Huawei is one of the largest telecommunications companies in the world. It’s often the subject of international attention due to its size, technology, and corporate structure. If you’ve ever wondered who owns Huawei, the answer is more complex than it seems. This article dives deep into Huawei’s history, ownership, management, financials, and subsidiaries.
History of Huawei
Huawei was founded in 1987 in Shenzhen, China, by Ren Zhengfei, a former engineer in the People’s Liberation Army. Initially, the company sold telephone exchange equipment imported from Hong Kong. Over time, Huawei began developing its own technology.
By the early 2000s, it expanded internationally and started competing with global giants like Cisco and Ericsson.
Huawei has focused heavily on innovation. It invested significantly in research and development, becoming a major player in telecom networks, smartphones, and cloud services. Despite international challenges, especially in the U.S., Huawei has remained a powerful force in global telecommunications.
Who Owns Huawei?
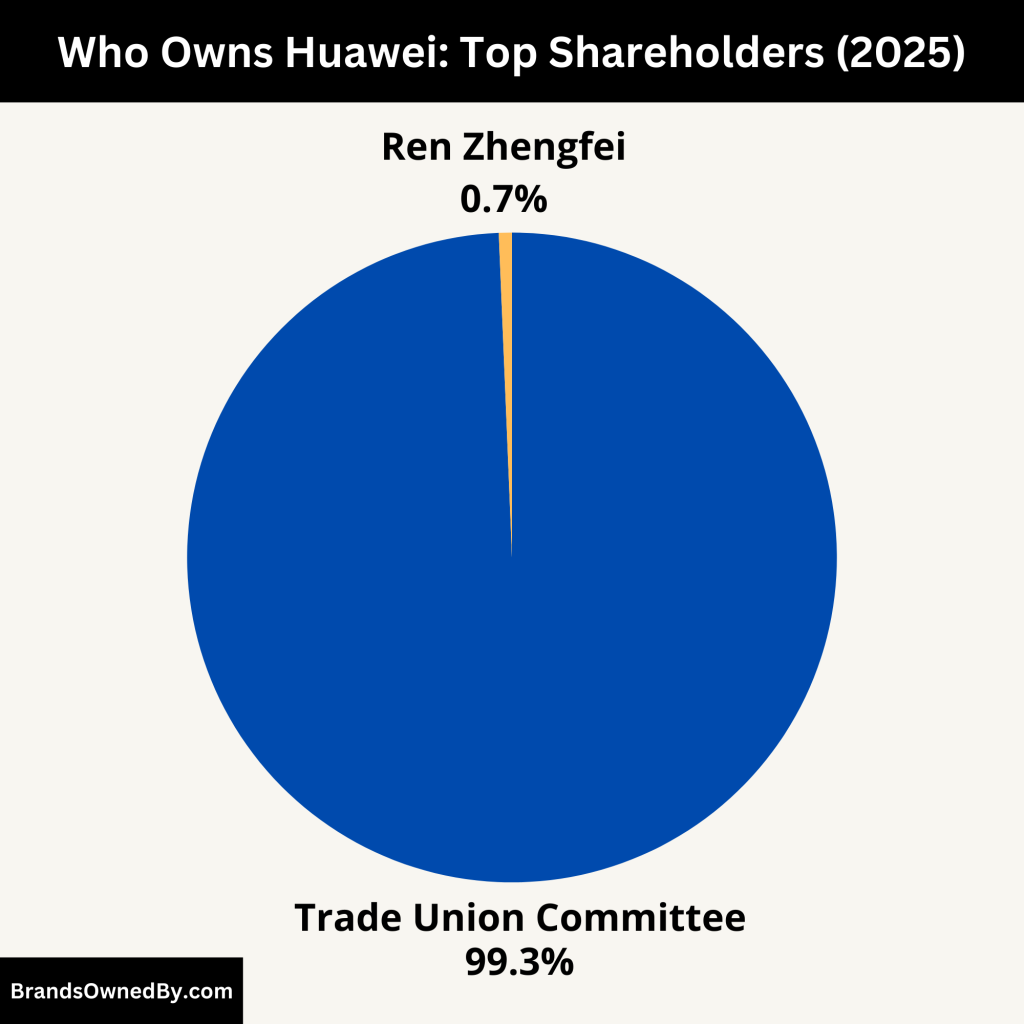
Huawei is a privately held company. It is not publicly traded on any stock exchange. The company is owned by its employees through an employee stock ownership plan (ESOP). However, this structure is not the same as a typical Western ESOP.
