Restaurant Brands International is one of the largest fast-food holding companies in the world. If you’re wondering who owns Restaurant Brands International, you’re not alone. The company owns some of the most well-known brands in the quick-service industry. This article explains its history, ownership, and operations in full detail.
History of Restaurant Brands International
The story of Restaurant Brands International (RBI) begins with two separate fast-food giants—Burger King and Tim Hortons. Each had a strong presence in its respective market before coming together in a landmark merger.
The Origins of Burger King
Burger King began in 1954 in Miami, Florida, founded by James McLamore and David Edgerton. It started with a focus on flame-grilled burgers, a method that became its signature. The Whopper, introduced in 1957, became one of the most recognized fast-food items globally.
Burger King grew through franchising, expanding across the U.S. and internationally. However, by the early 2000s, it faced tough competition from McDonald’s and suffered from inconsistent leadership and lagging sales. In 2010, Brazilian investment firm 3G Capital acquired Burger King for $3.26 billion. Under 3G’s ownership, Burger King was restructured. The company emphasized franchising, reduced corporate expenses, and streamlined operations. This revitalization paved the way for larger ambitions.
The Rise of Tim Hortons
Tim Hortons was founded in 1964 in Hamilton, Ontario, by NHL hockey star Tim Horton and entrepreneur Ron Joyce. The chain quickly became a household name in Canada, known for coffee, donuts, and a strong community presence. By the 1990s, Tim Hortons had surpassed McDonald’s as Canada’s leading food service operator.
Tim Hortons merged with Wendy’s in 1995 but was later spun off in 2006 to become an independent company again. By the early 2010s, Tim Hortons was facing pressure to expand outside Canada and grow shareholder value.
The 2014 Merger: Birth of RBI
In August 2014, Burger King and Tim Hortons announced a $12.5 billion merger deal. The merger was orchestrated by 3G Capital, which already owned a majority of Burger King. The new entity was named Restaurant Brands International (RBI).
The move was partially driven by tax strategy, as the new holding company would be headquartered in Canada, where corporate tax rates were lower. Despite political controversy over this “tax inversion,” the deal went through in December 2014. RBI became one of the largest quick-service restaurant companies globally.
Burger King and Tim Hortons retained their brand identities and operational independence, but their back-end systems, technology, and supply chains were integrated to drive efficiency and cost savings.
Expanding the Portfolio: Popeyes Acquisition
In 2017, Restaurant Brands International acquired Popeyes Louisiana Kitchen for $1.8 billion. Popeyes was a well-established U.S. fried chicken brand with a unique Cajun-inspired menu.
The acquisition gave RBI entry into the highly competitive chicken market and offered international growth potential. Popeyes would later go viral in 2019 with its spicy chicken sandwich, significantly boosting its brand visibility and sales.
Entry into the Sandwich Market: Firehouse Subs
In 2021, RBI continued its expansion by acquiring Firehouse Subs for $1 billion. Firehouse was a fast-casual sandwich brand founded in 1994 by former firefighters Chris and Robin Sorensen in Jacksonville, Florida.
Known for its hearty sandwiches and community-first mission, Firehouse added a new dimension to RBI’s portfolio. With a strong presence in the U.S., it gave RBI another path for growth in the North American market.
Focus on Global Franchising and Digital Innovation
After building a strong brand portfolio, RBI emphasized a franchise-heavy model. Over 99% of its restaurants are franchised, reducing corporate risk and focusing on scalability. The company also invested heavily in mobile apps, delivery platforms, and loyalty programs.
Global expansion has been a major focus, especially in Asia, Latin America, and Europe. RBI has also been working on sustainability, packaging innovation, and plant-based menu options to align with changing consumer trends.
By 2024, Restaurant Brands International had over 30,000 restaurants in more than 100 countries, positioning itself as a global leader in quick-service restaurants.
Who Owns Restaurant Brands International (RBI)?
