Nissan is one of the most recognized automobile manufacturers in the world. Many people wonder who owns Nissan and how its corporate structure works. The company’s journey spans over a century, involving mergers, alliances, and ownership changes.
History of Nissan
Nissan was founded in Japan in 1933 as Jidosha-Seizo Co., Ltd. It soon became Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. after merging with another firm. Initially, it focused on assembling trucks and military vehicles. Post World War II, Nissan expanded rapidly into passenger cars. By the 1960s and 70s, it began exporting globally, especially to the United States.
In 1999, Nissan entered into a critical alliance with the French carmaker Renault. This move saved Nissan from financial trouble. Later, Mitsubishi Motors joined the alliance, creating one of the largest automotive groups in the world.
Who Owns Nissan: Major Shareholders
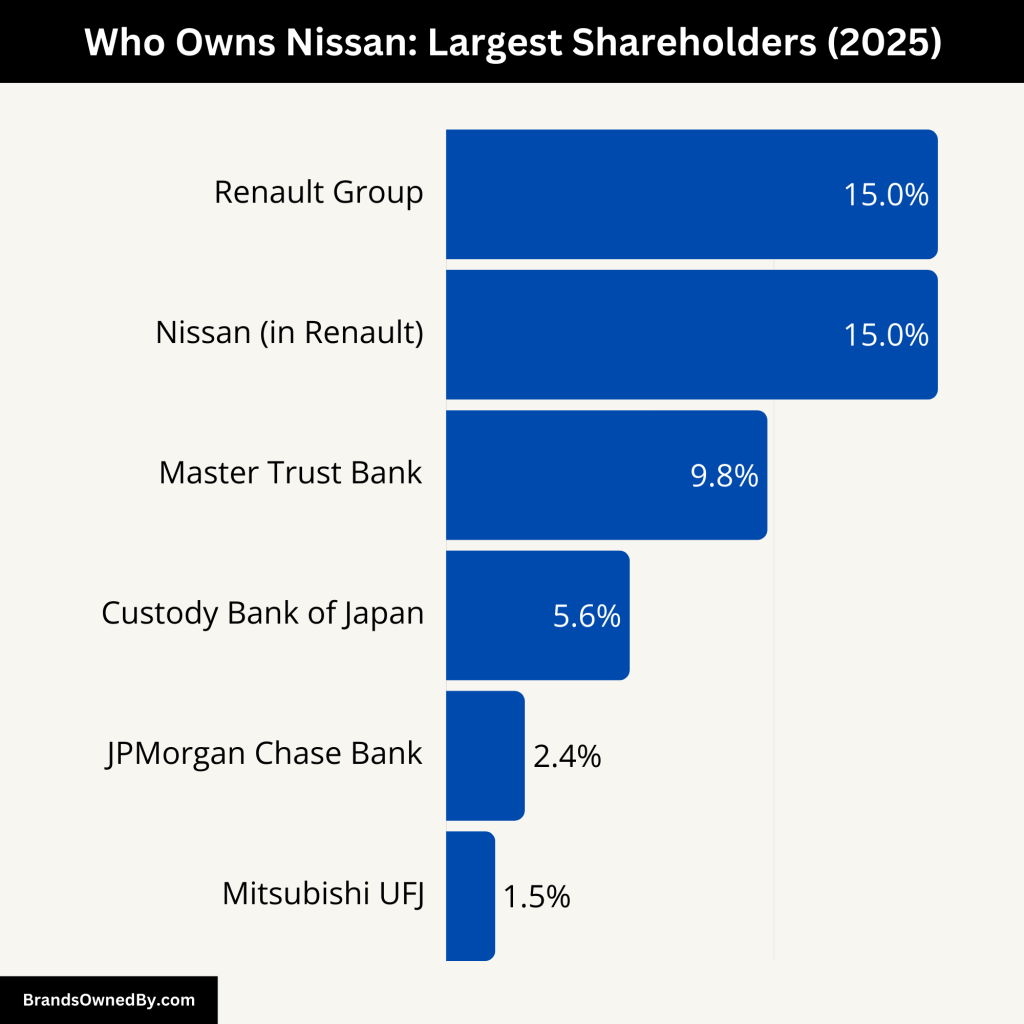
Nissan is a publicly traded company listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. However, it is part of the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance. The largest shareholder of Nissan is Renault S.A., which has had significant control since their partnership began in 1999.
