Mazda is a well-known name in the global automotive industry. But many people often ask, who owns Mazda today?
Despite partnerships and alliances with global players, Mazda remains one of the few truly independent Japanese car manufacturers.
Here’s a complete breakdown of its ownership, history, and more.
History of Mazda
Mazda was founded in 1920 in Hiroshima, Japan. Originally, it was called Toyo Cork Kogyo Co., Ltd., and it focused on manufacturing machine tools. In 1931, it released its first vehicle, a three-wheeled truck known as the Mazda-Go. The name “Mazda” was used for the first time during this launch.
In the 1960s, Mazda became known for its innovative rotary engines, used in cars like the Mazda Cosmo and RX series. By the 1970s and 1980s, it expanded globally, especially in North America. Mazda had a long-standing partnership with Ford starting in 1979, but this relationship eventually faded. Over the decades, Mazda has remained consistent in its engineering innovations and stylish design.
Who Owns Mazda?
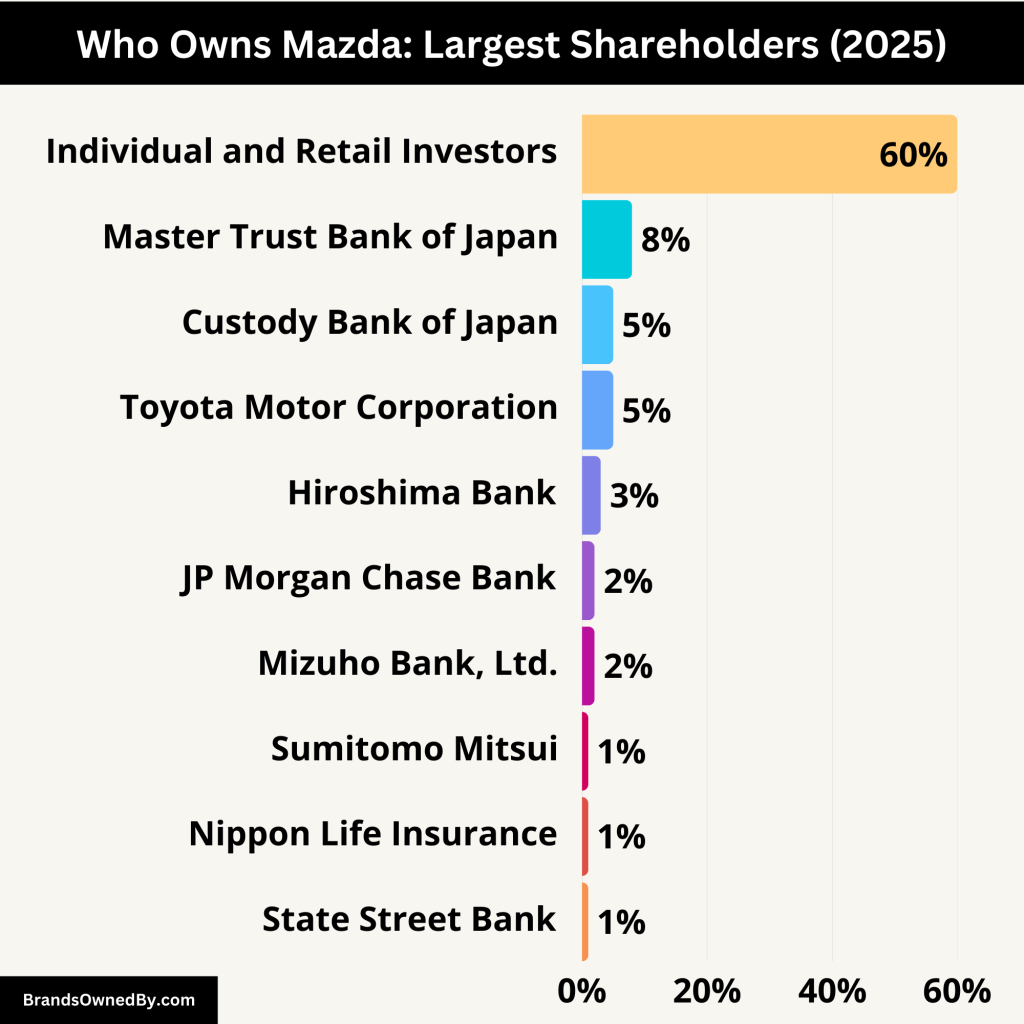
Mazda is a publicly traded company listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. It is not owned by a single person or company. Instead, it has a broad shareholder base that includes institutional investors, individual investors, and partner companies. Although some companies hold strategic stakes, no one owns a controlling interest in Mazda.