The largest individual shareholder and the only named person in the company’s structure is its founder, Ren Zhengfei. The rest of the shares are held by a trade union committee on behalf of the employees. No government or institutional investor officially holds shares in Huawei.
Here’s a breakdown of the major shareholders of Huawei:
| Shareholder | Ownership Percentage | Role | Control/Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huawei Investment & Holding Co., Ltd. Trade Union Committee | 99.35% | Holds shares on behalf of employee shareholders | Exercises voting rights through a Representatives’ Commission; controls majority stake |
| Ren Zhengfei | 0.65% | Founder of Huawei; individual shareholder | Significant strategic influence; senior leadership role in decision-making |
| Employee Shareholders (via Trade Union) | Indirect via Trade Union | Participate in profit-sharing through dividends | Do not directly vote; interests represented via the trade union and commission |
| Representatives’ Commission | N/A (not a shareholder per se) | Elected body representing employee shareholders | Elects the Board of Directors and Supervisory Board; manages corporate governance |
Huawei Investment & Holding Co., Ltd. Trade Union Committee
The majority of Huawei’s shares, approximately 99.35%, are held by the Trade Union Committee of Huawei Investment & Holding Co., Ltd. This entity acts as a proxy for the company’s employee shareholders. Due to Chinese legal restrictions limiting the number of shareholders in a limited liability company, the trade union serves as a collective holder for the employees’ shares. Employees participate in the company’s profits through dividends distributed by the trade union. However, these shares are non-tradable and must be returned to the company upon an employee’s departure.
Ren Zhengfei
Ren Zhengfei, the founder of Huawei, holds approximately 0.65% of the company’s shares as of 2025. Despite this relatively small stake, he maintains significant influence over the company’s strategic direction. Ren’s leadership and vision have been pivotal in Huawei’s growth, and he continues to play a central role in its operations.
Employee Shareholders
Huawei’s unique ownership structure includes a significant number of employee shareholders. As of December 2024, there were approximately 151,796 current and former employees participating in the company’s employee stock ownership plan (ESOP). These shares are held collectively through the trade union, and employees benefit from the company’s profits via dividends. The ESOP is designed to align employees’ interests with the company’s success, fostering a sense of ownership and commitment.
Representatives’ Commission
The Representatives’ Commission is a governing body elected by the employee shareholders. In February 2025, the fifth election was held, resulting in 161 Representatives and 37 Alternate Representatives being chosen. This Commission exercises shareholder rights on behalf of the employees, including electing the company’s Board of Directors and Supervisory Board. The Commission plays a crucial role in Huawei’s corporate governance, ensuring that employee interests are represented in major company decisions.
Who is the CEO of Huawei?
As of 2025, Huawei operates under a unique rotating leadership system rather than having a single, permanent CEO. This structure involves three senior executives who take turns serving as the Rotating and Acting Chairperson for six-month terms. This approach ensures a balance of power, promotes diverse perspectives, and maintains continuity in leadership.
Current Rotating Chairperson: Eric Xu (April 1 – September 30, 2025)
Eric Xu, also known as Xu Zhijun, is serving as Huawei’s Rotating and Acting Chairperson from April 1 to September 30, 2025. He has been with Huawei since 1993 and has held various key positions, including President of the Wireless Network Product Line, Chief Strategy & Marketing Officer, and Chairman of the Strategy & Development Committee. Xu is also the Deputy Chairman of the Board and plays a significant role in shaping Huawei’s strategic direction.
Previous Rotating Chairperson: Meng Wanzhou (October 1, 2024 – March 31, 2025)
Meng Wanzhou, daughter of Huawei’s founder Ren Zhengfei, served as the Rotating Chairperson from October 1, 2024, to March 31, 2025. She concurrently holds the position of Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and Deputy Chairwoman of the Board. Meng has been instrumental in leading Huawei’s financial strategies and has played a pivotal role in the company’s global operations.
