ByteDance has grown into one of the most influential tech companies in the world. With its popular platforms like TikTok and Toutiao, people often ask: who owns ByteDance? The answer is complex due to its private status, international reach, and diverse investor base.
ByteDance Company Profile
ByteDance is a Chinese multinational technology company best known for developing content platforms powered by artificial intelligence. It operates globally and is most famous for TikTok (international) and Douyin (Chinese version). The company is incorporated in the Cayman Islands but maintains its operational headquarters in Beijing, China, with major offices in Singapore, Los Angeles, London, and Dubai.
Founded in 2012, ByteDance has rapidly expanded into one of the most valuable private tech companies in the world. Its business spans content recommendation, short video, online news, productivity tools, virtual reality, and gaming.
ByteDance does not trade publicly, but it attracts heavy investment from global venture capital and private equity firms. It employs over 110,000 people worldwide and operates in more than 150 countries, making it one of the few Chinese companies with a strong global consumer reach.
ByteDance Founders
Zhang Yiming is the primary founder of ByteDance. Born in 1983 in Fujian, China, Zhang studied software engineering at Nankai University. After working at Microsoft and other startups, he started ByteDance to build content platforms that used AI to match users with personalized information.
Liang Rubo, a close associate and classmate of Zhang, co-founded the company. Liang was instrumental in managing human resources and internal systems and eventually became CEO in 2021.
Zhang Yiming served as CEO from 2012 to 2021. He stepped down to focus on long-term strategy, research, and product development. Liang Rubo then assumed leadership and continues to serve as the CEO in 2025.
Major Milestones in ByteDance History
2012 – ByteDance is founded by Zhang Yiming in Beijing. The company launches Toutiao, a news aggregation app that uses AI algorithms to recommend content.
2014–2015 – ByteDance attracts investment from major VC firms like Sequoia Capital and SIG Asia, helping it scale operations and AI capabilities.
2016 – ByteDance launches Douyin, a short video app for the Chinese market. Its intuitive interface and fast content consumption features make it an instant hit.
2017 – ByteDance enters the global market with TikTok. It also acquires Musical.ly, a lip-sync video app popular in the U.S. and Europe. The two platforms are merged in 2018 under the TikTok brand.
2019 – TikTok becomes one of the most downloaded apps globally, especially among Gen Z. ByteDance surpasses Uber as the world’s most valuable startup at the time.
2020 – Facing political scrutiny in the U.S., ByteDance works to localize TikTok’s operations with a U.S.-based team and data storage. It avoids a forced sale by making TikTok operationally independent.
2021 – Zhang Yiming steps down as CEO and is succeeded by Liang Rubo. ByteDance reorganizes into multiple business units to support global growth.
2022 – ByteDance acquires Moonton, a gaming company, marking its official entry into the gaming industry. It also accelerates the growth of CapCut and Lark (Feishu in China).
2023 – ByteDance expands further into enterprise software and launches several new features in TikTok Shop and Douyin Mall, increasing its influence in e-commerce.
2024 – ByteDance’s revenue hits an estimated $120 billion. The company focuses on AI-driven content generation, virtual reality through Pico, and expanding TikTok’s monetization tools.
2025 – ByteDance remains privately held but is reportedly considering an IPO for some of its subsidiaries. It continues global expansion while adapting to regulatory changes in the U.S., EU, and China.
ByteDance has transformed from a local Chinese startup into a global tech powerhouse, with an ecosystem spanning content, commerce, productivity, and entertainment.
