Hyundai is one of the most recognized names in the automotive world. But many people still ask, who owns Hyundai? The answer isn’t simple. Hyundai’s ownership is tied to a complex group structure involving family leadership, affiliated companies, and public shareholders.
History of Hyundai
Hyundai was founded in 1947 by Chung Ju-yung as a construction company. In 1967, it entered the automotive industry by launching the Hyundai Motor Company. Its first car, the Cortina, was produced in cooperation with Ford. Hyundai released its first Korean-designed and manufactured car, the Pony, in 1975.
Over time, Hyundai grew into a massive chaebol—a South Korean family-run conglomerate. In 2000, Hyundai Group was broken into several independent units, with Hyundai Motor Group becoming a key player in the global automotive market.
Who Owns Hyundai: Major Shareholders
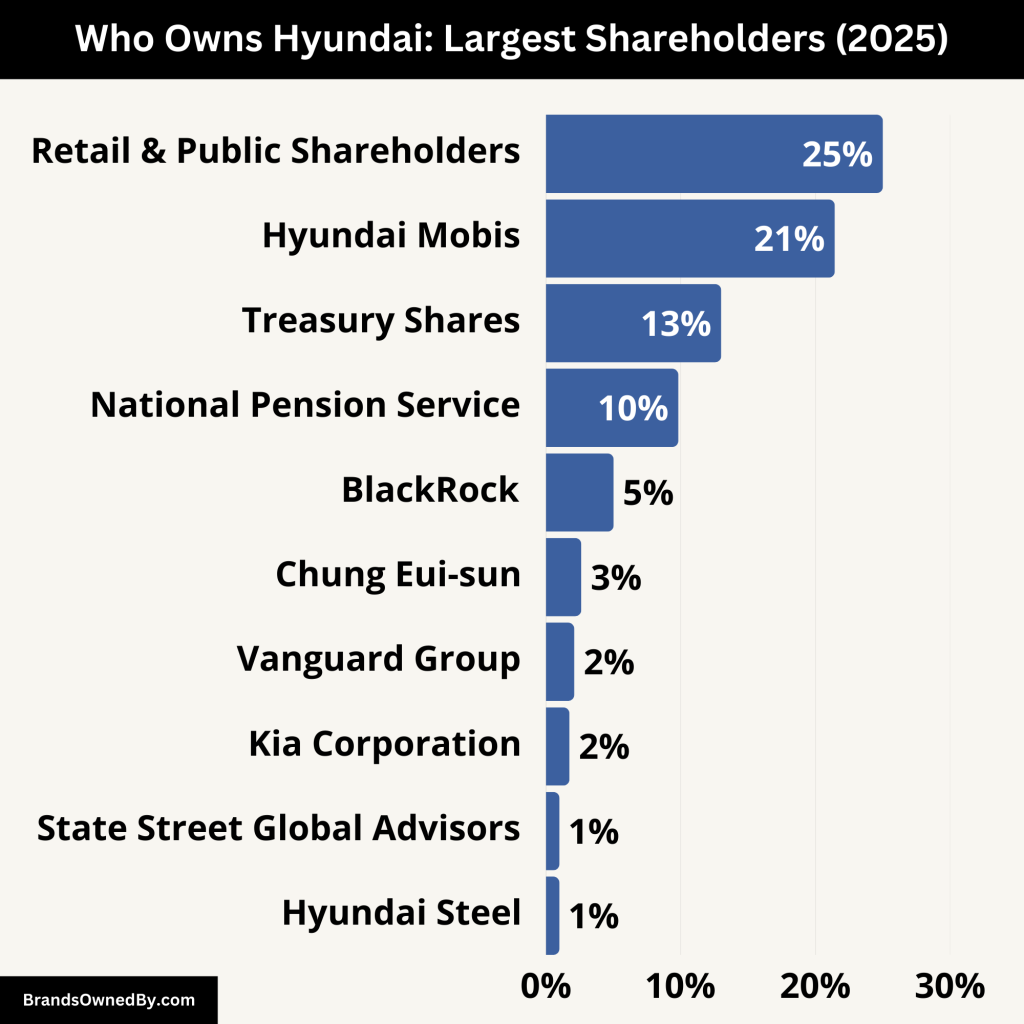
Hyundai Motor Company is the flagship subsidiary of Hyundai Motor Group. It is a publicly traded company listed on the Korea Exchange (KRX). Ownership is divided among family members, institutional investors, affiliated companies, and public shareholders.