Despite being based in Japan, Nissan has strong ties to French and global stakeholders due to this alliance. The ownership is structured to maintain mutual control among the partners.
Below is a detailed breakdown of Nissan’s current major shareholders:
| Shareholder | Ownership Percentage | Voting Rights | Role in Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renault Group | 15.0% | Yes | Largest strategic partner (reduced stake) |
| Nissan (in Renault) | 15.0% | No | Mutual alliance holding |
| Master Trust Bank of Japan | 9.8% | Yes | Institutional investor |
| Custody Bank of Japan | 5.6% | Yes | Institutional investor |
| JPMorgan Chase Bank | 2.4% | Yes | Foreign institutional investor |
| Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group | ~1.5% | Yes | Domestic financial institution |
| Retail and Public Shareholders | ~34.7% | Yes | Dispersed ownership |
| Mitsubishi Motors | 0% (strategic ally) | N/A | Part of alliance, no direct ownership |
Renault Group – 15% Ownership
As of early 2025, Renault S.A. owns 15% of Nissan, a reduction from its previous 43.4% stake. In early 2023, Renault transferred 28.4% of its shares into a French trust as part of a mutual rebalancing within the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance. Renault no longer holds majority voting rights over Nissan.
Although Renault can direct the trustee to sell those shares, Nissan retains the right of first offer if any sales occur. This restructured arrangement was designed to give Nissan more autonomy and create a more equal partnership between the two automakers.
Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. – 15% Ownership of Renault (Non-voting)
In return, Nissan owns 15% of Renault, but without any voting rights. This reciprocal shareholding has been in place since 2002, but does not provide Nissan with influence over Renault’s decisions. It is symbolic of the mutual dependence in the alliance, though actual control remains imbalanced.
The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd. – 9.8% Ownership
This institutional investor acts as a trust bank and pension fund manager in Japan. It holds 9.8% of Nissan shares on behalf of its clients, including government and corporate pension plans. It is one of Nissan’s largest Japanese institutional shareholders. While generally passive, its support reflects domestic confidence in Nissan.
Custody Bank of Japan, Ltd. – 5.6% Ownership
Another major institutional investor, Custody Bank of Japan (formerly part of Mizuho Trust), holds around 5.6% of Nissan shares. Like Master Trust, it manages assets for various clients and does not typically exercise direct control over business strategy.
JPMorgan Chase Bank – 2.4% Ownership
As a global custodian and investment manager, JPMorgan Chase holds approximately 2.4% of Nissan’s outstanding shares as of 2025. It represents international institutional holdings and reflects foreign investor confidence in the company.
Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group – ~1.5% Ownership
Mitsubishi UFJ, one of Japan’s largest financial groups, owns around 1.5% of Nissan’s stock through its banking and trust divisions. It is also a creditor and long-term business partner.
Retail and Other Public Shareholders – Approx. 34.7%
The remaining shares, roughly 34.7%, are widely distributed among retail investors, employee stockholders, and smaller institutions both in Japan and internationally. These investors have limited individual control but collectively affect the company’s market valuation and proxy votes.
Mitsubishi Motors – Strategic Partner (No Direct Ownership)
Mitsubishi Motors is part of the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance. However, it does not directly own Nissan shares. Instead, Nissan owns 34% of Mitsubishi Motors, giving it control over the smaller automaker. The alliance enables shared R&D, platform development, and strategic cooperation across global markets.
Who is the CEO of Nissan?
As of April 1, 2025, Ivan Espinosa serves as the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. He succeeded Makoto Uchida, who stepped down following the collapse of merger talks with Honda and mounting financial losses.
Espinosa has been with Nissan since 2003, holding various roles in product planning and strategy. Before his appointment as CEO, he was the Chief Planning Officer, where he played a pivotal role in developing Nissan’s electric vehicle lineup and global product strategy.
Leadership Transition and Strategic Focus
The leadership change comes at a critical juncture for Nissan, as the company faces significant challenges, including a projected net loss of up to £4 billion for the fiscal year 2024/2025. Espinosa’s appointment is part of a broader executive reshuffle aimed at revitalizing the company’s fortunes.
Under Espinosa’s leadership, Nissan is expected to focus on:
- Enhancing its electric vehicle portfolio to compete with global rivals.
- Streamlining operations to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Rebuilding trust with stakeholders and strengthening the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance.