Who Owns ByteDance: Major Shareholders
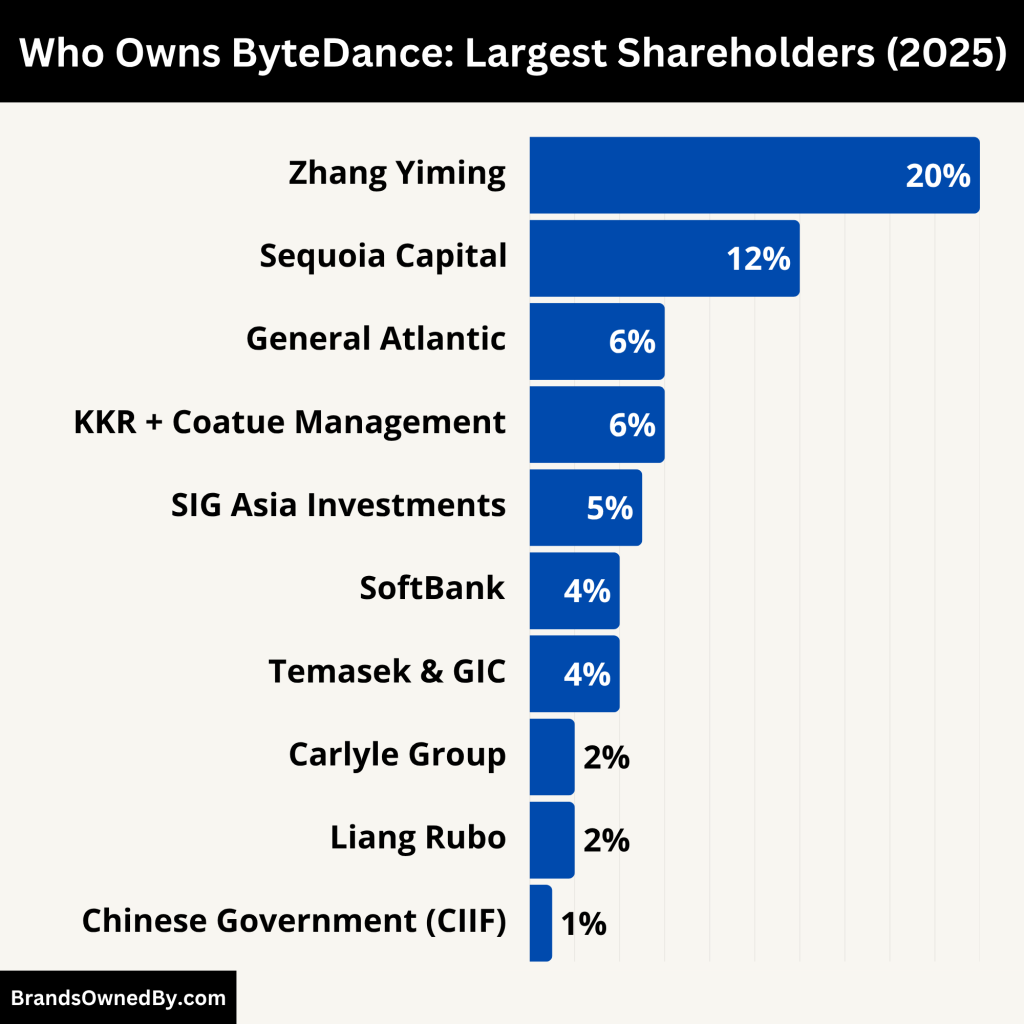
ByteDance is a privately held company. It is not publicly traded on any stock exchange. Ownership is split among its founders, employees, and several major institutional investors. The largest shareholder is still its founder, Zhang Yiming, though his influence has shifted in recent years as he stepped back from management roles.
As of 2025, ByteDance’s ownership remains private and multi-layered, with significant influence shared among:
- Founders (especially Zhang Yiming)
- Global institutional investors
- Employees
- Government stakeholders (limited to Chinese operations)
ByteDance is not owned or controlled by a single entity, which makes it uniquely structured among global tech giants.
Here’s a list of the major shareholders of ByteDance:
| Shareholder | Estimated Ownership (%) | Type | Role in ByteDance | Level of Influence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang Yiming | ~20% | Individual | Founder and largest individual shareholder | High (strategic influence) |
| ByteDance Employees (ESOP) | ~20% | Collective (Internal) | Financial incentive and talent retention | Moderate (limited voting rights) |
| Sequoia Capital (China & US) | 10–12% | Venture Capital | Early investor, board advisory role | High (board-level influence) |
| General Atlantic | ~6% | Private Equity | Strategic global expansion partner | Moderate to high |
| SIG Asia Investments | ~5% | Investment Firm | Early backer, financial partner | Moderate |
| SoftBank | 4–5% | Investment Firm | Passive investor, limited recent participation | Low |
| KKR + Coatue Management | ~6% (combined) | Investment Firms | Late-stage financial investors | Low to moderate |
| Carlyle Group | ~2% | Private Equity | New investor, advisory on IPO readiness | Emerging influence |
| Chinese Government (CIIF) | 1% (golden share) | State Entity | Content regulation within China, board seat in Chinese entity | High (China ops only) |
| Temasek & GIC | 3–4% (combined) | Sovereign Wealth Funds | Strategic global positioning, Singapore HQ influence | Moderate |
| Liang Rubo | ~2–3% | Individual | Co-founder, CEO since 2021 | High (operational leadership) |
Zhang Yiming – Founder and Largest Individual Shareholder
Zhang Yiming remains the largest individual shareholder of ByteDance. As of 2025, he holds approximately 20% equity in the company. Though he stepped down from his CEO role in 2021 and has taken a more passive role in operations, he retains significant influence as a founder and through his equity and board presence.