The largest shareholder is Hyundai Mobis, an auto parts affiliate within the Hyundai Motor Group. Through cross-shareholding among Hyundai Motor, Kia, and Hyundai Mobis, the founding Chung family retains effective control of the group.
Here are the major Hyundai shareholders who own it today:
| Shareholder | Ownership (%) | Type | Role / Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hyundai Mobis | 21.43% | Strategic affiliate | Largest shareholder; central to Hyundai Motor Group’s control via cross-shareholding |
| National Pension Service (NPS) | 9.82% | Domestic institutional | Major public pension fund; significant influence on governance and voting |
| BlackRock | ~5.02% | Foreign institutional | Passive investor; growing influence on ESG and governance matters |
| Vanguard Group | ~1.7–2.1% | Foreign institutional | Passive investor; aligns with global ESG policies and governance voting |
| State Street Global Advisors | ~1% | Foreign institutional | Passive investor; supportive of long-term shareholder value |
| Chung Eui-sun | 2.62% | Individual (founding family) | Executive Chair; small stake but large control through group structure |
| Kia Corporation | 1.74% | Cross-holding affiliate | Reinforces internal group structure and strategy alignment |
| Hyundai Steel | 0.56% | Group affiliate | Vertical supplier; minor stake but important operational role |
| Treasury Shares | 13.37% | Held by Hyundai Motor | Non-voting shares; used for strategic and financial purposes |
| Retail and Public Shareholders | ~20–25% | Individual investors | Dividends and minor voting rights; influence rising with shareholder activism |
Hyundai Mobis – Largest Shareholder
Hyundai Mobis holds approximately 21.43% of Hyundai Motor Company’s common shares, making it the largest single shareholder. As the group’s core auto parts and technology affiliate, Hyundai Mobis plays a central role in both supply and governance.
This ownership gives Hyundai Mobis significant voting power in corporate matters, enabling it to align decisions with the broader interests of Hyundai Motor Group. It also reinforces the circular shareholding structure that helps the Chung family retain control.
National Pension Service (NPS) – Strategic Institutional Shareholder
The National Pension Service of South Korea owns around 9.82% of Hyundai Motor. NPS is one of the world’s largest pension funds and a major institutional investor in South Korea.
While it does not actively participate in management, NPS’s voting decisions can sway shareholder meetings, particularly during proxy battles or governance reforms. Its investment is primarily financial, but its large stake gives it influence in corporate governance debates.
BlackRock – Major Foreign Investor
BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, owns about 5.02% of Hyundai Motor. Its investment is part of a diversified portfolio focused on long-term financial returns.
Although BlackRock is a passive investor, it increasingly exercises its voting rights on ESG issues. The firm has encouraged improved board independence and climate risk disclosures across the companies it invests in, including Hyundai.
Vanguard Group – Passive Institutional Shareholder
Vanguard is another major U.S.-based asset manager that holds a stake in Hyundai, estimated at 1.7–2.1%. Like BlackRock, Vanguard follows a passive investment strategy and seeks stable returns.
It generally supports company leadership but participates in shareholder votes that align with its global ESG and governance policies.
State Street Global Advisors
State Street, another large U.S. institutional investor, holds a smaller stake in Hyundai, estimated at around 1%. It acts as a passive manager, focused on long-term shareholder value.
State Street occasionally joins global institutional efforts to push for transparency and board-level accountability in multinational firms.
Chung Eui-sun – Executive Chair and Family Stakeholder
Chung Eui-sun, the Executive Chair of Hyundai Motor Group, holds approximately 2.62% of Hyundai Motor Company. Despite his relatively modest individual stake, he effectively controls the group through leadership roles and indirect influence across affiliates.
He is the third-generation leader of the founding Chung family. His stake is symbolic of the family’s continued presence and strategic direction within the group.
Kia Corporation – Group Affiliate and Shareholder
Kia owns about 1.74% of Hyundai Motor Company. As Hyundai’s largest automotive affiliate, Kia also has Hyundai as one of its major shareholders, reinforcing their mutual ownership loop.
This cross-holding stabilizes the internal governance structure and helps resist hostile takeovers. It also strengthens the alignment of business strategies across both companies.
