IHOP is one of the most recognized American restaurant chains, known for its pancakes and breakfast offerings. But who owns IHOP? This question brings us into the world of corporate ownership, franchise models, and holding companies. Let’s explore everything about IHOP’s ownership, financials, leadership, and more.
IHOP Company Profile
The International House of Pancakes (IHOP) is a well-known American restaurant chain that specializes in breakfast items like pancakes, waffles, and omelets, while also offering a full lunch and dinner menu. IHOP is best known for its all-day breakfast concept and friendly, family-oriented atmosphere.
Founding and Founders
IHOP was founded in 1958 by Al Lapin Jr. and his brother Jerry Lapin, along with early investors Albert Kallis and William Kaye. The first location opened in Toluca Lake, California. The concept was simple: serve high-quality pancakes and breakfast food at an affordable price in a casual dining environment. The business model quickly gained popularity and was franchised within just a few years.
Corporate Structure and Growth
Over the decades, IHOP grew steadily through franchising. Its success was driven by the breakfast-centric menu, consistent branding, and suburban expansion during the 1960s and 1970s. The company became publicly traded and was listed on the stock market in the 1970s, allowing it to fuel further growth.
In 2007, IHOP Corporation made a bold move by acquiring Applebee’s International for approximately $2.1 billion. After the acquisition, the company rebranded itself as DineEquity, Inc., which later became Dine Brands Global in 2018. This marked a shift from being a standalone restaurant chain to becoming the parent of multiple large-scale casual dining brands.
Today, IHOP operates over 1,700 restaurants in the U.S. and internationally, including in Canada, Mexico, the Middle East, and Asia. More than 99% of its restaurants are franchised, making it one of the largest full-service restaurant franchise systems in the world.
Major Milestones
- 1958: IHOP founded in California.
- 1960s: Begins franchising aggressively across the U.S.
- 1973: Becomes a publicly traded company.
- 2007: Acquires Applebee’s and forms DineEquity.
- 2018: Rebrands DineEquity as Dine Brands Global.
- 2022: Parent company acquires Fuzzy’s Taco Shop.
- 2023: Kieran Donahue appointed President and later CEO of IHOP.
Who Owns IHOP in 2025?
IHOP is owned by Dine Brands Global, Inc., a publicly traded restaurant holding company based in Pasadena, California. Dine Brands Global is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “DIN”. This means IHOP does not have a single private owner—instead, it is owned by thousands of public and institutional shareholders who own shares in Dine Brands Global.
IHOP operates as a wholly owned subsidiary of Dine Brands, which also owns Applebee’s Neighborhood Grill + Bar and Fuzzy’s Taco Shop. Although IHOP is a recognizable brand, it does not exist as an independent public company.
Here’s a quick summary of IHOP ownership structure:
- IHOP is not an independent company; it is fully owned by Dine Brands Global.
- Dine Brands Global is a public company, traded under the symbol DIN.
- Ownership of Dine Brands is split among institutional investors and the public.
- Franchisees own and operate nearly all IHOP locations, under agreements with Dine Brands.
- Dine Brands also owns Applebee’s and Fuzzy’s Taco Shop, forming a three-brand portfolio.
IHOP’s Parent Company: Dine Brands Global
Dine Brands Global was originally known as IHOP Corporation. In 2007, the company acquired Applebee’s and restructured to form a new corporate entity called DineEquity, Inc. This move transformed IHOP from just a restaurant brand into a multi-brand operator. In 2018, the company was rebranded again as Dine Brands Global, Inc., reflecting its broader portfolio and global ambitions.
Dine Brands now provides centralized support functions—such as marketing, technology, and real estate—to all its brands, including IHOP. IHOP remains the flagship breakfast brand under the company’s umbrella, contributing significantly to Dine Brands’ annual revenue.
Acquisition of Applebee’s and Expansion Strategy
The most important moment in IHOP’s ownership history was the 2007 acquisition of Applebee’s International, a move that cost about $2.1 billion. This strategic acquisition made IHOP Corporation one of the largest full-service restaurant companies in the world.