The largest shareholder is currently Toyota Motor Corporation, which holds a minority yet influential stake. This has created a strategic partnership, allowing both companies to collaborate on electric vehicles and technology development. However, Mazda continues to operate independently with its own management and board of directors.
Mazda Top Shareholders
Mazda’s shares are widely held, with a mix of institutional investors, strategic partners, banks, and retail investors. Here is a detailed breakdown of Mazda’s largest shareholders and their roles in the company:
| Shareholder | Ownership (%) | Type | Role in Mazda |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Master Trust Bank of Japan | 7.79% | Institutional (Trust) | Holds shares on behalf of investors; passive role with voting rights |
| Custody Bank of Japan | 5.29% | Institutional (Trust) | Custodian for institutions; no operational role |
| Toyota Motor Corporation | 5.05% | Strategic Corporate Partner | Largest corporate shareholder; tech collaboration, no managerial control |
| Hiroshima Bank | 3.04% | Regional Bank | Local partner; symbolic and financial support role |
| JP Morgan Chase Bank (Standing Proxy) | 1.95% | Foreign Institutional | Holds shares for global clients; passive investor |
| Mizuho Bank, Ltd. | 1.83% | Commercial Bank | Longtime financial partner; no active management role |
| Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation | 1.47% | Commercial Bank | Financial partner; provides banking services |
| Nippon Life Insurance Company | 1.26% | Insurance Company | Institutional investor; passive governance role |
| State Street Bank and Trust Company | 1.21% | Foreign Institutional | Holds shares for mutual funds; focuses on ESG and governance |
| Individual and Retail Investors | ~60% | Public Shareholders | Widespread ownership; participate in annual meetings and shareholder voting |
Toyota Motor Corporation – 5.05%
Toyota is the largest corporate shareholder in Mazda. It acquired its stake in 2017 as part of a long-term strategic partnership. Despite its minority position, Toyota collaborates closely with Mazda on electric vehicle technology, platform sharing, and manufacturing efficiency.
While Toyota does not have voting control over Mazda, its stake gives it a seat at the table in terms of technical collaboration and mutual projects. However, Mazda maintains full managerial independence.
The Master Trust Bank of Japan (Trust Account) – 7.79%
This is Mazda’s largest overall shareholder. The Master Trust Bank of Japan holds shares on behalf of pension funds and other institutional clients. It acts purely as a trustee and has no involvement in Mazda’s corporate operations.
Its influence lies mainly in voting at shareholder meetings. This bank plays a key governance role in many Japanese corporations due to the size of its holdings.
Custody Bank of Japan (Trust Account) – 5.29%
Like Master Trust Bank, Custody Bank of Japan acts as a custodian for institutional investors. It holds shares in the trust and does not exercise direct control over Mazda’s operations.
Its influence is passive but important, especially during shareholder votes on board appointments, dividend policies, or mergers.
Hiroshima Bank – 3.04%
Hiroshima Bank is a longtime financial partner of Mazda, rooted in their shared location. Mazda was founded in Hiroshima, and this relationship has endured over decades.
While Hiroshima Bank’s stake is relatively small, its support is symbolic and strategic. It reinforces Mazda’s presence and influence in its home prefecture.
JP Morgan Chase Bank (Standing Proxy) – 1.95%
This foreign institutional investor holds shares for overseas clients, likely investment funds and private wealth clients. JP Morgan does not engage in Mazda’s day-to-day affairs but may exercise its voting rights during annual meetings.
