WhatsApp is one of the world’s most-used messaging apps, but many users still wonder who owns WhatsApp. Since its launch, the app has changed hands and grown to serve over two billion users. This article breaks down its ownership, control, and financial status.
History of WhatsApp
WhatsApp was founded in 2009 by Jan Koum and Brian Acton, two former Yahoo employees. They wanted to build a simple, ad-free messaging app that worked across platforms. Due to its simplicity and end-to-end encryption, the app gained popularity quickly.
By 2013, it had over 400 million users.
In February 2014, Facebook announced it was acquiring WhatsApp for $19 billion in cash and stock. It was one of the largest tech acquisitions in history.
After the acquisition, WhatsApp continued to operate semi-independently, with Koum and Acton initially staying on.
However, both founders eventually left due to disagreements with Facebook’s vision for monetization and data sharing. Since then, WhatsApp has become more integrated into the broader Meta ecosystem.
Who Owns WhatsApp: Meta Shareholder List
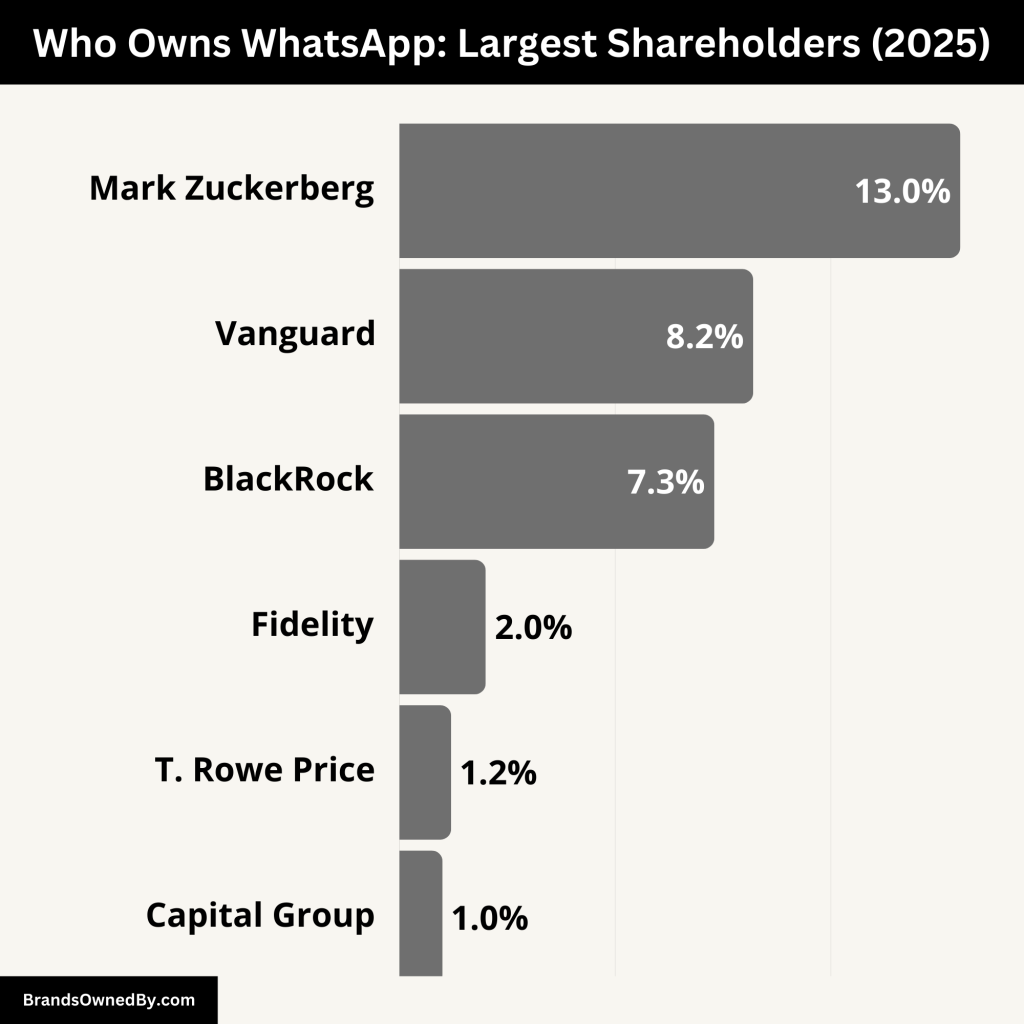
WhatsApp is fully owned by Meta Platforms, Inc. (formerly Facebook, Inc.). Meta acquired the company in 2014 and has held 100% ownership since. This means Meta is the sole parent company behind WhatsApp, making it a wholly owned subsidiary.
