Tencent Holdings Limited, commonly known as Tencent, is a Chinese multinational technology conglomerate renowned for its diverse range of services and products. Founded in 1998, Tencent has expanded its influence across various sectors, including social media, gaming, and fintech. A common inquiry about this tech giant is: who owns Tencent?
Understanding its ownership structure provides insight into the company’s strategic direction and market position.
History of Tencent
Tencent was established in 1998 by Ma Huateng (also known as Pony Ma), Zhang Zhidong, Xu Chenye, Chen Yidan, and Zeng Liqing.
The company’s initial success came with the launch of OICQ, later rebranded as QQ, an instant messaging platform that quickly gained popularity in China. Building on this foundation, Tencent expanded into various digital services, including the creation of WeChat in 2011, a multifunctional app that has become integral to daily life in China.
Tencent has diversified its portfolio, venturing into online gaming, fintech, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, solidifying its position as a global tech leader.
Who Owns Tencent?
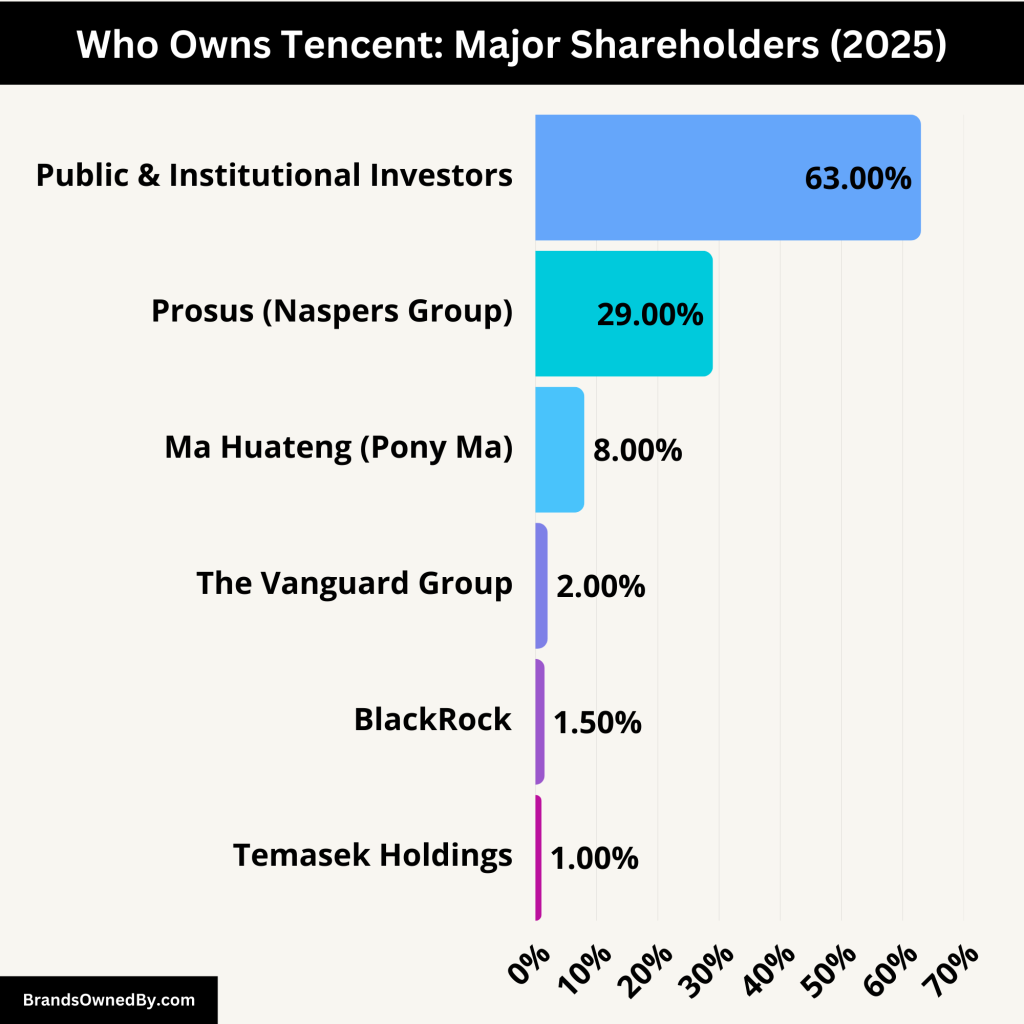
Tencent’s ownership is characterized by a mix of institutional and individual shareholders.