Decision-Making Structure at Nissan
Nissan’s corporate governance is overseen by a Board of Directors, which includes representatives from Nissan and its alliance partners. The CEO reports to the board and is responsible for the company’s overall strategic direction and operational performance.
The executive committee, reporting to the CEO, comprises key officers responsible for various functions:
- Guillaume Cartier: Chief Performance Officer and Chairperson of the Management Committee for AMIEO (Africa, Middle East, India, Europe, and Oceania).
- Eiichi Akashi: Chief Technology Officer, overseeing vehicle planning and component engineering.
- Teiji Hirata: Chief Monozukuri Officer, responsible for manufacturing and supply chain management.
- Jeremie Papin: Chief Financial Officer, managing the company’s financial strategy.
This leadership team is tasked with executing Nissan’s turnaround strategy and steering the company towards sustainable growth.
Past CEOs of Nissan
Nissan’s leadership history reflects its evolving strategic priorities:
- Makoto Uchida (2019–2025): Led efforts to stabilize the company amid global challenges and attempted a merger with Honda.
- Carlos Ghosn (2001–2017): Instrumental in forming the Renault-Nissan Alliance and leading Nissan’s initial turnaround.
- Hiroto Saikawa (2017–2019): Focused on corporate governance reforms post-Ghosn era.
Who Controls Nissan?
Nissan’s governance structure is overseen by its Board of Directors, which comprises a mix of internal executives and independent outside directors. As of April 1, 2025, the board includes:
- Yasushi Kimura: Independent Outside Director, Chair of the Board.
- Jean-Dominique Senard: Director, Vice Chair of the Board.
- Bernard Delmas: Independent Outside Director, Lead Independent Outside Director.
- Keiko Ihara: Independent Outside Director, Chair of the Compensation Committee.
- Motoo Nagai: Independent Outside Director, Chair of the Audit Committee.
- Andrew House: Independent Outside Director, Chair of the Nomination Committee.
- Brenda Harvey: Independent Outside Director.
- Teruo Asada: Independent Outside Director.
- Mariko Tokuno: Independent Outside Director.
- Pierre Fleuriot: Director.
- Makoto Uchida: Director.
- Hideyuki Sakamoto: Director
This diverse board composition ensures a balance of perspectives and expertise in guiding Nissan’s strategic decisions.
Executive Committee
The Executive Committee, reporting directly to CEO Ivan Espinosa, is responsible for the company’s operational management. Key members include:
- Guillaume Cartier: Chief Performance Officer and Chairperson of the Management Committee for AMIEO (Africa, Middle East, India, Europe, and Oceania), with expanded responsibilities in global marketing and customer experience.
- Eiichi Akashi: Chief Technology Officer and Executive Officer, overseeing vehicle planning and component engineering.
- Teiji Hirata: Chief Monozukuri Officer and Executive Officer, responsible for manufacturing and supply chain management.
- Jeremy Papin: Chief Financial Officer and Executive Officer.
- Stephen Ma: Chairperson of the Management Committee for China.
- Mitsuro Antoku: Chief Quality Officer.
- Toru Ihara: Chief Human Resources Officer.
This leadership team is tasked with executing Nissan’s strategic initiatives and driving the company’s transformation efforts.
Shareholders Influence
Nissan’s ownership structure includes significant stakes held by institutional investors and strategic partners. While Renault S.A. previously held a controlling interest, its stake has been reduced to 15%, aligning with Nissan’s efforts to assert greater autonomy. The company’s governance model emphasizes a balance between shareholder interests and independent oversight to ensure sustainable growth.
Who Makes Nissan Engines?
Nissan engines are primarily manufactured by the company itself through its various global production facilities. However, due to its alliance partnerships and joint ventures, engine production is sometimes shared or localized depending on the market.
Nissan’s Own Engine Plants
Nissan produces most of its engines in its own facilities around the world. Key engine manufacturing plants include:
Yokohama Plant (Japan)
- Established: 1935
- Role: Nissan’s oldest and most important powertrain facility.
- Output: Produces gasoline engines, electric motors (for EVs like the Leaf), and high-performance Nismo powertrains.
- Significance: Also home to the hand-assembled GT-R engines, crafted by Takumi master technicians.
Iwaki Plant (Japan)
- Established: 1994
- Output: High-efficiency gasoline engines, including those for mid-size and larger vehicles.
- Status (as of 2022): Transferred major operations to other facilities during global restructuring.
Decherd Powertrain Plant (Tennessee, USA)
- Opened: 1997
- Role: Main engine production hub for the North American market.
