IVECO is a well-known name in the world of commercial and industrial vehicles. When discussing who owns IVECO, it’s essential to understand the company’s roots, its current structure, key shareholders, and associated brands. This article gives a complete view of IVECO’s ownership and corporate profile as of 2025.
IVECO Company Profile
IVECO (Industrial Vehicles Corporation) is a global manufacturer of commercial and specialty vehicles. Headquartered in Turin, Italy, IVECO produces trucks, vans, buses, military vehicles, and firefighting equipment. It operates as part of Iveco Group N.V., an independent, publicly traded industrial holding company based in the Netherlands.
IVECO’s product lineup ranges from light commercial vehicles like the IVECO Daily to heavy-duty trucks such as the IVECO S-Way. The brand is recognized for its engineering in diesel engines, natural gas vehicles, and growing investment in electric and hydrogen-powered solutions. IVECO serves customers in over 160 countries through a wide production and distribution network.
Founders and Company Formation
IVECO was officially founded in 1975, but it was not the creation of a single individual. Instead, it was formed through the merger of five established companies from three European countries:
- Fiat Veicoli Industriali (Italy) – The industrial vehicle arm of Fiat S.p.A., and the largest of the five.
- OM (Officine Meccaniche) (Italy) – Known for trucks and agricultural equipment.
- Lancia Veicoli Speciali (Italy) – Specialized in defense and utility vehicles.
- Unic (France) – A well-established truck manufacturer.
- Magirus-Deutz (Germany) – Renowned for fire trucks and commercial vehicles.
The merger was led by Fiat as part of a strategy to create a European powerhouse in industrial transportation. This collective formation is why IVECO has no single founder but rather a legacy shaped by multiple industrial brands.
Major Milestones
1975 – IVECO is formed through the merger of five brands. It began operations with over 200,000 vehicles in its fleet.
1980 – Launches the first turbocharged diesel engine for light vehicles, a major innovation in performance and efficiency.
1991 – Introduces the EuroCargo and EuroTech ranges, which go on to win multiple international “Truck of the Year” awards.
1992 – IVECO acquires ENASA, the Spanish company behind the Pegaso truck brand, further expanding its European footprint.
1999 – Launches the Cursor engine family, offering a new standard in power and low emissions for heavy-duty vehicles.