As a global investment bank, JP Morgan’s involvement increases Mazda’s visibility among international investors.
Mizuho Bank, Ltd. – 1.83%
Mizuho Bank is one of Japan’s leading financial institutions and a significant lender to Mazda. Its ownership stake reflects this ongoing financial relationship.
Though Mizuho does not actively manage Mazda, it provides critical financial services and can influence corporate governance through its voting rights.
Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation – 1.47%
Another key financial institution with longstanding ties to Mazda. Like Mizuho, its stake represents a financial relationship rather than an operational role.
SMBC provides corporate loans, financial advisory services, and global banking support.
Nippon Life Insurance Company – 1.26%
Nippon Life is one of Japan’s largest life insurance companies. Its stake in Mazda is part of a broader investment portfolio. It does not have operational involvement but participates in shareholder governance.
State Street Bank and Trust Company – 1.21%
This U.S.-based institutional investor holds shares on behalf of international mutual funds and investment accounts. Its ownership stake shows Mazda’s attractiveness to foreign institutional investors.
As a passive investor, State Street’s main role is voting in line with governance and sustainability principles.
Individual and Retail Investors – Approximately 60%
A significant portion of Mazda shares is held by individual investors, mostly in Japan. These shareholders range from small-scale investors to long-term Mazda enthusiasts.
While individually they have little control, collectively they represent a large part of Mazda’s voting power. Their loyalty often plays a stabilizing role in shareholder decisions.
Who Controls Mazda?
Mazda is controlled by its executive leadership and board of directors. The company’s President and CEO, Masahiro Moro (as of 2023), leads its global operations. Decisions are made collectively by the management team, with oversight from a board made up of both internal executives and outside directors.
Even though Toyota owns a stake, it does not control Mazda. The company operates independently, with its own R&D, branding, and marketing strategies. Mazda’s management team makes decisions on product development, expansion, and innovation.
Executive Leadership: Operational Control
Mazda is led by its executive management team, which handles the company’s day-to-day operations. As of 2023, the President and CEO is Masahiro Moro. He succeeded Akira Marumoto and has over 30 years of experience with the company. Under his leadership, Mazda is focusing on electrification, premium positioning, and global expansion.
The executive team also includes:
- Kiyotaka Shobuda – Chairman of the Board (former President & CEO)
- Takeshi Mukai – Executive Vice President
- Tomiko Takeuchi – Chief Branding Officer and the first female executive officer in Mazda’s history
These leaders are responsible for product development, marketing, manufacturing, and global sales strategies. They execute the company’s long-term vision while managing risk and competition.
Board of Directors: Strategic Oversight
Mazda’s board of directors oversees executive decisions and ensures alignment with shareholder interests. The board includes both internal directors (executives) and external directors (independent experts and business leaders).
The board plays a vital role in:
- Approving corporate strategy
- Appointing or dismissing top executives
- Overseeing financial performance
- Enforcing ethical standards and compliance
External board members provide independent judgment and help avoid conflicts of interest. This adds transparency and improves governance, especially in a company with diverse shareholders.
Shareholder Influence: Governance Through Voting
Though no single shareholder controls Mazda outright, shareholders do influence the company through:
- Annual General Meetings (AGMs)
- Voting on board appointments
- Approving dividends and financial statements
Institutional investors like The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Custody Bank of Japan, and Toyota participate in these decisions. Their combined votes help shape company direction, but they do not interfere with operational control.
Toyota, despite being Mazda’s largest corporate shareholder, does not have seats on the board and does not dictate Mazda’s management decisions. The partnership remains collaborative, not controlling.
Audit & Supervisory Committee: Internal Control
Mazda also has an Audit & Supervisory Committee composed mainly of independent directors. This committee:
- Audits financial records
- Reviews internal controls
- Ensures compliance with laws and regulations
It helps strengthen transparency and holds management accountable for performance and conduct.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Mazda
In the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Mazda Motor Corporation reported record-high financial results. The company achieved net sales of ¥4.8277 trillion (approximately $33.3 billion), marking a 26% year-on-year increase. Operating income rose by 76% to ¥250.5 billion (about $1.6 billion), while net income attributable to owners of the parent company increased by 45% to ¥207.7 billion (around $1.3 billion).