The largest shareholder is Prosus, a global consumer internet group and one of the largest technology investors in the world. Prosus holds approximately 29% of Tencent’s shares, making it the most significant stakeholder. This substantial stake originated from an early investment by Naspers, Prosus’s parent company, which invested in Tencent during its nascent stages.
Another notable shareholder is Ma Huateng, Tencent’s co-founder and CEO, who owns around 8% of the company. The remaining shares are held by a combination of institutional investors and the public, reflecting Tencent’s status as a publicly traded company listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
List of Tencent Shareholders
Here’s a list of the major shareholders of Tencent:
| Shareholder | Ownership Percentage | Role & Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Prosus (Naspers Group) | ~29% | Largest shareholder, early investor, provides capital but does not control management decisions. |
| Ma Huateng (Pony Ma) | ~8% | Co-founder, CEO, and key decision-maker in Tencent’s strategic direction. |
| Public & Institutional Investors | ~63% | Shares are widely distributed among global investors, mutual funds, and hedge funds. |
| The Vanguard Group | ~2% | Major asset management firm investing in Tencent as part of its tech-focused portfolio. |
| BlackRock | ~1.5% | Largest asset manager globally, holds Tencent shares as part of its diversified tech investments. |
| Temasek Holdings | ~1% | Singapore government-owned investment firm with long-term stakes in Tencent. |
| Other Institutional & Retail Investors | Varies | Shares held by various hedge funds, pension funds, and individual investors worldwide. |
Prosus (Naspers Group) – 29%
Prosus, a subsidiary of Naspers, is Tencent’s largest shareholder, holding approximately 29% of the company. Naspers, a South African multinational, made a groundbreaking investment in Tencent in 2001 when it acquired a 46.5% stake for just $32 million. Over time, Naspers restructured its holdings under Prosus, which later reduced its stake to the current 29%. Despite being the largest shareholder, Prosus does not have a controlling interest, allowing Tencent’s management to operate independently.
Ma Huateng (Pony Ma) – ~8%
Ma Huateng, also known as Pony Ma, is the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Tencent. He owns roughly 8% of the company’s shares, making him the second-largest individual shareholder. As a key decision-maker, he has played a critical role in shaping Tencent’s strategy and expansion into various industries, including gaming, fintech, and artificial intelligence. His influence ensures that Tencent continues to pursue long-term innovation and growth.
The Vanguard Group – ~2%
The Vanguard Group, one of the world’s largest asset management firms, holds around 2% of Tencent’s shares. Vanguard’s investment in Tencent is part of its global strategy of investing in high-growth technology companies.
BlackRock – ~1.5%
BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, owns approximately 1.5% of Tencent’s shares. The firm has consistently invested in Tencent due to its strong performance in gaming, social media, and cloud computing.
Temasek Holdings – ~1%
Temasek Holdings, a Singaporean investment firm owned by the Singapore government, holds close to 1% of Tencent’s shares. Temasek has backed many Asian tech companies and sees Tencent as a valuable long-term investment.
Other Institutional Investors and Retail Shareholders
Beyond these major investors, Tencent’s shares are widely distributed among global hedge funds, mutual funds, and retail investors. Many individual shareholders own Tencent stock through Hong Kong’s stock exchange or through ADRs (American Depositary Receipts) in the U.S. market.
Who Controls Tencent?
Tencent’s control lies in the hands of its executive leadership, board of directors, and regulatory authorities. While the largest shareholder, Prosus, holds a 29% stake, it does not exercise direct control over the company’s operations. Instead, Tencent’s internal leadership, particularly CEO Ma Huateng, makes key decisions alongside the board and senior executives. Additionally, the Chinese government plays a regulatory role, influencing the company’s strategic direction.
Executive Leadership: Key Decision-Makers
Tencent’s management team is responsible for daily operations, strategic planning, and long-term growth initiatives. The most influential figures include:
- Ma Huateng (Pony Ma) – Co-founder, Chairman & CEO
As the co-founder and CEO, Ma Huateng is the most powerful figure at Tencent. He directly influences major strategic decisions, investments, and corporate direction. Despite holding only about 8% of Tencent’s shares, his leadership ensures that he remains at the helm of the company’s operations. - Martin Lau – President
Martin Lau has played a crucial role in Tencent’s expansion, particularly in its international investments. He oversees corporate strategy, mergers and acquisitions, and financial management. Lau’s leadership helps bridge Tencent’s business interests with its global partners and investors. - James Mitchell – Chief Strategy Officer
As Tencent’s Chief Strategy Officer, James Mitchell is responsible for global investment strategies. He has been instrumental in Tencent’s stake acquisitions in gaming companies such as Riot Games, Epic Games, and Supercell. His role ensures Tencent remains a dominant force in the gaming and tech industries. - Mark Ren – Chief Operating Officer (COO)
Mark Ren oversees Tencent’s gaming business and entertainment ventures. His work in managing Tencent’s massive gaming empire ensures that the company retains its leadership position in the global gaming industry.