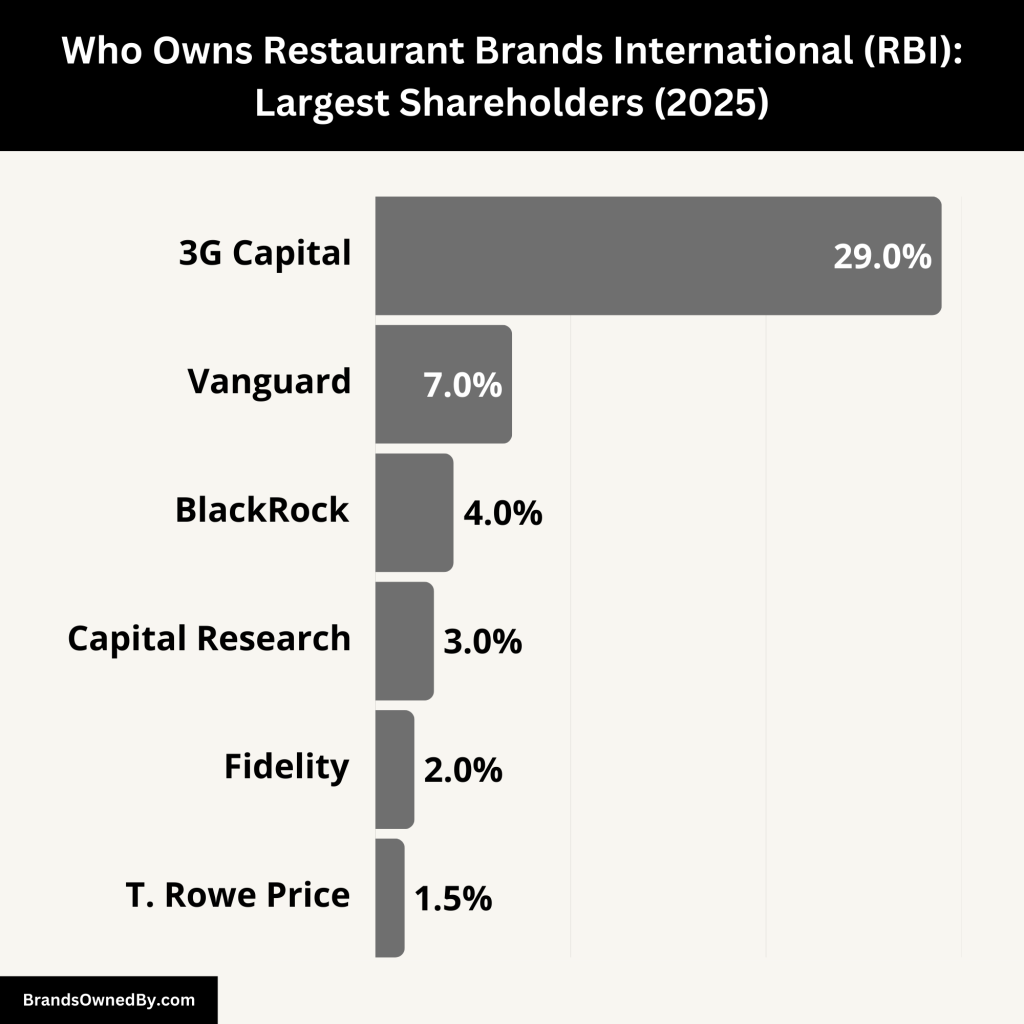
Restaurant Brands International is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE: QSR) and the Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX: QSR). The largest shareholder of RBI is still 3G Capital. Other institutional investors and mutual funds have also acquired significant stakes in the company.
Restaurant Brands International is publicly traded, which means its ownership is spread across a range of institutional investors, mutual funds, and retail shareholders. However, several major shareholders stand out due to the size of their holdings and influence.
Below is a breakdown of the major shareholders of Restaurant Brands International:
| Shareholder | Approx. Ownership | Type | Role and Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3G Capital | ~29% | Strategic Investor | Founding shareholder with board representation and major influence on strategy |
| The Vanguard Group | ~7% | Institutional Investor | Passive investor with voting power via ETFs and mutual funds |
| BlackRock | ~4% | Institutional Investor | ESG-focused investor, influences governance through proxy voting |
| Capital Research Global Investors | ~3% | Institutional Investor | Long-term investor aligned with growth strategies |
| Fidelity Investments | ~2% | Institutional Investor | Mutual fund and retirement plan exposure, passive influence |
| T. Rowe Price | ~1.5% | Institutional Investor | Research-driven investor, supports stable stock ownership |
| Public and Retail Investors | ~50% | Public/Retail | Includes individuals, pension funds, and smaller institutions with limited control |
3G Capital – Approx. 29%
3G Capital is the founding and largest shareholder of Restaurant Brands International. It led to the 2014 merger between Burger King and Tim Hortons, which created RBI. The Brazilian-American investment firm is known for its aggressive cost-cutting, operational efficiency, and long-term investment approach.
