- Harrods is a privately owned company with no public or minority shareholders. The entire business is held under a single-owner structure.
- Harrods is 100% owned by Qatar Investment Authority, the sovereign wealth fund of the State of Qatar, which holds full economic and voting control.
- The ownership was established in 2010, when Qatar Investment Authority acquired 100% of Harrods from former owner Mohamed Al-Fayed, ending his 25-year ownership.
- Since the 2010 acquisition, ownership has not changed, and Harrods has continued to operate as a wholly owned, privately held subsidiary under Qatar Investment Authority.
Harrods is a luxury department store based in Knightsbridge, London. It is one of the largest and most famous retail emporia in the world. The flagship store occupies more than one million square feet of selling space and houses hundreds of departments offering everything from haute couture fashion to gourmet food. Harrods is widely recognised for its premium service, iconic green exterior, and long association with high society and global visitors.
The store’s motto is Omnia Omnibus Ubique, which means “all things for all people, everywhere.” Its enduring reputation stems from over 175 years of retail evolution, cultural prominence, and continuous adaptation to changing consumer expectations.
Harrods has also extended its brand into specialist services such as Harrods Aviation and Harrods Estates, reflecting its diversification within luxury markets.
Harrods Founders
Harrods was founded in 1849 by Charles Henry Harrod in London. The business began as a single grocery shop on Brompton Road. Leadership later passed to his son, Charles Digby Harrod, who took control in the 1860s. Under their combined stewardship between 1849 and the late 19th century, Harrods evolved from a grocery business into an early department store.
Charles Henry Harrod
Charles Henry Harrod was born in 1799 in Lexden, Essex. He came from a modest background and began his professional life working in milling and grain trading. His early exposure to food supply chains shaped his understanding of quality, sourcing, and customer trust. In the early 1830s, Harrod moved to London, where he entered the grocery trade. He initially operated as a wholesaler, supplying tea and dry goods to local businesses.
In 1849, he took over a small grocery shop on Brompton Road, near what was then a developing residential area. His decision to focus on premium products and dependable service helped the shop stand out. Harrod emphasized consistency and customer loyalty, which proved crucial during periods of economic uncertainty. Although he did not live to see Harrods become a global luxury institution, his business philosophy laid the foundation for its future growth.
Charles Digby Harrod
Charles Digby Harrod, the son of Charles Henry Harrod, played a decisive role in transforming the family grocery business into a large-scale retail enterprise. After taking control of operations, he expanded the product range beyond food and household essentials. New categories included clothing, cosmetics, medicines, and specialty goods.
Under his leadership in the late 19th century, Harrods began evolving into a department store rather than a single-category retailer. He also oversaw early structural expansions of the premises. Charles Digby Harrod introduced a more systematic retail model, with defined departments and improved customer experience. His strategic expansion positioned Harrods as a destination store well before department stores became common in the UK.
Major Milestones
- 1799: Charles Henry Harrod is born in Essex, England.
- 1824: Harrod begins working independently in food and trade-related businesses in London.
- 1834: He establishes a wholesale grocery and tea business in Stepney.
- 1849: Harrod acquires a small shop on Brompton Road, marking the beginning of Harrods.
- 1861: Charles Digby Harrod assumes control of day-to-day operations.
- 1870s: The business expands beyond groceries into general retail categories.
- 1881: A major fire destroys much of the original store structure.
- 1883: Reconstruction begins with a larger and more ambitious retail layout.
- 1889: Harrod’s Stores Limited is formally incorporated.
- 1894: Harrods becomes one of the first London retailers to adopt electric lighting.
- 1898: Escalators are introduced to improve customer movement within the store.
- 1905: The iconic Knightsbridge building opens with its now-famous exterior.
- 1913: Large-scale architectural expansions reshape the modern flagship store.
- 1959: Harrods is acquired by House of Fraser.
- 1985: Mohamed Al-Fayed takes ownership, ushering in a new global era.
- 1994: Harrods is separated from House of Fraser and returns to private ownership.