Hyundai Steel – Strategic Group Affiliate
Hyundai Steel, another Hyundai Motor Group subsidiary, holds a small but strategic stake in Hyundai Motor Company (around 0.56%). As a supplier of steel and automotive components, Hyundai Steel’s investment is part of the broader web of internal group holdings.
Its role is primarily operational support, but its shares also contribute to maintaining the Chung family’s influence within the group.
Hyundai Motor Company Treasury Shares
Hyundai Motor itself holds treasury shares amounting to roughly 13.37% of its own stock. These shares are non-voting and are often used for employee stock options, acquisitions, or resale.
Although they don’t directly influence corporate decisions, treasury shares reduce the effective number of outstanding shares, thereby boosting the voting power of remaining shareholders.
Retail and Public Shareholders
Individual and domestic investors hold approximately 20–25% of Hyundai Motor shares. These investors include South Korean citizens and retail traders who buy shares through the Korea Exchange.
Though fragmented, they are an important part of the shareholder base and participate in dividends and voting when organized. Their influence is typically limited unless aggregated through shareholder advocacy groups.
Who Controls Hyundai?
Although Hyundai Motor Company is publicly traded, real control lies within the Hyundai Motor Group’s internal network, led by the founding Chung family. This control is maintained not just through share ownership, but also through executive positions, cross-shareholdings, and board-level influence. Let’s explore the key people and structures that drive decision-making at Hyundai.
Chung Eui-sun – Executive Chair of Hyundai Motor Group
Chung Eui-sun is the current Executive Chair of Hyundai Motor Group and the most powerful figure in the organization. He assumed the role in October 2020, succeeding his father, Chung Mong-koo, who transformed Hyundai into a global auto giant.
Although Eui-sun owns only 2.62% of Hyundai Motor Company’s shares, his leadership role gives him effective control. He is also a significant shareholder in Hyundai Mobis, the group’s most powerful affiliate, and holds influence across Kia and other subsidiaries.
Under his leadership, Hyundai has focused on electric vehicles (EVs), hydrogen technology, autonomous driving, and robotics. He spearheaded Hyundai’s acquisition of Boston Dynamics and the launch of its urban air mobility unit, Supernal.
Chung is known for his global outlook, tech-forward strategy, and push toward sustainability. His decisions shape the company’s future and long-term direction.
CEO of Hyundai Motor Company – Jaehoon Chang
The current President and CEO of Hyundai Motor Company is Jaehoon (Jay) Chang. He was appointed CEO in 2021 and reports directly to Chung Eui-sun.
Chang previously served as Executive Vice President and Head of Hyundai’s Business Division, with a strong background in global operations and strategic planning. As CEO, he oversees the company’s day-to-day operations, global production, brand development, and technology rollout.
Under his leadership, Hyundai has expanded its IONIQ electric vehicle lineup, improved digital transformation, and made strong pushes into North American and European markets. He also works closely with Genesis, Hyundai’s luxury brand, and leads initiatives in mobility services and connected car ecosystems.
While Chung Eui-sun sets the group’s long-term vision, Chang executes the company’s strategy on a global scale.
Board of Directors and Committees
Hyundai Motor Company is governed by a Board of Directors composed of both internal and external members. The board is responsible for:
- Approving major business strategies and financial policies
- Appointing and monitoring executives
- Overseeing corporate governance and compliance
There are multiple board committees, including:
- Audit Committee – Oversees financial reporting and internal controls
- Outside Director Nomination Committee – Recommends independent board members
- Compensation Committee – Reviews executive pay and incentive policies
- ESG Committee – Guides sustainability, ethics, and environmental policies
The inclusion of outside directors has increased in recent years to meet global governance standards, although internal stakeholders still maintain substantial influence.
Cross-Shareholding Control Structure
Hyundai Motor Group uses cross-shareholdings between key affiliates to maintain internal control without relying on a majority shareholder. The main loop includes:
- Hyundai Mobis owns 21.43% of Hyundai Motor Company
- Hyundai Motor Company owns 33.88% of Kia Corporation
- Kia Corporation owns 17.28% of Hyundai Mobis
This triangle creates stable control, allowing the founding family to lead the group without needing majority ownership in any single entity. This system also helps prevent hostile takeovers.
