Volkswagen is one of the world’s largest automobile manufacturers. Many people wonder who owns Volkswagen and how the company is structured. In this article, we will explore its history, ownership, leadership, financials, brands, and more.
History of Volkswagen
Volkswagen was founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi government. The goal was to create an affordable car for the average German citizen.
The company introduced the “Volkswagen Beetle,” which later became one of the best-selling cars worldwide.
After World War II, Volkswagen was rebuilt and grew rapidly. It became a symbol of Germany’s post-war economic recovery.
Over the decades, Volkswagen expanded by acquiring many other automotive brands and strengthening its global presence.
Who Owns Volkswagen: Top Shareholders
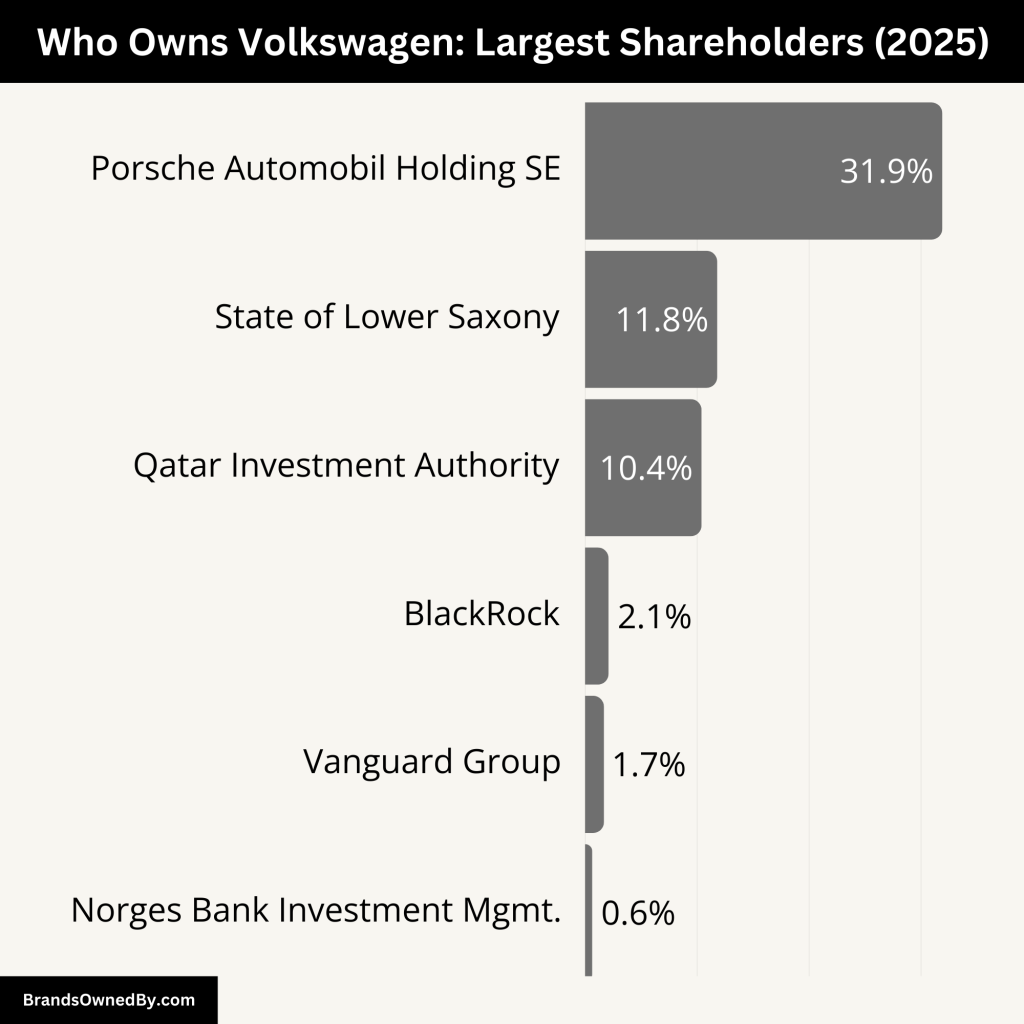
Volkswagen AG is a publicly traded company. However, it is mainly controlled by a few large shareholders. The largest stake is held by the Porsche-Piëch family through Porsche Automobil Holding SE.