- 2010: Qatar Investment Authority acquires Harrods.
- 2017: The company accelerates its digital and omnichannel retail strategy.
- 2020: Harrods launches standalone beauty-focused retail concepts.
- 2023: Greater emphasis is placed on experiential luxury and personalized services.
- 2025: Strategic international restructuring is announced to refine global operations.
Who Owns Harrods?
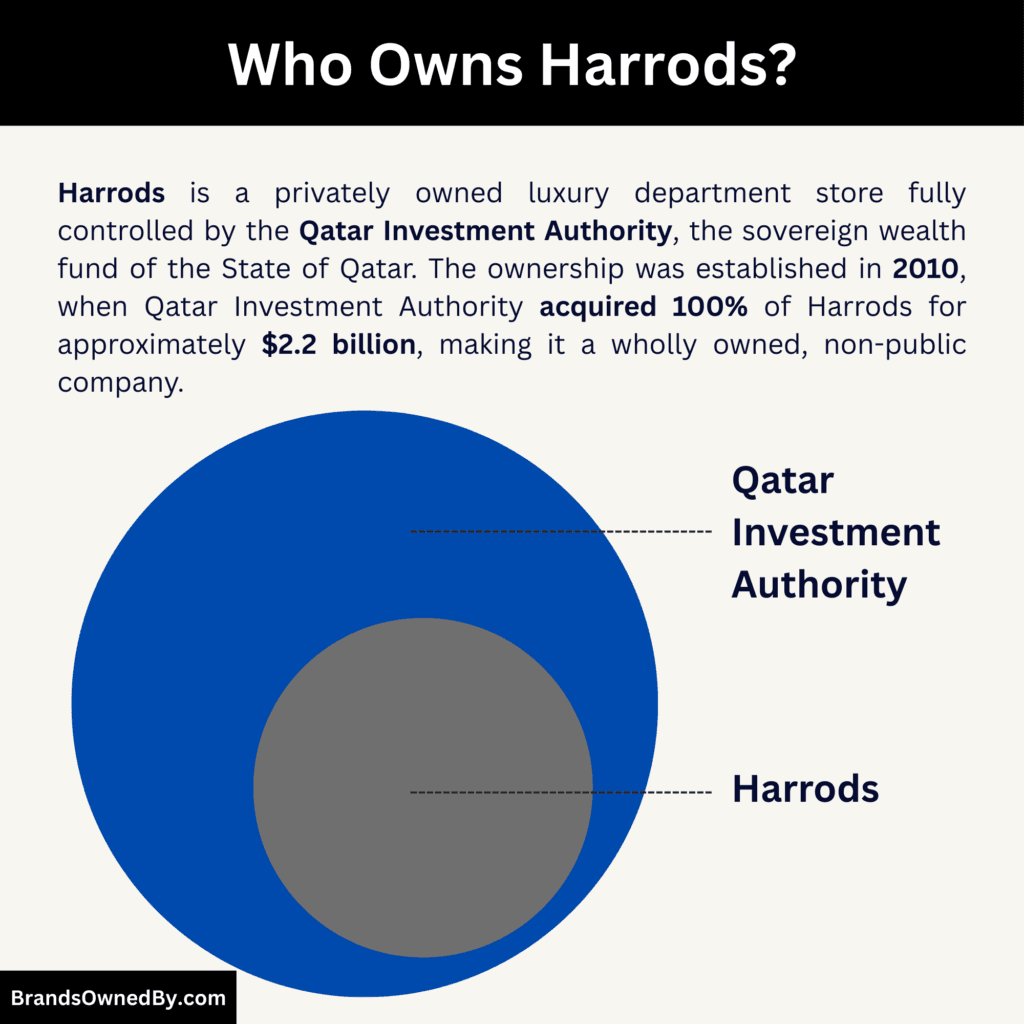
Harrods is a privately owned company. It is not listed on any stock exchange. The business is wholly owned by Qatar Investment Authority, the sovereign wealth fund of the State of Qatar.