Board of Directors: Governance and Oversight
Tencent’s board of directors provides oversight, ensuring that the executive team adheres to corporate governance standards. The board comprises both internal executives and independent directors, balancing internal decision-making with external perspectives.
Key members include:
- Ma Huateng (Chairman & CEO) – Leads the board and is the primary decision-maker.
- Martin Lau (President) – Represents executive leadership on the board.
- Independent Directors – Provide guidance and ensure compliance with financial and corporate governance policies.
The board plays an essential role in approving major business decisions, including acquisitions, financial planning, and strategic shifts.
Chinese Government Influence and Regulatory Oversight
Although Tencent is a private company, it operates under significant oversight from the Chinese government. The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) has implemented regulations that impact Tencent’s operations, including gaming restrictions, data security laws, and antitrust policies.
- State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR): Regulates Tencent’s mergers and acquisitions to prevent monopolistic practices.
- Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC): Oversees Tencent’s data privacy policies and content moderation on its platforms.
- Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT): Regulates Tencent’s telecom and internet-related businesses.
Additionally, Tencent, like other major Chinese tech firms, maintains a CCP committee within the company. This ensures alignment with national policies and regulatory compliance. While the government does not directly control Tencent, its policies can significantly influence the company’s strategic direction.
Influence of Institutional Shareholders
Despite being the largest shareholder, Prosus does not exercise operational control over Tencent. Similarly, major institutional investors like Vanguard, BlackRock, and Temasek Holdings invest in Tencent for financial returns rather than strategic control. However, these investors influence Tencent through shareholder meetings, voting rights, and investment decisions.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Tencent
In 2024, Tencent reported an annual revenue of approximately 660.26 billion CNY ($92.02 billion), reflecting an 8.41% growth compared to the previous year. This growth is attributed to the company’s strong presence in gaming, social media, and fintech sectors.
As of April 2025, the net worth of Tencent is around $590.32 billion.
This growth was driven by several key segments:
- Fintech and Business Services: Contributed RMB 203.76 billion to the total revenue.
- Online Gaming: Generated RMB 179.9 billion, with international gaming revenue reaching a record 30% of the total gaming revenue.
These figures highlight Tencent’s diversified revenue streams and its ability to adapt to evolving market demands.
Below is a table detailing Tencent’s annual revenue over the past ten years:
| Year | Revenue (USD billions) | YoY Growth (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 16.55 | — |
| 2016 | 22.87 | 38.2% |
| 2017 | 35.19 | 53.9% |
| 2018 | 47.25 | 34.3% |
| 2019 | 54.59 | 15.5% |
| 2020 | 69.85 | 28.0% |
| 2021 | 86.82 | 24.3% |
| 2022 | 82.41 | -5.1% |
| 2023 | 86.05 | 4.4% |
| 2024 | 92.02 | 6.9% |
Tencent’s Market Share and Competitors
Tencent Holdings Limited has established itself as a dominant force in China’s technology sector, with significant market shares across various industries, including social media, gaming, fintech, and cloud computing. Its flagship products, such as WeChat and Honor of Kings, have garnered substantial user bases, contributing to the company’s robust market position.
Social Media Market Share
As of December 2023, Tencent’s WeChat (known as Weixin in China) boasted approximately 1.2 billion monthly active users (MAUs) in China. This positions Tencent as a leader in the social media landscape, with a vast user base that engages with its diverse ecosystem of services. Competitors like Alibaba and Baidu reported user bases of approximately 1.15 billion and 1.1 billion, respectively, indicating a highly competitive environment.
Gaming Market Share
In the gaming industry, Tencent has achieved remarkable success with titles like Honor of Kings, which surpassed 100 million daily active users globally by the end of 2023. This success underscores Tencent’s significant influence in the global gaming market.
Fintech and Cloud Computing Market Share
Tencent’s fintech and business services segment emerged as the largest revenue source in 2023, representing 31% of the company’s total revenue and amounting to RMB189.0 billion. This highlights Tencent’s strong presence in the fintech industry. In the cloud computing sector, Tencent experienced a remarkable 30% year-over-year revenue increase, reaching RMB109.0 billion in 2023, reflecting effective strategies in a competitive market.