The German state of Lower Saxony also owns a significant portion. Another key investor is Qatar Investment Authority. Although shares are traded on public exchanges, real control stays with these major shareholders.
Here’s a list of the top shareholders of Volkswagen:
| Shareholder | Voting Rights (%) | Equity Ownership (%) | Role and Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porsche Automobil Holding SE | 53.3% | 31.9% | Controlled by Porsche-Piëch family, has majority control over board and strategy. |
| State of Lower Saxony | 20.0% | 11.8% | German state with veto power via the Volkswagen Law; holds two board seats. |
| Qatar Investment Authority | 17.0% | 10.4% | Strategic investor from the Middle East; holds two Supervisory Board seats. |
| BlackRock, Inc. | Minimal | 2.1% | Institutional investor via ETFs; minimal influence on governance. |
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | Minimal | 1.69% | Passive investor with limited voting; supports governance standards. |
| Norges Bank Investment Mgmt. | Minimal | 0.64% | Focused on ESG and long-term value; no direct board involvement. |
| Free Float / Public Investors | Varies | 9.7% | Includes retail investors and funds; limited control but key to market liquidity. |
Porsche Automobil Holding SE
Porsche Automobil Holding SE is the largest and most influential shareholder in Volkswagen AG. It is owned and controlled by the Porsche and Piëch families. As of 2025, Porsche SE holds 53.3% of Volkswagen’s voting rights and 31.9% of the total share capital.
Despite not owning the majority of Volkswagen’s equity, Porsche SE controls over half of the voting rights. This control gives them the power to influence major strategic decisions, including executive appointments and mergers. Their long-term vision strongly shapes Volkswagen’s corporate direction.
State of Lower Saxony
The state of Lower Saxony, a region in Germany where Volkswagen has historical and operational roots, holds 20.0% of voting rights and 11.8% of equity capital.
This is due to the “Volkswagen Law,” a special German law that allows Lower Saxony to wield outsized influence despite its minority stake. Under this law, Lower Saxony retains veto power over significant corporate decisions, such as mergers, capital increases, or changes in company structure. The state also occupies two seats on Volkswagen’s Supervisory Board.
Qatar Investment Authority (QIA)
Qatar Holding LLC, a subsidiary of the Qatar Investment Authority, owns 17.0% of voting rights and 10.4% of share capital.
QIA became a shareholder in 2009 and has since been considered a strategic long-term investor. It holds two seats on Volkswagen’s Supervisory Board. While Qatar does not participate in day-to-day management, its financial backing provides stability and confidence for global expansion and innovation.
BlackRock, Inc.
BlackRock is the largest asset manager in the world and a notable institutional investor in Volkswagen. As of 2025, it holds approximately 2.1% of Volkswagen’s share capital.
BlackRock’s stake is part of its passive investment portfolios and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). It does not exert significant influence over Volkswagen’s management but participates in general shareholder voting.
The Vanguard Group, Inc.
Vanguard holds around 1.69% of Volkswagen’s shares. Like BlackRock, Vanguard’s involvement is through passive index funds.
Its voting power is limited, and it has no board representation. However, Vanguard typically promotes corporate governance standards and may occasionally vote on resolutions related to sustainability or shareholder rights.
Norges Bank Investment Management
Norges Bank, which manages Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, owns about 0.64% of Volkswagen AG.
Norges is one of the world’s most respected institutional investors, known for its focus on transparency and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues. Though small, its stake adds to Volkswagen’s credibility in ESG-conscious markets.
Free Float and Public Shareholders
About 9.7% of Volkswagen’s ordinary shares are in free float. These are held by a mix of retail investors, mutual funds, private individuals, and hedge funds.
These shareholders provide liquidity in the public markets. While they do not influence corporate governance directly, their buying and selling behavior impacts Volkswagen’s share price and public perception.
Who is the CEO of Volkswagen?