2003 – Consolidates its firefighting vehicle brand under Magirus, becoming a global leader in fire and rescue solutions.
2006–2009 – Begins investing in sustainable technology, introducing CNG-powered trucks and hybrid electric buses.
2011 – Integrates operations under CNH Industrial, a global industrial group formed from the merger of Fiat Industrial and CNH Global.
2020 – Partners with Nikola Corporation to co-develop hydrogen and battery-electric trucks for the European market.
2022 – IVECO is spun off from CNH Industrial to become an independent company under Iveco Group N.V.
2024 – Launches its first full-electric heavy truck, the IVECO S-eWay, and expands its range of zero-emission commercial vehicles.
Who Owns IVECO in 2025?
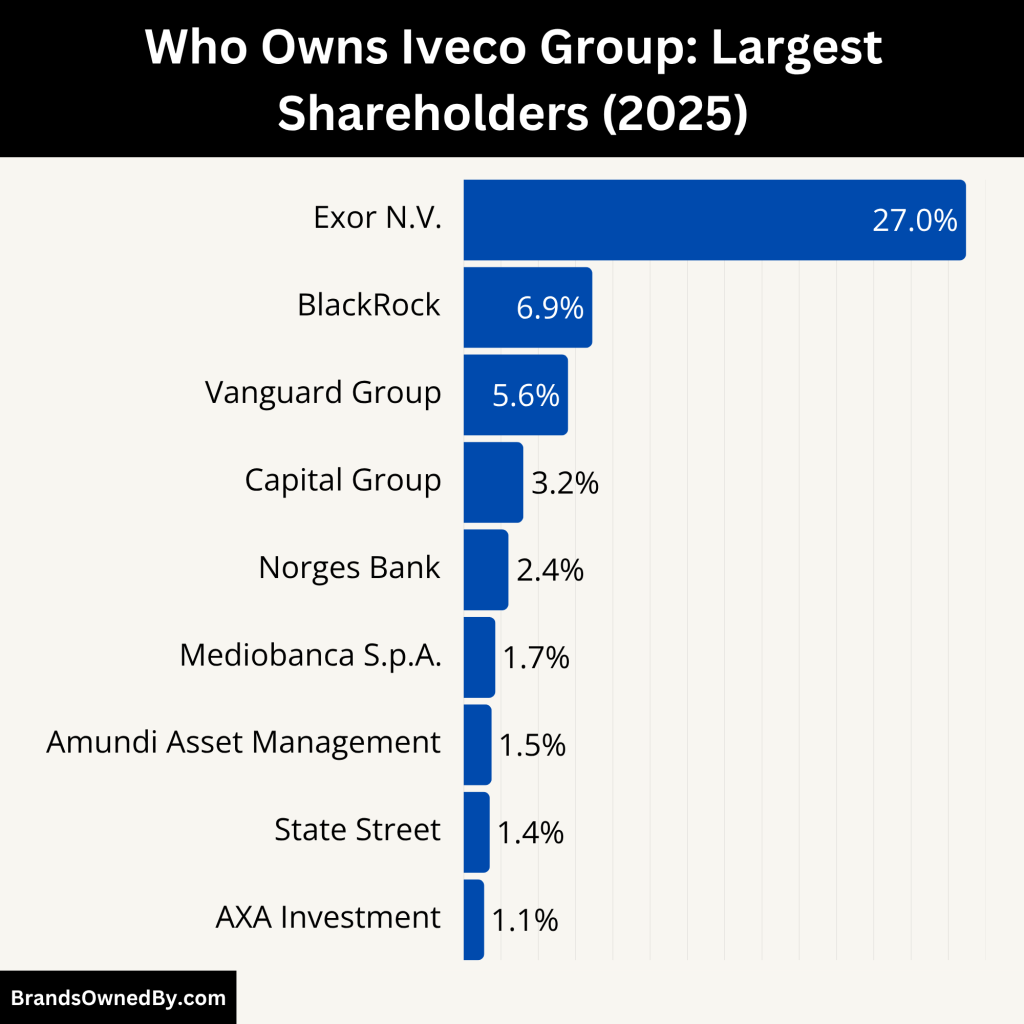
As of 2025, IVECO is wholly owned by Iveco Group N.V., a publicly traded holding company incorporated in the Netherlands. Iveco Group was established as an independent entity following its spin-off from CNH Industrial in January 2022. Since the spin-off, IVECO operates as a standalone company with its own management, board of directors, and financial reporting.
Iveco Group N.V. is listed on the Borsa Italiana (Italian Stock Exchange) under the ticker symbol “IVG.” It has a diverse shareholder base consisting of strategic shareholders, institutional investors, retail shareholders, and internal company holdings. Exor N.V. is the largest single shareholder, providing industrial oversight and long-term strategic vision.
Parent Company History
IVECO’s original parent company was Fiat S.p.A., which established IVECO in 1975 through a multi-national merger. Over the decades, IVECO remained under Fiat’s control, transitioning into Fiat Industrial in 2011, and later becoming part of CNH Industrial N.V. after the Fiat Industrial–CNH Global merger.
From 2013 to 2022, CNH Industrial operated IVECO as a key segment of its commercial and specialty vehicles division. However, in response to shifting industrial priorities and the growing demand for clean, connected transportation solutions, CNH decided to demerge its “on-highway” assets, forming
Group N.V. as a separate company.
Since the spin-off, IVECO has gained operational independence and expanded its strategy to focus on:
- Electric and alternative-fuel vehicles
- Defense and emergency services vehicles
- Public transportation solutions
- Global market expansion in Europe, South America, and Asia.