Major Competitors
Tencent faces competition from several key players across its business segments. Below is an overview of its primary competitors:
Alibaba Group
Alibaba is a formidable competitor, particularly in cloud computing and e-commerce. In the cloud services market, Alibaba Cloud has maintained a leading position, with a significant market share that surpasses Tencent’s offerings. The company’s strategic focus on artificial intelligence and recent partnerships, such as supporting iPhone’s AI services in China, further bolster its competitive edge.
Baidu Inc.
Baidu competes with Tencent in areas like artificial intelligence and cloud computing. Despite facing challenges in maintaining market share, Baidu continues to invest in AI technologies, including the development of its Ernie Bot, positioning itself as a notable player in the tech industry.
ByteDance Ltd.
ByteDance, known for its popular app TikTok (Douyin in China), has rapidly emerged as a significant competitor in the social media and content creation space. By December 2023, ByteDance’s user base exceeded one billion, reflecting its substantial influence and the competitive pressure it places on Tencent’s social media platforms.
NetEase Inc.
NetEase is a prominent competitor in the gaming industry, offering a range of popular online games. The company’s titles have garnered significant user engagement, contributing to its strong position in the gaming market and presenting a challenge to Tencent’s gaming dominance.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
In the cloud computing sector, Huawei competes with Tencent by offering a suite of cloud services. Despite experiencing fluctuations in market share, Huawei remains a key player, continually innovating and expanding its cloud computing solutions.
Companies Owned by Tencent
Tencent’s extensive portfolio includes full ownership and significant investments in various brands and companies:
WeChat (Weixin)
WeChat, known as Weixin in China, is a multifunctional messaging, social media, and mobile payment app developed by Tencent in 2011. It has evolved into a “super app,” offering services such as instant messaging, voice and video calls, social networking via Moments, mobile payments through WeChat Pay, and a platform for third-party services via Mini Programs. With over a billion users, WeChat plays a central role in Tencent’s ecosystem, integrating various services to enhance user engagement and retention.
Launched in 1999, QQ is an instant messaging platform that provides services including online social games, music, shopping, microblogging, and voice chat. It features Qzone, a social networking service where users can create blogs, share photos, and listen to music. As of March 2023, QQ had approximately 597 million monthly active accounts, maintaining its relevance in the Chinese digital landscape.
Tencent Music Entertainment (TME)
Tencent Music Entertainment Group was established in 2016 through the merger of Tencent’s QQ Music division and China Music Corporation. TME operates leading music streaming platforms in China, including QQ Music, Kugou Music, Kuwo Music, and WeSing. These platforms collectively serve over 800 million active users, with approximately 120 million paying subscribers. TME’s services encompass music streaming, online karaoke, and live streaming concerts, solidifying its dominance in China’s online music industry.
Tencent Video (WeTV)
Tencent Video is a prominent Chinese video streaming platform offering a wide range of content, including licensed movies, TV shows, and original productions. Its international version, WeTV, extends its reach to audiences outside China. Tencent Video focuses on original content creation, such as micro-movies and homemade dramas, to differentiate itself in the competitive streaming market. The platform also provides video-on-demand services and supports television broadcasts with various functional enhancements.
Tencent Pictures
Tencent Pictures serves as the film production and distribution arm of Tencent, with a strategic focus on online content and feature film investment. Through its subsidiary, Tencent Penguin Pictures, the company emphasizes original productions and has been involved in notable films, including “Men in Black: International” and the upcoming “Top Gun” sequel. This involvement underscores Tencent’s commitment to expanding its footprint in the entertainment industry.
Riot Games
Riot Games, the developer behind the globally acclaimed game “League of Legends,” became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Tencent in 2015. The acquisition allowed Tencent to strengthen its position in the global gaming market, leveraging Riot Games’ expertise in developing and operating successful esports titles.
Supercell
Tencent acquired a majority stake of approximately 70.03% in Supercell, the Finnish mobile game developer known for hits like “Clash of Clans” and “Brawl Stars.” Supercell operates independently, maintaining its unique company culture and development approach, while benefiting from Tencent’s extensive resources and market reach.
Sumo Digital
Tencent holds a 100% stake in Sumo Digital, a British video game developer recognized for its work on titles such as “Sackboy: A Big Adventure” and contributions to the “Forza” series. The acquisition aligns with Tencent’s strategy to expand its presence in the global gaming industry by partnering with established developers.