Upcoming Rotating Chairperson: Ken Hu (Expected from October 1, 2025)
Ken Hu is anticipated to assume the role of Rotating Chairperson starting October 1, 2025. He has been with Huawei since 1990 and has served in various leadership roles, including President of Huawei’s China market, President of Global Sales, and Chief Strategy and Marketing Officer. Hu is known for his contributions to Huawei’s globalization efforts and strategic planning.
Permanent Leadership: Ren Zhengfei
Ren Zhengfei, the founder of Huawei, continues to serve as the company’s CEO since its inception in 1987. While he has delegated day-to-day operations to the rotating chairpersons, Ren remains a central figure in Huawei’s strategic decisions and long-term vision. His leadership has been pivotal in navigating the company through various global challenges.
Decision-Making Structure
Huawei’s rotating leadership model is designed to prevent the concentration of power and encourage collaborative decision-making. Each rotating chairperson leads the Board of Directors and the Executive Committee during their tenure, ensuring that strategic decisions are made collectively. This system fosters a culture of shared responsibility and aligns with Huawei’s commitment to sustainable growth and innovation.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Huawei
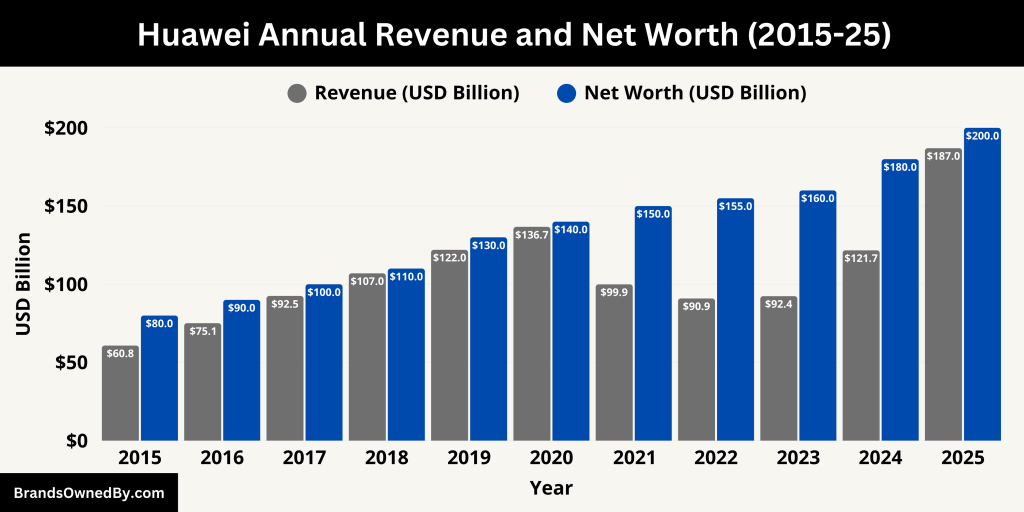
In 2024, Huawei achieved a significant milestone with a total revenue of CNY 862.1 billion, equivalent to approximately USD 121.7 billion. This marked a 22.4% increase from the previous year, showcasing the company’s resilience and growth across various sectors. However, the net profit declined by 28%, amounting to CNY 62.6 billion (around USD 8.6 billion), primarily due to increased investments in research and development and the absence of gains from divested subsidiaries that had bolstered the previous year’s profits.
As of mid-2025, Huawei has not yet released its full financial report for the year. However, based on industry analyses and projections, the company is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Analysts forecast that Huawei’s revenue for 2025 could reach approximately USD 187 billion, with a net profit of around USD 13.2 billion, driven by advancements in 5G infrastructure, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence sectors.
Net Worth and Valuation
Estimating Huawei’s exact net worth is challenging due to its status as a privately held company. However, considering its substantial revenue streams, extensive assets, and significant investments in research and development, various analyses suggest that Huawei’s net worth could be valued at over $200 billion. If the company were publicly traded, its market capitalization might potentially exceed $300 billion, reflecting its strong position in the global technology market.