His voting rights are still powerful in long-term strategic matters. Zhang also continues to be involved in ByteDance’s long-term innovation strategy and investments in AI and emerging markets.
Liang Rubo – Co-founder and CEO
Liang Rubo, who succeeded Zhang as CEO, holds an estimated 2%–3% stake in ByteDance. As the current CEO and one of the co-founders, Liang plays a vital leadership role. His influence stems less from ownership and more from his position as head of the executive team and his deep understanding of the company’s structure.
His role has become especially crucial in regulatory discussions in China and managing ByteDance’s decentralized global operations.
ByteDance Employees – Collectively Significant Stakeholders
ByteDance employees own approximately 20% of the company through an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP). This structure has helped ByteDance retain top talent in both China and global offices.
The employee equity is held under a separate holding structure managed by senior management. It comes with limited voting rights, but gives staff financial participation in the company’s performance. As of 2025, employees remain the second-largest collective shareholder group after institutional investors.
Sequoia Capital – Major Institutional Investor
Sequoia Capital China and Sequoia Capital U.S. combined are estimated to own around 10%–12% of ByteDance. Sequoia was one of the earliest institutional backers of the company and has participated in nearly every major funding round.
Though Sequoia does not control daily operations, it holds board-level influence and strategic advisory power, particularly related to ByteDance’s overseas expansion and financial planning.
General Atlantic – Strategic Global Backer
General Atlantic holds an estimated 6% stake in ByteDance. It invested during the 2018 and 2020 funding rounds when ByteDance was raising capital to resist regulatory pressure and expand globally.
General Atlantic has provided expertise in Western markets and played a key role in helping ByteDance navigate U.S. policy environments, especially around TikTok’s structure. Its influence is advisory and strategic.
SoftBank – Minor but Stable Stakeholder
SoftBank owns around 4%–5% of ByteDance as of 2025. The company initially aimed for a larger stake but scaled back in later rounds. Despite a general retreat from several tech startups, SoftBank has retained its position in ByteDance due to the company’s continued growth.
SoftBank is a passive investor with no board seat, but it benefits financially from ByteDance’s rising valuation.
SIG Asia Investments – Early Backer
SIG (Susquehanna International Group) owns roughly 5% of ByteDance. It was one of the first institutional investors in the company and played a key role in seed and Series A funding.
SIG is a silent but loyal stakeholder and holds strong ties to ByteDance’s early engineering and product development teams. It does not intervene in operational decisions but has benefited significantly from the company’s appreciation in value.
KKR and Coatue Management – Financial Investors
KKR and Coatue Management, both large U.S.-based investment firms, have a combined holding of approximately 6% in ByteDance. Their investment came through late-stage funding rounds in 2021–2023, helping ByteDance avoid IPO pressure.
These firms have been passive investors, providing capital but not interfering in management. Their equity is expected to be monetized either through secondary share sales or potential IPOs of ByteDance subsidiaries.
Carlyle Group – New Strategic Investor
As of 2024, Carlyle Group has acquired a small but notable stake (~2%) in ByteDance via a secondary market purchase. Carlyle is reportedly working with ByteDance on financial structuring in preparation for potential public listings of its non-China business units.
Carlyle’s influence is emerging but still limited to financial guidance and advisory roles.
Chinese Government’s Golden Share – Domestic Control Influence
The Chinese government, through the China Internet Investment Fund (CIIF), owns a 1% “golden share” in the ByteDance subsidiary that oversees Douyin and other China-based operations.
This golden share gives the government:
- A board seat in ByteDance’s Chinese entity.
- Oversight and control of content and data governance.
- No ownership over TikTok or global operations.
This structure ensures regulatory compliance within China, but it does not give the government commercial ownership or voting power over ByteDance’s global businesses.