As of 2025, Oliver Blume serves as the CEO of Volkswagen AG, steering the company through a transformative era marked by electrification, digitalization, and global restructuring.
Oliver Blume: CEO of Volkswagen AG
Appointed on September 1, 2022, Oliver Blume assumed the role of Chairman of the Board of Management at Volkswagen AG, succeeding Herbert Diess. Blume concurrently holds the position of CEO at Porsche AG, a dual role he maintains to oversee ongoing restructuring efforts within both companies.
Blume’s career with the Volkswagen Group began in 1994, encompassing leadership roles at Audi, SEAT, Volkswagen, and Porsche. His tenure at Porsche, starting in 2015, is noted for significant growth and innovation.
Strategic Initiatives Under Blume
Under Blume’s leadership, Volkswagen has embarked on several strategic initiatives:
- Electrification and Sustainability: Continuing the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and sustainable mobility solutions.
- Cost-Cutting Measures: Implementing a €10 billion cost-reduction plan to enhance financial stability amid competitive pressures.
- Global Restructuring: Adjusting operations in key markets like China to align with local demands and reduce excess capacity.
- Labor Relations: Engaging with labor unions to navigate workforce adjustments while aiming to maintain cooperative relationships.
Governance Structure of Volkswagen AG
Volkswagen AG’s governance is characterized by a dual-board system:
- Supervisory Board: Oversees the Executive Board and includes representatives from major shareholders and employee organizations. Hans Dieter Pötsch serves as the Chairman of the Supervisory Board.
- Executive Board: Responsible for day-to-day management, led by CEO Oliver Blume.
Major shareholders exert significant influence over governance:
- Qatar Investment Authority: Owns 17.0% of voting rights, contributing to strategic direction through board representation.
- Porsche Automobil Holding SE: Holds 53.3% of voting rights, enabling substantial control over strategic decisions.
- State of Lower Saxony: Possesses 20.0% of voting rights, with legal provisions granting veto power over key resolutions.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Volkswagen
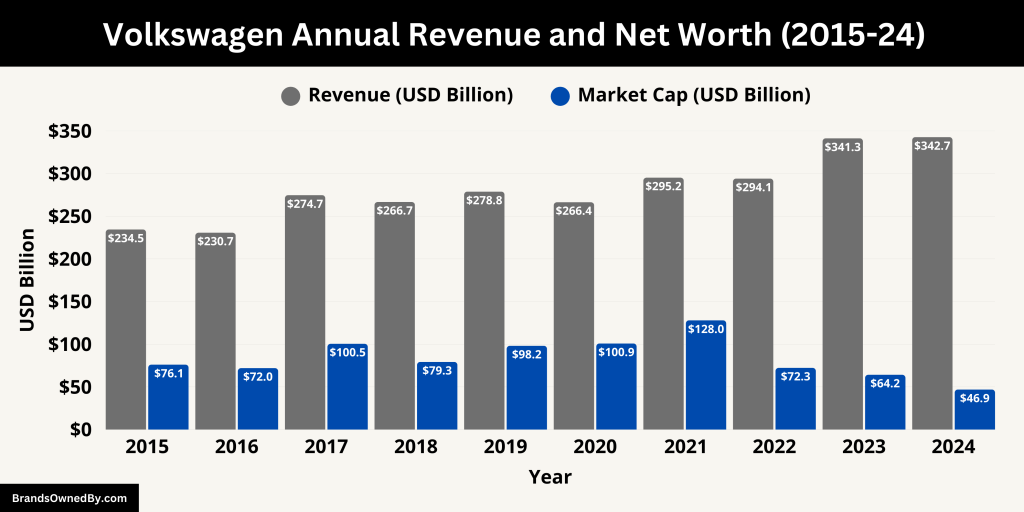
In fiscal year 2024, Volkswagen AG reported total revenue of €324.7 billion, a modest increase from €322.3 billion in 2023. This growth was primarily driven by the Financial Services division, while the core automotive business experienced a slight decline due to reduced vehicle volumes.