Strategic Influence Beyond Ownership
Although Chung Eui-sun and his allies do not hold majority shares, their strategic share placement, executive positions, and control of board appointments give them powerful influence. Institutional investors like NPS and BlackRock may vote on resolutions, but they rarely challenge management.
Together, these elements give Hyundai Motor Group tight centralized control, balancing public accountability with long-term family leadership.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Hyundai
Hyundai Motor Company has consistently ranked among the largest automakers in the world in terms of revenue and asset value. It operates globally, with manufacturing plants, R&D centers, and sales networks across Asia, North America, Europe, and emerging markets.
The company’s financial strength comes from a diverse portfolio that includes Hyundai, Genesis, and its strong affiliations with Kia, Hyundai Mobis, and Hyundai Steel. Over the past decade, Hyundai has weathered global disruptions, chip shortages, and the COVID-19 pandemic, while successfully transitioning toward electric vehicles and future mobility.
Hyundai’s 2024 Financial Performance
- Annual Revenue (2024): ₩162.3 trillion KRW (approx. $121.8 billion)
- Net Profit (2024): ₩13.7 trillion KRW (approx. $10.3 billion)
- Market Capitalization (2024): ₩60 trillion KRW (approx. $45 billion)
- Total Assets: ₩270+ trillion KRW
The strong performance in 2024 was driven by high-margin EV models (especially under the IONIQ and Genesis brands), premium car sales in North America, and robust demand in India and Europe. Improved supply chain conditions and higher ASP (average selling price) also contributed.
Below is a table showing Hyundai Motor Company’s annual revenue and estimated net worth/market capitalization over the last 10 years. All figures are approximated and converted to USD for consistency (exchange rates and inflation considered):
| Year | Revenue (USD Billion) | Net Worth / Market Cap (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 121.8 | 45.0 |
| 2023 | 116.7 | 44.5 |
| 2022 | 112.0 | 38.2 |
| 2021 | 105.5 | 39.6 |
| 2020 | 87.9 | 35.4 |
| 2019 | 90.7 | 32.1 |
| 2018 | 88.0 | 34.7 |
| 2017 | 85.0 | 35.2 |
| 2016 | 82.2 | 33.8 |
| 2015 | 81.0 | 31.4 |
| 2014 | 88.1 | 34.6 |
Key Trends and Financial Insights
- 2014–2016: Hyundai saw strong performance in emerging markets and steady growth in North America.
- 2017–2019: Revenue stagnated slightly due to global market saturation, rising R&D costs, and competition.
- 2020: COVID-19 impacted global sales, but Hyundai was more resilient than some rivals.
- 2021–2022: Rapid rebound with increased demand for SUVs and a surge in EV interest.
- 2023–2024: Hyundai’s transformation into a tech-driven mobility company led to record-breaking revenue and profits.
Brands and Companies Owned by Hyundai
Hyundai Motor Company is the flagship of the broader Hyundai Motor Group, one of South Korea’s largest chaebols. The group consists of dozens of affiliates operating in automotive manufacturing, logistics, parts supply, finance, steel, robotics, and mobility services.
Below are the most important companies either fully owned or strategically controlled by Hyundai through equity stakes or cross-shareholding:
| Company / Brand | Type | Ownership / Control | Description / Strategic Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kia Corporation | Automotive | Hyundai owns 33.88% | Produces mainstream vehicles and EVs; shares platforms with Hyundai |
| Hyundai Mobis | Automotive parts | Largest shareholder of Hyundai (21.43%) | Core supplier of modules, electronics, and EV components; controls Hyundai via shareholding |
| Genesis Motor | Luxury vehicle brand | 100% owned by Hyundai | Independent premium car brand; enhances Hyundai’s global image and margins |
| Hyundai Steel | Steel manufacturing | Controlled affiliate | Supplies automotive steel; supports vertical integration and quality control |
| Hyundai Glovis | Logistics & transport | Hyundai is major shareholder | Handles global vehicle shipping, supply chain management, and recycling |
| Hyundai Wia | Auto & industrial parts | Group affiliate | Produces engines, machine tools, and defense parts |
| Boston Dynamics | Robotics | 80% owned by Hyundai Motor Group | U.S.-based robotics company; core to Hyundai’s AI and automation strategy |
| Supernal | Urban Air Mobility (UAM) | 100% owned subsidiary | Develops eVTOL aircraft for future urban transport |
| Motional | Autonomous driving | 50% JV with Aptiv | Focused on self-driving technologies and robo-taxi deployment |