Meta Platforms, Inc. is a publicly traded company, and therefore, the ownership of WhatsApp is tied to Meta’s shareholders. These include individual investors, institutional shareholders, and Meta insiders.
Here’s a breakdown of Meta shareholders and investors who now fully own WhatsApp:
| Shareholder | Ownership % (Meta) | Type | Role/Influence in WhatsApp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mark Zuckerberg | ~13% of total shares >50% voting power | Individual / Insider | Founder, CEO, and Chairman of Meta; has majority voting power and full strategic control over WhatsApp |
| Vanguard Group | ~8.2% | Institutional Investor | Passive investor; significant economic interest but no operational control |
| BlackRock Inc. | ~7.3% | Institutional Investor | Passive investor; participates in governance through voting but no day-to-day influence |
| Fidelity Investments | ~1.5%–2% | Institutional Investor | Medium-sized shareholder; economic interest without decision-making power |
| T. Rowe Price | ~1.2% | Institutional Investor | Long-term investor; supports strategic growth but not involved in daily decisions |
| Capital Group Companies | ~1.1%–1.3% | Institutional Investor | Holds a small but notable stake; involved via corporate governance voting |
| Meta Employees & Executives | ~1% (estimated total) | Internal Shareholders | Collectively hold shares through RSUs and stock options; limited strategic influence |
| Retail/Public Investors | ~20%+ | Public Shareholders | Broad group of retail investors via stock markets and ETFs; no direct control |
Mark Zuckerberg (Founder, CEO, and Chairman of Meta)
Mark Zuckerberg is the largest individual shareholder of Meta Platforms. He owns approximately 13% of Meta’s total shares but holds over 50% of voting power due to Meta’s dual-class share structure. Class A shares offer one vote per share, while Class B shares—mainly held by Zuckerberg—offer ten votes per share.
This dual-share structure gives Zuckerberg effective control over Meta and, by extension, WhatsApp. He can override other shareholders in strategic decisions. His influence ensures that Meta’s long-term goals, including those involving WhatsApp, reflect his personal vision.
Vanguard Group
The Vanguard Group is one of the largest institutional investors in Meta. It holds roughly 8.2% of Meta’s Class A shares, making it a significant financial stakeholder.
As a passive investment firm managing trillions in assets, Vanguard does not participate in daily decision-making. However, it votes on shareholder matters and influences governance through board engagement. Vanguard’s interest in Meta indirectly gives it an economic stake in WhatsApp’s performance.
BlackRock Inc.
BlackRock, another major asset management company, owns around 7.3% of Meta’s Class A shares. Like Vanguard, BlackRock focuses on long-term returns and passive investment strategies.
While it has no direct say in how WhatsApp operates, BlackRock’s shareholder votes can influence Meta’s board elections, corporate policies, and governance standards.
Fidelity Investments
Fidelity is a smaller institutional investor in Meta, with a stake of approximately 1.5%–2%. It manages funds that include Meta shares in retirement plans, mutual funds, and ETFs.
Fidelity has no operational control over Meta or WhatsApp. However, its presence among the top shareholders shows broader investor interest in Meta’s business portfolio, including WhatsApp.
T. Rowe Price
T. Rowe Price is another large mutual fund company that holds a notable portion of Meta shares—estimated at around 1.2%.
Though not a controlling shareholder, its investment reflects strong institutional confidence in Meta’s platforms. This includes revenue and growth potential from WhatsApp’s business and payment tools.
Capital Group Companies
Capital Group holds roughly 1.1%–1.3% of Meta’s Class A shares. It is one of the oldest investment firms in the U.S., often focused on large-cap technology companies.
As a long-term investor, Capital Group monitors corporate performance closely, and its votes can sway outcomes in Meta’s annual meetings.
Meta Employees and Executives
Many Meta employees, especially those in senior roles, hold company stock as part of their compensation packages. These shares can be in the form of Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) or stock options.
While individually small, collectively this group can hold a meaningful percentage of Meta’s Class A shares. However, none have the voting power or influence comparable to Mark Zuckerberg.
Retail and Public Shareholders
A significant portion of Meta’s shares—around 20% or more—is held by public investors through brokerage accounts, mutual funds, and ETFs. These retail investors have no direct influence but contribute to market dynamics.
Who Controls WhatsApp?