The company’s operating profit decreased by 15.4% to €19.1 billion, down from €22.5 billion in 2023. This decline was attributed to a significant rise in fixed costs, including extraordinary expenses of €2.6 billion, mainly for restructuring efforts.
Net income for 2024 fell by 30.6% to €12.39 billion, impacted by higher costs and declining sales in key markets such as China.
Vehicle sales totaled 9.0 million units, a 3.5% decrease from 9.4 million units in 2023. The company faced challenges in China, where competition from local manufacturers intensified, though growth in South America provided some offset.
2025 Outlook and Net Worth
Volkswagen anticipates a revenue increase of up to 5% in 2025, despite ongoing economic uncertainties and industry challenges. The company projects an operating margin between 5.5% and 6.5%, reflecting efforts to improve efficiency and profitability.
As of April 2025, Volkswagen AG’s market capitalization, a common measure of net worth, is estimated at $54.39 billion. This valuation reflects investor sentiment amid the company’s strategic shifts and market dynamics.
Volkswagen continues to invest in electrification, digitalization, and restructuring to navigate the evolving automotive landscape. The company’s commitment to innovation and adaptation positions it to address future challenges and opportunities.
Here’s an overview of the annual revenue and net worth of Volkswagen for the last 10 years:
| Year | Revenue (USD bn) | Market Cap (USD bn) |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 234.5 | 76.13 |
| 2016 | 230.7 | 71.97 |
| 2017 | 274.7 | 100.48 |
| 2018 | 266.7 | 79.25 |
| 2019 | 278.8 | 98.16 |
| 2020 | 266.4 | 100.86 |
| 2021 | 295.2 | 128.00 |
| 2022 | 294.1 | 72.28 |
| 2023 | 341.3 | 64.19 |
| 2024 | 342.7 | 46.91 |
Brands and Companies Owned by Volkswagen
As of 2025, the Volkswagen Group encompasses a diverse portfolio of brands and subsidiaries, each catering to specific market segments and contributing to the company’s global presence.
Below is a detailed overview of these entities:
| Company/Brand | Ownership Stake by Volkswagen Group | Ownership Details |
|---|---|---|
| Volkswagen Passenger Cars | 100% | Volkswagen Passenger Cars is the core brand of the group. It offers a broad range of vehicles, from compact cars to SUVs, and plays a central role in Volkswagen’s global strategy. It is the most significant volume driver and leads the group’s shift toward electric mobility with models like the ID.3 and ID.4. |
| Audi | 99.64% | Audi is one of the group’s premium brands, part of the Progressive Brand Group. It is a key player in Volkswagen’s efforts to compete in the luxury vehicle market. Audi contributes to the group with innovative technologies, including autonomous driving and electric vehicles, such as the e-tron series. |
| Porsche | 75% (via Porsche Holding SE) | Porsche is a high-performance luxury brand under the Progressive Brand Group. Although it operates independently, it is majority-controlled by Volkswagen through Porsche Holding SE. Porsche contributes significantly to Volkswagen’s high-margin luxury vehicle segment and its shift toward electric mobility, exemplified by the Taycan EV. |
| Škoda | 100% | Škoda is a value-oriented brand in the Core Brand Group of Volkswagen. It is popular in emerging markets such as Eastern Europe and India. Škoda produces affordable cars and electric vehicles, such as the Enyaq iV, and utilizes Volkswagen’s platforms and technologies. |
| SEAT and CUPRA | 100% (SEAT), 100% (CUPRA) | SEAT operates in the small car and urban mobility segments. CUPRA, a performance-focused sub-brand of SEAT, has emerged as a standalone brand within Volkswagen. CUPRA offers sporty, stylish models like the Formentor, while SEAT continues to target urban and younger demographics. Both are crucial to Volkswagen’s European strategy. |
| Bentley | 100% | Bentley is an ultra-luxury brand under the Progressive Brand Group. It contributes to Volkswagen’s portfolio of high-end vehicles. Bentley is transitioning to electric vehicles, ensuring its continued relevance as the luxury market shifts toward sustainability. |