Although 3G has sold off some of its stake over the years, it still owns close to 29% of RBI’s outstanding shares. This gives it considerable voting power and influence over corporate strategy. 3G Capital also maintains board representation and has had strong input in selecting the company’s executive leadership. It continues to be the strategic anchor of RBI, with an outsized influence relative to its stake.
The Vanguard Group – Approx. 7%
Vanguard is one of the world’s largest asset management firms. It owns about 7% of the RBI through various mutual funds and ETFs. Vanguard is considered a passive investor, meaning it does not actively manage RBI or influence day-to-day decisions. However, due to its large stake, it plays a key role during shareholder votes on major issues like executive pay, board elections, and mergers.
Vanguard’s investment signals confidence in the RBI’s long-term business model and global expansion potential.
BlackRock – Approx. 4%
BlackRock, another top global investment firm, holds around 4% of RBI shares. Similar to Vanguard, BlackRock’s involvement is primarily through index funds and ETFs. While it does not exert direct control, it has influence through proxy voting and corporate governance advocacy.
BlackRock supports sustainable growth strategies and has encouraged companies in its portfolio to focus on climate and social issues. It has historically supported the RBI’s board decisions, but may engage if ESG standards are not met.
Capital Research Global Investors – Approx. 3%
Capital Research Global Investors is a division of Capital Group, one of the oldest investment management organizations in the U.S. It owns an estimated 3% of RBI shares. Known for long-term investments, Capital Research typically takes a hands-off approach in governance but aligns with management strategies focused on growth and profitability.
This shareholder adds depth to the institutional ownership of RBI, supporting stability and long-term planning.
Fidelity Investments – Approx. 2%
Fidelity, through its mutual funds and retirement products, holds about 2% of RBI. While smaller than Vanguard or BlackRock, Fidelity is still a significant investor. Its involvement suggests retail investors also have strong exposure to the RBI through 401(k) plans and managed portfolios.
Fidelity doesn’t play an active governance role but is a key part of the financial ecosystem that supports publicly traded firms.
T. Rowe Price – Approx. 1.5%
T. Rowe Price is another institutional investor with a stake of about 1.5%. The firm is known for its research-driven investment approach. While not highly influential, it contributes to RBI’s investor base and supports liquidity in the stock.
T. Rowe Price typically aligns with existing management unless there is a notable conflict in governance or performance.
Public and Retail Investors – Approx. 50% Combined
The remaining 50% or so of RBI shares are held by a mix of retail investors, pension funds, insurance companies, and smaller mutual funds. These investors usually have limited influence individually, but collectively form a major block of ownership.
Retail investors are everyday shareholders who buy stock through brokers or apps. While they may not attend annual meetings or vote regularly, they benefit from dividends, stock appreciation, and brand loyalty.
Who Controls Restaurant Brands International?
While Restaurant Brands International has many shareholders, actual control lies with a select group of individuals and entities who guide its strategy, make key decisions, and oversee operations. These include the board of directors, the executive leadership team, and the company’s most influential shareholder, 3G Capital.
Role of 3G Capital in Corporate Control
3G Capital, as the largest shareholder, retains considerable control over RBI’s long-term direction. Although its ownership has declined since the 2014 merger, it still owns nearly 29% of the company. This gives 3G substantial voting power and the ability to influence board appointments and executive decisions.
Many past and current RBI board members and executives have ties to 3G Capital. Its continued presence ensures a strong alignment between shareholder interests and management priorities. 3G also promotes cost-efficiency, lean operations, and aggressive international growth, all of which are reflected in RBI’s strategy.