Below is an overview of the historical revenue and net worth of Huawei:
| Year | Revenue (USD Billion) | Estimated Net Worth (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 (est.) | 187.0 | 200+ |
| 2024 | 121.7 | ~180 |
| 2023 | 92.4 | ~160 |
| 2022 | 90.9 | ~155 |
| 2021 | 99.9 | ~150 |
| 2020 | 136.7 | ~140 |
| 2019 | 122.0 | ~130 |
| 2018 | 107.0 | ~110 |
| 2017 | 92.5 | ~100 |
| 2016 | 75.1 | ~90 |
| 2015 | 60.8 | ~80 |
Companies Owned by Huawei
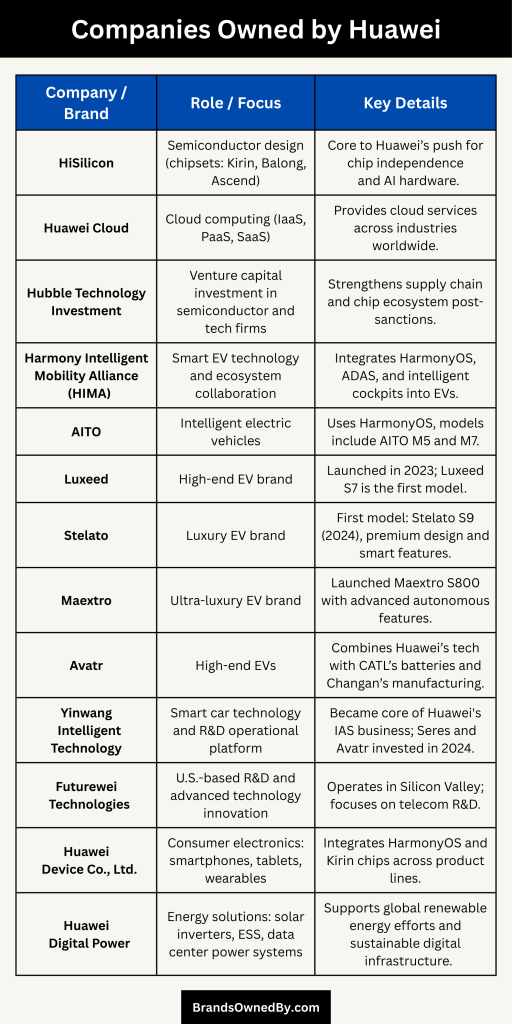
Huawei has expanded its business portfolio significantly over the years, establishing and collaborating with various companies and brands across multiple sectors. As of 2025, Huawei’s ownership and partnerships span telecommunications, semiconductors, cloud computing, automotive, and more.
Below is a detailed overview of the major companies and brands associated with Huawei:
| Company/Brand | Role/Focus | Ownership/Partnership | Key Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| HiSilicon | Semiconductor design (chipsets: Kirin, Balong, Ascend) | Wholly owned by Huawei | Core to Huawei’s push for chip independence and AI hardware. |
| Huawei Cloud | Cloud computing (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) | Wholly owned by Huawei | Provides cloud services across industries worldwide. |
| Hubble Technology Investment | Venture capital investment in semiconductor and tech firms | Wholly owned by Huawei | Strengthens supply chain and chip ecosystem post-sanctions. |
| Harmony Intelligent Mobility Alliance (HIMA) | Smart EV technology and ecosystem collaboration | Strategic alliance led by Huawei | Integrates HarmonyOS, ADAS, and intelligent cockpits into EVs. |
| AITO | Intelligent electric vehicles | Co-developed with Seres Group | Uses HarmonyOS, models include AITO M5 and M7. |
| Luxeed | High-end EV brand | Jointly developed with Chery | Launched in 2023; Luxeed S7 is the first model. |
| Stelato | Luxury EV brand | Huawei–BAIC BluePark joint brand | First model: Stelato S9 (2024), premium design and smart features. |
| Maextro | Ultra-luxury EV brand | Huawei–JAC Group partnership | Launched Maextro S800 with advanced autonomous features. |
| Avatr | High-end EVs | Joint venture with Changan and CATL | Combines Huawei’s tech with CATL’s batteries and Changan’s manufacturing. |
| Yinwang Intelligent Technology | Smart car technology and R&D operational platform | Wholly owned by Huawei (with investor stakes) | Became core of Huawei’s IAS business; Seres and Avatr invested in 2024. |
| Futurewei Technologies | U.S.-based R&D and advanced technology innovation | Wholly owned subsidiary | Operates in Silicon Valley; focuses on telecom R&D. |
| Huawei Device Co., Ltd. | Consumer electronics: smartphones, tablets, wearables | Wholly owned by Huawei | Integrates HarmonyOS and Kirin chips across product lines. |
| Huawei Digital Power | Energy solutions: solar inverters, ESS, data center power systems | Wholly owned by Huawei | Supports global renewable energy efforts and sustainable digital infrastructure. |
HiSilicon
HiSilicon is Huawei’s wholly-owned semiconductor subsidiary, specializing in the design of integrated circuits. Established in 1991, HiSilicon is renowned for developing the Kirin series of system-on-chips (SoCs) used in Huawei’s smartphones, as well as other chipsets like Balong for modems and Ascend for AI applications. Despite challenges due to U.S. sanctions, HiSilicon remains a pivotal component of Huawei’s strategy to achieve self-reliance in semiconductor technology.