The acquisition was completed in 2010. Qatar Investment Authority purchased 100% of Harrods from its previous private owner, Mohamed Al-Fayed. The transaction was executed through Qatar Holding, which is the direct investment subsidiary of Qatar Investment Authority.
Since the acquisition, Harrods has remained fully private. There are no public shareholders, no institutional minority investors, and no employee ownership stakes. All ownership, voting rights, and economic interests are controlled by Qatar Investment Authority.
Parent Company of Harrods: Qatar Investment Authority
The parent company of Harrods is the Qatar Investment Authority. Harrods operates as a wholly owned subsidiary within this structure. Qatar Investment Authority, commonly known as QIA, is the sovereign wealth fund of the State of Qatar. It is responsible for managing and investing the country’s surplus revenues, primarily generated from oil and natural gas exports.
QIA was established in 2005. Its core mandate is long-term capital preservation and growth. Unlike private investment firms, QIA does not operate for short-term profit. Its objective is to diversify Qatar’s national wealth, reduce dependence on hydrocarbons, and secure financial stability for future generations.
Ownership and Control of Qatar Investment Authority
Qatar Investment Authority is 100% owned by the State of Qatar. It has no private shareholders. The fund operates under state authority and reports to Qatar’s top economic leadership.
Ultimate oversight rests with the Amir of Qatar, who appoints the chairman and approves the fund’s strategic direction. QIA is governed by a board of directors and senior executives who manage investment policy, risk, and portfolio allocation. Day-to-day operations are led by the CEO and executive management team, while major investment decisions align with national economic objectives.
This governance model places QIA firmly under sovereign control rather than political or commercial influence from outside investors.
What Qatar Investment Authority Does
QIA functions as a global institutional investor. It allocates capital across public markets, private equity, real estate, infrastructure, and strategic direct investments. The fund invests both directly and through subsidiaries and joint ventures.
Its investment approach is long-term and diversified. QIA targets high-quality assets with durable value, strong brands, and global relevance. It often takes controlling stakes or significant minority positions, depending on strategic importance.
The fund operates across multiple regions, including Europe, North America, Asia, and the Middle East.
Major Businesses and Investments Held by QIA
Qatar Investment Authority has one of the most diversified sovereign portfolios in the world. Its holdings span banking, real estate, hospitality, transportation, technology, energy, and consumer brands.
- Qatar National Bank – Majority-owned by Qatar Investment Authority. It is the largest bank in the Middle East and serves as Qatar’s primary domestic and international banking institution.
- Katara Hospitality – Fully owned by Qatar Investment Authority. It owns and operates luxury hotels and resorts across Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
- Hassad Food – Wholly owned by Qatar Investment Authority. It manages agricultural assets and food production investments in Australia, North America, and other regions.
- Qatar Airways Group – Majority owned by Qatar Investment Authority. It includes Qatar Airways and related aviation businesses operating a global airline network.
- Volkswagen AG – Qatar Investment Authority is one of the largest shareholders. The stake provides exposure to brands such as Audi, Porsche, Bentley, and Lamborghini.
- Siemens AG – Qatar Investment Authority holds a significant equity stake. The investment aligns with infrastructure, energy, and industrial technology sectors.
- Barclays – Qatar Investment Authority is a major shareholder. The stake originated during the global financial crisis and remains part of its financial services portfolio.
- Credit Suisse – Qatar Investment Authority was a significant shareholder prior to Credit Suisse’s acquisition by UBS, reflecting long-term exposure to global banking.
- J Sainsbury – Qatar Investment Authority has held a notable equity stake in the UK grocery retailer.
- Canary Wharf Group – Co-owned by Qatar Investment Authority. The group controls the Canary Wharf financial district in London.
- The Shard – Owned by Qatar Investment Authority. It is a major mixed-use commercial and hospitality landmark in London.
- Chelsea Barracks – Owned by Qatar Investment Authority. It is one of London’s most valuable residential redevelopment projects.