WhatsApp is controlled by Meta’s leadership. The final authority rests with Mark Zuckerberg as Meta’s CEO and chairman. Because of Meta’s dual-class share structure, Zuckerberg has majority voting power. This gives him strong control over strategic decisions, including WhatsApp’s future.
Meta’s board and executive team oversee WhatsApp’s development. Will Cathcart is the current head of WhatsApp. He reports to Meta’s top leadership and is responsible for the app’s daily operations, feature rollouts, and compliance policies.
Major decisions—like introducing payments or business tools—go through Meta’s executive leadership.
Below is a detailed overview of who controls and runs WhatsApp:
Mark Zuckerberg: The ultimate decision-maker
Mark Zuckerberg is the co-founder, Chairman, and CEO of Meta Platforms, Inc. He exercises majority voting control over Meta due to the company’s dual-class share system. Zuckerberg owns a relatively small percentage (~13%) of Meta’s total stock but holds over 50% of voting rights through Class B shares.
This gives him effective veto power and strategic oversight over every major product owned by Meta, including WhatsApp. No other individual or institutional investor can outvote him in shareholder matters.
Zuckerberg’s influence over WhatsApp includes its data privacy policies, monetization strategies (such as WhatsApp Business), and alignment with Meta’s broader vision of interoperability and the metaverse.
Will Cathcart: Head of WhatsApp
Will Cathcart is the Head of WhatsApp, a role he has held since 2019. He previously worked on the Facebook app and joined Meta in 2010. Cathcart oversees WhatsApp’s product development, engineering, growth, and security initiatives.
He is responsible for:
- Leading the development of WhatsApp features like end-to-end encryption, payments, and Communities
- Managing compliance with global regulations such as the EU’s Digital Markets Act
- Representing WhatsApp in public policy discussions, especially around privacy and encryption
Though he runs day-to-day operations, Cathcart reports to Meta’s top executives, including Zuckerberg and the broader Meta leadership team. He does not operate with full independence, as WhatsApp is fully embedded within Meta’s infrastructure and strategic roadmap.
Meta’s Executive Leadership
Control of WhatsApp also extends to other senior executives at Meta who influence company-wide decisions. These include:
- Andrew Bosworth (CTO) – Oversees the Family of Apps, including WhatsApp, and aligns product vision across the company
- Susan Li (CFO) – Oversees Meta’s financial strategy, including investments in WhatsApp’s infrastructure and monetization tools
- Chris Cox (Chief Product Officer) – Plays a key role in product integration across Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, and WhatsApp
- Nick Clegg (President of Global Affairs) – Manages policy, legal issues, and regulatory matters affecting WhatsApp globally
Together, this executive team ensures WhatsApp operates in line with Meta’s policies on security, growth, monetization, user experience, and global compliance.
Meta Board of Directors
Meta’s Board of Directors also plays a role in guiding overall strategy, including initiatives that affect WhatsApp. While Mark Zuckerberg holds the most influence, the board includes industry leaders from diverse sectors. The board advises on acquisitions, compliance, and long-term innovation goals that WhatsApp is part of.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of WhatsApp
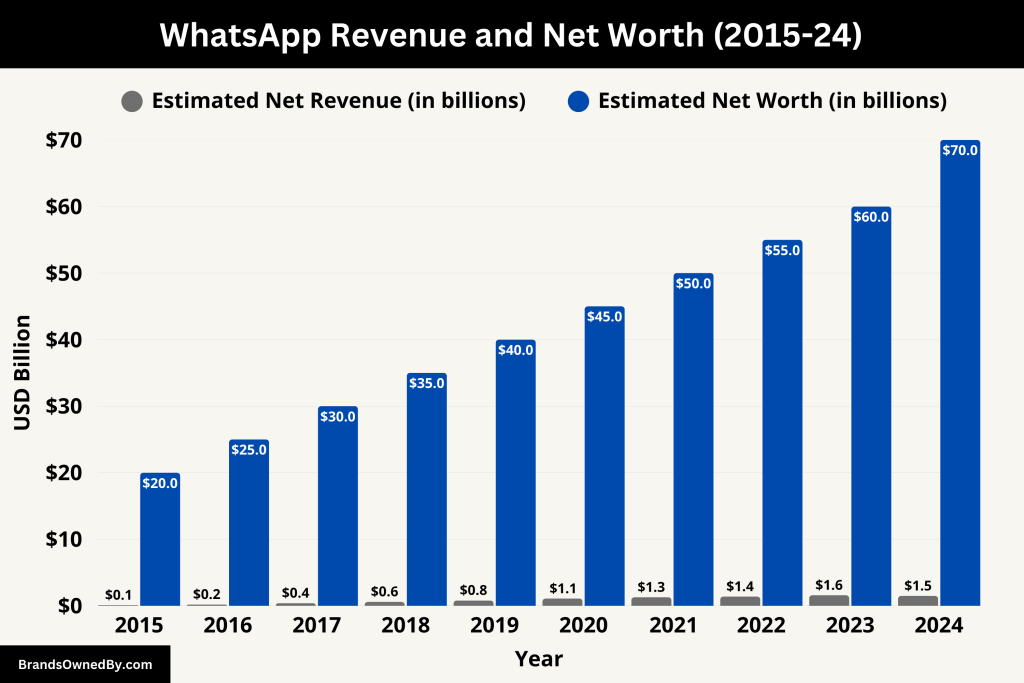
In 2024, WhatsApp’s estimated annual revenue reached approximately $1.5 billion. This growth was primarily driven by its business-focused services:
- WhatsApp Business API: This service allows medium and large businesses to communicate with customers at scale. Companies pay to send messages to customers, with fees based on the country and message volume.