Temasek and GIC – Singapore-Based Institutional Investors
Temasek Holdings and GIC, sovereign wealth funds of Singapore, hold a combined 3%–4% in ByteDance. They invested during the 2020–2022 rounds to diversify ByteDance’s investor base geographically.
Temasek has played a role in anchoring ByteDance’s international headquarters in Singapore, which now leads TikTok’s global expansion and data compliance operations.
Who is the CEO of ByteDance?
As of 2025, Liang Rubo is the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of ByteDance. He succeeded the company’s founder Zhang Yiming in 2021 and has since led the company through its most complex era of global expansion, regulatory challenges, and operational decentralization.
Background of Liang Rubo
Liang Rubo is a Chinese entrepreneur and one of the co-founders of ByteDance. He studied software engineering at Nankai University, where he met Zhang Yiming. Before joining ByteDance full-time, Liang worked with Zhang at several startups. At ByteDance, he initially led the company’s HR and management systems, building the internal infrastructure that allowed ByteDance to scale globally.
Despite being a low-profile figure publicly, Liang is known internally for his strong operational skills and deep understanding of product development.
CEO Role and Leadership Responsibilities
Liang Rubo oversees ByteDance’s vast ecosystem, including its major business units:
- TikTok (international short video)
- Douyin (Chinese short video)
- Toutiao (AI-driven news)
- CapCut (video editing)
- Lark / Feishu (workplace productivity)
- Pico (VR division)
- Nuverse and Moonton (gaming)
As CEO, Liang has spearheaded:
- Organizational restructuring into semi-independent business units
- Strengthening data compliance and privacy controls
- Expansion of ByteDance’s enterprise software and e-commerce businesses
- Building a more localized governance model in international markets
Liang balances the demands of regulators in China, the U.S., and the EU while continuing to scale the company’s revenue and innovation footprint.
Executive Decision-Making Structure
ByteDance operates under a matrix structure, with Liang Rubo at the center of strategic oversight. Each major business unit has a CEO or general manager who reports to him. Global legal, finance, and policy teams also report directly to Liang.
He is supported by a global executive committee, including:
- Heads of TikTok and Douyin
- Chief Financial Officer
- Chief Technology Officer
- Chief Legal and Policy Officers
Despite ByteDance being privately held, Liang frequently engages with investors, regulators, and internal stakeholders to guide product direction and financial strategy.
Previous CEOs of ByteDance
Zhang Yiming was the original CEO from 2012 to 2021. He stepped down to focus on long-term strategy and innovation, though he remains the company’s largest individual shareholder and strategic advisor.
Liang Rubo became CEO in May 2021 and has held the position through 2025. No other person has served as CEO between Zhang and Liang.
Current Status in 2025
As of 2025, Liang Rubo continues to serve as CEO. Under his leadership, ByteDance has:
- Surpassed $120 billion in annual revenue
- Positioned TikTok as the world’s top app for youth engagement
- Grown ByteDance’s productivity and AI tools into global enterprise markets
- Navigated increasing scrutiny and regulatory pressure in key global markets
Liang’s calm, systems-driven leadership style contrasts with Zhang Yiming’s visionary profile, but he has proven effective in scaling and stabilizing ByteDance during a period of intense global transformation.
ByteDance Annual Revenue and Net Worth
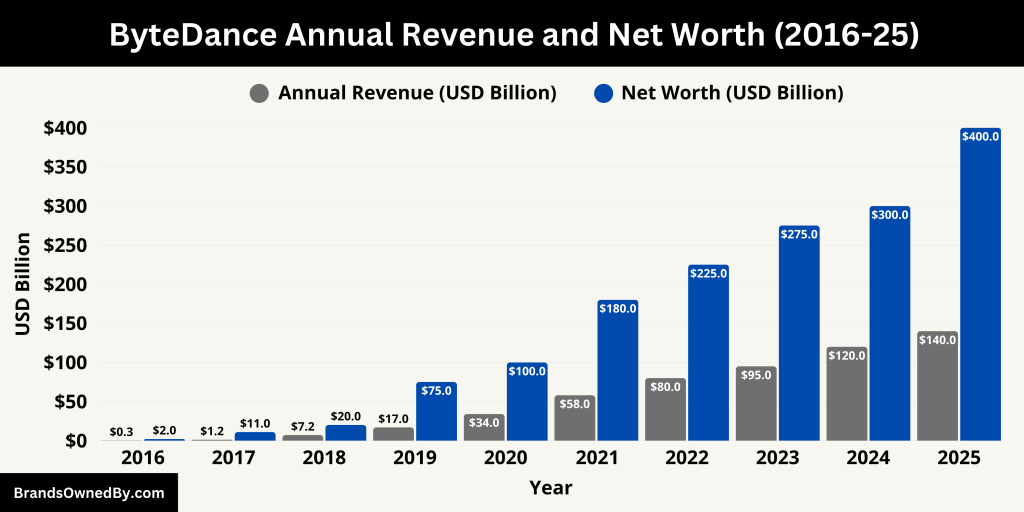
ByteDance continues to post strong financials. As of 2024:
- Annual Revenue: Estimated at $120 billion.