- Harrods – Wholly owned by Qatar Investment Authority. It operates as a flagship luxury retail asset.
- Printemps – Qatar Investment Authority holds an investment stake in the French luxury department store group.
Role of QIA in Harrods’ Governance
As the parent company, Qatar Investment Authority exercises full ownership and strategic oversight of Harrods. It appoints the board and approves long-term strategic initiatives. Operational control remains with Harrods’ executive leadership, but all major decisions ultimately fall under QIA’s authority.
This parent-subsidiary relationship allows Harrods to operate independently at a retail level while benefiting from the financial strength, stability, and long-term vision of a sovereign owner.
Harrods Acquisition
In May 2010, ownership of Harrods changed hands after 25 years under Mohamed Al-Fayed. The store was acquired by Qatar Holding LLC, the direct investment arm of the Qatar Investment Authority (QIA). This transaction transferred 100% ownership of Harrods to QIA’s investment vehicle. It ended Al-Fayed’s tenure as owner and positioned Harrods under sovereign wealth fund control.
Background to the Sale
Harrods had been owned by Egyptian-born businessman Mohamed Al-Fayed since 1985. During his ownership, Harrods grew in reputation as a global luxury destination.
However, by the late 2000s, discussions began around a potential sale. Al-Fayed initially denied that the store was for sale, but negotiations accelerated in early 2010.
Al-Fayed’s decision to sell was partly driven by his desire to retire from active management and ensure the store’s future under a well-funded investor capable of long-term strategic support. His family trust engaged Lazard International as an adviser to manage the transaction process.
Buyer: Qatar Holding and Qatar Investment Authority
The buyer was Qatar Holding LLC, which operates as the investment division of the Qatar Investment Authority. QIA is the sovereign wealth fund of the State of Qatar, responsible for investing the country’s surplus oil and gas revenues into global assets.
Qatar Holding was specifically chosen by the Al-Fayed family trust because of its financial capacity and strategic vision to support Harrods as a long-term luxury brand. The acquisition placed Harrods alongside other international assets in QIA’s diversified portfolio.
The sale agreement was signed in the early hours of 8 May 2010. The transaction price was widely reported in the market at around £1.5 billion, which equated approximately to $2.2 billion at that time. While the exact terms were not publicly disclosed, this figure was cited by multiple financial reports and the press.
As part of the deal, Al-Fayed stepped down from day-to-day management. He was initially given the title of honorary chairman for a transitional period, though operational control shifted to the new owners.
Strategic Rationale for the Acquisition
From QIA’s perspective, the acquisition of Harrods served several strategic purposes:
- Global Luxury Asset: Harrods was recognised as one of the world’s premier luxury retail brands. Adding it to QIA’s portfolio enhanced its presence in the global consumer and lifestyle sectors.
- Long-Term Investment: As a sovereign wealth fund, QIA focuses on long-term holdings rather than short-term returns. Harrods fits this strategy due to its strong brand equity and tourism draw.
- Brand Expansion: QIA saw potential to leverage Harrods in broader luxury and retail initiatives, including international brand extensions and digital commerce.
Post-Acquisition Governance
After the acquisition, Harrods continued to operate as a wholly owned private company under QIA’s control. The board and executive leadership report ultimately to QIA’s appointed directors.
Operational decisions are handled by Harrods’ CEO and management team, while strategic direction is overseen by executives aligned with Qatar Holding’s objectives.
The acquisition marked a shift from single-family ownership to sovereign wealth ownership. It remains one of the most notable luxury retail transactions of the early 21st century.
Who is the CEO of Harrods?
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Managing Director of Harrods is Michael Ward. He has held this top executive role since 2005, making him one of the longest-serving leaders in the company’s modern history.
He continued in the position through the transition of ownership to Qatar Investment Authority and remains the principal executive responsible for Harrods’ strategy, operations, and growth in the luxury retail sector.