| Lamborghini | 100% | Lamborghini, a globally recognized luxury supercar brand, operates within the Progressive Brand Group. Known for its performance and exclusivity, it shares technological resources with Audi, particularly in terms of powertrains and AWD systems. Lamborghini’s transition to hybrid and electric vehicles is a key development in the brand’s future. |
| Ducati | 100% | Ducati is an iconic motorcycle manufacturer owned by Audi (Volkswagen Group). Known for high-performance motorcycles, Ducati adds a unique element to Volkswagen’s portfolio of high-performance products. It benefits from collaboration with other brands, particularly in terms of design and technology. |
| Bugatti Rimac | 45% (Volkswagen Group via Porsche) | Bugatti Rimac is a joint venture between Volkswagen (via Porsche) and Rimac. The venture is focused on producing hyper-luxury electric vehicles, including the Bugatti Chiron and Rimac Nevera. It combines Bugatti’s luxury expertise with Rimac’s cutting-edge electric technologies. |
| Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles | 100% | Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles focuses on light trucks, minibuses, and vans, contributing to the group’s efforts in providing mobility solutions for businesses and logistics. This brand plays a critical role in Europe and other markets for commercial transportation. |
| TRATON SE | 90% (Direct ownership by VW) | TRATON is the Volkswagen Group’s commercial vehicle division, encompassing brands like MAN, Scania, and Navistar. It operates independently but remains an important part of the group, focusing on heavy-duty vehicles, trucks, and buses. TRATON plays a crucial role in Volkswagen’s strategy for future transportation and the electrification of the freight sector. |
| Scout Motors | 100% | Scout Motors is a new electric vehicle brand, owned by Volkswagen, aimed at the American market. It will produce electric trucks and SUVs, providing Volkswagen with a foothold in the competitive U.S. truck market. Scout is integral to Volkswagen’s North American strategy for EVs. |
| PowerCo | 100% | PowerCo is Volkswagen’s subsidiary focused on developing and producing batteries for electric vehicles. As part of Volkswagen’s transition to electric mobility, PowerCo will play a key role in securing the battery supply chain for the group, particularly through its gigafactory network. |
| MOIA | 100% | MOIA is Volkswagen’s urban mobility services company, focusing on ride-sharing and electric shuttles. It operates in several German cities, offering a more sustainable and convenient transport option, contributing to the group’s efforts in modern mobility solutions and reducing urban traffic congestion. |
| Italdesign Giugiaro | 100% | Italdesign is an Italian design and engineering firm that collaborates with Volkswagen Group on vehicle designs and concept prototypes. It helps in shaping the future of Volkswagen’s model lineup, especially in terms of aesthetics and innovative vehicle designs. |
| Diconium | 100% | Diconium is a digital services company focused on supporting Volkswagen’s digital transformation. It works on developing e-commerce platforms, connected car services, and improving customer experiences across the group’s various brands. |
| IAV | 100% | IAV is an engineering partner that assists Volkswagen with advanced technology development, including electric powertrains, autonomous driving systems, and digital vehicle systems. It is an integral part of Volkswagen’s research and development efforts for the future of mobility. |
| Joint Ventures in China (FAW-Volkswagen and SAIC Volkswagen) | 50% (each) | These joint ventures with FAW Group and SAIC Motor Corporation allow Volkswagen to cater to the massive Chinese automotive market. FAW-Volkswagen focuses on Volkswagen and Audi models, while SAIC Volkswagen focuses on Škoda and Volkswagen vehicles. These partnerships help Volkswagen adapt to local consumer needs and regulations. |
Volkswagen Passenger Cars
Volkswagen Passenger Cars is the core brand of the Volkswagen Group. It represents the company’s largest volume in terms of global sales. Positioned as the heart of the group, it offers a full lineup, from entry-level city cars to large family SUVs. It also spearheads the group’s electric revolution with models like the ID.3, ID.4, and ID.7. Volkswagen Passenger Cars is managed directly under the Core Brand Group to ensure economies of scale and brand cohesion across multiple markets.