This deal was unique because IHOP, at the time a smaller brand in terms of overall revenue, acquired a much larger company. The acquisition was funded largely through debt and involved re-franchising many of Applebee’s corporate-owned stores to reduce operational costs. This dramatically expanded the company’s reach and shifted its business model toward being a franchise-focused holding company.
Following the acquisition, IHOP Corporation changed its name to DineEquity, Inc., symbolizing the integration of two major restaurant brands. In 2018, it became Dine Brands Global, Inc., a name that better represented its multinational operations and brand diversification.
Other Ownership Details
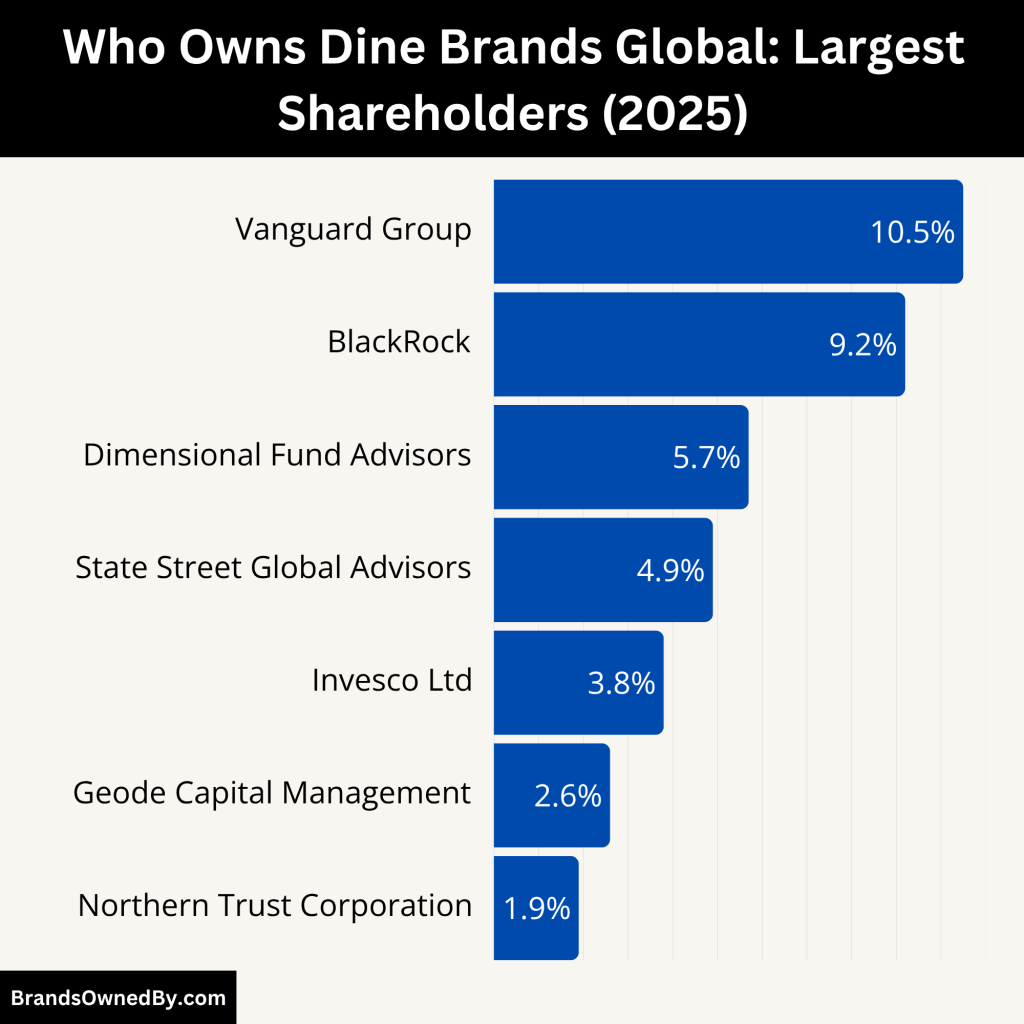
Dine Brands Global is owned by a wide range of investors. There is no single controlling owner, but the largest shareholders are typically institutional investors such as:
- The Vanguard Group
- BlackRock Inc.
