ryan played foundational roles during CVS’s expansion phase in the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
CVS Annual Revenue and Net Worth
As of December 2025, CVS Health reports annual revenue of approximately $394 billion, while its net worth, measured by market capitalization, stands at $101 billion. These figures reflect the scale of CVS Health’s operations and the market’s valuation of its integrated healthcare model, which combines retail pharmacy, insurance, pharmacy benefits management, and clinical care services.
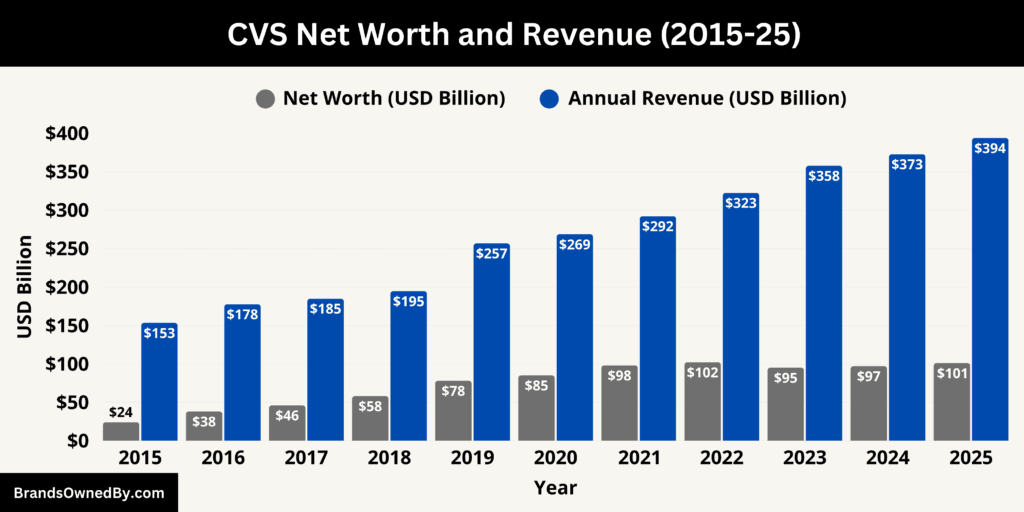
Revenue 2025
CVS Health’s revenue is generated through several major reporting segments, each contributing a significant portion of overall sales.
Pharmacy & Consumer Wellness: The pharmacy segment remains one of the largest contributors to CVS Health’s revenue base. For example, in quarterly reporting, this segment alone generated over $33.5 billion in revenue during a portion of 2025, driven by prescription fills, ancillary pharmacy services, and front-store sales of health and wellness products. Prescription volume growth and strategic acquisitions of prescription files from other chains added to revenue strength in this segment.
Health Care Benefits: This segment primarily includes insurance premium revenue from Aetna’s health plans. In a reported period in 2025, the health care benefits segment delivered approximately $36.3 billion in revenue, reflecting both Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial plan enrollments. Premium revenue forms a predictable and recurring source of income for the company.
Health Services (PBM and Caremark): The Health Services segment — which includes pharmacy benefit management through CVS Caremark and other care services — also contributes tens of billions of dollars. Quarterly results from 2025 indicate this segment generated approximately $46.5 billion in revenue, driven by PBM contracts, specialty pharmacy services, and integrated care solutions.
These segment figures illustrate how CVS Health’s diversified business model distributes revenue across insurance (Health Care Benefits), pharmacy benefit management (Health Services), and retail pharmacy (Pharmacy & Consumer Wellness). The combination of these segments supports a full-year total revenue nearing $394 billion for 2025.
Net Worth
CVS Health’s net worth of $101 billion as of December 2025 is best understood through its market capitalization, which is calculated by multiplying the company’s total outstanding shares by the current stock price on the New York Stock Exchange. The market cap reflects investor expectations of future earnings, growth prospects, competitive position, and industry risk.
A market capitalization figure places CVS Health’s implied value at $101 billion. This valuation incorporates not only current operational performance but also strategic positioning in insurance, pharmacy benefits management, and healthcare delivery.
Unlike revenue, which measures total sales, net worth via market cap gauges how investors value future profitability and risk. In CVS Health’s case, the market cap reflects confidence in its diversified revenue streams but also accounts for sector challenges such as reimbursement pressures, pharmacy margin constraints, and regulatory exposures.
Relationship Between Revenue and Valuation
The contrast between high revenue and a more moderate market cap underscores an important financial distinction: total revenue does not directly equate to company value. While CVS Health’s revenue approaches $400 billion, its market cap of $101 billion factors in profit margins, debt obligations, competitive risks, and anticipated future performance.
Investors evaluate earnings quality, cost structures, and growth potential rather than revenue totals alone when assigning valuation.
In practical terms, CVS Health’s diversified revenue composition — including insurance premiums, benefits management fees, and pharmacy sales — stabilizes earnings but also involves varying cost dynamics that influence profitability. Insurance and PBM segments may have lower or fluctuating margins, while retail pharmacy margins are sensitive to drug reimbursement rates and competition.
These factors influence how revenue translates into net income and, ultimately, market valuation.