- Output: 4-cylinder and V6 engines for Nissan vehicles like Altima, Frontier, and Pathfinder.
- Special Note: Also produced engines for Infiniti and Mercedes-Benz under a Daimler-Nissan agreement (now concluded).
Sunderland Plant (UK)
- Output: Engines and components for European-market vehicles like the Qashqai and Juke.
- Transition: Gradual shift towards electric motor production as Nissan expands its EV lineup.
Alliance-Based Engine Production
Nissan collaborates with partners in the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance for engine development and production in certain regions.
Renault-Nissan Engine Sharing
- Engines Co-developed: Small turbocharged petrol engines, diesel units (primarily for Europe), and modular powertrains.
- Examples:
- The HR13 1.3L turbo engine co-developed with Renault, used in the Nissan Qashqai and Renault Captur.
- The 1.5 dCi diesel engine also used in several Renault and Nissan models.
Mitsubishi Collaboration
- Since Nissan owns 34% of Mitsubishi Motors, some kei cars and compact engines are developed jointly.
- Mitsubishi also supplies engines for specific Nissan-branded vehicles in Japan under an OEM arrangement.
Joint Ventures and Local Production
Dongfeng Nissan (China)
- Role: Local engine manufacturing for Nissan models sold in China.
- Plants: Produce internal combustion engines and components locally to meet regional content regulations.
NMKV (Nissan-Mitsubishi Joint Venture for Kei Cars)
- Develops and manufactures small-displacement engines for kei cars sold in Japan.
- Shared engineering and production platforms help reduce costs and improve compliance with kei car regulations.
Electric Vehicle Motor Manufacturing
With the rise of EVs, Nissan has expanded motor production for its electric vehicles:
Yokohama Plant (Japan)
- Produces electric motors for the Nissan Leaf, Ariya, and e-Power hybrids.
Sunderland Plant (UK)
- Recently upgraded to manufacture electric powertrains for European-market EVs.
Decherd Plant (USA)
- Expected to participate in EV powertrain manufacturing for North American expansion starting late 2025.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Nissan
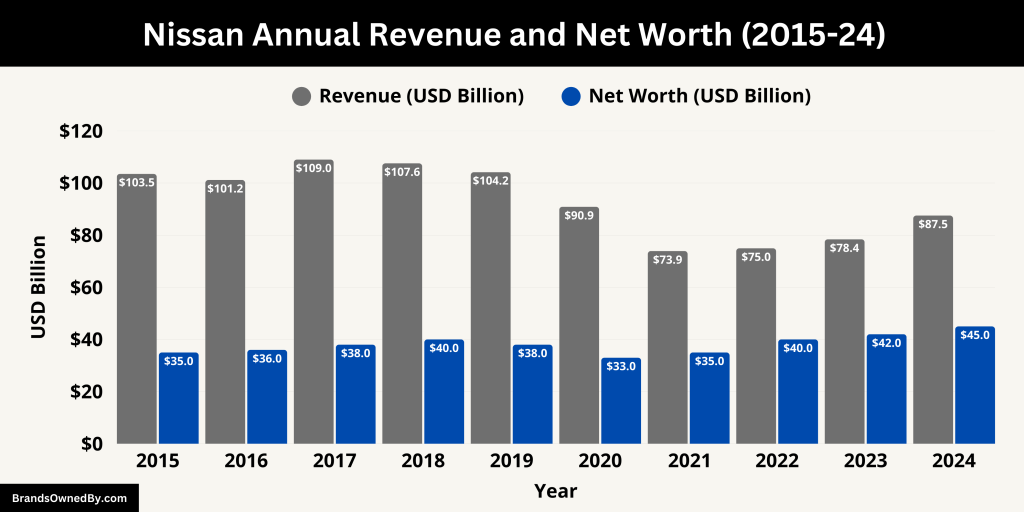
In the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. reported consolidated net revenue of ¥11.52 trillion, equivalent to approximately $87.53 billion. This marked an 11.63% increase from the previous fiscal year, driven by a rebound in global vehicle sales and improved supply chain stability.
For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2025, Nissan initially projected net revenue of ¥14.0 trillion. However, due to challenging market conditions and strategic adjustments, the company revised its forecast to ¥12.7 trillion, approximately $87.5 billion. This downward revision reflects a more cautious outlook amid ongoing industry uncertainties.