- Dimensional Fund Advisors
- State Street Corporation
These firms manage billions in assets and hold significant stakes in Dine Brands on behalf of mutual funds, retirement plans, and private clients. While they do not manage daily operations, they do influence major decisions through shareholder voting rights.
The franchise model used by IHOP further decentralizes ownership at the store level. Although Dine Brands owns the IHOP brand and collects royalties and fees, the majority of individual IHOP restaurants are operated by independent franchisees who invest their own capital.
Who is the CEO of IHOP?
The overall Chief Executive Officer overseeing IHOP is John W. Peyton. He has served as CEO of Dine Brands Global since January 2021, the publicly traded parent company of IHOP, Applebee’s, and Fuzzy’s Taco Shop.
Peyton’s career includes leadership roles at Realogy Franchise Group, where he was President and CEO, and a 17-year tenure at Starwood Hotels & Resorts. In March 2025, he added the role of Interim President of Applebee’s while maintaining his CEO responsibilities.
President of IHOP Brand
Within the IHOP brand specifically, the top leader is Lawrence Kim, who was appointed Brand President in January 2025. In this role, Kim reports directly to CEO John Peyton. He is responsible for IHOP’s strategic direction across operations, marketing, culinary innovation, technology, and franchise development.
Leadership Structure and Decision Making
- John Peyton sets corporate-wide direction, allocates capital, and ensures synergy across Dine Brands’ brands.
- Lawrence Kim handles day-to-day leadership at IHOP—defining menu innovation, franchise relations, digital transformation, and marketing execution.
- The Dine Brands board of directors, along with Peyton and Kim, guides executive appointments, brand strategy, and long-term goals.
Past Leadership at IHOP
Before Lawrence Kim, IHOP was led by various executives:
- Tony Moralejo served as President of Applebee’s, while brand-level IHOP oversight was handled by the corporate team.
- Kieran Donahue served as IHOP’s Chief Marketing Officer from 2021 to late 2024, modernizing the brand’s loyalty programming and digital outreach.
- Previous CEO-level roles within Dine Brands included Julia Stewart, who guided the IHOP–Applebee’s acquisition, and Jay Johns, an early IHOP president.
Leadership Style and Legacy
- John Peyton emphasizes cross-brand integration, as showcased by the launch of dual-branded IHOP–Applebee’s locations.
- Lawrence Kim focuses on menu innovation, operations excellence, and boosting franchise growth.
- This leadership structure ensures that IHOP benefits from both corporate scale and brand-level attention.
IHOP Annual Revenue and Net Worth
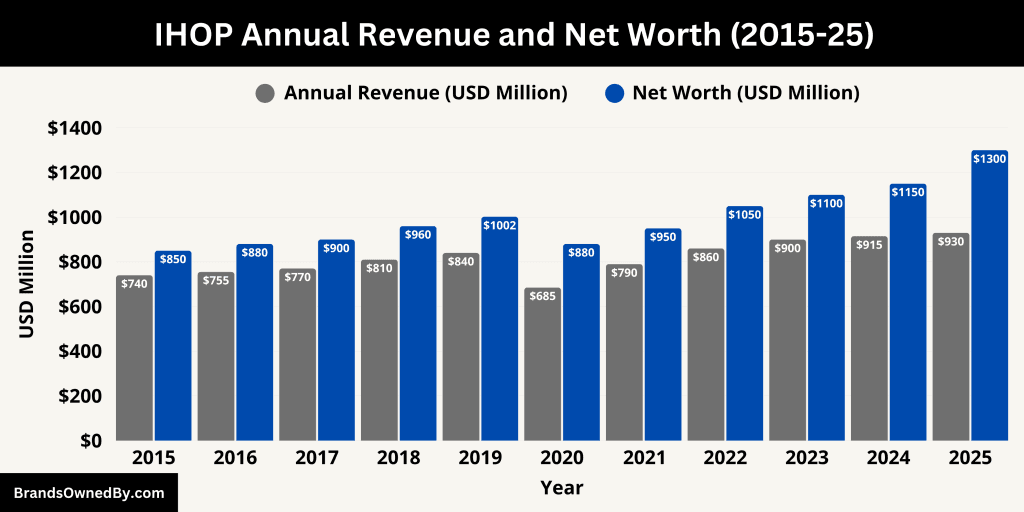
As of 2025, IHOP generates an estimated $930 million in annual systemwide sales. This figure includes revenue from both franchise-operated and company-owned restaurants. Since more than 99% of IHOP locations are franchised, the bulk of IHOP’s revenue for the corporate entity comes from franchise royalties, initial franchise fees, and restaurant support services, rather than direct sales.