Huawei Cloud
Huawei Cloud is the company’s cloud computing arm, offering a range of services including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). With data centers across the globe, Huawei Cloud provides solutions for industries such as finance, healthcare, and education, supporting digital transformation initiatives worldwide.
Hubble Technology Investment
Hubble Technology Investment is Huawei’s venture capital subsidiary, established in 2019. It focuses on investing in semiconductor and technology companies to strengthen Huawei’s supply chain and technological capabilities. By 2021, Hubble had invested in over 40 companies, playing a crucial role in Huawei’s efforts to mitigate the impact of external restrictions on its operations.
Harmony Intelligent Mobility Alliance (HIMA)
HIMA is Huawei’s collaborative platform with various automotive manufacturers to develop intelligent electric vehicles (EVs). Under this alliance, Huawei contributes its expertise in ICT, including HarmonyOS, autonomous driving technologies, and smart cockpit solutions. Key brands under HIMA include:
AITO
AITO (Adding Intelligence to Auto) is a brand co-developed by Huawei and Seres Group. Launched in 2021, AITO vehicles integrate Huawei’s HarmonyOS and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), offering a seamless smart driving experience. Models like the AITO M5 and M7 exemplify this collaboration.
Luxeed
Luxeed is a premium EV brand resulting from Huawei’s partnership with Chery. Introduced in 2023, Luxeed vehicles, such as the Luxeed S7, feature Huawei’s HarmonyOS and cutting-edge autonomous driving capabilities, targeting the high-end electric sedan market.
Stelato
Stelato is a luxury EV brand developed through a collaboration between Huawei and BAIC BluePark. Launched in 2024, the brand’s inaugural model, the Stelato S9, showcases Huawei’s intelligent vehicle technologies combined with BAIC’s manufacturing prowess.
Maextro
Maextro is an ultra-luxury EV brand established by Huawei and JAC Group in 2024. The Maextro S800, its flagship model, integrates Huawei’s full-stack intelligent vehicle solutions, including L3 autonomous driving features, catering to the premium segment of the EV market.
Avatr
Avatr is a joint venture involving Huawei, Changan Automobile, and CATL. This brand focuses on developing high-end intelligent EVs, with models like the Avatr 11 and 12 incorporating Huawei’s smart vehicle technologies and CATL’s battery solutions.
Yinwang Intelligent Technology
Yinwang Intelligent Technology is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Huawei, established in January 2024. It serves as the operational entity for Huawei’s Intelligent Automotive Solution (IAS) business unit. Yinwang focuses on providing comprehensive smart vehicle solutions, including autonomous driving systems and intelligent cockpits. In August 2024, companies like Avatr Technology and Seres Group invested in Yinwang, each acquiring a 10% stake, valuing the company at approximately RMB 115 billion.
Futurewei Technologies
Futurewei Technologies is Huawei’s U.S.-based research and development subsidiary. Located in Silicon Valley, Futurewei focuses on advanced technologies, including telecommunications and networking innovations, contributing to Huawei’s global R&D efforts.