Here’s an overview of Iveco Group N.V. shareholder structure (2025):
| Shareholder | Approx. Ownership % | Type | Role/Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exor N.V. | ~26.95% | Strategic/Industrial | Largest shareholder, board influence |
| BlackRock Inc. | ~6.9% | Institutional (Passive) | Voting on ESG and governance |
| Vanguard Group | ~5.6% | Institutional (Passive) | Focus on governance and long-term value |
| Capital Group | ~3.2% | Institutional (Active) | Strategic input on growth and returns |
| Norges Bank (NBIM) | ~2.4% | Sovereign Wealth Fund | Long-term sustainability and ethics |
| Mediobanca S.p.A. | ~1.7% | Strategic/Financial | Industrial heritage and advisory role |
| Amundi Asset Management | ~1.5% | Institutional (ESG) | Climate strategy and risk mitigation |
| State Street Global Advisors | ~1.4% | Institutional (Passive) | Proxy voting on global governance |
| AXA Investment Managers | ~1.1% | Institutional (ESG) | Risk oversight and policy support |
| Public and Retail Shareholders | ~25–28% | Individual/Collective | Trading-based influence, sentiment |
| Treasury & Employee Holdings | ~2.5–3% | Internal | Leadership alignment, compensation plans |
Acquisition Insights and Historical Mergers
Though IVECO has not undergone a recent acquisition itself, its formation in 1975 was the result of a strategic consolidation of five major European vehicle manufacturers. These mergers were instrumental in creating a unified brand:
- Fiat Veicoli Industriali (Italy) – The industrial arm of Fiat S.p.A.
- OM (Italy) – Officine Meccaniche, a manufacturer of trucks and industrial equipment
- Lancia Veicoli Speciali (Italy) – Specialized in defense and heavy-duty vehicles
- Unic (France) – A leading French truck brand with distribution in Western Europe
- Magirus-Deutz (Germany) – Famous for firefighting vehicles and high-capacity trucks
These legacy brands laid the foundation for IVECO’s strong engineering and design capabilities, many of which still influence its product lines today.
In the following decades, IVECO continued selective brand acquisitions and integrations, including:
- ENASA / Pegaso (Spain) – Acquired in 1990s to expand into the Iberian market
- Seddon Atkinson (UK) – Acquired in 1990 for British truck market presence
- Heuliez Bus (France) – Brought into IVECO Bus to strengthen public transport offerings
- Sofim (France/Italy) – Integrated into IVECO’s powertrain strategy
Although IVECO has not been acquired by another company since the spin-off, it has engaged in strategic partnerships, such as its collaboration with Nikola Corporation to develop zero-emission trucks for the European market. This partnership includes joint production facilities in Germany and co-development of hydrogen-powered and battery-electric trucks.
Legal and Structural Details
- Legal Name: Iveco Group N.V.
- Headquarters: Turin, Italy (operational), Amsterdam, Netherlands (legal)
- Stock Listing: Borsa Italiana – Ticker: IVG
- Board Structure: Independent, with representatives from Exor and institutional investors
- CEO (2025): Gerrit Marx
- Ownership Type: Public company, no majority owner
Strategic Independence and Governance
Since 2022, IVECO operates independently, with its own:
- Product development roadmap
- Sustainability and ESG strategy
- Capital investment plan
- Divisional leadership for brands like IVECO, Magirus, and IVECO Bus
Its separation from CNH Industrial has allowed Iveco Group to focus exclusively on commercial transportation, public mobility, and energy-efficient vehicle platforms.
Today, Iveco Group competes directly with companies like Daimler Truck, Volvo Group, Traton (MAN and Scania), and Renault Trucks in the global market for medium- and heavy-duty vehicles.
Who Makes IVECO Engines?
IVECO engines are manufactured by FPT Industrial, which stands for Fiat Powertrain Technologies Industrial. Although FPT Industrial and IVECO are both part of the broader Iveco Group, they are operated as separate but closely integrated divisions. FPT Industrial is the exclusive powertrain supplier for IVECO trucks and vehicles.
FPT Industrial: IVECO’s Engine Partner
FPT Industrial is the powertrain division of Iveco Group and is responsible for the design, engineering, production, and global distribution of engines used in all IVECO vehicles. It produces a full range of engines covering diesel, compressed natural gas (CNG), liquefied natural gas (LNG), biomethane, and electric powertrains.
As of 2025, FPT Industrial supplies IVECO with:
- Light-duty engines for the IVECO Daily
- Mid-range engines for the IVECO Eurocargo
- Heavy-duty engines for the IVECO S-Way, T-Way, and X-Way
- Alternative fuel engines (CNG/LNG) and electric drivelines for zero-emission trucks
FPT Industrial engines are known for their fuel efficiency, low emissions, high torque output, and modular design that allows customization based on vehicle class and end-use.
Engine Families Used by IVECO
IVECO trucks primarily use the following FPT-developed engine families:
- F1A and F1C Engines – Used in the IVECO Daily, these engines cover light-duty commercial applications, with diesel and electric variants.
- Tector Engines – Mid-range engines used in Eurocargo models; available in Euro VI and natural gas versions.