IHOP typically earns 4% to 5% royalty fees on gross sales from its franchisees, along with additional marketing and licensing fees. The brand continues to maintain a steady stream of income due to its franchise-heavy model, which offers low operational risk and high margins for the corporate entity. Despite challenging macroeconomic conditions in early 2025, IHOP experienced modest same-store sales growth and opened several new locations, especially in suburban and international markets. These developments contributed to overall revenue stability.
Net Worth of IHOP
The standalone net worth of IHOP, based on its brand valuation, franchise income potential, and strategic market position, is estimated to be between $1.1 billion and $1.3 billion as of mid-2025. This valuation considers IHOP’s strong brand equity, its recurring royalty revenue streams, and its expansive franchise network spanning over 1,700 restaurants globally.
While IHOP is not a publicly traded entity, analysts often assess its worth using a revenue multiple commonly applied to franchise-driven restaurant brands. With consistent annual revenues nearing $1 billion and strong EBITDA margins typical of an asset-light model, IHOP remains one of the most valuable breakfast-focused brands in the U.S. casual dining sector.
Financial Strength and Market Performance
IHOP’s financial strength lies in its ability to scale operations with limited capital investment, thanks to its franchising model. Most of its capital expenditures are related to brand marketing, menu innovation, and technology integration rather than restaurant development. This model helps IHOP remain cash-flow positive and resilient to market fluctuations.
Its growing international footprint, ongoing digital transformation, and introduction of hybrid concepts—such as co-branded IHOP-Applebee’s locations—have all contributed to maintaining a strong market position. IHOP’s financial performance continues to support Dine Brands Global’s long-term earnings, reaffirming its role as a core growth engine within the portfolio.
Here is an overview of 10-year historical revenue and estimated net worth of IHOP from 2015-2025:
| Year | Estimated Annual Revenue (Systemwide Sales) | Estimated Net Worth |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | $740 million | $850 million |
| 2016 | $755 million | $880 million |
| 2017 | $770 million | $900 million |
| 2018 | $810 million | $960 million |
| 2019 | $840 million | $1.02 billion |
| 2020 | $685 million (COVID impact) | $880 million |
| 2021 | $790 million | $950 million |
| 2022 | $860 million | $1.05 billion |
| 2023 | $900 million | $1.10 billion |
| 2024 | $915 million | $1.15 billion |
| 2025 | $930 million | $1.20–1.30 billion |
Brands Owned by IHOP
As of 2025, IHOP owns and operates multiple business units and brand extensions within its own brand framework. Below is a detailed overview of the major brands owned by IHOP:
| Brand/Entity Name | Type | Year Introduced | Description | Operational Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IHOP Restaurants | Franchise Network | 1958 | Full-service breakfast-centric restaurants with over 1,700 locations. | Dine-in, franchising, global growth |
| IHOP Express | Fast-Service Format | Early 2000s | Smaller-format IHOP for travel hubs, campuses, and military bases. | Quick service, non-traditional venues |
| Flip’d by IHOP | Fast-Casual Spinoff | 2020 (launched) | Urban-focused concept offering portable breakfast, pancake bowls, coffee. | Fast-casual, mobile-first strategy |
| IHOP Digital Platforms | Digital Division | 2018 (revamped) | Includes IHOP mobile app, online ordering, and loyalty rewards system. | App orders, loyalty, digital revenue |
| MyHop Loyalty Program | Customer Engagement Tool | 2018 | Points-based rewards for frequent IHOP customers with personalized offers. | Customer retention, repeat traffic |
| IHOP Retail Licensing | CPG Licensing Division | Mid-2010s | Grocery products like pancake mixes, syrups, coffee, licensed to partners. | Retail visibility, off-premise sales |
| Franchise Development Unit | Internal Operations | 1970s (formalized) | Handles franchisee recruitment, vetting, and expansion planning. | Franchise sales and market expansion |
| Design & Construction Services | Internal Department | Ongoing | Provides build-out standards, architecture guidelines, and approvals. | Restaurant openings and conversions |
| International Licensing Division | Global Operations | 2000s | Manages IHOP brand adaptations and licensing in foreign markets. | International compliance and growth |
| Co-Branded Partnerships | Strategic Ventures | 2023 (scaled) | Includes IHOP presence in travel centers, dual-branded IHOP-Applebee’s sites. | Shared locations, operational synergy |
IHOP Restaurants (Franchise Network)
The primary business operated by IHOP is its franchise network of restaurants, which includes over 1,700 locations worldwide as of 2025. While the majority are located in the United States, IHOP has expanded into Mexico, the Middle East, South America, India, and Southeast Asia. These restaurants are operated by independent franchisees under multi-unit agreements. IHOP provides brand oversight, menu development, marketing, and quality assurance for the entire network.