Early Life and Career
Michael Ward was born in 1956 in the United Kingdom. He began his professional career as a chartered accountant, training with Ernst & Young in 1980. Over the following decade, he progressed into senior financial and executive roles:
- In 1986, he became Group Finance Director at Bassett Food PLC.
- By 1989, he was Finance Director at H.P. Bulmer Holdings PLC.
- In 1994, he transitioned fully into retail as Managing Director of Lloyds Chemist PLC.
- Prior to joining Harrods, he held senior leadership and private equity roles, including at Apax Partners.
He was first appointed by then-owner Mohamed Al-Fayed and retained the leadership mandate after Harrods was sold to Qatar Investment Authority. Over his tenure, Ward has guided Harrods through major brand expansions, digital transformation efforts, and structural investments in the flagship London store.
Roles and Responsibilities
As CEO and Managing Director, Michael Ward is responsible for:
- Setting Harrods’ strategic direction.
- Managing executive leadership and senior teams.
- Overseeing customer experience, brand partnerships, and global retail initiatives.
- Ensuring operational excellence across more than 300 departments within the Knightsbridge store.
- Leading engagement with international luxury brands and strategic partners.
Ward also serves in prominent positions outside Harrods, including as Chairman of Walpole, the official sector body representing the British luxury industry. This role reflects his influence across the broader UK luxury sector.
CEO Salary
As of the latest available data:
- Michael Ward was reported as Harrods’ highest-paid director.
- His total compensation was approximately £2.1 million in the most recent published year, down from around £2.3 million previously.
These figures reflect his base salary, bonuses, and other executive pay elements typically associated with his role as chief executive leader. Harrods does not publicly disclose detailed executive pay breakdowns, but independent reports indicate that Ward’s compensation places him among the highest-paid executives in UK retail leadership as of 2024–2025.
Succession and Leadership Team
Harrods operates under a centralised executive leadership model with the CEO at the top of the decision-making structure. Michael Ward has ultimate executive authority over strategy, operations, brand direction, and senior appointments. He reports to the board, which represents the interests of the parent company, Qatar Investment Authority.
Beneath the CEO, Harrods is managed by a tightly structured executive committee. This includes roles responsible for retail operations, merchandising, digital commerce, supply chain, property, marketing, and people management. Each function operates with defined accountability due to the complexity and scale of the Knightsbridge flagship store.
In recent years, Harrods has strengthened its senior leadership to reflect shifts in luxury retail. New and expanded roles have focused on customer experience, category specialisation, and omnichannel retail. The creation and elevation of a Chief Retail–level function signaled a stronger emphasis on in-store performance, brand partnerships, and department-level execution.
Succession planning at Harrods is conservative and long-term. The company prioritises continuity over frequent leadership turnover. Senior executives are often promoted internally or hired with deep experience in luxury retail rather than general retail. Any future CEO transition would require board approval and alignment with the parent company’s long-term strategy.
Harrods Annual Revenue and Net Worth
As of January 2026, Harrods reported annual revenue of approximately $1.45 billion. This figure reflects the full scope of the company’s global retail operations, including flagship store sales, digital commerce, food and hospitality services, and other ancillary revenue streams. Harrods’ net worth is estimated at $6.2 billion, driven by the value of its flagship Knightsbridge real estate, brand equity, and diversified income sources.