Audi
Audi is part of Volkswagen’s Progressive Brand Group, focused on the premium automotive segment. It operates independently but reports directly to the Volkswagen Group. Audi not only sells luxury sedans and SUVs but also leads the group’s innovation efforts, especially in autonomous driving, connectivity, and electrification. It is a strategic pillar in competing against BMW and Mercedes-Benz. Audi is also responsible for subsidiaries like Audi Sport GmbH and owns Ducati and Lamborghini under its management umbrella.
Porsche
Porsche AG remains a crown jewel for Volkswagen Group, although it now operates separately following its partial IPO in 2022. However, Porsche Holding SE, which is controlled by the Porsche and Piëch families, is Volkswagen’s majority shareholder. Porsche contributes heavily to Volkswagen’s profitability, generating some of the highest margins across all brands. Porsche’s emphasis on high-performance and luxury electric vehicles like the Taycan and Macan EV is critical for Volkswagen’s premium electrification strategy.
Škoda
Škoda Auto is managed within Volkswagen’s Core Brand Group. It plays a crucial role in expanding Volkswagen’s presence in emerging markets like Eastern Europe, India, and Southeast Asia. Škoda benefits from Volkswagen’s platforms and technologies but tailors its models to be more affordable and durable, making them ideal for cost-sensitive regions. Volkswagen uses Škoda to increase overall global volumes while protecting its own brand’s premium positioning in Europe.
SEAT and CUPRA
SEAT, headquartered in Spain, targets younger buyers with sporty, stylish, and affordable cars. However, Volkswagen has repositioned the SEAT brand towards urban mobility, while pushing CUPRA as a stand-alone performance brand. CUPRA models are built on Volkswagen Group platforms (like MQB and MEB for EVs) but tuned for sportiness. Volkswagen Group uses SEAT/CUPRA to maintain a strong foothold in Southern Europe and to appeal to youth-oriented markets.
Bentley
Bentley Motors, based in the UK, is part of Volkswagen’s Progressive Brand Group. Bentley is positioned as an ultra-luxury brand, competing with Rolls-Royce and Aston Martin. It shares technology with Audi and Porsche, especially in platforms and drivetrain technologies. For example, the Bentley Bentayga shares its underpinnings with the Audi Q7 and Porsche Cayenne. Bentley’s transition to full electric by 2030 aligns with Volkswagen Group’s decarbonization strategy.
Lamborghini
Lamborghini is managed under Audi’s supervision within the Progressive Brand Group. It leverages Audi’s engineering resources while maintaining its Italian exotic brand identity. Its supercars, such as the Aventador and Huracán, share elements like AWD systems and V10/V12 engines developed with Audi. Lamborghini’s upcoming hybrid and electric models will use Volkswagen Group’s platforms, making it vital for expanding the Group’s high-performance EV capabilities.
Ducati
Ducati, the famed motorcycle manufacturer, is owned by Audi, and thus indirectly part of Volkswagen AG. Ducati strengthens Volkswagen’s portfolio in two-wheeled mobility. It is considered a high-margin niche brand, contributing modestly to revenue but greatly enhancing brand prestige. Ducati technology increasingly aligns with Volkswagen’s sustainability goals, with developments in electric motorcycles underway.
Bugatti Rimac
Volkswagen Group, through Porsche AG, owns a 45% stake in the Bugatti Rimac joint venture. Bugatti, formerly a wholly owned Volkswagen brand, was spun into this partnership with Rimac, a Croatian EV hypercar manufacturer. This strategic move enables Volkswagen to remain invested in hyper-luxury and hyper-performance vehicles while sharing costs and R&D burdens with Rimac’s cutting-edge EV technology.
Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles
This brand is responsible for light commercial vans, minibuses, and pickups. It shares many platforms and technologies with Volkswagen Passenger Cars and occasionally Ford (through a recent global alliance). Vehicles like the Transporter, Caddy, and Amarok are essential for Volkswagen’s light logistics and small business clientele, especially in Europe.
TRATON SE
TRATON is Volkswagen Group’s heavy-duty vehicle division, encompassing brands like MAN, Scania, and Navistar. It operates independently but is majority-owned by Volkswagen AG. TRATON focuses on trucks and buses globally and is critical for Volkswagen’s goal to electrify heavy transportation. TRATON is a major driver of innovation in hydrogen trucks and autonomous freight transport.