- Cursor Engines – Heavy-duty engine series used in S-Way, X-Way, and T-Way trucks. These include the Cursor 9, Cursor 11, and Cursor 13, available in diesel, LNG, and biomethane configurations.
The Cursor 13 Natural Gas engine is particularly notable as it powers the IVECO S-Way LNG trucks, which are used for long-distance transport with a lower carbon footprint.
Engine Production Locations
FPT Industrial operates several engine manufacturing plants across Europe and South America, with key facilities in:
- Turin, Italy – Engineering and assembly of medium- and heavy-duty engines
- Foggia, Italy – Light engine manufacturing
- Sete Lagoas, Brazil – Serving the Latin American market
- Córdoba, Argentina – Regional engine production hub
These facilities ensure that IVECO has direct access to a wide range of engines aligned with Euro VI, Stage V, and other emissions standards.
Engine Technology and Innovations
IVECO and FPT Industrial work together on innovations such as:
- Natural gas and biomethane propulsion
- Electric and hybrid powertrains
- Hydrogen combustion engine development
- Engine connectivity for real-time diagnostics and predictive maintenance
By integrating closely with FPT Industrial, IVECO is able to offer vehicles that meet a wide range of performance, environmental, and economic requirements across international markets.
Who is the CEO of IVECO?
Olof Persson assumed the role of CEO of Iveco Group on July 1, 2024, succeeding Gerrit Marx. Prior to this, Persson was an independent board member at Iveco Group and co‑developed the company’s five‑year strategic plan. His appointment reflects a deliberate choice for continuity in execution and leadership during a critical growth phase.
Professional Background of Olof Persson
- Born in Sweden in 1964, Persson has a Bachelor of Science in Economics from Karlstad University.
- His career includes leadership roles at ABB, Bombardier Transportation, Volvo Aero (President, 2006–2008), Volvo Construction Equipment (2008–2011) and as President and CEO of Volvo Group from 2011 to 2015.
- In 2022, he joined Iveco Group’s board, which deepened his familiarity with the company’s operations before taking over as CEO.
Leadership Style and Early Actions
Persson is praised for his focus on “laser focus” execution, stakeholder engagement, and alternative propulsion strategies. His leadership has secured confidence in continuity for the company’s ambitious decarbonization goals and digitization roadmap.
Former CEO: Gerrit Marx
Gerrit Marx served as CEO from January 1, 2022, to June 30, 2024, guiding Iveco Group through its debut as an independent entity post spin-off.
Background and Achievements
- Marx combines an engineering and business background with a degree in Mechanical Engineering, an MBA, and a doctorate in Business Administration.
- His early career included McKinsey (1999–2007), senior roles at Daimler (global controlling, then President of Daimler Trucks China), and leading Skoda China under Volkswagen.
- In 2012, he became part of Bain Capital’s leadership team, also serving as interim CEO of Wittur Group.
- He joined CNH Industrial in 2019 as President of Commercial & Specialty Vehicles before becoming Iveco Group’s founding CEO in 2022.
Strategic Impact
- Under Marx, Iveco Group accelerated its focus on digital connectivity, alternative powertrains, and structural clarity through internal reorganization.
- He oversaw the launch of the five-year plan targeting 20 % revenue growth by 2028 and paved the way for partnerships with Ford Trucks, Hyundai, and Nikola.
- IVECO shares more than doubled during his tenure, demonstrating a strong market response to the group’s renewed direction.
Departure
In April 2024, it was announced Marx would leave to become CEO of CNH Industrial, effective July 1, 2024. This move is part of broader Agnelli/Exor group leadership restructuring.
CEO Transition and Governance
- The Board of Directors, led by Suzanne Heywood (Chair), orchestrated a smooth transition from Marx to Persson. This maintained momentum behind IVECO’s strategic roadmap.
- Iveco Group’s Capital Markets Day and investor presentations pivoted seamlessly to Persson’s forward leadership.
Decision-Making Structure
Iveco Group operates with a dual-layer governance system:
- The Board of Directors oversees strategy, governance, and CEO appointments.
- The Executive Committee, under the CEO, manages day-to-day operations across the five business units: Truck, Bus, Powertrain, Defence Vehicles & ASTRA, and Firefighting.
IVECO’s model balances industrial oversight with functional autonomy, enabling business-unit agility while maintaining alignment to group-wide objectives.
