Alfa Romeo is one of the most iconic Italian carmakers, and many people search for who owns Alfa Romeo today. The brand has changed hands several times and now sits under a large global automotive group. Its ownership, leadership, and portfolio reflect a modern strategy focused on performance and electrification.
Key Takeaways
- Alfa Romeo is fully owned by Stellantis N.V. and has no independent shareholders or separate stock listing; all control flows through Stellantis’ board and executive leadership.
- The largest controlling shareholder of Stellantis is Exor N.V. (Agnelli family), followed by the Peugeot family holding group and the French state investment bank Bpifrance, with the remaining shares held by major institutional investors.
- Strategic decisions for Alfa Romeo are made at the Stellantis level, including funding, product platforms, factories, and electrification plans; Alfa Romeo’s CEO executes the strategy but does not control ownership.
Alfa Romeo Profile
Alfa Romeo is a legendary Italian car manufacturer known for its blend of artistic design, engineering excellence, and racing spirit. Since its origins over a century ago, the brand has combined Italian craftsmanship, technical innovation, and a passion for speed.
Through decades of change, Alfa Romeo has maintained a distinct identity rooted in Milan, a dedication to driving pleasure, and a reputation for sporty, elegant vehicles. Today, under its current global owner, the brand continues to evolve — honoring its heritage while adapting to modern automotive technologies and markets.
Founders and Origins
The story of Alfa Romeo begins with the early 20th-century automotive ventures in Italy. The precursor was Società Italiana Automobili Darracq (SAID), which established a plant in what became the Portello district of Milan. SAID was part of a French automaker’s efforts to produce cars locally.
When SAID faced financial troubles in 1909, a group of Italian investors stepped in. Among them was aristocrat Ugo Stella, who acquired the shares and led the formation of a new company. On 24 June 1910, the new company was officially founded under the name Anonima Lombarda Fabbrica Automobili (A.L.F.A.).
At that time, engineer Giuseppe Merosi was hired as chief designer. He was responsible for designing the brand’s very first cars — including the 1910 “24 HP.” That model marked the beginning of what would become a storied lineage of Alfa vehicles.
Then, in 1915, Italian entrepreneur and engineer Nicola Romeo took control of A.L.F.A. His takeover was decisive. Under his leadership, the company would gain stability and direction. By 1918, legal and financial steps formalized the transformation. Ultimately, the name “Alfa Romeo” was adopted — combining the original acronym with Romeo’s surname.
Through these founding figures — Stella, Merosi, and Romeo — Alfa Romeo inherited a mix of entrepreneurial ambition, engineering skill, and a desire to build more than just cars: to craft automotive passion.
Major Milestones
- 1910: Alfa Romeo was founded on June 24 as A.L.F.A. in Milan. The first model, the 24 HP, was designed by Giuseppe Merosi and introduced the brand’s engineering direction.
- 1911: Alfa Romeo entered motorsport for the first time. The brand competed in the Targa Florio, launching a long racing tradition.
- 1915: Nicola Romeo took control of the company during World War I. Automobile production slowed as the factory shifted to military equipment manufacturing.
- 1918: Alfa Romeo restructured after the war. Focus returned to road vehicles and racing.
- 1920: Alfa Romeo became the official company name. The Torpedo 20–30 HP became the first car to carry the Alfa Romeo badge.
- 1923: Vittorio Jano joined as chief engineer. His engineering transformed Alfa Romeo into a racing powerhouse.
- 1925: Alfa Romeo won the first Automobile World Championship with the P2. The victory placed the brand among elite global manufacturers.
- 1932: Alfa Romeo launched its legendary racing department. The Scuderia Ferrari partnership formally began.
- 1933: Alfa Romeo withdrew from direct factory racing. Ferrari continued racing Alfa cars independently.
- 1940: Alfa Romeo production halted due to World War II damage. The Portello factory suffered heavy bombing.
- 1946: Alfa Romeo resumed manufacturing. Recovery began in post-war Italy.
- 1950: Alfa Romeo won the first Formula One World Championship through Giuseppe Farina.
- 1954: Alfa Romeo introduced the Giulietta. It marked a shift toward affordable performance cars.
- 1963: Alfa Romeo expanded production facilities. The Arese factory became a major manufacturing hub.