Mazda’s market capitalization is around $3.1 billion as of April 2025. Though this can fluctuate. The company invests heavily in technology and sustainability, which supports its long-term financial position.
Here’s a breakdown of Mazda’s historical revenue for the last 10 years:
| Fiscal Year | Revenue (¥ Trillions) | Revenue (USD Billions) | Growth from Previous Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 4.8277 | 33.3 | +26% |
| 2023 | 3.8359 | 25.8 | +15% |
| 2022 | 3.3292 | 22.9 | +10% |
| 2021 | 3.1488 | 21.6 | +4% |
| 2020 | 3.1564 | 21.7 | -9% |
| 2019 | 3.3677 | 23.0 | +2% |
| 2018 | 3.3954 | 23.1 | +5% |
| 2017 | 3.2425 | 21.9 | +7% |
| 2016 | 3.0787 | 20.8 | +3% |
| 2015 | 2.9079 | 19.5 | +9% |
Brands Owned by Mazda
Mazda is not known for owning a diverse range of car brands like some larger automotive companies. Instead, it focuses on its core Mazda brand. However, it does operate and manage several important subsidiaries and regional branches, which contribute to its global reach and operational effectiveness.
| Brand/Entity | Role/Description |
|---|
| Mazda Motor Corporation | The parent company responsible for the design, development, and manufacturing of Mazda vehicles globally. |
| Mazda Motor of America, Inc. | Handles sales, distribution, and marketing in the United States and North America. |
| Mazda Europe GmbH | Manages Mazda’s operations across Europe, including sales, marketing, and customer service. |
| AutoAlliance (Thailand) Co., Ltd. | Joint venture with Ford, producing vehicles for both brands in the Asia-Pacific region. |
| Mazda Logistics Co., Ltd. | Manages the global logistics of Mazda’s vehicle and parts supply chain. |
| Mazda de Mexico Vehicle Operation (MMVO) | Manufacturing facility in Mexico producing vehicles for the North and South American markets. |
| Mazda Australia Pty Ltd | Handles marketing, sales, and distribution of Mazda vehicles in Australia. |
| Mazda Foundation | A philanthropic organization supporting social welfare, education, and environmental sustainability. |
Mazda Motor Corporation
The parent company itself is a globally recognized brand. Mazda Motor Corporation handles the design, development, and manufacturing of vehicles under the Mazda name, a brand known for its innovation in both performance and fuel efficiency. It is the cornerstone of Mazda’s business, responsible for the production of a wide range of cars from compact sedans like the Mazda 3 to SUVs like the Mazda CX-5.
Mazda is renowned for its Skyactiv technology, a suite of engineering advancements designed to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and increase driving performance. The brand also emphasizes KODO design philosophy, which aims to infuse vehicles with a sense of vitality and elegance. Over the years, Mazda has also introduced more premium models under its Mazda CX and Mazda6 lines.
Mazda Motor of America, Inc.
This subsidiary is the main entity responsible for the sales, distribution, and marketing of Mazda vehicles in the United States. Located in Irvine, California, Mazda North American Operations (MNAO) oversees all of Mazda’s operations in the U.S. and North America. The company plays a crucial role in shaping Mazda’s brand image in one of its largest markets.
Mazda’s American operations include manufacturing in the U.S. (at a plant in Flat Rock, Michigan, which was part of a joint venture with Ford before Ford’s exit), a network of dealerships, and customer service operations. The brand focuses on providing drivers with an alternative to the more mainstream American brands by offering a blend of luxury, performance, and value.
Mazda Europe GmbH
This subsidiary handles all of Mazda’s business across the European market. It is headquartered in Leverkusen, Germany, and oversees sales, marketing, and customer service across Europe, which is a key region for the company. Mazda Europe tailors its operations to meet the specific needs of European consumers, emphasizing the compact and efficient models that appeal to urban drivers.