IVECO Annual Revenue and Net Worth
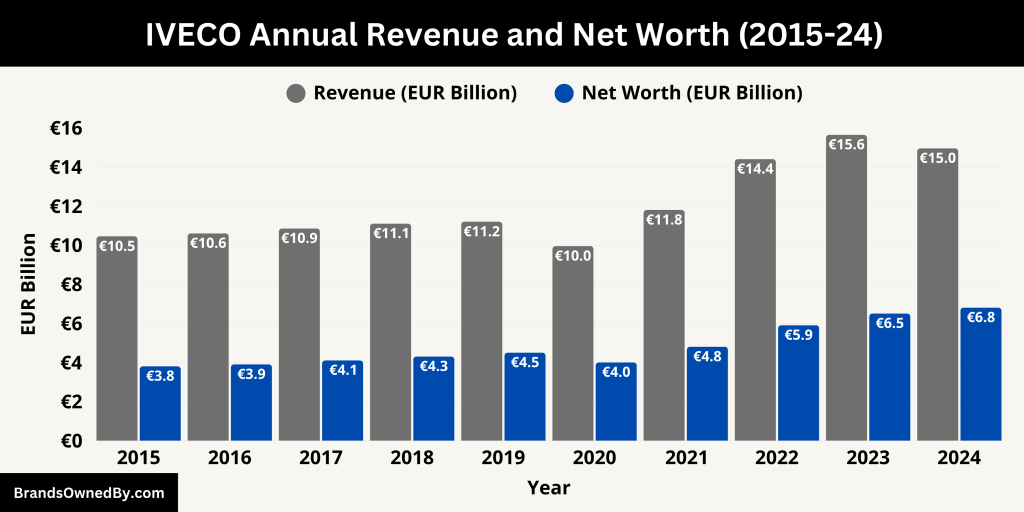
In 2024, IVECO’s truck and powertrain segment generated about €14.95 billion in net revenue—slightly down from roughly €15.64 billion in 2023. This reflects a mid-single-digit decline primarily due to weaker overall volume in heavy- and medium-duty truck sales. However, the company continued to show pricing strength, with steady revenue realization per unit.
Although unit shipments fell in Q1 of 2025, the truck segment benefited from positive pricing and cost control. The outlook indicates stabilization in European heavy-duty truck registrations, estimated between 280,000 and 290,000 units in 2025.
Profitability and Operating Performance
Despite revenue contraction, IVECO’s truck-related operations remained profitable. The Industrial Activities achieved €851 million in adjusted EBIT, an improved margin of roughly 5.7%, compared to 5.4% in the previous year.
Looking ahead, IVECO projects long-term annual net revenue in truck and related industrial activities to reach approximately €19 billion by 2028, targeting a 7–8% EBIT margin through enhanced pricing, cost improvements, and industrial partnerships.
Net Worth
Although Iveco Group is valued collectively, the truck business forms its core industrial backbone. As of mid‑2025, the entire Iveco Group’s market capitalization was between €4.1–4.2 billion, with an enterprise value (EV) around €8.7 billion. Given that trucks represent roughly 75–80% of Industrial Activities revenue, a rough EV attribution to the truck bus and powertrain units falls between €6.5–7 billion.
On a standalone basis, IVECO trucks demonstrate attractive valuation metrics, with EV/EBITDA multiples near 7–8×. This reflects operational resilience, pricing power, and profitable margins within the commercial vehicle landscape.