As of May 2025, Nissan’s market capitalization stood at approximately ¥1.59 trillion, or $10.6 billion, representing a 24.46% decrease over the past year. This decline in market value underscores the challenges faced by the company in a competitive automotive landscape.
Below is an overview of Nissan’s revenue and net worth, along with net income for the last 10 years:
| Fiscal Year | Revenue (USD Billion) | Net Income (USD Billion) | Net Worth (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 87.53 | 2.94 | 45.00 |
| 2023 | 78.42 | 1.64 | 42.00 |
| 2022 | 74.98 | 1.92 | 40.00 |
| 2021 | 73.91 | -4.22 | 35.00 |
| 2020 | 90.89 | -6.18 | 33.00 |
| 2019 | 104.17 | 2.87 | 38.00 |
| 2018 | 107.56 | 6.72 | 40.00 |
| 2017 | 109.00 | 6.17 | 38.00 |
| 2016 | 101.17 | 4.35 | 36.00 |
| 2015 | 103.51 | 4.16 | 35.00 |
Companies Owned by Nissan
As of 2025, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. owns and operates a diverse portfolio of brands, subsidiaries, and joint ventures that span various segments of the automotive industry. These entities contribute to Nissan’s global presence and strategic initiatives in performance, luxury, customization, and emerging markets.
Here’s a list of the brands and companies owned by Nissan:
| Company/Brand | Ownership Stake (%) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Nissan | 100% (Parent Brand) | Core brand producing a wide range of passenger cars, EVs (like the Leaf and Ariya), trucks, and SUVs globally. |
| Infiniti | 100% | Nissan’s luxury vehicle division offering premium sedans and SUVs primarily in North America, China, and the Middle East. |
| Nismo | 100% (via NM&C) | Nissan’s motorsports and performance division, involved in racing and performance-tuned road cars. Integrated with Autech into Nissan Motorsports & Customizing Co., Ltd. |
| Autech | Merged with Nismo | Specialized in vehicle customization and conversion. Now part of Nissan Motorsports & Customizing Co., Ltd. |
| Nissan Motorsports & Customizing Co., Ltd. (NM&C) | 100% | A 2022 merger of Nismo and Autech under a single performance and customization subsidiary. |
| Nissan Shatai | 45.8% | A Nissan-controlled manufacturing subsidiary focused on light commercial and special-purpose vehicles. |
| Dongfeng Nissan | 50% | Joint venture with Dongfeng Motor Group producing Nissan cars for the Chinese market. Includes the Venucia brand. |
| Venucia | Operated under Dongfeng Nissan | Sub-brand tailored for the Chinese domestic market. Offers budget-friendly and electric vehicles. |
| Mitsubishi Motors | 34% | Nissan is the largest shareholder. Acquired stake in 2016. Mitsubishi operates independently within the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance. |
Nissan
The core brand of Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., Nissan produces a wide range of vehicles, including sedans, SUVs, trucks, and electric vehicles. Known for models like the Altima, Rogue, and Leaf, the brand emphasizes innovation, reliability, and value.
Infiniti
Infiniti is Nissan’s luxury vehicle division, established in 1989. It offers premium sedans, SUVs, and crossovers, focusing on performance, design, and advanced technology. Infiniti serves markets in North America, China, the Middle East, and other regions.
Nismo
Nismo, short for Nissan Motorsports International, is Nissan’s performance and motorsports division. It develops high-performance versions of Nissan vehicles and participates in racing events like Super GT and Formula E. Nismo also offers aftermarket performance parts and accessories.
Autech
Autech specializes in vehicle customization and conversion, offering modified versions of Nissan vehicles with unique styling and features. In 2022, Autech merged with Nismo to form Nissan Motorsports & Customizing Co., Ltd., combining performance and customization expertise.
Nissan Shatai
Nissan Shatai is a manufacturing subsidiary focused on producing light commercial vehicles, multipurpose special vehicles, and specially-equipped vehicles. It operates assembly lines in Hiratsuka and Kanda, Japan, and produces models like the Nissan NV200 and Elgrand. Nissan owns approximately 45.8% of Nissan Shatai.
Dongfeng Nissan
Dongfeng Nissan is a 50-50 joint venture between Nissan and Dongfeng Motor Group in China. Established in 2003, it produces and sells Nissan-branded vehicles in the Chinese market. The joint venture also developed the Venucia brand, targeting second- and third-tier Chinese cities.