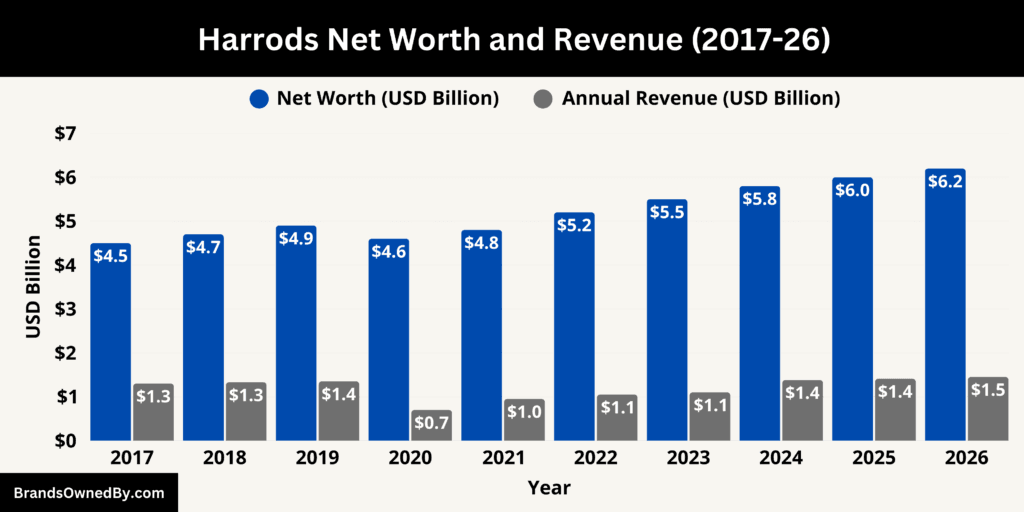
Revenue Performance and Key Drivers
Harrods’ $1.45 billion annual revenue is generated primarily from direct retail sales at its Knightsbridge flagship store. The store operates more than 300 individual departments across fashion, accessories, jewellery, watches, beauty, food, and home categories. High-value categories such as women’s designer fashion, fine jewellery, watches, and beauty account for a disproportionate share of total sales due to higher average transaction values.
Flagship Retail Sales (Approx. $900–$950 million annually)
The core revenue source is the Knightsbridge flagship store, which accounts for roughly 65% of total revenue. The store operates more than 300 departments and sells across luxury fashion, jewellery, watches, beauty, home, and gifting.
Around 70% of in-store sales are generated through concession agreements with luxury brands. Under this model, brands such as Gucci, Dior, Chanel, Rolex, and Cartier operate dedicated spaces and share revenue with Harrods. This structure limits inventory risk while producing stable, high-margin income.
High-ticket categories drive revenue concentration. Fine jewellery, watches, women’s fashion, and beauty together contribute more than half of retail turnover due to high average transaction values and repeat international clientele.
Food Halls, Restaurants, and Catering (Approx. $250–$280 million annually)
Harrods’ food business is a standalone revenue engine. The Food Halls, restaurants, private dining rooms, and catering services generate close to 20% of total revenue.
Unlike fashion retail, food revenue is daily, repeat-driven, and less seasonal. Local London customers contribute consistently, while tourists drive peak volumes. This segment provides cash-flow stability and offsets volatility in discretionary luxury spending.
E-commerce and International Sales (Approx. $150–$170 million annually)
Online sales account for roughly 10–12% of revenue. The platform focuses on beauty, fashion, and gifting, with international shipping supporting customers outside the UK.
Digital sales do not replace flagship performance. Instead, they extend customer lifetime value by enabling repeat purchases after in-store visits. Growth in this segment has been steady rather than explosive, reflecting Harrods’ store-led luxury model.
Aviation, Private Services, and Other Income (Approx. $50–$70 million annually)
Harrods also generates revenue from Harrods Aviation, private shopping services, VIP experiences, and branded services. These activities represent a small share of total revenue but operate at very high margins and serve ultra-high-net-worth clients.
Harrods Net Worth
Harrods’ estimated $6.2 billion net worth, as of January 2026, is anchored first and foremost in physical real estate ownership.
Knightsbridge Flagship Real Estate (Approx. $3.5–$4.0 billion)
The single largest component of Harrods’ net worth is its fully owned Knightsbridge property, covering more than 1 million square feet in one of London’s most expensive retail districts.
The building is owner-occupied, not leased. This means its full market value is embedded in Harrods’ enterprise value. Comparable commercial assets in Knightsbridge support a valuation in the multi-billion-dollar range, making this the dominant net-worth driver.
Operating Business Value (Approx. $1.5–$1.7 billion)
This represents the value of Harrods as an operating retail business. It includes retail operations, food services, e-commerce, aviation services, and licensing activities.