Board of Directors
RBI’s board of directors is responsible for overseeing the company’s operations and protecting shareholder interests. The board includes a mix of independent directors, 3G affiliates, and industry experts. Its duties include approving budgets, evaluating mergers and acquisitions, and selecting the executive team.
While the board represents various stakeholders, members associated with 3G Capital have historically held key decision-making roles, ensuring that 3G’s vision continues to influence corporate governance.
The board also ensures compliance with regulations, sets executive compensation, and approves key strategic initiatives like international expansions and acquisitions.
CEO of Restaurant Brands International: Joshua Kobza
As of 2023, the CEO of Restaurant Brands International is Joshua Kobza. He took over the role in March 2023, replacing José Cil. Kobza has been with RBI since its creation and has held several key positions, including Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and Chief Operating Officer (COO).
Joshua Kobza is known for his analytical skills, operational focus, and experience in global franchising. At just 36 when he became CEO, he represented a younger generation of leadership. His deep familiarity with RBI’s operations, technology strategy, and franchise structure gives him a strong advantage.
Under Kobza’s leadership, RBI has focused on modernizing digital infrastructure, improving restaurant performance, and accelerating international growth. He also emphasizes tech-driven innovation, particularly in mobile ordering, customer loyalty platforms, and restaurant automation.
Kobza reports directly to the board and plays a central role in implementing the company’s vision across all its brands—Burger King, Tim Hortons, Popeyes, and Firehouse Subs.
Executive Leadership Team
Supporting the CEO is a seasoned executive leadership team with heads of key departments such as finance, operations, marketing, supply chain, technology, and brand management. Each of RBI’s brands also has its own president or brand lead, ensuring that each business unit maintains its unique identity while aligning with group-level strategy.
The executive team is structured to allow for both global coordination and brand-specific innovation. This dual focus allows RBI to maintain consistency in operations while customizing approaches for different markets and customer preferences.
Summary of Control Structure
In summary, control of Restaurant Brands International is shared among:
- 3G Capital (strategic direction and board influence)
- The Board of Directors (corporate oversight and governance)
- Joshua Kobza, CEO (day-to-day operations and strategic execution)
- Executive Leadership Team (functional and brand-level management)
Together, they ensure that RBI remains competitive, profitable, and aligned with shareholder expectations across a global landscape.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Restaurant Brands International
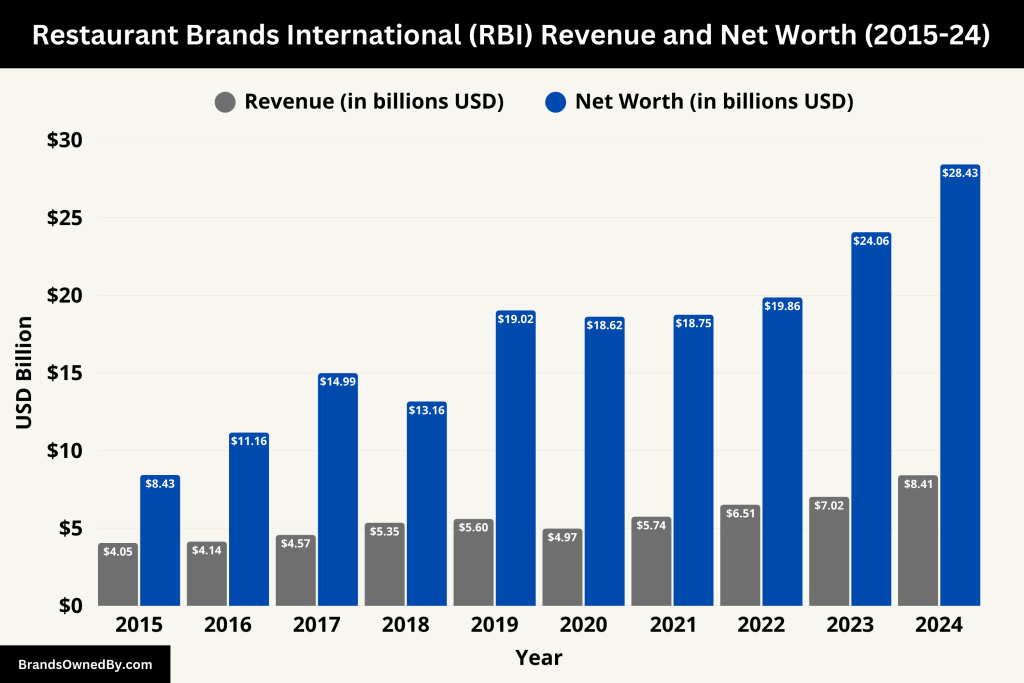
In 2024, Restaurant Brands International (RBI) achieved a total annual revenue of $8.41 billion, marking a 19.7% increase compared to the previous year. This growth was driven by strong performances across its brands, particularly Tim Hortons and Burger King, as well as strategic acquisitions like Carrols Restaurant Group and Popeyes China.