- 1966: Alfa Romeo debuted the Duetto Spider. The model became a design icon.
- 1972: Alfa Romeo opened the Pomigliano d’Arco plant. Production expanded in southern Italy.
- 1980: Alfa Romeo faced financial distress. State ownership increased.
- 1986: Alfa Romeo was sold to Fiat Group. This privatized the brand.
- 1995: Alfa Romeo launched the modern 156. It revived interest in the brand globally.
- 2005: Alfa Romeo re-entered international touring car racing. Brand visibility increased.
- 2015: Alfa Romeo introduced the Giulia. A new performance era began.
- 2017: Alfa Romeo returned to Formula One as a brand partner.
- 2021: Alfa Romeo became part of Stellantis. Corporate structure changed following the FCA and PSA merger.
- 2022: Alfa Romeo announced its full electrification roadmap. Transition planning began.
- 2023: Alfa Romeo introduced next-generation hybrid platforms. Innovation strengthened.
- 2024: Alfa Romeo expanded global digital sales models. Customer engagement evolved.
- 2025: Alfa Romeo operates under Stellantis. Focus remains on performance, luxury, and electrification.
Who Owns Alfa Romeo: Major Shareholders
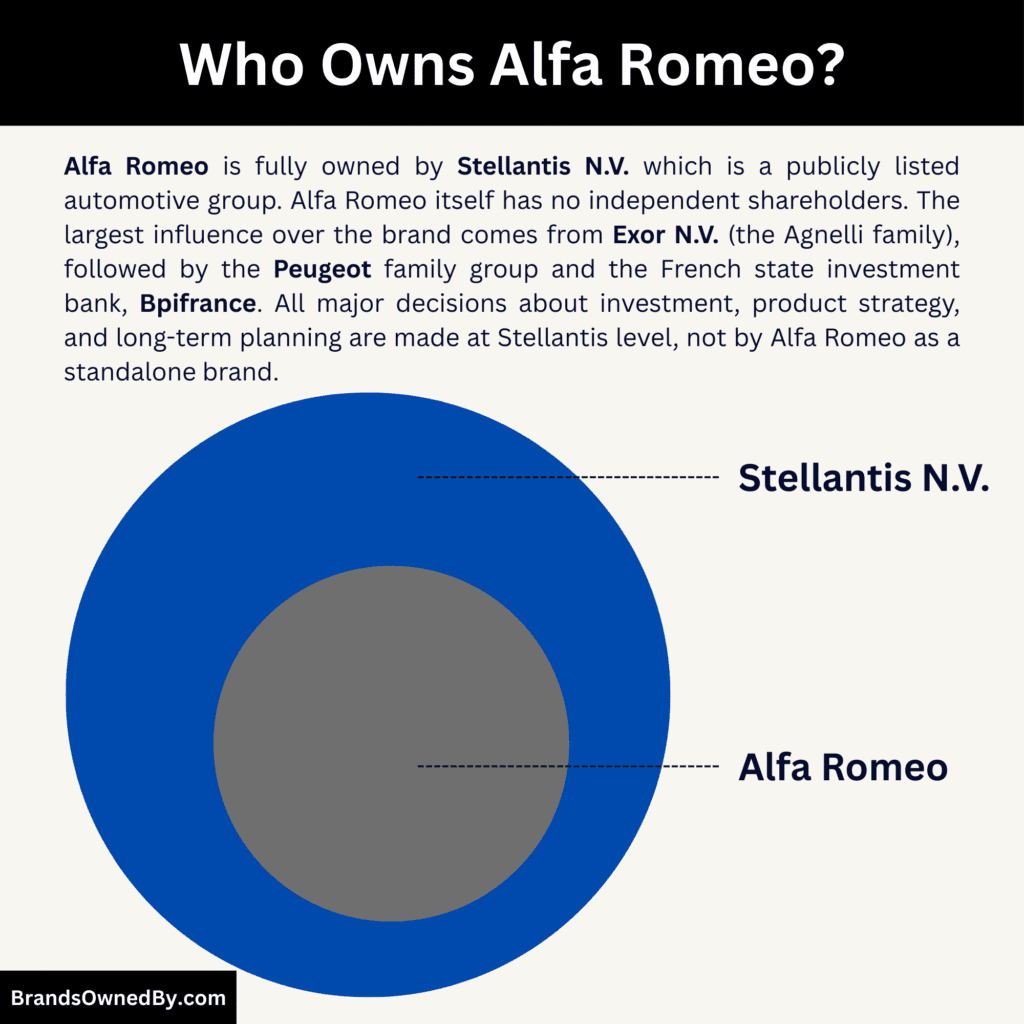
Alfa Romeo is owned by Stellantis N.V., one of the world’s largest automotive groups. Stellantis owns Alfa Romeo outright and manages it as part of its global brand portfolio. Alfa Romeo has no separate shareholders, no individual stock listing, and no independent board.
