Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly known as SpaceX, has revolutionized the aerospace industry since its inception. Founded by Elon Musk in 2002, the company aims to reduce space transportation costs and enable the colonization of Mars. A frequent question arises: who owns SpaceX?
Understanding its ownership structure provides insight into the company’s strategic direction and decision-making processes.
SpaceX History
Elon Musk established SpaceX in 2002 with the vision of making space travel more affordable and paving the way for Mars colonization. The company’s early years focused on developing the Falcon 1 rocket, which became the first privately developed liquid-fueled rocket to reach orbit in 2008.
This success was followed by the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets, both designed for reusability to significantly cut costs. SpaceX also developed the Dragon spacecraft, which transports cargo—and later, crew—to the International Space Station (ISS).
In 2020, SpaceX made history by launching NASA astronauts to the ISS, marking the first commercial company to do so.
Who Owns SpaceX?
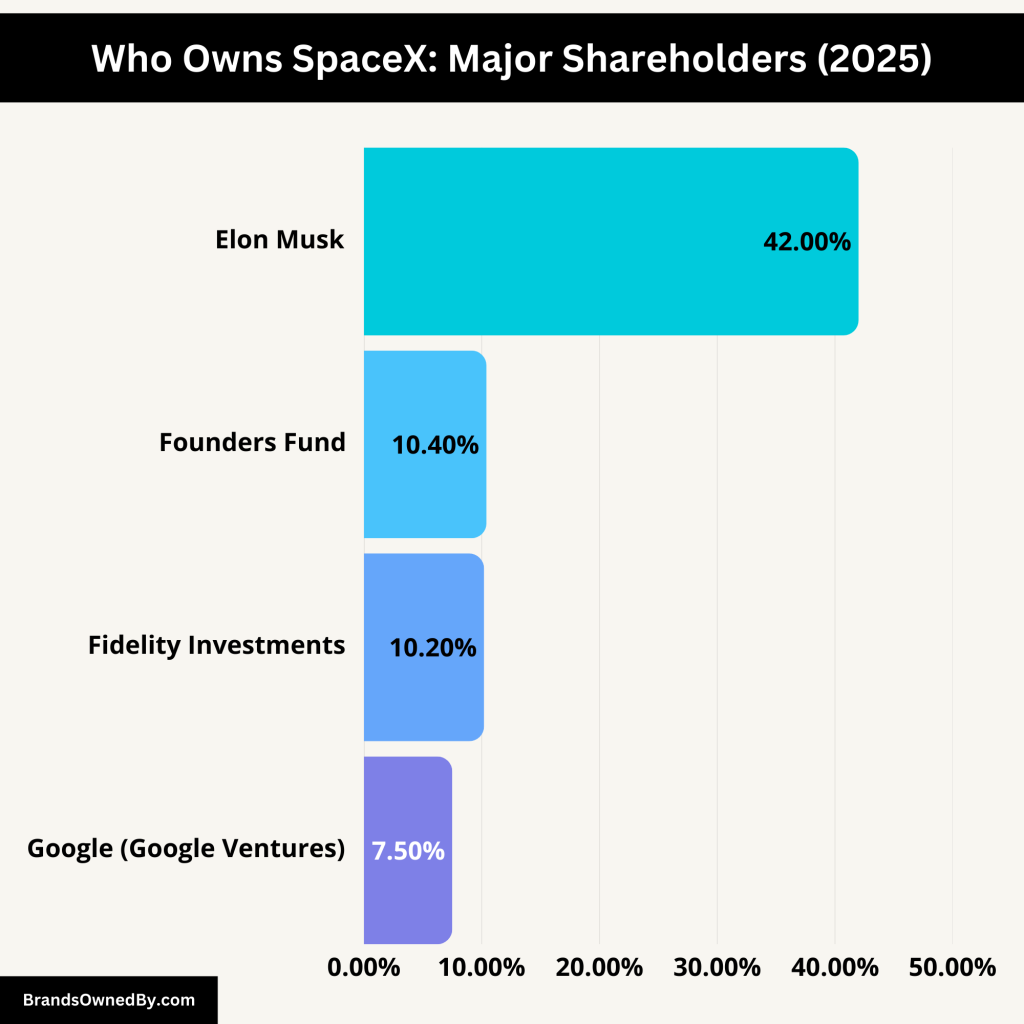
SpaceX remains a privately held company, with ownership divided among its founder, key investors, and employees. Elon Musk is the largest shareholder, holding approximately 42% of the company’s stock. This significant stake allows him substantial influence over the company’s strategic decisions.