- Net Worth (Company Valuation): Approximately $400 billion, based on private market valuations and investor estimates.
As of 2025, ByteDance continues its strong financial performance. Both revenue and market valuation have climbed steadily, driven by sustained growth of its core platforms and new business ventures.
Revenue Growth
- 2024 Revenue: Approximately $120 billion, driven by advertising, in‑app purchases, enterprise tools, and content monetization.
- 2025 Projected Revenue: Estimated to reach between $140 billion, reflecting continued expansion of TikTok, Douyin, and rising series of enterprise and e‑commerce offerings.
Revenue growth factors include:
- Global ad spend recovery post‑pandemic.
- New e‑commerce integration, especially in Douyin and TikTok Shop.
- Rapid enterprise SaaS adoption of Lark/Feishu.
- Emerging monetization streams from VR (Pico) and gaming (Moonton).
Revenue Breakdown by Segment
| Business Segment | 2024 Revenue Share | 2025 Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| TikTok + Douyin Ads | ~65% | Increased due to improved ad targeting and commerce tie‑ins |
| In‑App Purchases & Gifts | ~10% | Growing with user engagement and live‑stream culture |
| Enterprise Tools (Lark) | ~8% | Higher adoption in Asia Pacific and Europe |
| E‑commerce (Shop/Mall) | ~12% | Expanding into new regions and product categories |
| Gaming + VR | ~5% | Modest growth; becoming a more significant future stream |
Net Worth
As of June 2025, ByteDance’s estimated net worth—commonly reflected through its market valuation—has risen to approximately $400 billion. This valuation makes it one of the most valuable privately held technology companies in the world. It has surpassed several public companies in terms of valuation, despite remaining unlisted.
ByteDance’s net worth is calculated based on investor assessments in secondary share markets, private funding rounds, and internal financial performance. In 2024, the company was valued at around $300 billion. The growth in 2025 reflects sustained revenue expansion, better monetization of global platforms, and increasing investor confidence in its diversified business model.
Drivers of Valuation Growth
The rise in ByteDance’s net worth is primarily driven by its consistent multi-channel revenue streams. Platforms like TikTok and Douyin generate billions in advertising revenue, while new verticals such as e-commerce, enterprise software, gaming, and virtual reality have added additional growth engines.
Another key factor is the successful scaling of ByteDance’s enterprise SaaS tools, such as Lark/Feishu, which are now widely adopted in Asia and growing in European markets. The strong performance of TikTok Shop and Douyin Mall in social commerce also contributes significantly to the company’s valuation.
Private Company Status
Since ByteDance is still a privately held firm, its net worth is not subject to daily market fluctuations like publicly traded companies. However, it is closely tracked by private investors, venture capital firms, and financial analysts. Secondary market transactions involving ByteDance shares in 2025 have priced the company in the upper range of $350 billion, reinforcing this valuation range.
Despite speculation about a future IPO, ByteDance has maintained its private status. This allows it to operate with flexibility and focus on long-term product innovation without quarterly public market pressure.
Global Standing
With a valuation nearing $370 billion, ByteDance ranks among the top global tech firms by worth—just behind the likes of Amazon, Alphabet, and Meta. It also surpasses other Chinese tech giants like Baidu and JD.com, and rivals Tencent in valuation on some metrics.
ByteDance’s financial growth and valuation reflect its global influence, product innovation, and ability to generate diversified revenue—positioning it as a critical player in the next generation of digital platforms.