Every major decision about Alfa Romeo is made inside the Stellantis corporate structure. This includes leadership appointments, long-term product planning, factory decisions, and investment strategy.
Parent Company: Stellantis N.V.

Stellantis N.V. is the parent company of Alfa Romeo and one of the largest automotive groups in the world. It was formed through the merger of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles and PSA Group. The company is legally headquartered in the Netherlands and operates globally across Europe, North America, South America, and Asia.
Alfa Romeo is positioned inside Stellantis as a premium performance brand. It is grouped with brands that emphasize heritage, design, and driving dynamics rather than mass-market volume. Stellantis defines Alfa Romeo’s long-term goals, approves major projects, and assigns resources to the brand based on its performance within the group portfolio.
Stellantis controls nearly every strategic element of Alfa Romeo’s business, including:
- Product platforms and engineering direction
- Electric vehicle development roadmap
- Manufacturing location decisions
- Brand placement in global markets
- Technology integration
- Global marketing and investment planning.
Alfa Romeo does have its own management. However, that management does not operate independently. The brand’s CEO reports directly to the Stellantis executive leadership team. Budgets, model approvals, and product timelines are reviewed and authorized at the group level. Final authority always rests with Stellantis, not with Alfa Romeo itself.
Alfa Romeo Acquisition by Stellantis
Alfa Romeo was not acquired in isolation by its current owner. The brand became part of Stellantis through a large-scale corporate merger. It moved under Stellantis when its former parent company merged with another global automaker.
This makes Alfa Romeo’s ownership different from a typical acquisition. There was no purchase of the brand alone. Instead, Alfa Romeo changed hands because the company that owned it merged with another automotive group.
The FCA–PSA Merger Explained
Alfa Romeo was part of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA). In 2021, FCA merged with PSA Group, which owned brands such as Peugeot, Citroën, and Opel.
This merger created Stellantis N.V.
Stellantis did not buy Alfa Romeo outright. It inherited the brand when FCA and PSA combined their operations, assets, and brands into one company. From that moment, Alfa Romeo became a wholly owned brand within Stellantis.
The merger was structured as a merger of equals. Neither FCA nor PSA was fully bought out by the other. Ownership of Stellantis was divided among the major shareholders of both former groups.
Why Stellantis Wanted Alfa Romeo
Stellantis did not gain Alfa Romeo as the primary “target” of the merger. But Alfa Romeo quickly became an important strategic asset within the new group.
The brand offers Stellantis something that few of its other brands do:
- A century-old motorsport heritage
- Strong Italian design identity
- A premium performance image
- Recognition in global enthusiast markets.
Alfa Romeo gives Stellantis access to market segments occupied by other performance and luxury brands. It strengthens the group’s brand portfolio in Europe, North America, and selected international markets.
For Stellantis, Alfa Romeo is not a volume brand. It is a brand image asset designed to support group prestige and technological reputation.
How Ownership Legally Changed
When Stellantis was formed, all FCA brands automatically transferred into the new corporate entity. This included Alfa Romeo.
Ownership transfer occurred at the group level:
- Fiat Chrysler Automobiles ended as a standalone company
- PSA Group ceased to exist separately
- Stellantis became the new legal owner of all brands.
All intellectual property, manufacturing rights, and contractual relationships related to Alfa Romeo transferred into Stellantis’ control through this corporate reorganization.
There was no cash acquisition of Alfa Romeo as a brand. Ownership changed through stock exchanges between FCA and PSA shareholders.
What Changed After the Acquisition
After becoming part of Stellantis, Alfa Romeo entered a new operational structure.