SpaceX Shareholders
Several major stakeholders contribute to SpaceX’s ownership structure:
| Shareholder | Approximate Ownership Percentage | Notes |
|---|
| Elon Musk | 42% | Founder and CEO of SpaceX. |
| Founders Fund | 10.4% | Venture capital firm led by Peter Thiel. |
| Fidelity Investments | 10.2% | Financial services corporation. |
| Google (Google Ventures) | 7.5% | Invested $900 million in 2015. |
| Baillie Gifford | Not publicly disclosed | UK-based investment management firm. |
| Sequoia Capital | Not publicly disclosed | American venture capital firm. |
| Valor Equity Partners | Not publicly disclosed | Private equity firm. |
| Draper Fisher Jurvetson | Not publicly disclosed | Venture capital firm. |
| Capricorn Investment Group | Not publicly disclosed | Investment firm. |
Elon Musk
Elon Musk is the founder, CEO, and largest shareholder of SpaceX, holding approximately 42% of the company’s stock. His ownership provides him with significant control over the company’s direction, innovations, and decision-making.
Musk’s vision is to make life multi-planetary and his leadership has driven SpaceX’s development of reusable rockets, the Starship program, and the Starlink satellite constellation.
His role extends beyond ownership, as he actively oversees technological advancements, partnerships, and funding strategies that fuel SpaceX’s long-term ambitions.
Founders Fund
Founders Fund is a venture capital firm co-founded by Peter Thiel. It holds about 10.4% of SpaceX, making it one of the largest external investors. The fund is known for backing transformative technologies and disruptive companies, making SpaceX a fitting addition to its portfolio.
Founders Fund’s investment supports SpaceX’s ambitious projects, including satellite internet services, deep-space exploration, and commercial spaceflight initiatives. Their continued support indicates long-term confidence in the company’s growth and sustainability.
Fidelity Investments
Fidelity Investments is a major institutional investor in SpaceX, holding approximately 10.2% of the company. Fidelity is one of the largest asset management firms globally, and its stake in SpaceX signifies strong institutional backing.
This investment plays a crucial role in providing SpaceX with financial stability and funding for research, development, and expansion. Fidelity’s involvement suggests confidence in SpaceX’s long-term profitability, especially in projects like Starlink and crewed space missions.
Google (Alphabet Inc.)
In 2015, Google (now Alphabet Inc.) invested in SpaceX, acquiring a 7.2% stake in the company. This investment aligns with Google’s interest in expanding global internet access through satellite technology. SpaceX’s Starlink project, which aims to provide worldwide high-speed internet coverage, complements Google’s efforts to connect underserved regions.
While Google does not control SpaceX’s operations, its financial backing and technological partnerships contribute to the development and deployment of satellite internet services.
Other Private Investors and Employees
Aside from major institutional investors, SpaceX’s ownership includes smaller private investors and employees who hold equity in the company. SpaceX offers stock options to its employees, allowing them to share in the company’s success.
This approach helps retain top talent and aligns employees’ interests with the company’s long-term goals. As SpaceX remains privately held, these investors play a role in maintaining its independence from public market pressures.
Who Controls SpaceX?
Control of SpaceX primarily rests with Elon Musk, given his substantial ownership and role as CEO. His vision drives the company’s strategic initiatives, from reusable rockets to Mars colonization plans. While major investors like Founders Fund, Fidelity, and Google have representation and influence, Musk’s leadership is central to decision-making processes.
SpaceX operates under a private governance structure, with Musk serving as both CEO and Chief Engineer. This dual role allows him to guide both business operations and technological innovation. The company’s board of directors includes representatives from key investors, but Musk holds significant influence over major strategic decisions.
Musk’s control extends to the company’s funding strategies, partnerships, and long-term goals. He has the final say on major projects, including the development of Starship, Starlink expansion, and deep-space exploration initiatives. His leadership has enabled SpaceX to remain agile, pursuing ambitious projects without the constraints of public market pressures.
Despite Musk’s dominant influence, SpaceX’s investors and board members provide guidance on financial and operational matters. They ensure the company remains on track toward achieving profitability and sustained growth while balancing innovation with commercial viability.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of SpaceX
As a private entity, SpaceX’s financial details are not publicly disclosed. However, estimates suggest significant growth in recent years. In 2024, the company’s valuation soared to approximately $350 billion, reflecting its success in satellite launches, ISS missions, and the expanding Starlink internet service.
These ventures have contributed to substantial revenue streams, solidifying SpaceX’s position in the aerospace sector.