Companies Owned by CVS
CVS Health operates a broad portfolio of companies, brands, and healthcare entities that extend far beyond retail pharmacy. These businesses are owned and operated directly by the company and are designed to work together as an integrated healthcare platform.
Below is a list of the major companies and brands owned by CVS as of December 2025:
| Company / Brand | Business Type | Year Integrated / Acquired | Core Function | Strategic Role Within CVS Health |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVS Pharmacy | Retail Pharmacy Chain | Founded 1963 | Prescription dispensing, vaccinations, front-store retail | Primary consumer access point and national retail pharmacy footprint |
| CVS Caremark | Pharmacy Benefits Management (PBM) | 2007 (Caremark merger) | Prescription plan administration, formulary design, specialty pharmacy | Cost control, prescription volume aggregation, payer integration |
| Aetna | Health Insurance | 2018 | Commercial, Medicare Advantage, and Medicaid-related insurance | Premium revenue, care coordination, payer-provider integration |
| MinuteClinic | Retail Medical Clinics | 2006 | Walk-in care, vaccinations, preventive services | Expands primary and episodic care access within CVS stores |
| Oak Street Health | Primary Care Clinics | 2023 | Value-based primary care for Medicare patients | Long-term care delivery and Medicare-focused growth |
| Omnicare | Institutional Pharmacy Services | 2015 | Pharmacy services for nursing homes and assisted living | Expands CVS into long-term and senior care markets |
| Coram | Home Infusion & Specialty Care | 2014 | Home infusion therapy and clinical support | High-cost specialty drug administration outside hospitals |
| Navarro Discount Pharmacy | Regional Retail Pharmacy | 2018 | Community pharmacy services in South Florida | Localized retail presence with bilingual outreach |
| HealthHUB (CVS-owned format) | Enhanced Store Concept | 2019 | Chronic care services, health devices, expanded clinics | Converts retail stores into healthcare access hubs |
| CVS Private-Label Brands | Consumer Health Products | Ongoing | OTC drugs, wellness, beauty, household goods | Margin expansion and product differentiation |
| Accordant | Specialty Care Management | 2013 | Case management for rare and complex diseases | Supports specialty pharmacy and PBM clinical programs |
| Target Pharmacy Assets | Retail Pharmacy Operations | 2015 | In-store pharmacy and clinic operations | Expanded national footprint through asset acquisition |
| Specialty Pharmacy Operations | Specialty Drug Services | Ongoing | High-cost biologics and complex therapies | Supports PBM contracts and specialty care coordination |
| Home Health & Ancillary Services | Clinical Support Services | Ongoing | Home care, monitoring, patient support programs | Extends care beyond retail and clinical settings |
CVS Pharmacy
CVS Pharmacy is the core retail brand of CVS Health. It operates thousands of drugstore locations across the United States that dispense prescriptions, deliver vaccinations, and sell over-the-counter and front-store items.
The retail network is the company’s primary consumer channel and a physical platform for clinical services, prescription fulfillment, and digital pickup. CVS Pharmacy is operated directly by CVS Health and serves as the anchor for in-store clinical offerings and HealthHUB conversions.
CVS Caremark
CVS Caremark is the pharmacy benefits management (PBM) arm of CVS Health. It administers prescription drug programs for employers, insurers, and government plans. Caremark handles drug formulary design, claims processing, network contracting, specialty pharmacy services, and cost-management programs.
The unit processes hundreds of millions of prescription claims annually and negotiates drug pricing and rebates on behalf of plan sponsors. Caremark is central to CVS Health’s vertical integration because it links retail dispensing, specialty pharmacy, and plan administration.
Aetna
Aetna is CVS Health’s health insurance business. Acquired in 2018, Aetna provides commercial, Medicare Advantage, and Medicaid-related health plans. It generates recurring premium revenue and manages care networks, utilization programs, and value-based contracting. Aetna’s membership and plan assets give CVS Health scale in managed care and create opportunities to coordinate benefits, pharmacy services, and in-person care across CVS Pharmacy and clinical assets.
MinuteClinic
MinuteClinic operates nurse practitioner- and physician assistant-staffed walk-in clinics inside many CVS Pharmacy locations. These clinics provide basic urgent care, vaccinations, chronic condition checkups, and preventive screenings. MinuteClinic expands access to primary and episodic care at retail locations, supports care continuity with pharmacy services, and generates visit-based revenue while improving patient convenience.
Oak Street Health
Oak Street Health is a network of physician-led primary care centers focused on Medicare-eligible patients and value-based care delivery. Acquired in 2023, Oak Street’s clinics aim to provide longitudinal primary care, care coordination, and population health management for older adults. Oak Street brings a clinic network and care model that CVS Health planned to scale into an integrated primary-care offering tied to Medicare Advantage strategies and community-based care.
Coram
Coram is CVS Health’s home infusion and enteral nutrition services business. Acquired in the mid-2010s, Coram provides specialty drug infusion and home-based clinical monitoring for patients who require complex therapies outside the hospital. Coram’s services include nursing oversight, patient education, and clinical coordination to manage high-cost, specialty drug regimens in patients’ homes.