Here is a table showing ByteDance’s historical revenue and estimated net worth over the last 10 years (2016–2025):
| Year | Annual Revenue (USD) | Estimated Net Worth / Valuation (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | ~$300 million | ~$2 billion | Early growth stage, driven by Toutiao and Douyin beta launch |
| 2017 | ~$1.2 billion | ~$11 billion | Douyin launched in China; international expansion began |
| 2018 | ~$7.2 billion | ~$20 billion | TikTok merged with Musical.ly; global brand started gaining traction |
| 2019 | ~$17 billion | ~$75 billion | Explosive TikTok growth; rapid user acquisition worldwide |
| 2020 | ~$34 billion | ~$100 billion | Pandemic-fueled engagement; increased ad revenue and content consumption |
| 2021 | ~$58 billion | ~$180 billion | Continued growth despite U.S. regulatory pressure on TikTok |
| 2022 | ~$80 billion | ~$225 billion | TikTok Shop and Lark expanded; enterprise and commerce growth |
| 2023 | ~$95 billion | ~$275 billion | Investments in VR (Pico) and gaming; global headcount increased |
| 2024 | ~$120 billion | ~$300 billion | High-margin monetization of TikTok and Douyin, strong enterprise tools |
| 2025 | ~$140–150 billion | ~$400 billion | Peak diversification with AI, enterprise, and e-commerce contributing heavily |
Companies Owned by ByteDance
ByteDance has expanded far beyond its roots in short-form video to become a diversified tech empire. As of 2025, the company owns and operates a wide array of platforms, services, and subsidiaries across content, productivity, commerce, education, entertainment, and enterprise software.
Below is a breakdown of ByteDance’s major brands and companies as of 2025:
| Brand/Company | Type | Year Launched / Acquired | Primary Focus | Primary Market(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TikTok | Product | 2017 (Merged with Musical.ly in 2018) | Short-form video, ads, social commerce | Global (U.S., Europe, Asia) |
| Douyin | Product | 2016 | Short-form video, livestreaming, e-commerce | China |
| Toutiao | Product | 2012 | AI-powered news and content aggregation | China |
| CapCut (JianYing) | Product | 2019 | Video editing and content creation | Global (CapCut), China (JianYing) |
| Lark (Feishu) | Product | 2019 | Enterprise collaboration tools (docs, chat, meetings) | Asia-Pacific, China, expanding globally |
| TikTok Shop / Douyin Mall | Business Line | 2021 | In-app e-commerce and livestream shopping | TikTok: Global / Douyin: China |
| Moonton Technology | Acquisition | 2021 | Mobile game development (Mobile Legends) | Southeast Asia, Global |
| Nuverse | Subsidiary | 2019 | Gaming division and game publishing | Global |
| Pico | Acquisition | 2021 | Virtual reality hardware and immersive content | China, select global markets |
| Lemon8 | Product | 2020 | Lifestyle content + e-commerce (beauty, fashion) | Japan, Southeast Asia, expanding in U.S. |
| Helo | Product | 2018 | Regional language content platform | India (prior to ban), Southeast Asia |
| Resso | Product | 2020 | Music streaming with social features | India, Brazil, Indonesia |
| BytePlus | Subsidiary | 2021 | AI and cloud solutions for businesses | Global (B2B clients) |
| Zhangmen / Qingbei (scaled down) | Former EdTech Arm | 2020 (scaled down post-2021) | Online education and tutoring | China |
| Vigo Video | Product (Merged) | 2017 (Merged into TikTok by 2020) | Short video | India, Southeast Asia (discontinued) |
| Hypstar | Product (Merged) | 2017 (Merged into TikTok) | Regional short video platform | Southeast Asia (discontinued) |
| News Republic | Acquisition | 2017 (Discontinued) | News aggregator | Global (shut down post-2019) |
TikTok
TikTok is ByteDance’s flagship international product. It is a short-form video app launched globally in 2017 following the acquisition and merger with Musical.ly. TikTok has become a cultural phenomenon worldwide, particularly in the U.S., Europe, and Southeast Asia. It serves over 1.5 billion active users and is a major driver of ad revenue and commerce through features like TikTok Shop, Live Gifting, and Creator Marketplace.
Douyin
Douyin is the Chinese version of TikTok. It operates independently within China’s regulatory framework and has grown into an ecosystem far beyond entertainment. Douyin integrates short videos, e-commerce, mini-programs, and livestreaming, making it one of the most influential platforms in China. It is a major revenue engine for ByteDance’s domestic business and generates more income than TikTok due to advanced monetization.