| Hyundai Capital | Financial services | Hyundai + GE Capital | Provides auto financing and leasing in global markets |
| Hyundai Card | Credit and digital finance | Group affiliate | Offers credit card and digital finance products in South Korea |
| Hyundai Rotem | Rail & defense systems | Group company | Manufactures trains, defense vehicles, and heavy equipment |
| Hyundai AutoEver | IT services | Group affiliate | Provides software, infotainment, and digital mobility solutions |
| Hyundai Engineering | Engineering & construction | Group affiliate | Designs and builds industrial plants and infrastructure projects |
| Hyundai Engineering & Construction (Hyundai E&C) | Construction | Related through wider Hyundai networks | One of Korea’s top builders; involved in global and domestic projects |
| Innocean Worldwide | Marketing & advertising | Group subsidiary | Hyundai’s in-house global marketing and creative agency |
| HTWO | Hydrogen fuel cell brand | Hyundai Motor’s fuel cell division | Develops hydrogen mobility solutions for commercial and passenger vehicles |
| IONIQ | EV sub-brand | Owned by Hyundai | Dedicated to fully electric models (IONIQ 5, 6, and upcoming 7) |
| Genesis Studio | Retail experience brand | Under Genesis | Provides luxury car showroom experiences globally |
| Bluelink | Connected car platform | Developed by Hyundai | Hyundai’s telematics system for vehicle connectivity, remote control, and security |
| Hyundai Transys | Transmission systems | Group affiliate | Specializes in vehicle transmissions and mobility powertrain solutions |
| Hyundai MNSOFT | Navigation software | Group IT firm | Builds map data, digital dashboards, and infotainment platforms |
| AIRS Company | AI development unit | Hyundai Motor Group | Develops AI and deep learning technologies for mobility and automation |
| Hyundai AutoLand | Smart factory brand | Hyundai Motor | Modern, digitalized auto manufacturing facilities under Hyundai’s Smart Factory strategy |
| Hyundai Kefico | Electronics & control systems | Group subsidiary | Specializes in vehicle electronic control systems and powertrains |
Kia Corporation
Kia is the second-largest automobile manufacturer in South Korea and a key subsidiary of Hyundai Motor Group. Although Hyundai does not fully own Kia, it holds 33.88% of Kia’s shares, giving it significant strategic control.
Kia contributes heavily to group revenue and product diversity, focusing on compact cars, SUVs, and EVs. Kia has been critical in the success of the group’s global EV strategy, especially with models like the EV6 and EV9. It shares platforms and technologies with Hyundai, including battery tech and infotainment systems.
Kia also holds shares in Hyundai Mobis, reinforcing the group’s internal ownership loop and defending against hostile takeovers.
Hyundai Mobis
Hyundai Mobis is Hyundai’s core parts and modules supplier. It is publicly listed but is effectively controlled by Hyundai Motor Group through cross-shareholding and board alignment.
Hyundai Mobis develops key technologies like ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems), inverters, powertrains, and EV components. It supplies both Hyundai and Kia, and its strong presence helps Hyundai Motor Group maintain vertical integration.
Hyundai Mobis is also the largest shareholder of Hyundai Motor Company with a 21.43% stake, making it essential to Hyundai’s control structure.
Genesis Motor
Genesis is Hyundai’s standalone luxury vehicle brand, launched in 2015. It was created to compete with premium automakers such as Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Lexus.
Although not a separate legal company, Genesis operates independently under Hyundai’s umbrella. The brand has received global acclaim for its design, safety, and technological innovation. Its popular models include the GV70, G80, and electric GV60.
Genesis is central to Hyundai’s efforts to boost profit margins, attract high-end customers, and gain prestige in Western markets, especially the U.S. and Europe.
Hyundai Steel
Hyundai Steel is South Korea’s second-largest steel producer and a critical supplier of automotive-grade steel to Hyundai and Kia.
While it operates independently, it is tightly integrated into the group’s supply chain and controlled via shareholding relationships. It ensures cost efficiency, quality control, and material consistency for Hyundai’s vehicle manufacturing process.
Hyundai Steel also participates in group-wide ESG initiatives, focusing on carbon-neutral steel to support EV production goals.
Hyundai Glovis
Hyundai Glovis is the group’s logistics and shipping company. It manages vehicle transportation, parts logistics, inventory planning, and international shipping.