Alfa Romeo gained access to shared:
- Development platforms
- Powertrain systems
- Electrification programs
- Software architecture
- Global supply chain.
This reduced the need for the brand to develop everything independently. Costs fell. Speed to market improved.
Decision-making became more centralized. Approval for new models now requires alignment with group-wide product strategy.
Alfa Romeo’s leadership can innovate, but must work within the Stellantis framework.
Being part of Stellantis removed Alfa Romeo’s dependence on one regional parent.
Global financing and resource pools allow:
- Long-term product planning
- More stable capital investment
- Access to corporate R&D funding.
This created greater security for the brand’s future.
Was Alfa Romeo at Risk of Closure?
At the time Stellantis was formed, Alfa Romeo was not guaranteed continued investment. The company’s leadership made it clear that all brands would be evaluated on performance.
However, Alfa Romeo retained its position. Stellantis committed to a multi-year model plan and placed the brand inside its long-term portfolio.
That commitment confirmed that Alfa Romeo was not acquired for resale but for development.
Who Ultimately Controls Alfa Romeo?
Alfa Romeo does not answer to one owner. It answers to a system of ownership.
Control flows like this:
- Shareholders control Stellantis.
- Stellantis controls Alfa Romeo.
- Alfa Romeo executes within that structure.
Strategic decisions such as model cancellations, factory investment, brand expansion, or electrification timelines are finalized at Stellantis headquarters. Alfa Romeo’s own leadership team proposes plans, but they must be approved at the group level.
Where Are Alfa Romeo Cars Manufactured?
Alfa Romeo produces its vehicles in a small number of specialised factories rather than across dozens of locations. Manufacturing is concentrated in Italy for core models, with selected production in other countries depending on market and model type. This structure allows the brand to preserve Italian identity while benefiting from global manufacturing scale.
Manufacturing Headquarters and Italian Production Base
Italy remains the heart of Alfa Romeo manufacturing. Engineering leadership, final design approvals, and high-value production are centered in Italy. Vehicles built in Italy are positioned as premium and performance flagships, reinforcing Alfa Romeo’s “Made in Italy” image.
Cassino Plant, Italy
The Cassino factory in central Italy is one of Alfa Romeo’s most important facilities. This plant produces key models that define the brand globally. It is the home of the Giulia and Stelvio lines and is built for rear-wheel and all-wheel-drive architectures.
This facility specialises in premium construction standards, advanced robotics, and high-precision assembly. Cassino represents Alfa Romeo’s modern Italian manufacturing capability and plays a central role in quality control.
Pomigliano d’Arco Plant, Naples Area, Italy
Pomigliano d’Arco near Naples is another major production site. This factory is where the Tonale is built — Alfa Romeo’s compact SUV aimed at a wider global audience.
The plant is one of Stellantis’ most advanced production centres in southern Europe. It supports flexible production systems and hybrid manufacturing technologies, aligning with Alfa Romeo’s electrification strategy.
Modena and Specialty Production
Historic Alfa Romeo production once included Modena for high-performance manufacturing activities. While this is no longer a mass-production centre for Alfa Romeo, northern Italy remains the heart of its heritage engineering and performance development.
Limited production runs and performance projects typically involve Italian facilities or Italian-led engineering teams.
Poland (International Production Support)
Not all Alfa Romeo vehicles are built in Italy. Certain models for specific markets are produced in Poland at Stellantis-operated facilities. This is primarily to control costs, scale production efficiently, and serve European distribution networks.
Polish production supports Alfa Romeo’s global volumes without diluting its Italian identity, since product development and quality control remain Italy-led.
Global Manufacturing Strategy
Alfa Romeo’s production model is based on:
- Italian design and engineering leadership
- Selective outsourcing for scale
- Shared platforms inside Stellantis
- Centralised quality control.
This ensures that the brand does not become overextended in manufacturing while remaining focused on craftsmanship and performance identity.
Does Alfa Romeo Build Cars Outside Europe?
As of 2025, Alfa Romeo does not run its own factories in North America or Asia. Cars sold in those markets are imported from Europe. This reinforces the brand’s Italian image but also limits production speed and local flexibility.
Stellantis may choose to expand manufacturing outside Europe in the future if volumes justify it. For now, Alfa Romeo remains predominantly European-built.
Who is the CEO of Alfa Romeo?