- Click-to-WhatsApp Ads: These ads enable users to initiate WhatsApp conversations with businesses directly from ads on Facebook and Instagram. This format has become Meta’s fastest-growing ad product, projected to potentially reach $10 billion in revenue in 2024.
- WhatsApp Pay: Launched in select markets like India and Brazil, WhatsApp Pay allows users to send money directly through the app. While free for individuals, WhatsApp charges businesses a fee for payments received.
Despite this growth, WhatsApp’s revenue still represents a small fraction of Meta’s total earnings. However, its strategic importance continues to rise, especially in emerging markets.
Net Worth Estimate
While Meta does not publicly disclose WhatsApp’s standalone valuation, industry analysts estimate WhatsApp’s net worth in April 2025 to be between $50 billion and $70 billion. This valuation considers several factors:
- User Base: WhatsApp boasts over 2.95 billion monthly active users as of 2025, making it one of the most widely used messaging apps globally.
- Revenue Growth Potential: Analysts project that WhatsApp’s business messaging revenue could soar from about $1.5 billion to $7.3 billion by the end of the decade.
- Market Expansion: With the increasing adoption of digital communication, especially in regions like India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia, WhatsApp’s market penetration and monetization opportunities are expected to grow substantially.
These factors contribute to a robust valuation, positioning WhatsApp as a significant asset within Meta’s portfolio and a key driver for future growth.
Below is an overview of WhatsApp’s historical revenue and net worth:
| Year | Estimated Annual Revenue | Estimated Net Worth (Valuation) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | ~$0.1 billion | ~$20 billion | WhatsApp still ad-free; early stages of user growth post-acquisition. |
| 2016 | ~$0.2 billion | ~$25 billion | Continued growth in emerging markets; no monetization yet. |
| 2017 | ~$0.4 billion | ~$30 billion | First signs of monetization planning. Business API begins testing. |
| 2018 | ~$0.6 billion | ~$35 billion | WhatsApp Business app launches; slow revenue growth starts. |
| 2019 | ~$0.8 billion | ~$40 billion | Business API expands; early enterprise messaging revenue. |
| 2020 | ~$1.1 billion | ~$45 billion | Surge in messaging usage during COVID-19 pandemic. |
| 2021 | ~$1.3 billion | ~$50 billion | WhatsApp Pay launches in India and Brazil; growing commercial use. |
| 2022 | ~$1.4 billion | ~$55 billion | Expansion of Click-to-WhatsApp ads; stronger business engagement. |
| 2023 | ~$1.6 billion | ~$60 billion | Integration with Meta ads ecosystem drives revenue up. |
| 2024 | ~$1.5 billion | $50–70 billion | Strong usage growth, but monetization pace slows slightly. |
Brands Owned by WhatsApp
As of now, WhatsApp does not own any independent companies or brands. It operates exclusively as a product and subsidiary within Meta Platforms, Inc. Since its acquisition by Meta in 2014, WhatsApp has remained a self-contained messaging platform and has not acquired, merged with, or created any separate brands under its own name.
However, WhatsApp does have two distinct product extensions under its umbrella, which can be considered internal brands or services:
WhatsApp Messenger
This is the core product of WhatsApp — a free, end-to-end encrypted messaging and calling app available on Android, iOS, and the web. It allows users to:
- Send text messages, voice notes, images, videos, and documents
- Make one-on-one and group voice or video calls
- Create groups and broadcast lists
- Use end-to-end encryption for all communication
As of 2025, WhatsApp Messenger has over 2.95 billion monthly active users, making it the world’s most popular messaging app.