IHOP’s restaurant model includes:
- Standalone IHOP locations
- IHOP Express (smaller-footprint, quick-service formats for airports, travel centers, and college campuses)
- Ghost Kitchens and Delivery-Only Outlets in urban markets
IHOP owns the rights to all operational branding, product licensing, menu concepts, and restaurant formats under this network.
IHOP Express
IHOP Express is a fast-service variation of the standard IHOP restaurant, designed for non-traditional venues such as airports, malls, universities, and military bases. This model has grown steadily, particularly in areas with limited space or where quick turnaround is crucial. These outlets are streamlined versions with smaller menus, faster service, and lower buildout costs.
IHOP Express is directly managed through corporate oversight and franchise agreements with specialized operators in hospitality or travel sectors.
Flip’d by IHOP
Flip’d by IHOP is a fast-casual spinoff launched to compete with on-the-go breakfast and lunch chains. Originally piloted in 2020 and refined by 2023, Flip’d locations are smaller than traditional IHOP restaurants. They feature counter service, mobile ordering, and a menu tailored for fast-paced urban customers, including breakfast sandwiches, pancake bowls, coffee, and smoothies.
As of 2025, Flip’d operates in key metro markets such as New York City, Chicago, and Denver, with plans for expansion through franchise agreements. While operated under the IHOP brand, Flip’d maintains a separate operational identity and tech infrastructure focused on mobile-first consumer behavior.
IHOP Digital Platforms
IHOP owns and manages its digital platforms, which include:
- IHOP Mobile App: Used for mobile ordering, loyalty rewards, and promotions.
- MyHop Loyalty Program: A rewards program that offers discounts, birthday specials, and return incentives to frequent customers.
- IHOP.com: The official website used for menu access, location search, franchising inquiries, and digital ordering.
These platforms are proprietary to IHOP and are supported internally by IHOP’s technology and digital marketing teams. They have become a vital part of revenue generation, especially through delivery partnerships and app-exclusive deals.
Licensing & Retail Product Lines
IHOP licenses its brand for retail grocery products, including pancake syrups, frozen pancakes, coffee blends, and baking mixes. These are manufactured and distributed through third-party agreements but under the control of IHOP’s brand licensing division.
These retail products are available in major supermarkets and convenience chains across North America. IHOP’s licensing revenue, while not as large as its franchise income, provides steady brand visibility and off-premise income.
Strategic Partnerships (Operated Under IHOP Oversight)
IHOP also engages in strategic partnerships for co-branded ventures, such as:
- IHOP inside TravelCenters of America
- IHOP airport food service contracts via partnerships with concession operators
- Dual-branded IHOP + Applebee’s test locations, though the real estate and branding are managed through joint franchise agreements under Dine Brands’ shared infrastructure
While these are not wholly separate companies, IHOP has active operational control or oversight on brand compliance and customer experience in each of these partnerships.