Toutiao
Toutiao (“Headlines”) is ByteDance’s original AI-powered news aggregation platform. It offers personalized content based on user behavior and remains highly popular in China. It set the foundation for ByteDance’s core algorithm technology. While its international relevance is limited, Toutiao still commands significant influence in the Chinese digital news and information space.
CapCut (JianYing in China)
CapCut is ByteDance’s video editing tool available globally. It allows users to edit videos for TikTok, YouTube, Instagram, and more. The app has become one of the most downloaded editing tools worldwide due to its simplicity, advanced features, and seamless integration with TikTok. Its Chinese version, JianYing, is equally popular among content creators in China.
Lark (Feishu in China)
Lark (called Feishu domestically) is ByteDance’s enterprise collaboration suite. It combines messaging, video conferencing, cloud docs, calendars, and workplace automation. Feishu has strong adoption in China’s enterprise tech space, while Lark is expanding steadily in Southeast Asia, India, and emerging markets. ByteDance has invested heavily in this to compete with Microsoft Teams and Slack.
TikTok Shop / Douyin Mall
TikTok Shop (international) and Douyin Mall (China) are ByteDance’s social commerce arms. They integrate directly into the main platforms, allowing users to browse, promote, and purchase products inside the apps. ByteDance is rapidly scaling this segment, combining influencer marketing, live shopping, and direct fulfillment. This vertical has transformed the platforms into hybrid entertainment-commerce ecosystems.
Moonton Technology
Moonton is a mobile gaming company acquired by ByteDance in 2021. It is the developer of the hit game Mobile Legends: Bang Bang, one of Southeast Asia’s most played multiplayer games. The acquisition marked ByteDance’s serious entry into mobile gaming. Moonton operates under the Nuverse gaming umbrella.
Nuverse
Nuverse is ByteDance’s global video gaming division. It focuses on publishing and developing games for mobile and PC platforms. It operates separately from Moonton but collaborates on infrastructure and user acquisition. Nuverse’s portfolio includes role-playing games, strategy titles, and casual games targeting global audiences.
Pico
Pico is ByteDance’s virtual reality (VR) hardware and software company. It produces VR headsets and immersive content platforms. ByteDance acquired Pico to compete with Meta’s Oculus in the global VR space. Though still a niche area, Pico is seen as a long-term bet on immersive computing and metaverse technologies.
Lemon8
Lemon8 is a lifestyle platform that combines social content and e-commerce. It targets fashion, wellness, and beauty enthusiasts. It operates mainly in Japan and Southeast Asia, with ongoing expansion in Western markets. ByteDance designed Lemon8 to rival apps like Instagram and Pinterest, with deeper shopping and creator tools.
Helo
Helo is a regional social content platform designed for Indian and South Asian markets. It emphasizes regional language content and community building. Though scaled down following the TikTok ban in India, ByteDance continues to support Helo in emerging markets.
Resso
Resso is ByteDance’s music streaming app focused on emerging markets like India, Brazil, and Indonesia. It integrates music discovery with social features such as comments, mood-based playlists, and sharing. Resso was created to extend ByteDance’s influence in the digital music space and to support music licensing across its platforms.
BytePlus
BytePlus is the company’s enterprise technology arm. It provides external clients with access to ByteDance’s advanced AI and recommendation systems, cloud services, data analytics tools, and AR capabilities. BytePlus powers parts of the TikTok algorithm, facial filters, and real-time personalization for partners across industries.
Zhangmen Education (divested)
ByteDance once had a strong presence in online education through platforms like Qingbei and OpenLanguage. Due to government crackdowns on edtech in China, ByteDance divested or scaled down many of these operations. However, certain AI-based tutoring and training tools remain in development within BytePlus and Feishu ecosystems.
Other Acquisitions and Minor Entities
- Vigo Video (discontinued): A short video app merged into TikTok.
- Hypstar (merged): Regional video platform that was integrated into TikTok.
- News Republic (defunct): An international news aggregator once owned by ByteDance, now discontinued.