Santo Ficili is the Chief Executive Officer of Alfa Romeo as of 2025. He leads the brand under Stellantis N.V. and is responsible for shaping Alfa Romeo’s strategy, operational direction, and brand identity worldwide.
Alfa Romeo does not operate as an independent company. Ficili works inside the Stellantis management framework, which means his authority is focused on execution and brand leadership rather than corporate ownership or financial control. Final decisions on large investments, factory allocation, and long-term planning must be approved by Stellantis’ senior leadership and board.
Under Ficili, Alfa Romeo is focused on refining its product lineup, strengthening its global positioning, and aligning future models with Stellantis’ electrification roadmap.
Professional Background and Career
Santo Ficili has built his career inside Fiat, FCA, and now Stellantis. He is not an outside hire. He is an internal executive with decades of experience across industrial operations, market expansion, and strategic planning.
Earlier in his career, Ficili worked in manufacturing management and regional leadership roles, focusing on efficiency, production quality, and organizational restructuring. Over time, he moved into senior management positions that involved overseeing multiple markets and coordinating between engineering, sales, and operations teams.
His appointment as CEO of Alfa Romeo signals Stellantis’ preference for continuity and operational leadership rather than a marketing-led approach. Ficili is known for being methodical and results-driven rather than public-facing.
Leadership Structure Under Santo Ficili
Alfa Romeo operates inside a centralized corporate structure. Ficili leads the brand’s internal management team, but he reports directly to Stellantis’ global leadership.
Key areas where Ficili has authority include product direction, brand identity, and day-to-day operations. However, areas such as capital investment, factory funding, and product platform assignments require approval at the group level.
In practical terms, this means Ficili designs plans, but Stellantis authorizes the resources. His leadership is influential, but not absolute.
Role and Responsibilities
As CEO, Santo Ficili oversees every operational function within Alfa Romeo.
He manages the direction of design language, the pacing of new model introductions, and the strategic position of Alfa Romeo in different markets. He works closely with engineering teams to balance performance, compliance, and innovation.
He also coordinates with manufacturing teams across Europe to ensure production quality and efficiency. At the same time, he must align Alfa Romeo’s commercial strategy with Stellantis’ broader objectives.
His role is both creative and operational. He protects Alfa’s heritage while modernizing the brand for future competitiveness.
Alfa Romeo Annual Revenue and Net Worth

As of 2025, Alfa Romeo is projected to generate about $1 billion in annual revenue. Based on that performance, it’s estimated brand net worth as of December 2025 is roughly $4 billion. This figure reflects not just current sales, but also brand equity, future earnings potential, and its strategic value inside Stellantis.
2025 Revenue Overview
The projected $1 billion revenue for 2025 shows Alfa Romeo operating as a focused premium brand rather than a high-volume manufacturer. Its lineup is smaller than mass-market brands, but pricing is higher, and many models sit in the performance and premium segments. That combination supports meaningful revenue even on relatively modest unit volumes.
This revenue level also reflects Alfa Romeo’s transition under Stellantis. The brand now shares platforms, technology, and engineering with other group brands. That reduces development costs and allows more of each dollar of revenue to support brand and product expansion instead of being consumed by standalone R&D.
While $1 billion is small compared to global automotive giants, it is significant for a specialist marque. It is enough to justify continued investment in core models, electrified powertrains, and global marketing, especially when supported by Stellantis’ wider capital base.
Revenue in the Context of Stellantis
Alfa Romeo’s $1 billion projected revenue represents only a small fraction of Stellantis’ total sales, but its importance is not measured by volume alone. Stellantis uses Alfa Romeo as a premium and performance flag-bearer. The brand helps lift the group’s overall image and gives Stellantis a presence in enthusiast and luxury-leaning segments that pure volume brands cannot fully reach.
From a group perspective, Alfa Romeo’s revenue must cover its direct operating costs and contribute to overhead, but it also adds intangible value. Heritage, motorsport history, design prestige, and customer loyalty all contribute to the wider Stellantis portfolio. This is why a $1 billion revenue brand can still justify multi-year investment cycles inside a much larger group.
Alfa Romeo’s Net Worth
An estimated net worth of around $4 billion as of December 2025 reflects several factors.