Franchise Development & Real Estate Entities
IHOP maintains internal teams and operating units responsible for:
- Franchise Sales & Development: Manages recruitment and onboarding of new franchisees globally.
- Restaurant Design & Construction: Oversees prototyping, design standards, and franchise build-outs.
- International Licensing Divisions: Tailors IHOP concepts for international operators and regional compliance.
These departments function as semi-autonomous entities within IHOP’s structure and manage both domestic and international growth.
Final Thoughts
So, who owns IHOP? It’s not a single entrepreneur or family. IHOP is owned by Dine Brands Global, a public company traded on the stock market. Its major shareholders are large institutional investors like BlackRock and Vanguard. IHOP operates with a strong franchise model and continues to grow under experienced leadership. It is one of the most successful American dining chains, with a rich history and a solid financial foundation.
FAQs
Who is the parent company of IHOP?
The parent company of IHOP is Dine Brands Global, Inc., a publicly traded restaurant holding company that also owns Applebee’s and Fuzzy’s Taco Shop.
Is IHOP an Israeli company?
No, IHOP is not an Israeli company. It is an American restaurant brand founded in California in 1958 and headquartered in Pasadena, California.
Does McDonald’s own IHOP?
No, McDonald’s does not own IHOP. IHOP is owned by Dine Brands Global, which has no affiliation with McDonald’s Corporation.
What country owns IHOP?
IHOP is owned by a U.S.-based company. It is an American brand, and its parent company, Dine Brands Global, is incorporated and headquartered in the United States.
Who is the largest IHOP franchisee?
As of 2025, the largest IHOP franchisee is Sun Holdings, Inc., which operates hundreds of IHOP units across the U.S. The company is known for managing a diverse portfolio of franchise brands.
Is IHOP owned by Denny’s?
No, IHOP and Denny’s are competitors, not connected. Denny’s operates as an independent public company, while IHOP is owned by Dine Brands Global.
Who did IHOP merge with?
IHOP did not merge with another company but rather acquired Applebee’s International in 2007. This acquisition led to the formation of the parent company, originally called DineEquity, now Dine Brands Global.
Who built the first IHOP?
The first IHOP was built by Al Lapin Jr. and his brother Jerry Lapin, along with early investors William Kaye and Albert Kallis, in Toluca Lake, California, in 1958.
Is the first IHOP still open?
The original IHOP location in Toluca Lake is no longer in operation as the same unit, but the area still has IHOP restaurants. The original building has been repurposed over the years.
Who owns IHOP restaurant?
IHOP restaurants are primarily franchise-owned. The IHOP brand and franchise system are owned by Dine Brands Global, while individual locations are operated by independent franchisees.
Who owns IHOP and Applebee’s?
Both IHOP and Applebee’s are owned by Dine Brands Global, a restaurant holding company that manages and supports both brands.
When did IHOP buy Applebee’s?
IHOP acquired Applebee’s International in 2007 for approximately $2.1 billion, transforming into a multi-brand restaurant group.
Does IHOP own Applebee’s?
Technically, IHOP does not own Applebee’s. Both IHOP and Applebee’s are owned by the same parent company, Dine Brands Global.
Is IHOP a franchise?
Yes, IHOP operates as a franchise-based business model, with over 99% of its restaurants run by independent franchisees under license from the company.
Is IHOP a family restaurant?
Yes, IHOP is widely considered a family restaurant. It offers a family-friendly menu, casual dining atmosphere, and pricing designed for groups and children.
What made IHOP a successful brand?
IHOP’s success comes from its all-day breakfast model, strong brand recognition, and affordable pricing. Its franchise model allowed rapid expansion with low operational risk. Menu innovation, marketing campaigns like “IHOb,” and strategic acquisitions like Applebee’s also contributed to its long-term growth and customer loyalty.
Does Applebee’s own IHOP?
No, Applebee’s and IHOP are sister brands. Both are owned by Dine Brands Global.
Where is IHOP headquartered?
IHOP’s corporate headquarters is in Glendale, California, USA.
Is IHOP publicly traded?
IHOP itself is not directly listed. Its parent, Dine Brands Global, is publicly traded on the NYSE under the symbol DIN.