SpaceX Revenue Growth
- 2015: Estimated revenue of $1 billion
- 2018: Estimated revenue of $2 billion
- 2020: Estimated revenue of $3 billion
- 2022: Estimated revenue of $5 billion
- 2024: Estimated revenue exceeding $8 billion.
SpaceX Valuation Milestones
- 2002: SpaceX’s initial valuation was approximately $27 million.
- 2005: The company’s valuation increased to around $163 million.
- 2008: Valuation reached approximately $410 million.
- 2010: The company was valued at about $1 billion.
- 2015: Valuation rose to approximately $10 billion.
- 2017: SpaceX’s valuation increased to $21.2 billion following a funding round.
- 2019: The company’s valuation reached $33.3 billion.
- 2024: SpaceX’s valuation soared to approximately $350 billion, reflecting its success in satellite launches, ISS missions, and the expanding Starlink internet service.
Market Share and Competitors
SpaceX has disrupted the aerospace industry, capturing a considerable market share in commercial satellite launches and resupply missions.
Arianespace
A European company known for the Ariane 5 rocket, Arianespace serves commercial and governmental clients. It holds a significant share of the European and global commercial launch market but has struggled to compete with SpaceX’s lower launch costs.
United Launch Alliance (ULA)
A joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin, ULA provides reliable launch services using rockets like Atlas V and Delta IV. It serves primarily government and military clients, holding a strong position in the U.S. defense sector.
Blue Origin
Founded by Jeff Bezos, Blue Origin focuses on reusable rocket technology and aims to serve both commercial and tourism markets. While not yet a major competitor in satellite launches, its New Glenn rocket poses a future challenge to SpaceX.
Brands Owned by SpaceX
SpaceX has developed several key projects and subsidiaries:
Starlink
Starlink is a satellite-based internet service operated by SpaceX. It aims to provide high-speed internet access worldwide, particularly in remote and underserved regions. With a growing constellation of thousands of satellites in low Earth orbit, Starlink has amassed millions of subscribers and plays a key role in SpaceX’s revenue generation.
Starship
Starship is SpaceX’s next-generation spacecraft designed for deep-space exploration, lunar missions, and Mars colonization. It is a fully reusable system intended to replace the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy. The Starship program is central to Musk’s vision of making life interplanetary, with ongoing testing and planned missions to the Moon and beyond.
Dragon
Dragon is a spacecraft developed by SpaceX for cargo and crew transportation to the ISS. The Crew Dragon variant is NASA-certified for human spaceflight and has successfully transported astronauts under the Commercial Crew Program. It represents SpaceX’s capability to provide commercial crewed space missions.
Conclusion
SpaceX’s ownership structure, led by Elon Musk and supported by prominent investors, has been instrumental in its groundbreaking achievements. The company’s focus on innovation, reusability, and ambitious projects continues to reshape the aerospace industry, bringing humanity closer to becoming a multiplanetary species.
FAQs
Who is the largest shareholder of SpaceX?
Elon Musk is the largest shareholder, owning approximately 42% of SpaceX.
Is SpaceX a publicly traded company?
No, SpaceX remains a privately held company.
What is the valuation of SpaceX?
As of 2024, SpaceX’s valuation reached approximately $350 billion.
Does Google own a part of SpaceX?
Yes, Google invested in SpaceX in 2015, acquiring a 7.2% stake.
Is SpaceX owned by NASA?
No, SpaceX is a privately owned company and is not owned by NASA. However, NASA has been a significant partner, awarding SpaceX contracts for cargo and crew missions to the International Space Station (ISS) under the Commercial Crew and Commercial Resupply Services programs. SpaceX operates independently, with its ownership held by Elon Musk and private investors.
Is SpaceX owned by Tesla?
No, SpaceX is not owned by Tesla. While Elon Musk is the CEO of both companies, they operate independently. Tesla focuses on electric vehicles and renewable energy, while SpaceX is dedicated to space exploration and satellite technology. There is no direct ownership connection between the two companies.
How does SpaceX make money?
SpaceX generates revenue from multiple sources, including:
- Satellite launches: SpaceX provides commercial and government launch services using its Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets.
- Starlink internet service: SpaceX sells satellite internet subscriptions through Starlink, targeting remote and underserved areas.
- NASA contracts: SpaceX receives funding from NASA for cargo and crew transportation to the ISS.
- Military and government contracts: SpaceX works with the U.S. Department of Defense for national security space missions.
- Commercial spaceflight: SpaceX has started offering private space travel experiences, such as the Inspiration4 and Polaris missions.