The company reported system-wide sales of nearly $45 billion across its global network of over 30,000 restaurants in more than 120 countries and territories. Notably, the fourth quarter of 2024 saw revenue of $2.30 billion, with a 26.15% year-over-year growth, indicating strong momentum heading into 2025.
As of April 2025, RBI’s market capitalization stands at approximately $28.43 billion, reflecting a 14.47% increase over the past year. This growth in market cap underscores investor confidence in the company’s strategic direction and financial health.
Additionally, RBI’s enterprise value, which accounts for market cap, debt, and cash, is reported at $43.02 billion. This figure provides a comprehensive view of the company’s total value, considering both its equity and debt obligations.
Here’s a breakdown of RBI’s historical revenue and net worth:
| Year | Annual Revenue (USD) | Market Capitalization (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | $8.41 billion | $28.43 billion |
| 2023 | $7.02 billion | $24.06 billion |
| 2022 | $6.51 billion | $19.86 billion |
| 2021 | $5.74 billion | $18.75 billion |
| 2020 | $4.97 billion | $18.62 billion |
| 2019 | $5.60 billion | $19.02 billion |
| 2018 | $5.35 billion | $13.16 billion |
| 2017 | $4.57 billion | $14.99 billion |
| 2016 | $4.14 billion | $11.16 billion |
| 2015 | $4.05 billion | $8.43 billion |
Companies Owned by Restaurant Brands International (RBI)
Restaurant Brands International (RBI) owns and operates some of the world’s most iconic and fast-growing quick-service restaurant brands. These brands serve millions of customers daily in over 120 countries. RBI follows a franchise-heavy model, with most of its restaurants run by independent operators.
Below are the key companies and brands that make up RBI’s portfolio:
| Company / Brand | Ownership % | Ownership Type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Burger King | 100% | Full Ownership | Acquired via merger with Tim Hortons in 2014. Flagship brand. |
| Tim Hortons | 100% | Full Ownership | Canadian icon merged with Burger King in 2014 to form RBI. |
| Popeyes Louisiana Kitchen | 100% | Full Ownership | Acquired in 2017 for $1.8 billion. Fast-growing international brand. |
| Firehouse Subs | 100% | Full Ownership | Acquired in 2021 for $1 billion. Fast-casual sandwich chain. |
| Carrols Restaurant Group | 100% (in process) | Full Ownership (pending) | Announced acquisition in 2024. One of RBI’s largest franchise operators. |
| Popeyes China | 100% | Full Ownership | Acquired from master franchisee in 2024 to accelerate growth in Asia. |
| Tims China | Minority stake (~15–20%) | Joint Venture (equity interest) | Operated by TH International Limited. RBI provides brand support and holds minority equity. |
Burger King
Burger King is RBI’s largest and most globally recognized brand. It was founded in 1954 and became part of RBI following the 2014 merger with Tim Hortons. The chain is known for flame-grilled burgers, particularly the Whopper, and has a strong global presence with over 19,000 restaurants across 100+ countries.
Under the RBI, Burger King has undergone extensive rebranding and store remodeling. Its “Reclaim the Flame” plan, launched in 2022, aimed to improve restaurant design, drive-thru speed, and digital experiences. Burger King is RBI’s primary revenue generator, contributing a significant share of system-wide sales.
Tim Hortons
Tim Hortons is Canada’s largest quick-service restaurant chain and the foundation of RBI’s creation. It was founded in 1964 and is best known for its coffee, Timbits, and breakfast items. Tim Hortons merged with Burger King in 2014 to form RBI.