Omnicare
Omnicare serves long-term care facilities, skilled nursing centers, and assisted living communities with pharmacy dispensing, medication management, and clinical support. Acquired as part of CVS Health’s expansion into institutional pharmacy services, Omnicare supplies unit-dose medications, compliance packaging, and consulting services to the long-term care market.
Navarro Discount Pharmacy
Navarro Discount Pharmacy operates a regional chain concentrated in South Florida. Acquired by CVS Health, Navarro continues to operate under its own brand in core local markets. Navarro provides retail pharmacy services, community outreach, and Spanish-language customer support in areas where it maintains strong market recognition.
HealthHUB
HealthHUB is CVS Health’s enhanced store concept rolled out inside selected CVS Pharmacy locations. HealthHUBs offer expanded clinical services, chronic care management resources, durable medical equipment, and broader care-management capabilities than a standard store. They are designed to serve as neighborhood access points for more comprehensive, integrated health services.
Store Private-Label Brands and Consumer Product Lines
CVS Health operates multiple private-label and owned consumer brands sold through CVS Pharmacy. These include national private-label lines for snacks and household goods, health and wellness supplements, and beauty/skin-care brands developed for the retail channel. Private labels provide margin capture on front-store items and differentiate product assortments across locations.
Accordant
Accordant provides rare disease case management and support services for patients on specialty therapies. Operated as a CVS Health subsidiary, Accordant works with payers and providers to coordinate access, adherence, and clinical support for complex conditions, complementing Caremark’s specialty pharmacy capabilities.
Target Pharmacy Assets
CVS Health acquired the pharmacy operations and related assets from Target in the mid-2010s and assumed operation of thousands of in-store pharmacies and clinics previously branded under Target. Those pharmacy assets were integrated into CVS Pharmacy operations and contributed to CVS’s national pharmacy footprint.
Longs Drugs and Other Regional Chains
Over time, CVS Health has absorbed multiple regional pharmacy chains—Longs Drugs (in the U.S. Pacific market), Sav-On/Osco conversions from Albertson integrations, and other acquired pharmacy networks. These acquisitions were integrated into the CVS Pharmacy banner or operated as regionally branded subsidiaries where advantageous.
Specialty and Ancillary Service Units (Specialty Pharmacy, Home Health, Clinical Services)
Beyond named brands, CVS Health operates specialty pharmacy businesses, home-health services, infusion centers in limited geographies, and other ancillary clinical units that support high-cost or complex therapy management. These units feed into Caremark’s specialty channel and support payers and providers with clinical programs, prior authorization services, and specialty distribution.
Final Thoughts
CVS Pharmacy operates at the center of a much larger healthcare structure, and understanding who owns CVS brings clarity to how the company functions and makes decisions. CVS is not controlled by a single individual or family. It is owned by CVS Health, a publicly traded corporation whose shares are primarily held by large institutional investors.
This ownership model places governance in the hands of the board and shareholders, while daily operations are led by professional management. With retail pharmacies, insurance, pharmacy benefits management, clinics, and owned consumer brands working together, CVS has evolved into an integrated healthcare platform. Its ownership structure explains both its scale and its strategic focus on long-term healthcare delivery rather than short-term retail growth.
FAQs
Who owns CVS Health?
CVS Health is a publicly traded company. It is owned by its shareholders, which include large institutional investors, mutual funds, retail investors, and company insiders. There is no single controlling owner.
Who owns most CVS?
No one owns a majority of CVS. The largest shareholders are institutional investors. The Vanguard Group and BlackRock are the two biggest, each holding roughly 9%–10% of CVS Health’s outstanding shares.
Who owns CVS Caremark?
CVS Caremark is fully owned and operated by CVS Health. It functions as CVS Health’s pharmacy benefits management (PBM) division.
Does Target own CVS now?
No. Target does not own CVS. CVS Health acquired Target’s pharmacy operations in 2015 and now operates CVS-branded pharmacies inside Target stores.
Is CVS owned by Vanguard?
No. The Vanguard Group does not own CVS outright. Vanguard is the largest shareholder, but it owns less than 10% of the company and does not control operations.
Does Warren Buffett own CVS stock?
There is no evidence that Warren Buffett personally owns a significant stake in CVS Health. CVS Health is also not a major disclosed holding of Berkshire Hathaway.
Who owns CVS Health Corporation?
CVS Health Corporation is owned by its shareholders. Ownership is dominated by institutional investors such as Vanguard, BlackRock, Capital Research, Dodge & Cox, and State Street, along with public and insider shareholders.
What companies does CVS own?
CVS Health owns and operates CVS Pharmacy, CVS Caremark, Aetna, MinuteClinic, Oak Street Health, Omnicare, Coram, Navarro Discount Pharmacy, and multiple private-label consumer brands sold through CVS stores.
What does CVS stand for?
CVS stands for Consumer Value Stores, the original name of the company when it was founded.
Who is the founder of CVS?
CVS was founded in 1963 by Stanley P. Goldstein and Sidney Goldstein, along with their partner Ralph P. Hoagland III.