This valuation is supported by recurring revenue, strong margins from concession retail, and diversified income streams. The operating business generates sufficient cash flow to sustain reinvestment without external financing.
Brand Value and Intellectual Property (Approx. $700–$900 million)
Harrods owns one of the most valuable luxury retail brands globally. The brand allows Harrods to:
- Command premium revenue shares from concession partners
- Secure exclusive product launches
- Monetise its name through licensing and international extensions
This brand equity is a measurable economic asset. It directly increases enterprise value rather than functioning as a marketing abstraction.
Subsidiary Businesses and Services (Approx. $200–$300 million)
This includes Harrods Aviation, Harrods Estates, and other controlled service businesses. While smaller in scale, these units contribute predictable income and enhance valuation through diversification.
Brands Owned by Harrods
Harrods operates as a multi-division luxury enterprise, not merely a department store. Its ownership structure includes retail, food, hospitality, aviation, property services, digital commerce, and private client operations. All entities are directly controlled by Harrods itself and aligned under a single brand ecosystem.
Below is a list of the major brands owned by Harrods as of January 2026:
| Company / Brand | Type | Year Launched | Core Function | Key Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harrods Limited | Operating company | 1849 | Core retail business | Owns and operates the Harrods department store, managing over 300 retail departments, supplier relationships, concessions, logistics, and corporate operations |
| Harrods Aviation | Subsidiary | 1983 | Private aviation services | Provides aircraft handling, VIP lounges, and hangar services at London airports for private and business jets |
| Harrods Estates | Subsidiary | 1897 | Luxury real estate services | Offers residential sales, lettings, and advisory services focused on prime London property markets |
| Harrods Interiors | Business unit | 1990s | Interior design & furnishings | Delivers bespoke interior design, furniture sourcing, and project management for private clients and developers |
| Harrods Food Halls | Business unit | 1898 | Gourmet food retail | Operates premium food halls, fresh produce, patisserie, catering, and branded food gifting |
| Harrods Restaurants | Business unit | Various | Hospitality & dining | Manages all cafés, restaurants, private dining rooms, and culinary concepts within Harrods |
| Harrods Online | Digital division | 2000 | E-commerce & digital retail | Handles global online sales, international shipping, click-and-collect, and private client digital services |
| H beauty | Standalone brand | 2020 | Beauty-only retail | Operates standalone beauty stores focusing on cosmetics, skincare, fragrance, and wellness |
| Harrods Private Shopping | Service division | Early 2000s | VIP retail services | Provides appointment-only shopping, personal stylists, private suites, and bespoke sourcing |
| Harrods Corporate Gifting | Business unit | 2000s | Corporate & private gifting | Specialises in luxury hampers, branded gifts, and bespoke gifting solutions for institutions and corporations |
Harrods Limited
Harrods Limited is the core operating company that owns and runs the Harrods department store business. It controls all retail, food, hospitality, digital commerce, and service operations conducted under the Harrods name. The company manages more than 300 in-store departments, oversees supplier and concession agreements, and employs thousands of staff across retail, logistics, and corporate functions. All brand extensions and subsidiaries ultimately sit under Harrods Limited.
Harrods Aviation
Harrods Aviation is a wholly owned subsidiary of Harrods. It operates private aviation services at London airports, primarily serving business jets and high-net-worth travelers. The company provides aircraft handling, VIP passenger services, and hangar facilities. Harrods Aviation functions independently from retail operations but leverages the Harrods brand to serve an elite client base. It is one of the most established private aviation service providers in the UK.
Harrods Estates
Harrods Estates is Harrods’ luxury real estate arm. It offers high-end residential property sales, lettings, and advisory services in London, particularly in Knightsbridge and surrounding prime locations. The business caters to international buyers and investors seeking premium residential assets. Harrods Estates operates as a regulated property agency while benefiting from brand alignment with the flagship store and concierge services.