Here is a 10-year historical revenue and estimated net worth of IVECO covering the years 2015 to 2024:
| Year | Estimated Truck Revenue (EUR Bn) | Estimated Net Worth / EV (EUR Bn) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 14.95 | 6.8 | Revenue decline due to lower volumes; strong pricing; 5.7% EBIT margin |
| 2023 | 15.64 | 6.5 | Record revenue post spin-off; industrial margin recovery |
| 2022 | 14.40 | 5.9 | First year as independent Iveco Group; solid launch year |
| 2021 | 11.80 | 4.8 | Strong recovery post-COVID under CNH Industrial |
| 2020 | 9.95 | 4.0 | COVID-19 impact year; significant drop in demand |
| 2019 | 11.20 | 4.5 | Stable pre-pandemic performance under CNH |
| 2018 | 11.10 | 4.3 | Launch of new S-Way truck generation boosts market position |
| 2017 | 10.85 | 4.1 | European truck demand expands; modest growth |
| 2016 | 10.60 | 3.9 | Slight growth in Western Europe; weak Latin America |
| 2015 | 10.45 | 3.8 | Recovery from Eurozone slowdown; investment in Euro VI trucks |
Brands Owned by IVECO
Here is a list of brands and entities owned and operated directly by IVECO as of June 2025:
| Brand | Segment | Launch Year | Production Focus | Key Features & Markets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVECO Daily | Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs) | 1978 | Vans, chassis cabs, minibuses (3.3–7.2 tons) | Available in diesel, electric (eDaily); used in urban logistics, municipal services |
| IVECO Eurocargo | Medium-Duty Trucks | 1991 | Rigid trucks (7.5–19 tons) | Urban and regional deliveries; CNG and hybrid versions available |
| IVECO S-Way | Heavy-Duty Trucks | 2019 (replacing Stralis) | Long-haul trucks (18+ tons) | Diesel, LNG, biomethane options; full connectivity, advanced cab comfort |
| IVECO T-Way | Off-Road Heavy Trucks | 2021 (replacing Trakker) | Construction and mining vehicles | High-durability for extreme terrain; used in infrastructure, oil & gas sectors |
| IVECO X-Way | On/Off-Road Hybrid Trucks | 2017 | Multi-role trucks (tipper, mixer, crane) | Combines on-road efficiency with off-road readiness; strong in infrastructure logistics |
IVECO Daily
The IVECO Daily is a standalone light commercial vehicle brand under IVECO, operating as a full product line targeting urban logistics, small-scale goods transport, and specialized municipal use. Introduced in the 1970s, the Daily has grown into one of Europe’s most recognized LCV platforms.
By 2025, the Daily lineup includes:
- Internal combustion and electric variants (eDaily)
- Chassis cab, van, minibus, and 4×4 versions
- Payloads ranging from 3.3 to 7.2 tons
The eDaily variant launched in recent years has strengthened IVECO’s entry into the fully electric light transport segment, with battery modularity and rapid charging becoming core features.
IVECO Eurocargo
The IVECO Eurocargo brand covers the medium-duty truck segment, traditionally ranging from 7.5 to 19 tonnes. It is produced in Brescia, Italy, and sold in over 60 countries.
Eurocargo has become a mainstay in distribution, utility services, and municipal fleets. It is valued for:
- Urban maneuverability
- Versatile configurations for various body types
- High fuel efficiency and advanced driver assistance systems
By 2025, IVECO continues to invest in Eurocargo’s hybrid and compressed natural gas (CNG) variants to meet emission standards across European cities.
IVECO S-Way
The IVECO S-Way is IVECO’s flagship heavy-duty truck brand, launched in 2019 to replace the Stralis series. Designed for long-haul and international freight, it offers high cab comfort, fuel-efficient engines, and integrated telematics for fleet management.
As of 2025, S-Way models are available with:
- Diesel, LNG (liquefied natural gas), and biomethane engines
- Full connectivity suite through IVECO Driver Pal (Amazon Alexa integration)
- Advanced aerodynamic design for reduced fuel consumption
S-Way remains the backbone of IVECO’s logistics presence in Europe and South America.
IVECO T-Way
The IVECO T-Way serves the construction, mining, and off-road logistics industries. It replaced the Trakker line in 2021 and is built for heavy-duty off-road use, particularly in rugged environments.
The T-Way platform features:
- High ground clearance and reinforced suspension
- Axle configurations from 4×4 to 8×8
- Models certified for extreme load capacity and terrain adaptability
It is widely used in the Middle East, Africa, and Latin America for infrastructure and resource extraction projects.
IVECO X-Way
The IVECO X-Way brand is a specialized heavy truck series designed to bridge the gap between on-road and off-road applications. It targets sectors like construction logistics, utility infrastructure, and light-duty quarry transport.
By 2025, it is offered with:
- Configurations optimized for concrete mixers, tippers, and cranes
- Euro VI and natural gas powertrain options
- Lighter chassis designs that maximize payload while offering off-road readiness
X-Way serves markets requiring flexibility in terrain and regulatory compliance without compromising performance.