Scout Motors
Volkswagen revived the historic American Scout brand to enter the U.S. off-road EV market. Scout Motors is wholly owned by Volkswagen AG and will manufacture rugged electric pickups and SUVs. This move diversifies Volkswagen’s U.S. strategy, which historically relied mainly on sedans and crossovers, giving it access to America’s lucrative truck market.
PowerCo
PowerCo SE is a wholly owned subsidiary of Volkswagen Group, responsible for battery cell production and energy solutions. It was created to ensure a steady, vertically integrated supply of batteries for the Group’s EV ambitions. PowerCo is building multiple gigafactories across Europe and North America, reducing reliance on external suppliers like CATL or LG Chem.
MOIA
MOIA is Volkswagen’s standalone urban mobility company. It focuses on ride-sharing and future transport services. It operates mainly in German cities, offering electric shuttle services, and is part of Volkswagen’s broader effort to transition from a traditional automaker to a mobility services provider.
Italdesign Giugiaro
Italdesign, based in Italy, offers design, prototyping, and engineering services. While it operates independently, it is owned by Audi and contributes significantly to Volkswagen’s concept car and EV prototype designs. Italdesign also supports third-party clients, enhancing Volkswagen’s overall brand influence in the global automotive design landscape.
Diconium
Diconium, majority-owned by Volkswagen, is pivotal for the Group’s digital transformation. It helps create digital ecosystems for Volkswagen’s customers, like online sales platforms, connected car features, and digital customer experiences.
IAV
Volkswagen is a significant shareholder in IAV, one of Germany’s leading automotive engineering firms. IAV supports Volkswagen Group with advanced technology development, including autonomous driving systems, electric powertrains, and digital architecture for vehicles.
Joint Ventures in China (FAW-Volkswagen and SAIC Volkswagen)
Volkswagen operates two massive joint ventures in China:
- FAW-Volkswagen: Partnership with First Automotive Works (FAW) for both VW and Audi brands.
- SAIC Volkswagen: Partnership with Shanghai Automotive Industry Corporation (SAIC) focusing on Volkswagen and Skoda brands.
These ventures are critical because China is Volkswagen’s largest single market, accounting for over 40% of its global sales. Volkswagen uses these partnerships to develop China-specific vehicles, including affordable EVs under new sub-brands like ID. family for China.
Conclusion
Volkswagen is a massive automotive empire with a unique ownership structure. If you ever wondered who owns Volkswagen, it is clear that the Porsche-Piëch family, Lower Saxony, and Qatar Investment Authority are the main power holders. Public shareholders play a smaller role. Through strategic leadership and an impressive brand portfolio, Volkswagen continues to shape the global automotive industry.
FAQs
Who owns the most shares of Volkswagen?
The Porsche-Piëch family, through Porsche Automobil Holding SE, owns the largest portion with over 53% of voting rights.
Is Volkswagen a publicly traded company?
Yes, Volkswagen is publicly traded. Its shares are listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange.
How much of Volkswagen does Qatar own?
Qatar Investment Authority owns about 10.5% of Volkswagen’s share capital.
Who controls Volkswagen’s board?
The board is controlled by major shareholders, primarily the Porsche-Piëch family and the state of Lower Saxony, through their voting power and legal rights.
Who is VW owned by?
Volkswagen is primarily owned by Porsche Automobil Holding SE (which holds a majority of voting rights) and the State of Lower Saxony in Germany. Other shareholders include Qatar Investment Authority and institutional investors like BlackRock and Vanguard.
Is Porsche 100% owned by VW?
No, Porsche is not 100% owned by Volkswagen. However, Volkswagen owns a majority stake in Porsche Automobil Holding SE (about 53.3% of voting rights), which controls the Porsche brand.
Do the Chinese own Volkswagen?
No, China does not own Volkswagen. However, Volkswagen has a significant presence in China, where it operates joint ventures with local companies. This includes partnerships with SAIC Motor and FAW Group for manufacturing and selling cars in the Chinese market.