Harrods Interiors
Harrods Interiors provides bespoke interior design and furnishing services. It works with private clients, developers, and international customers on luxury residential projects. Services include furniture sourcing, design consultation, and full interior project management. This division allows Harrods to extend its luxury offering beyond retail into long-term lifestyle services.
Harrods Food Halls
The Harrods Food Halls operate as a distinct business unit within Harrods. They generate significant standalone revenue through gourmet food retail, fresh produce, patisserie, and specialty dining. The Food Halls also support catering, hampers, and corporate gifting. While housed within the flagship store, the food business is operationally separate from fashion retail and has its own supply chains and supplier relationships.
Harrods Restaurants
Harrods Restaurants encompass all dining concepts operated within the Harrods ecosystem. This includes casual dining, fine dining, private dining rooms, cafés, and bars. These restaurants serve both shoppers and destination diners. The division operates with dedicated culinary teams, menu development, and hospitality management distinct from retail departments.
Harrods Online
Harrods Online is the company’s e-commerce and digital retail platform. It supports international shipping, click-and-collect, and private client digital services. The platform focuses primarily on fashion, beauty, accessories, and gifting. Harrods Online is not a separate legal company but operates as a dedicated digital business unit with its own technology, logistics, and customer service teams.
H beauty
H beauty is a beauty-focused retail brand created and owned by Harrods. It operates as a standalone concept separate from the Knightsbridge flagship. H beauty stores focus exclusively on cosmetics, skincare, fragrance, and wellness. The brand targets a broader demographic than the main Harrods store while maintaining premium positioning. H beauty represents Harrods’ most significant brand extension beyond its flagship location.
Harrods Private Shopping
Harrods Private Shopping is a dedicated service division serving ultra-high-net-worth clients. It offers appointment-only shopping, private suites, personal shoppers, bespoke sourcing, and international delivery. This unit generates high-margin revenue through personalised services rather than volume sales and plays a key role in client retention.
Harrods Corporate Gifting
Harrods Corporate Gifting provides curated luxury gifts for corporations, institutions, and private clients. It focuses heavily on branded hampers, premium food products, and bespoke gift solutions. This unit operates year-round but peaks during holiday and corporate gifting seasons.
Final Thoughts
Harrods remains one of the world’s most distinctive luxury retailers, shaped as much by its ownership as by its heritage. For anyone asking who owns Harrods, the answer explains its long-term stability and careful approach to growth. Being privately held allows the business to focus on brand strength, customer experience, and asset preservation rather than short-term market pressures. That structure continues to define how Harrods operates, invests, and positions itself globally.
FAQs
Who owns Harrods now?
Harrods is owned by Qatar Investment Authority, which holds 100% of the company. It is privately owned and not publicly traded.
Who owns Harrods London?
The Harrods London department store is owned by Qatar Investment Authority, which controls the entire Harrods business, including the Knightsbridge flagship.
When did Fayed buy Harrods?
Mohamed Al-Fayed bought Harrods in 1985.
Who bought Harrods?
Harrods was bought in 2010 by Qatar Investment Authority, through its investment arm, Qatar Holding.
Who owned Harrods before Fayed?
Before Mohamed Al-Fayed, Harrods was owned by House of Fraser, which had acquired Harrods in 1959.
Who owns Harrods department store?
The Harrods department store is wholly owned by Qatar Investment Authority. There are no minority or public shareholders.
How much did Mohamed Al Fayed sell Harrods for?
Mohamed Al-Fayed sold Harrods in 2010 for approximately $2.2 billion.
Does Qatar still own Harrods?
Yes. Qatar, through Qatar Investment Authority, still owns Harrods and has maintained full ownership since 2010.
Who owned Harrods before Fayed?
Prior to Mohamed Al-Fayed’s acquisition in 1985, Harrods was owned by House of Fraser.
How much was Harrods sold for?
Harrods was sold in 2010 for an estimated $2.2 billion.
Who owns Harrods Aviation?
Harrods Aviation is owned directly by Harrods, not by the parent company. It operates as a wholly owned subsidiary of the Harrods group.