First, the brand’s projected $1 billion revenue, combined with typical premium-brand profit multiples, supports a valuation of several times annual sales.
Second, Alfa Romeo’s historical and emotional value is high. Few brands have over a century of heritage, racing history, and a global enthusiast base. That heritage translates into brand equity that a group like Stellantis would not easily replace.
Third, Alfa Romeo owns or controls valuable intangible assets. These include the trademark, logo, model names, engineering know-how, and a recognized design identity. When bundled together, those elements justify a valuation far above the simple book value of physical assets like factories or machinery.
The $4 billion figure, therefore, reflects an approximate “brand value” or embedded net worth inside Stellantis, not a precise market price. It is a reasonable working estimate given the brand’s current revenue, positioning, and long-term potential.
Brands Owned by Alfa Romeo
Alfa Romeo owns and controls brand-specific internal units, heritage divisions, engineering operations, motorsport programs, and institutional entities that exist only to serve the Alfa Romeo brand.
Below is a list of the major divisions, entities, and brands owned by Alfa Romeo as of December 2025:
| Entity / Brand | Type | Primary Function | Scope of Operations | Strategic Importance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfa Romeo Centro Stile | Design Division | Controls exterior and interior design language | Global | Preserves brand identity across models |
| Alfa Romeo Engineering Division | Engineering Unit | Vehicle development, performance tuning | Global | Ensures Alfa driving dynamics |
| Alfa Romeo Classiche | Heritage Division | Certification, restoration guidance | Global | Manages heritage and collector relations |
| Museo Storico Alfa Romeo | Cultural Institution | Archive and exhibition center | Italy | Brand history and public engagement |
| Alfa Corse | Motorsport Division | Racing programs and partnerships | International | Performance credibility and R&D |
| Autodelta (Heritage Brand) | Legacy Performance Brand | Historical racing identity | Global | Performance legacy and limited branding |
| Alfa Romeo Licensing & IP Office | Commercial Unit | Merchandising and trademark use | Global | Monetizes brand identity |
| Alfa Romeo Dealer Operations | Retail Network | Sales and service management | Worldwide | Customer experience consistency |
| Alfa Romeo Product Management | Business Unit | Model planning and lifecycle control | Global | Guides product portfolio strategy |
| Alfa Romeo Brand Marketing | Marketing Division | Global campaigns and messaging | All markets | Brand positioning and awareness |
| Alfa Romeo Quality Operations | Operations Unit | QA and customer feedback | Global | Maintains reliability standards |
| Alfa Romeo Customer Care | Support Unit | Owner services and support | International | Loyalty and retention |
Alfa Romeo Centro Stile
Centro Stile Alfa Romeo is the brand’s in-house design organization. It defines exterior design language, interior layout philosophy, and materials direction across the full product range.
The unit is responsible for preserving the “Alfa look” regardless of platform sharing inside Stellantis. While engineering systems may be shared at group level, Centro Stile ensures Alfa Romeo vehicles remain visually distinct and emotionally recognizable. It also oversees concept design studies and long-term aesthetic evolution.
Alfa Romeo Engineering and Product Development Division
This division coordinates product development for Alfa Romeo models. It does not operate independently from Stellantis engineering systems, but it does exist as a brand-specific authority for vehicle tuning, performance calibration, and dynamic behavior.
Engine response, steering setup, suspension tuning, and driving feel are designed to maintain Alfa Romeo’s historical character even when vehicles are built on shared platforms. The division ensures that driving characteristics remain consistent whether the car is an entry model or a performance variant.
Alfa Romeo Classiche
Alfa Romeo Classiche manages brand heritage and historical assets. It handles authentication, restoration guidance, archival documentation, and official vehicle certification programs.
This entity supports collectors worldwide. It provides factory validation for classic Alfa Romeo vehicles, confirms build specifications, and preserves original design records. The division also supports heritage exhibitions and collector programs.
Museo Storico Alfa Romeo
The Alfa Romeo Museum in Arese operates under Alfa Romeo brand control. It functions as a heritage asset and cultural institution rather than a commercial business.
It houses historic vehicles, prototypes, and technical documents. It also acts as the brand’s official historical archive. The museum plays a major role in brand storytelling, exhibitions, and preservation strategy.
Alfa Corse
Alfa Corse is the motorsport identity of Alfa Romeo. It manages brand involvement in competitive racing programs and motorsport partnerships.