Hyundai Motor Company owns a large stake in Hyundai Glovis, and the company plays a vital role in the efficient global distribution of Hyundai and Kia vehicles.
It also operates in used car auctions, fleet management, and automotive recycling, enhancing circular economy initiatives within the group.
Hyundai Wia
Hyundai Wia manufactures key components such as engines, modules, and machine tools. It supplies both Hyundai and Kia and contributes to the group’s high level of in-house manufacturing.
It is also involved in the production of defense equipment and industrial robots, expanding Hyundai’s technological reach.
Hyundai Motor holds a strategic stake in the company, which reinforces its vertical integration.
Boston Dynamics
Boston Dynamics, the U.S.-based robotics firm known for its agile robots like Spot and Atlas, was acquired by Hyundai Motor Group in 2021. Hyundai owns around 80% of the company.
Boston Dynamics is now a core part of Hyundai’s future mobility and AI vision, contributing to factory automation, urban mobility, and AI-powered robotics. The company is also working with Hyundai’s EV and logistics teams to develop smart warehouses and delivery systems.
Supernal
Supernal is Hyundai’s urban air mobility (UAM) subsidiary based in the U.S. It aims to commercialize electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft by 2028.
Backed by Hyundai’s investment in aerospace R&D and mobility tech, Supernal plays a key role in positioning the group as a pioneer in next-generation transportation. It collaborates with global aviation partners and regulatory bodies to bring flying vehicles to market.
Motional (Joint Venture with Aptiv)
Motional is a joint venture between Hyundai Motor Group and Aptiv, a global leader in automotive technology. Each company owns 50% of the venture.
Motional focuses on autonomous driving technologies and operates pilot programs in the U.S. using Hyundai IONIQ 5-based robo-taxis. It is a cornerstone of Hyundai’s long-term push into Level 4+ autonomy and future mobility services.
Hyundai Capital and Hyundai Card
These financial service companies are jointly owned by Hyundai Motor Group and other partners like GE Capital.
- Hyundai Capital provides car loans, leasing, and auto financing services across several countries.
- Hyundai Card issues credit cards and digital finance products with a strong presence in Korea.
Both entities support vehicle sales, improve customer retention, and provide recurring revenue streams beyond manufacturing.
Hyundai Rotem
Hyundai Rotem specializes in manufacturing railroad systems, defense equipment, and plant machinery. Though technically separate from Hyundai Motor Company, it remains part of Hyundai Motor Group’s extended industrial network.
It is known for producing high-speed trains, urban transit systems, and main battle tanks (K2 Black Panther). Hyundai Rotem supports Hyundai’s expansion into smart mobility infrastructure and national defense contracts, particularly in South Korea and the Middle East.
Hyundai AutoEver
Hyundai AutoEver is the IT and digital solutions arm of Hyundai Motor Group. It provides software platforms, cloud infrastructure, and connected mobility services for Hyundai, Kia, and Genesis vehicles.
It is instrumental in the development of the Bluelink system, OTA updates, cybersecurity, and smart factory technologies. AutoEver is deeply involved in Hyundai’s transformation into a software-defined vehicle (SDV) manufacturer.
Hyundai Engineering
Hyundai Engineering Co., Ltd. is a global engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) company. It designs and builds chemical plants, power plants, infrastructure, and industrial facilities in Asia, the Middle East, and beyond.
While it functions independently, Hyundai Engineering supports Hyundai Motor’s global footprint by building factories, mobility campuses, and EV manufacturing hubs.
Hyundai Engineering & Construction (Hyundai E&C)
Hyundai E&C is one of South Korea’s oldest and largest construction firms. Though it’s no longer directly controlled by Hyundai Motor Company, it remains historically connected through the broader Hyundai industrial lineage.
It handles large infrastructure projects, including roads, bridges, skyscrapers, and international developments. Hyundai E&C often works alongside Hyundai Engineering on major Hyundai Motor Group projects abroad.
Innocean Worldwide
Innocean is the in-house marketing and advertising agency of Hyundai Motor Group. It manages global branding, creative content, digital campaigns, and event sponsorships.
Innocean plays a key role in promoting Hyundai and Kia in global markets, including producing campaigns for the Super Bowl, FIFA World Cup, and Olympic Games. It also operates regional offices in the U.S., Europe, and Asia.