Mitsubishi Motors
Nissan owns a 34% stake in Mitsubishi Motors, making it the largest shareholder. Acquired in 2016, this strategic partnership expanded Nissan’s global reach and product offerings, particularly in Southeast Asia. Mitsubishi continues to operate as an independent brand within the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance.
Venucia
Venucia is a brand developed by Dongfeng Nissan to cater to the Chinese market, especially in emerging cities. It offers affordable vehicles tailored to local preferences and regulations. Venucia operates under the Dongfeng Nissan joint venture.
Final Words
Understanding who owns Nissan reveals a global alliance involving Japan and France. Renault holds the largest share, giving it major control. Nissan operates many brands and subsidiaries across the globe. The alliance structure continues to shape the company’s future. With a strong focus on innovation and electric vehicles, Nissan remains a major player in the global auto market.
FAQs
Why is Nissan called Nissan?
Nissan’s name is derived from the combination of two words: “Nihon” (Japan) and “Sangyo” (industry), forming “Nissan.” The brand name was created in the early 1930s when the company was first established and is meant to reflect its Japanese origins and industrial focus.
What does Nissan mean in Japanese?
In Japanese, “Nissan” (日産) can be translated as “sun” (日) and “production” or “company” (産), symbolizing the company’s origins in Japan and its emphasis on manufacturing. The name is a play on Japan’s national identity and Nissan’s position as a global leader in the automotive industry.
Who is the real owner of Nissan?
Nissan is a publicly traded company, so it does not have a single “owner.” The company’s largest shareholder is the Renault Group (15% stake), followed by other institutional investors and private shareholders. Additionally, Nissan is part of the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance, making ownership a collaborative effort between these companies.
Is Nissan still Japanese-owned?
Yes, Nissan remains a Japanese company. While it has international partnerships and collaborations, it is headquartered in Yokohama, Japan, and remains largely controlled by Japanese shareholders, with a significant stake held by the French Renault Group.
Did Toyota buy Nissan?
No, Toyota did not buy Nissan. The two companies are separate entities and competitors in the automotive industry. However, both are major players in the global automotive market and have engaged in collaborations in the past, but have not merged.
Which country owns Nissan?
Nissan is a Japanese-owned company. It was founded in Japan and continues to operate from its headquarters in Yokohama, Japan. However, it has significant international partnerships, particularly with the French company Renault.
Did Renault buy Nissan?
Renault did not fully buy Nissan, but it holds a significant stake in the company. Renault owns about 15% of Nissan, and the two companies formed the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance, where they share technologies, resources, and manufacturing facilities, but remain independent entities.
Who is the father of Nissan?
The “father” of Nissan is considered to be Yoshisuke Aikawa, who founded the company in 1933. Aikawa was a prominent figure in the creation of Nissan as he consolidated various smaller companies to create the automobile giant.
What family owns Nissan?
Nissan does not have a single family ownership. It is a publicly traded company. However, it is closely linked to the Aikawa family’s legacy, as Yoshisuke Aikawa, the founder, was instrumental in Nissan’s creation. Today, Nissan’s major shareholders are large institutional investors, with Renault holding a significant stake.
What is the original name of Nissan?
Nissan was originally named “Toyo Motor Co., Ltd.” when it was founded in 1933. In 1934, it was rebranded as Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., marking the official birth of the Nissan brand.
Who owns Nissan Rogue?
The Nissan Rogue is owned by Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. It is one of the brand’s best-selling models, produced by the company and sold through its global network of dealerships.
Where is Nissan’s headquarters?
Nissan’s headquarters is located in Yokohama, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. The company operates several facilities worldwide, but its central management and strategic decisions are made at this location.
Is Nissan a good car?
Nissan is generally regarded as a reliable and well-engineered car brand. It offers a range of vehicles, including compact cars, sedans, SUVs, and electric vehicles like the Nissan Leaf. Nissan cars are known for their affordability, fuel efficiency, and technological innovations, particularly in electric vehicle development.
Who owns Nissan company?
The Nissan company is primarily owned by institutional shareholders and is publicly traded. The major shareholder is Renault, which holds about 15% of Nissan’s shares. Other significant shareholders include Japanese and international institutional investors.
Who manufactures Nissan?
Nissan vehicles are manufactured by Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. itself, which operates production plants worldwide. The company manufactures its own engines, car bodies, and other components. Nissan also partners with other companies in the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance for certain models and joint manufacturing operations.