Final Thoughts
IVECO has come a long way from its roots in Italy to become a global force in commercial vehicle manufacturing. Understanding who owns IVECO today helps explain the strategic focus on innovation, sustainability, and operational efficiency. Under Iveco Group’s independent leadership and supported by Exor, the brand is well-positioned to lead the transition to cleaner and smarter transport solutions.
FAQs
When did Ford buy IVECO?
Ford never bought IVECO. However, IVECO and Ford formed a joint venture in 1986 called IVECO Ford Truck Ltd in the UK, which lasted until 2003. During this time, the two companies co-produced trucks for the European market. IVECO later bought out Ford’s share, ending the partnership.
Is IVECO Ford or Fiat?
IVECO is neither Ford nor Fiat today, though it has historical ties to Fiat. IVECO was founded by Fiat S.p.A. in 1975 through a merger of multiple truck manufacturers. It was formerly a part of Fiat and later CNH Industrial, but became independent in 2022 under Iveco Group N.V.
How do you pronounce IVECO?
IVECO is pronounced as “ee-VECK-oh” with the emphasis on the second syllable. It’s commonly pronounced this way across Europe.
What is the full form of IVECO?
The name IVECO is an acronym for Industrial Vehicles Corporation. It reflects the brand’s creation through a merger of multiple European industrial vehicle manufacturers in 1975.
What is the new name for IVECO?
There is no new name for IVECO. It continues to operate under the same name. However, its parent entity is now called Iveco Group N.V., a publicly listed company since January 2022.
Is IVECO owned by Fiat?
No, IVECO is no longer owned by Fiat. It was originally established by Fiat and remained under its control for many years. However, since 2022, it is an independent company under Iveco Group, which is no longer part of Fiat or Stellantis.
Who owns IVECO trucks?
IVECO trucks are owned and produced by IVECO, which is a division of Iveco Group N.V. The company is publicly traded, and its largest shareholder is Exor N.V., the holding company controlled by the Agnelli family (also former Fiat owners).
Which country makes IVECO?
Italy is the country where IVECO is based and where most of its key operations and engineering are located. IVECO manufactures vehicles in Italy and also operates plants in Spain, Germany, France, Argentina, and Brazil.
Who makes IVECO trucks?
IVECO trucks are manufactured by IVECO, the commercial vehicle division of Iveco Group. The company designs and assembles trucks in its own plants across Europe and Latin America.
Is IVECO owned by Stellantis?
No, IVECO is not owned by Stellantis. While it was historically connected to Fiat (which later merged into Stellantis), IVECO is now a separate public company, independent of Stellantis since 2022.
Is IVECO owned by Ford?
No, IVECO is not owned by Ford. They previously had a joint venture in the UK (IVECO Ford), but IVECO bought Ford’s stake in 2003. Ford and IVECO are now completely independent from one another.
Who makes IVECO engines?
IVECO engines are made by FPT Industrial, which is also part of Iveco Group. FPT Industrial manufactures diesel, natural gas, and electric powertrains used in all IVECO trucks and vans.
What is IVECO’s country of origin?
IVECO’s country of origin is Italy. It was founded in 1975 in Turin, where its global operations are still headquartered.
Who owns Iveco Group?
Iveco Group is a publicly traded company, headquartered in Amsterdam with operational headquarters in Turin. The largest shareholder is Exor N.V., which owns a significant stake and provides strategic oversight.
Who makes IVECO vans?
IVECO vans, including the well-known IVECO Daily, are designed and produced by IVECO. They are assembled in IVECO’s own manufacturing facilities, with final production sites located in Italy and Spain.
Who was IVECO originally owned by?
IVECO was originally owned by Fiat through Fiat Veicoli Industriali. It was created by merging five different companies under Fiat’s control in 1975.
Is IVECO part of CNH Industrial?
Not anymore. IVECO was part of CNH Industrial until 2022. It became an independent company under Iveco Group N.V. after a corporate spin-off.
Does Exor own IVECO?
Yes, Exor N.V. is the largest shareholder of Iveco Group. It holds around 27% of the company as of 2025.
Where is IVECO headquartered?
IVECO is headquartered in Turin, Italy. Iveco Group N.V., its parent company, is legally based in the Netherlands.
What does IVECO manufacture?
IVECO manufactures trucks, buses, military vehicles, firefighting vehicles, and special-use commercial vehicles.
Is IVECO a publicly traded company?
Yes, Iveco Group N.V. is listed on the Borsa Italiana under the ticker symbol “IVG.”