Is Bugatti owned by Volkswagen?
Yes, Bugatti was owned by Volkswagen Group, but in 2021, the brand was sold to the Rimac Group, a Croatian electric vehicle manufacturer, marking the end of its ownership under Volkswagen.
Is Lamborghini owned by VW?
Yes, Lamborghini is owned by Volkswagen through its subsidiary Audi AG. Audi has had control of Lamborghini since 1998.
Is VW a luxury brand?
Volkswagen itself is generally considered a mass-market brand rather than a luxury one. However, it does have a luxury division in Audi, which produces high-end vehicles. Volkswagen Group also owns other luxury brands like Porsche and Bentley.
Is Volkswagen still German?
Yes, Volkswagen is still a German company, headquartered in Wolfsburg, Germany. It remains one of the largest automobile manufacturers globally.
Which country is the owner of Volkswagen?
Volkswagen is a German company, and its largest shareholders are based in Germany, including Porsche Automobil Holding SE and the State of Lower Saxony.
Did Volkswagen buy Bentley?
Yes, Volkswagen acquired Bentley in 1998. It is now a part of Volkswagen’s luxury brand portfolio.
Did VW buy Audi?
Yes, Volkswagen owns Audi. Volkswagen acquired Audi in 1964 through its subsidiary Auto Union.
Does Volkswagen own Rolls-Royce?
No, Volkswagen does not own Rolls-Royce. Rolls-Royce is owned by the BMW Group, not Volkswagen.
What 12 companies are owned by Volkswagen?
Some of the major companies owned by Volkswagen include:
- Audi
- Porsche
- Bentley
- Bugatti (now part of Rimac Group)
- Lamborghini
- SEAT
- Skoda
- MAN
- Scania
- Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles
- Ducati (motorcycles, owned through Audi)
- Tata Motors (minor stake)
Does Porsche own VW?
No, Porsche does not own Volkswagen. However, Porsche Automobil Holding SE (which is controlled by the Porsche and Piëch families) owns a majority stake in Volkswagen and has a significant influence over its strategic decisions.
Does VW own Ferrari?
No, Volkswagen does not own Ferrari. Ferrari is an independent company, with its majority ownership held by Exor, the holding company of the Agnelli family (owners of Fiat).
Who is the biggest owner of Volkswagen?
The largest shareholder of Volkswagen is Porsche Automobil Holding SE, which holds 53.3% of the voting rights in the company.
Is BMW owned by Volkswagen?
No, BMW is not owned by Volkswagen. BMW is an independent German automobile manufacturer and competes with Volkswagen in the luxury vehicle market.
How many companies does Volkswagen own?
Volkswagen owns several companies across various automotive sectors. Some of the key brands and subsidiaries include Audi, Porsche, Bentley, Lamborghini, SEAT, Skoda, MAN, and Scania, among others. The total number of subsidiaries is difficult to pin down precisely but likely exceeds 12 in terms of major brands and manufacturing operations.
Which company owns Volkswagen?
No one company owns Volkswagen outright. It is owned by a combination of major shareholders, primarily Porsche Automobil Holding SE (majority shareholder), the State of Lower Saxony, Qatar Investment Authority, and institutional investors.
Who bought Volkswagen?
Volkswagen was founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front and was not bought by another company. The ownership has evolved over time with various changes in shareholding, including the acquisition of Porsche shares and state involvement.
Who makes Volkswagen cars?
Volkswagen cars are manufactured by the Volkswagen Group, which is a major automotive conglomerate. This group also produces vehicles under various other brand names, including Audi, Porsche, and SEAT.
Who makes VW cars?
Volkswagen cars are made by the Volkswagen Group, which produces vehicles under the Volkswagen nameplate, along with several other brands.
Who is the founder of Volkswagen?
The founder of Volkswagen is Ferdinand Porsche, who designed the Volkswagen Beetle under the order of Adolf Hitler in the 1930s as part of a project to create an affordable “people’s car” for Germany. The company was officially founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front.