WhatsApp Business
Launched in January 2018, WhatsApp Business is a standalone app designed for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). It offers:
- Business profiles with descriptions, addresses, hours, and websites
- Automated messages such as greetings, away messages, and quick replies
- Product catalogs for showcasing items or services
- Labels for organizing customer conversations
The app is free, but WhatsApp monetizes its Business API (used by larger businesses) by charging per message sent to customers.
This version has gained popularity in regions like India, Brazil, and Indonesia, where small businesses heavily rely on WhatsApp to communicate with customers.
WhatsApp Business API
Though not a separate app, the WhatsApp Business API is a powerful enterprise solution for medium and large companies. It integrates with customer support and CRM platforms like:
- Zendesk
- Twilio
- MessageBird
- Freshchat.
Companies pay based on template message types, country pricing, and monthly conversation volume. This API is a major revenue stream for WhatsApp, especially in markets with high digital commerce usage.
Internal Tools (Non-public brands)
WhatsApp also operates several internal or unreleased tools, primarily for analytics, moderation, business onboarding, and platform compliance. These are not public-facing or branded, so they are not considered official sub-brands.
Conclusion
So, who owns WhatsApp? The answer is Meta Platforms, Inc., with Mark Zuckerberg holding the ultimate control through his leadership and voting power. Since its acquisition in 2014, WhatsApp has remained a vital part of Meta’s product lineup. While it doesn’t own other companies, it plays a key role in Meta’s communication and business services strategy. Understanding WhatsApp’s ownership helps shed light on its data policies, monetization plans, and future direction.
FAQs
Who is the founder of WhatsApp?
WhatsApp was founded by Jan Koum and Brian Acton in 2009. They were former Yahoo employees.
When did Facebook buy WhatsApp?
Facebook (now Meta) acquired WhatsApp in February 2014. The deal was finalized in October 2014.
Does Mark Zuckerberg own WhatsApp?
Mark Zuckerberg does not directly own WhatsApp. But he controls Meta, which fully owns WhatsApp. Through this, he holds significant influence.
Is WhatsApp owned by Google?
No, WhatsApp is not owned by Google. It is owned by Meta Platforms, Inc.
How does WhatsApp make money?
WhatsApp makes money mainly through WhatsApp Business APIs and transaction fees in its payments features. It does not run traditional ads.
Is WhatsApp still private?
WhatsApp uses end-to-end encryption for messages. However, it shares some metadata with Meta, especially for business interactions.
Who is the CEO of WhatsApp?
WhatsApp does not have a CEO in the traditional sense, as it is not an independent company. Instead, it is a subsidiary of Meta Platforms, Inc. The executive in charge of WhatsApp is Will Cathcart, who holds the title of Head of WhatsApp.
Will Cathcart oversees the platform’s product strategy, privacy features, engineering, and global operations. He reports directly to senior leadership at Meta, including CEO Mark Zuckerberg. Major decisions related to WhatsApp’s direction, funding, and integration with other Meta products are ultimately made by Zuckerberg and Meta’s executive team.
How WhatsApp owner makes money?
The owner of WhatsApp is Meta Platforms, Inc., and it makes money from WhatsApp mainly through its business-focused services, not from regular users.
Key revenue streams include:
- WhatsApp Business API: Medium and large businesses pay to send notifications and customer service messages to users. Pricing varies by region and message type.
- Click-to-WhatsApp Ads: These are ads shown on Facebook or Instagram that open a WhatsApp chat. Businesses pay Meta for these ads.
- WhatsApp Pay (in select regions): Although basic money transfers are free, Meta plans to monetize financial services by charging transaction fees to businesses.
WhatsApp does not currently show ads inside the app for users, though Meta has explored future monetization options such as in-chat promotions or premium services.
Who pays for WhatsApp?
Regular users do not pay to use WhatsApp. The app is free to download and use, with no subscription fees. Instead, the cost of running WhatsApp is covered by Meta, which earns revenue from businesses using its communication tools.
Businesses and advertisers are the ones who pay:
- Businesses pay for sending bulk or automated messages via WhatsApp Business API.
- Advertisers pay Meta when they run “Click-to-WhatsApp” ads on Facebook and Instagram to engage with customers.
This business model allows WhatsApp to stay free for over 2.9 billion users worldwide while still generating revenue.