Visual Arts
Tencent owns 100% of Visual Arts, a Japanese company specializing in the production of visual novels and related media. This acquisition reflects Tencent’s interest in diversifying its content offerings and tapping into the Japanese entertainment market.
Shift Up
Tencent holds a 35% stake in Shift Up, a South Korean game development studio known for creating titles like “Destiny Child.” This investment demonstrates Tencent’s commitment to collaborating with international developers to broaden its gaming portfolio.
KakaoTalk
Tencent has an approximate 13.84% stake in KakaoTalk, a South Korean messaging app that offers services such as free calls and text messaging. The investment allows Tencent to gain insights into the South Korean market and explore potential synergies between the platforms.
Snap Inc.
Tencent holds a 14.96% stake in Snap Inc., the parent company of Snapchat. This strategic investment enables Tencent to participate in the global social media landscape and explore opportunities for collaboration in content and technology.
Conclusion
Tencent’s ownership structure is a blend of significant institutional investment and executive leadership holdings. With Prosus as the largest shareholder and Ma Huateng at the helm, the company maintains a balance between external investment influence and internal strategic control.
Tencent’s financial strength, extensive market presence, and diverse portfolio make it one of the most powerful tech conglomerates in the world. Despite increasing regulatory scrutiny in China and competition from global tech giants, Tencent continues to expand through strategic investments and innovation. Its influence spans multiple industries, from gaming and social media to fintech and artificial intelligence.
As it evolves, Tencent remains a dominant force in shaping the digital landscape both in China and internationally.
FAQs
Who is the largest shareholder of Tencent?
The largest shareholder of Tencent is Prosus, a subsidiary of Naspers, holding approximately 29% of the company’s shares. This stake originated from an early investment by Naspers, which has since played a crucial role in Tencent’s growth.
Does the Chinese government own Tencent?
Tencent is a publicly traded company, but like all major Chinese tech firms, it operates under regulatory oversight from the Chinese government. While the government does not directly own Tencent, it can influence the company through regulations, policies, and partnerships with state-affiliated firms.
How much of Tencent does Ma Huateng own?
Ma Huateng, also known as Pony Ma, owns approximately 8% of Tencent. As the co-founder and CEO, he remains one of the most influential figures in the company’s decision-making process.
What is Tencent’s biggest source of revenue?
Tencent generates most of its revenue from online gaming, followed by social media, fintech, and cloud computing. The company’s gaming division includes titles like “Honor of Kings,” “PUBG Mobile,” and investments in companies like Riot Games and Epic Games.
What companies does Tencent own?
Tencent owns or holds major stakes in several companies, including Riot Games, Supercell, Epic Games, Tencent Music Entertainment, WeChat, and QQ. It also has investments in global companies like Tesla, Snap Inc., and Spotify.
How does Tencent compare to Alibaba?
Tencent and Alibaba are two of China’s largest tech giants but operate in different primary markets. Tencent dominates social media, gaming, and fintech, while Alibaba is a leader in e-commerce and cloud computing. They compete in areas like digital payments, cloud services, and artificial intelligence.
What is Tencent’s market value?
Tencent’s market value fluctuates with stock performance, but as of 2025, its market capitalization is estimated to be around $590 billion. This makes it one of the most valuable technology companies globally.
Does Tencent own TikTok?
No, Tencent does not own TikTok. TikTok is owned by ByteDance, a Chinese technology company. Tencent and ByteDance are competitors in the social media and content creation space, with ByteDance operating TikTok and Tencent owning WeChat and QQ.
Does Tencent own 100% of Riot?
Yes, Tencent owns 100% of Riot Games. While Tencent has full control, Riot Games operates independently, maintaining its distinct development culture.
Does Tencent own PUBG?
Tencent does not own PUBG outright, but it has a significant stake in the game’s development. Tencent is responsible for publishing PUBG Mobile in China and is involved in the distribution and operation of the game in various regions.
Is Spotify owned by Tencent?
No, Spotify is not owned by Tencent. Spotify is an independent company headquartered in Sweden. However, Tencent has a minority stake in Spotify, which was part of a strategic investment in the music streaming service.
Is Call of Duty owned by Tencent?
No, Call of Duty is not owned by Tencent. The franchise is owned by Activision Blizzard. Tencent, however, holds a significant stake in Activision Blizzard and has been involved in distributing the mobile version of Call of Duty in some regions.
Who runs Tencent?
Tencent is run by its founder and chairman, Pony Ma Huateng. Pony Ma has led the company since its inception in 1998 and has been instrumental in its growth into one of the world’s largest tech companies.