HTWO
HTWO is Hyundai’s hydrogen-focused brand, launched in 2020. It centralizes all activities related to hydrogen fuel cell systems, including the NEXO SUV, commercial trucks, and maritime solutions.
HTWO works with governments and private firms to build hydrogen infrastructure, supporting Hyundai’s goal to lead in the hydrogen economy. It also exports fuel cell systems to other automakers and industrial partners.
IONIQ
IONIQ is Hyundai’s dedicated electric vehicle (EV) brand, launched in 2020. It includes the IONIQ 5, IONIQ 6, and upcoming IONIQ 7 SUV.
Unlike Hyundai’s other cars, IONIQ models are built on the E-GMP platform, a modular EV-specific architecture. The brand combines technology, sustainability, and design innovation, aimed at competing with Tesla and European EV brands.
Genesis Studio
Genesis Studio is a premium retail and customer experience concept for Genesis vehicles. These are showroom-like venues in major cities that allow customers to explore and interact with vehicles in a luxury, non-sales-driven environment.
Studios are located in cities like New York, Seoul, Munich, and Shanghai, reflecting Genesis’ strategy to distinguish itself from traditional car dealerships.
Bluelink
Bluelink is Hyundai’s connected car platform, offering features like remote vehicle control, live traffic updates, emergency assistance, theft alerts, and smart navigation.
Developed internally and powered by Hyundai AutoEver, Bluelink is available in Hyundai, Kia, and Genesis vehicles. It supports Hyundai’s push toward digital mobility services and AI-integrated driving.
Hyundai Transys
Hyundai Transys specializes in powertrains and transmissions for both internal combustion and electric vehicles. It is a merger of two former group companies: Hyundai Powertech and Hyundai Dymos.
Transys supplies gearboxes, seats, and drivetrain components to Hyundai and Kia, and plays a role in next-gen EV driveline systems.
Hyundai MNSOFT
Hyundai MNSOFT develops navigation software, digital dashboards, and map data for in-vehicle systems. Its solutions are found in Hyundai, Kia, and Genesis vehicles.
The company is at the forefront of HD mapping, augmented reality navigation, and cloud-based updates, essential for autonomous driving and connected car ecosystems.
AIRS Company
AIRS Company is Hyundai’s AI research division, originally spun out as part of its internal innovation initiative. It develops machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision technologies for smart mobility.
Its AI algorithms support voice assistants, predictive maintenance, driver monitoring systems, and factory optimization.
Hyundai AutoLand
Hyundai AutoLand refers to Hyundai’s series of smart manufacturing facilities, starting with the innovation-focused plant in Ulsan. These factories use AI, robotics, and IoT to optimize production of both EVs and traditional vehicles.
AutoLand factories are designed to support carbon neutrality, energy efficiency, and flexible assembly lines for multiple powertrains.
Hyundai Kefico
Hyundai Kefico specializes in automotive electronics, including engine control units (ECUs), sensors, and powertrain controllers.
It plays a pivotal role in Hyundai’s efforts to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and expand into electrification. Its tech is integrated into both Hyundai and Kia models globally.
Final Thoughts
So, who owns Hyundai? Hyundai Motor is publicly traded, but it remains under the firm control of the Chung family. Through strategic cross-shareholding and affiliate companies like Hyundai Mobis and Kia, the family continues to guide the group’s direction.
Hyundai is more than just a carmaker. It is a global mobility powerhouse that includes luxury vehicles, robotics, and even flying cars. Its blend of family leadership and corporate structure makes it unique among global automakers.
FAQs
Who is the current owner of Hyundai?
Chung Eui-sun is the Executive Chair and effectively controls Hyundai Motor Group, though the company is publicly traded.
Is Hyundai a publicly owned company?
Yes. Hyundai Motor Company is listed on the Korea Exchange. However, control is concentrated within the founding family and group affiliates.
What is Hyundai’s biggest shareholder?
Hyundai Mobis is the largest shareholder, holding over 21% of Hyundai Motor Company.
Does Hyundai own Kia?
Yes. Hyundai Motor owns a significant stake in Kia, and both are part of Hyundai Motor Group.
What companies are under Hyundai?
Major companies include Hyundai Motor, Kia, Genesis, Hyundai Mobis, Hyundai Wia, and Boston Dynamics, among others.