Huawei Device Co., Ltd.
Huawei Device Co., Ltd. is responsible for the company’s consumer electronics division. It oversees the development and production of smartphones, tablets, wearables, and other consumer devices, integrating Huawei’s proprietary technologies like HarmonyOS and Kirin chipsets.
Huawei Digital Power
Huawei Digital Power specializes in providing digital energy solutions, including solar inverters, energy storage systems, and data center energy infrastructure. This division plays a significant role in supporting global efforts toward sustainable and renewable energy adoption.
Final Thoughts
So, who owns Huawei?
The company is owned almost entirely by its employees through a trade union-managed structure. Ren Zhengfei, its founder, holds a small personal stake but wields significant influence. Huawei’s ownership model is unique, combining employee control with a lack of public investors or state ownership. This structure has helped Huawei maintain stability and independence despite global challenges. Its financial health, management approach, and diversified subsidiaries ensure Huawei remains a global tech leader.
FAQs
Who owns Huawei now in 2025?
Huawei is still owned by its employees through a trade union-managed employee stock ownership plan. Ren Zhengfei remains the only named individual shareholder.
Is Huawei publicly traded?
No, Huawei is not listed on any stock exchange. It is a private company and does not issue public shares.
Why is Huawei banned in some countries?
Huawei has faced bans in countries like the U.S. and Australia due to concerns about national security and its alleged ties to the Chinese government. Huawei has denied all allegations of espionage.
Why was Huawei banned in the US?
Huawei was banned in the US due to national security concerns. The US government alleged that Huawei’s telecommunications equipment could be used by the Chinese government for espionage. As a result, in 2019, the company was placed on the Entity List by the U.S. Department of Commerce, restricting it from doing business with American firms without special licenses. The ban affected Huawei’s access to key technologies, including Google services and advanced semiconductors.
Is Huawei Chinese or Japanese?
Huawei is a Chinese company. It was founded in 1987 by Ren Zhengfei in Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China. It is not Japanese. Huawei remains one of China’s largest technology firms and a global leader in telecommunications and electronics.
Why is Huawei banned from Google?
Huawei lost access to Google Mobile Services (GMS) in May 2019 after the U.S. government placed it on the Entity List. This forced Google to suspend its business dealings with Huawei, including licensing of Android with Google apps. As a result, Huawei phones launched after this decision no longer come with pre-installed Google apps like Gmail, Maps, or the Play Store.
Huawei is owned by which country?
Huawei is privately owned and based in China. It is not owned by the Chinese government or any other state. However, due to its strategic importance and the structure of employee ownership, the company is often seen as closely aligned with national interests.
Where is Huawei located?
Huawei’s global headquarters is located in Shenzhen, in Guangdong Province, China. The company also operates R&D centers and offices in over 170 countries, making it a major global player in telecommunications and consumer electronics.
What is the net worth of Ren Zhengfei?
As of 2025, Ren Zhengfei’s estimated net worth is around USD 1.5 to 2 billion. Unlike many tech founders, Ren does not hold shares in publicly listed companies, and Huawei is a private entity. His wealth primarily comes from his stake in the employee-owned structure of Huawei.
Who owns Huawei in Vietnam?
Huawei Vietnam is a local subsidiary of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. It is fully controlled by the parent company in China. There is no local ownership in Vietnam; operations are managed through the company’s regional offices and staff in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
Who owns Huawei phones?
Huawei phones are manufactured and distributed by Huawei Device Co., Ltd., a wholly owned subsidiary of Huawei Technologies. The phones are owned by individual customers and telecom partners globally, with the company retaining ownership of design, software, and hardware production.
Is Huawei state owned?
Huawei is not state-owned. It is a private company owned by its employees through an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP). Founder Ren Zhengfei holds a small minority share, while the rest is collectively owned by current and former employees.
Is Huawei owned by the Chinese government?
No, Huawei is not directly owned by the Chinese government. However, due to its importance in national infrastructure and its strategic role in technology, the company is perceived as being closely tied to government interests. This perception has fueled scrutiny from Western countries, but legally, it remains a private, employee-owned company.