Final Thoughts
Understanding who owns ByteDance is crucial to grasping how the company operates globally. While Zhang Yiming remains its largest individual shareholder, major institutional investors and employees also hold significant stakes. ByteDance’s decentralized model and strong portfolio of apps keep it competitive in both Chinese and global markets. Despite government scrutiny and regulatory challenges, ByteDance continues to expand across content, AI, and hardware segments.
FAQs
Who owns the ByteDance company?
ByteDance is a privately held company. It is owned by a mix of founders, global investors, institutional shareholders, and employees. Its largest individual shareholder is Zhang Yiming, the company’s founder. Major institutional stakeholders include Sequoia Capital China, General Atlantic, and SIG (Susquehanna International Group), among others. No single entity fully owns ByteDance; it is shared across multiple investors and founders.
Who are the largest shareholders of ByteDance?
As of 2025, the largest shareholders of ByteDance include:
- Zhang Yiming (Founder): Holds approximately 20–25% of equity with over 50% voting control through dual-class shares.
- Sequoia Capital China: Estimated to own around 10–12%.
- General Atlantic: Owns close to 7–8%.
- SIG (Susquehanna International Group): Holds about 7%, including early investment shares.
- KKR, SoftBank, Coatue Management, and other private equity and venture firms hold additional smaller stakes.
ByteDance employees also collectively own a significant percentage through equity compensation.
Who owns CapCut?
CapCut is fully owned and operated by ByteDance. It was developed in-house as a video editing tool to support content creators, especially on TikTok and Douyin. It operates globally and has become one of the top editing apps worldwide.
Who is CEO of ByteDance?
As of 2025, the CEO of ByteDance is Liang Rubo, a co-founder and long-time executive at the company. Liang took over as CEO in 2021 after Zhang Yiming stepped down. Liang oversees ByteDance’s global strategy, operations, and technology. While Zhang remains influential as a board member and major shareholder, Liang is the public-facing leader and strategic head of the company.
Are Tencent and ByteDance the same company?
No, Tencent and ByteDance are not the same company. They are separate, competing tech giants based in China. Tencent is publicly listed and known for WeChat, Tencent Games, and its investment portfolio. ByteDance is a privately held company best known for TikTok and Douyin. The two have had a competitive relationship, especially in the short-form content and gaming sectors.
What’s the Zhang Yiming net worth?
As of 2025, Zhang Yiming’s net worth is estimated to be between $42–45 billion. This wealth comes primarily from his founding stake in ByteDance, where he still holds a large share and controls significant voting rights. He is consistently ranked among the richest tech entrepreneurs globally.
Who really owns ByteDance?
ByteDance is ultimately owned collectively by:
- Founders, including Zhang Yiming (largest individual stakeholder)
- Global and Chinese venture capital firms
- Institutional investors like KKR, Sequoia, and General Atlantic
- Current and former employees through equity programs
There is no single owner. However, Zhang Yiming has the most control due to his voting power through dual-class shares.
Who owns TikTok?
TikTok is owned by ByteDance, its parent company. TikTok was launched internationally by ByteDance and later merged with the U.S.-based app Musical.ly. It is operated under TikTok Ltd., which is based in the U.S. and Singapore but ultimately controlled by ByteDance in China. While TikTok maintains some operational independence, ByteDance owns and controls the platform entirely.
Who currently owns ByteDance?
ByteDance is privately owned. Zhang Yiming, employees, and major investors like Sequoia, SoftBank, and General Atlantic share ownership.
Is ByteDance publicly traded?
No, ByteDance is not listed on any stock exchange. It remains a private company.
Does China own ByteDance?
China does not own ByteDance outright. However, a government-linked entity holds a golden share in ByteDance’s China-based subsidiary.
Who founded ByteDance?
Zhang Yiming founded ByteDance in 2012. Liang Rubo co-founded it with him.
Is TikTok owned by ByteDance?
Yes, TikTok is owned by ByteDance. It operates under a separate business unit from Douyin.
Who is the CEO of ByteDance?
Liang Rubo is the current CEO of ByteDance. He took over the role in 2021.
What is ByteDance worth in 2025?
ByteDance is valued at around $400 billion as of June 2025.
How much revenue does ByteDance make?
ByteDance generated an estimated $120 billion in revenue in 2024.
Does ByteDance own any gaming companies?
Yes, ByteDance owns Moonton, the developer of Mobile Legends.
What is ByteDance’s business model?
ByteDance earns revenue through advertising, digital goods, e-commerce, and enterprise software.