Mazda’s European operations are highly focused on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints. In recent years, Mazda has introduced more fuel-efficient models and even hybrid versions of popular models like the Mazda 3 and Mazda CX-30. This aligns with the EU’s strict emissions regulations, making Mazda’s role in the region critical for achieving its sustainability goals.
AutoAlliance (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
AutoAlliance is a joint venture between Mazda and Ford Motor Company, based in Thailand. It manufactures vehicles for both companies in the Asia-Pacific region, and its factory in Rayong is a major production facility for Mazda. This venture focuses primarily on producing Mazda 2 and Mazda 3 sedans, as well as various models for the Ford brand.
Although Ford exited the partnership, the factory remains a key component of Mazda’s Asian operations. The venture allows Mazda to produce high-quality vehicles for the ASEAN market, which is one of the fastest-growing automotive markets globally.
Mazda Logistics Co., Ltd.
Mazda Logistics handles all aspects of logistics for the company’s global operations, focusing on parts supply and transportation. This subsidiary ensures that Mazda vehicles and components are delivered efficiently from the factories to global markets. Mazda Logistics manages the inventory and supply chain systems that support the distribution of finished cars to dealerships worldwide.
In addition to vehicle logistics, Mazda Logistics also provides key services such as the transportation of parts for assembly, ensuring that Mazda’s just-in-time manufacturing process runs smoothly. The company plays an essential role in keeping Mazda’s operations efficient and cost-effective.
Mazda de Mexico Vehicle Operation (MMVO)
Mazda also operates a manufacturing facility in Mexico, known as Mazda de Mexico Vehicle Operation (MMVO). This plant, located in Salamanca, Guanajuato, produces vehicles for the North and South American markets. The facility produces models like the Mazda 2 and Mazda CX-5 and serves as an important part of Mazda’s strategy to supply the Americas with affordable and high-quality vehicles.
The Mexican manufacturing facility has been part of Mazda’s strategy to expand its production capabilities in the Americas, lowering production costs while maintaining high quality. This facility is particularly important for Mazda’s competitiveness in the price-sensitive markets of Latin America and the United States.
Mazda Australia Pty Ltd
Mazda Australia is a subsidiary that manages the marketing, sales, and distribution of Mazda vehicles in the Australian market. Mazda Australia has been one of the top performers for Mazda in the Asia-Pacific region. The company tailors its operations to meet the preferences of Australian consumers, who value rugged and reliable vehicles.
Mazda’s Australian market features a lineup that caters to both urban customers and outdoor enthusiasts, with popular models like the Mazda CX-5 and Mazda BT-50 (a rugged utility vehicle). Mazda Australia also plays an integral role in research and development, with a focus on adapting global models to Australian conditions.
Mazda Foundation
Though not a traditional “brand,” the Mazda Foundation serves an important purpose in Mazda’s corporate structure. The foundation was created to support philanthropic activities, especially in the areas of environmental sustainability, education, and social welfare. The Mazda Foundation plays an important role in fostering a positive brand image for Mazda by contributing to various charitable and community programs globally.
Final Words on Mazda Ownership
Mazda is one of the few car companies that has retained its independence despite global partnerships. So, who owns Mazda?
The answer is that Mazda is owned by a mix of institutional investors, Toyota (as a partner), and individual shareholders. Toyota may be its largest single shareholder, but Mazda still manages its operations independently.
With strong leadership, focused innovation, and a loyal customer base, Mazda continues to thrive in the competitive automotive world.
FAQs
Is Mazda owned by Toyota?
No, Toyota owns about 5% of Mazda. They are strategic partners but operate independently.
Does Ford still own Mazda?
No, Ford sold its shares in Mazda. Their partnership ended in the early 2010s.
Who is the CEO of Mazda?
As of 2023, Masahiro Moro is the President and CEO of Mazda Motor Corporation.
Is Mazda a Japanese company?
Yes, Mazda is headquartered in Hiroshima, Japan and remains a Japanese company.
Does Mazda own any other car brands?
No, Mazda only produces vehicles under the Mazda brand. It does not own separate car brands.