The brand has over 5,700 locations, primarily in Canada, but it has expanded to markets like China, the UK, and the Middle East. Tim Hortons continues to lead in the Canadian QSR market share and contributes substantial revenue for RBI through a strong franchising model.
RBI has focused on modernizing the Tim Hortons menu, expanding mobile ordering, and enhancing drive-thru technology.
Popeyes Louisiana Kitchen
Popeyes joined the RBI family in 2017 after a $1.8 billion acquisition. Known for its bold, Louisiana-style fried chicken and biscuits, Popeyes has become one of the fastest-growing chicken chains globally.
It has over 4,300 locations and is expanding aggressively, particularly in Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. The brand gained viral popularity with the 2019 launch of its chicken sandwich, which led to massive sales growth and brand awareness.
RBI supports Popeyes with supply chain improvements and new market development strategies. It’s considered a major growth engine for the company.
Firehouse Subs
Firehouse Subs was acquired by RBI in 2021 for $1 billion. It was founded in 1994 by former firefighters and is known for its hot, hearty sandwiches and community-focused mission. The brand operates over 1,200 restaurants, primarily in the U.S.
Though smaller than RBI’s other chains, Firehouse Subs fits well into the company’s portfolio as a fast-casual brand. RBI plans to accelerate its expansion, leveraging its global franchising infrastructure to take Firehouse into new international markets.
Carrols Restaurant Group (Franchise Operator)
In 2024, the RBI announced it would acquire Carrols Restaurant Group, one of its largest Burger King franchisees. Carrols owns and operates over 1,000 Burger King and Popeyes restaurants, mostly in the U.S.
The acquisition allows RBI to take more direct control over store-level operations, especially as part of its Burger King revitalization strategy. Carrols will serve as a foundation for corporate-run restaurant innovation and testing.
Popeyes China (Master Franchisee)
In early 2024, RBI acquired full ownership of Popeyes China, which was previously operated by a master franchisee. The acquisition is part of a broader strategy to expand the Popeyes brand in Asia, where fried chicken demand is growing rapidly.
This move gives RBI direct control over growth strategy, marketing, and restaurant development in one of the world’s most important fast-food markets. Popeyes China plans to open hundreds of new stores in the coming years.
Tims China (Joint Venture – Indirect Ownership)
Tims China is a joint venture between RBI and Cartesian Capital Group. While RBI does not directly own a controlling stake, it holds an equity interest in the venture, which operates over 900 Tim Hortons locations in China.
Tims China went public via a SPAC merger in 2022 and is growing rapidly. RBI contributes branding, menu innovation, and strategic guidance to the venture, making it an important part of RBI’s Asian expansion strategy.
Conclusion
Restaurant Brands International is owned by a mix of institutional investors and retail shareholders, but 3G Capital remains its largest and most influential stakeholder. The company controls four iconic restaurant brands that serve millions daily. With global expansion plans and steady revenue growth, RBI continues to be a powerful player in the fast-food sector.
FAQs
What is Restaurant Brands International?
It is a Canadian-based multinational fast-food holding company that owns Burger King, Tim Hortons, Popeyes, and Firehouse Subs.
Who is the largest shareholder of Restaurant Brands International?
3G Capital is the largest shareholder, owning about 29% of the company.
Is Restaurant Brands International publicly traded?
Yes, it is listed on the NYSE and TSX under the ticker symbol QSR.
Who is the CEO of Restaurant Brands International?
Joshua Kobza is the current CEO, appointed in 2023.
What companies are owned by Restaurant Brands International?
RBI owns Burger King, Tim Hortons, Popeyes Louisiana Kitchen, and Firehouse Subs.
Who is the parent company of Tim Hortons?
The parent company of Tim Hortons is Restaurant Brands International (RBI), which owns 100% of the brand. RBI was formed in 2014 through a merger between Burger King and Tim Hortons.
Who is the owner of 3G Capital?
3G Capital is a Brazilian-American private investment firm co-founded by Jorge Paulo Lemann, Marcel Telles, and Carlos Alberto Sicupira. They are the primary owners and major figures behind 3G Capital, known for their active involvement in the management of companies they invest in.