While Alfa Romeo does not operate a large standalone racing team in 2025, Alfa Corse exists to support track-focused development projects, brand alliances, and technical programs linked to motorsport.
This includes vehicle development inspired by racing, limited-series performance programs, and collaborations related to track capability and performance engineering.
Autodelta
Autodelta was Alfa Romeo’s historic performance engineering arm. It is no longer an active operating business, but remains trademarked and preserved as a heritage performance identity.
Autodelta represents Alfa Romeo’s racing innovation era from the mid-20th century and is occasionally referenced for limited editions or branding projects related to performance history.
Alfa Romeo Corporate Programs and Licensing Operations
Alfa Romeo controls its own licensing unit. It manages:
- Brand merchandising
- Intellectual property enforcement
- Apparel collaborations
- Collectibles
- Promotional partnerships.
This ensures Alfa Romeo’s trademarks are protected and commercially exploited through controlled partnerships around the world.
Alfa Romeo Dealer Operations and Market Divisions
Although sales networks are technically coordinated within Stellantis, Alfa Romeo maintains direct brand-level control over its dealer identity and retail experience.
Each country or region operates an Alfa Romeo division focused on:
- Retail operations
- Dealer training
- Brand presentation
- Warranty programs
- Customer experience standards.
This maintains uniformity across markets while allowing localized strategy.
Final Words
Alfa Romeo is a legendary Italian brand with a complex but fascinating ownership journey. Today, it is owned by Stellantis, a global automotive giant with Exor as its largest shareholder. The brand continues to evolve, combining heritage with modern electrification and performance goals. Its leadership, financial backbone, and strategic direction all reflect Stellantis’ long-term vision for premium automotive engineering.
FAQs
Who owns Alfa Romeo car company?
Alfa Romeo is owned by Stellantis N.V., one of the world’s largest automotive groups. Alfa Romeo is not a standalone company and does not have its own shareholders. It operates as a fully controlled brand inside Stellantis.
Which company owns Alfa Romeo?
The company that owns Alfa Romeo is Stellantis N.V., formed through the merger of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles and PSA Group. Stellantis also owns many other global car brands, but Alfa Romeo is run as a separate brand internally.
Where is Alfa Romeo made?
Alfa Romeo cars are mainly manufactured in Italy, including factories in Cassino and Pomigliano d’Arco. Some models are produced in other European locations for efficiency, but design, engineering, and brand leadership remain Italian.
Who makes Alfa Romeo cars?
Alfa Romeo cars are built by Stellantis manufacturing plants using Alfa Romeo’s design and engineering standards. The brand operates under Stellantis but maintains its own product identity, styling, and performance goals.
Is Alfa Romeo owned by Ferrari?
No, Ferrari does not own Alfa Romeo. Although the two brands share historical connections and racing heritage, they are completely separate companies today. Ferrari is an independent company. Alfa Romeo belongs to Stellantis.
Is Alfa Romeo basically a BMW?
No, Alfa Romeo is not related to BMW in ownership or engineering control. Alfa Romeo and BMW are rivals in the performance-car market, but they operate under different companies and follow different design and engineering philosophies.
Is Alfa Romeo owned by Maserati?
No, Maserati does not own Alfa Romeo. Both are Italian brands, but they are separate entities under Stellantis. They operate with different leadership, strategies, and model lineups.
Which car is called “poor man’s Ferrari”?
People often informally refer to models like the Alfa Romeo Giulia Quadrifoglio or the Mazda MX-5 Miata as “poor man’s Ferrari” because they offer sporty driving at a lower price point. This is a nickname, not an official term.
Do Alfa Romeo use Fiat engines?
Some Alfa Romeo models share engineering platforms and components with other Stellantis brands, including Fiat. However, Alfa Romeo also uses brand-specific tuning, unique performance engines, and its own calibration strategies. Not all Alfa Romeo engines are Fiat engines, and performance models use different hardware and tuning.
Why did Ferrari leave Alfa Romeo?
Ferrari was never “owned” by Alfa Romeo. The two brands had historic cooperation in motorsport and engineering decades ago under the Fiat group. Ferrari later became a fully independent company. There was no formal separation from Alfa Romeo because they were never merged into one company.