Cargill is one of the largest privately held corporations in the United States. Despite its size and influence in global agriculture and food industries, many people still ask: who owns Cargill? This article explores its ownership, leadership, financials, and the companies it controls.
Cargill Company Profile
Cargill is a U.S.-based global food, agriculture, financial, and industrial conglomerate. It is the largest privately held company in the United States by revenue. Headquartered in Minnetonka, Minnesota, it operates in over 70 countries and employs more than 160,000 people worldwide as of 2025.
Overview and Company Details
Cargill connects farmers with markets, customers with ingredients, and people with essential services. It handles a wide variety of operations such as grain trading, meat processing, oilseed crushing, cocoa and chocolate manufacturing, animal feed production, and agricultural risk management.
It also has interests in bio-industrial products, renewable energy, and carbon reduction initiatives, as part of its sustainability efforts. Its presence spans North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa, making it one of the most integrated supply chain operators in the world.
In 2025, Cargill’s revenue crossed $174 billion, and it maintains an estimated net worth between $60–80 billion. It continues to invest in innovation and climate-smart agriculture while expanding in fast-growing markets.
Cargill Founders
Cargill was founded in 1865 by William Wallace Cargill, who purchased a small grain flat house in Conover, Iowa. This simple trading post marked the beginning of what would grow into a multinational empire.
His descendants—along with the MacMillan family, who joined by marriage—have kept ownership of the company for over 160 years. Together, these two families have preserved the company’s private status through multiple generations.
Major Milestones
- 1865: William Wallace Cargill founded the company in Conover, Iowa.
- 1875–1900s: Expansion into grain storage, trading, and rail-linked transportation.
- 1930s: Survived the Great Depression by diversifying into feed and seeds.
- 1960s–1980s: Expanded globally across Latin America, Europe, and Asia.
- 1995: Entered financial services and commodity trading on a large scale.
- 2000: Acquired businesses in meat, poultry, and animal nutrition.
- 2011: Acquired Provimi, a major European animal nutrition firm.
- 2015: Entered aquaculture with the $1.5 billion acquisition of EWOS.
- 2021: Acquired Sanderson Farms (in partnership with Continental Grain) and merged it with Wayne Farms.
- 2023: Began large-scale investment in regenerative agriculture and sustainable farming.
- 2024: Reported record profits amid volatility in global food markets due to climate disruptions and supply chain shifts.
- 2025: Launched a new digital platform to connect farmers with global buyers using AI and blockchain-based traceability.
Who Owns Cargill: Major Shareholders
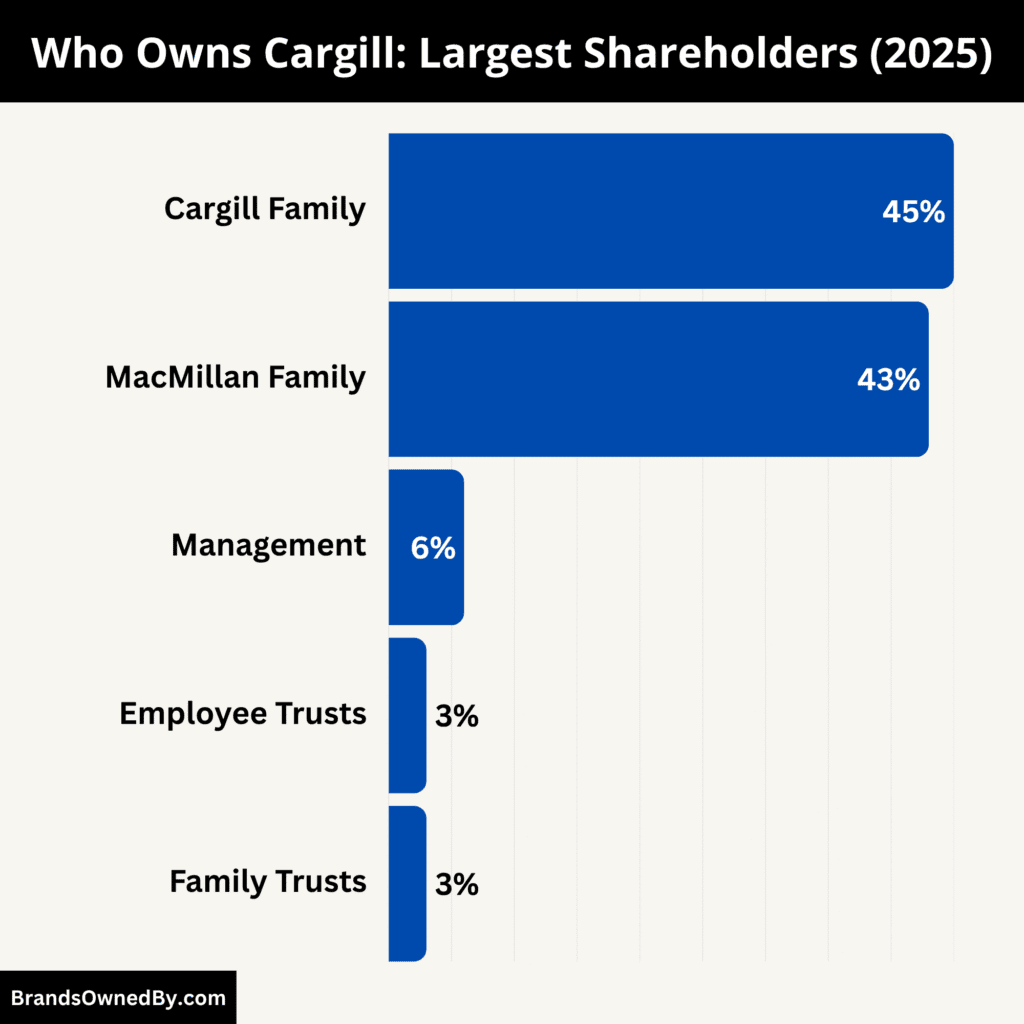
Cargill is a privately held company, which means it is not listed on any stock exchange. It is owned primarily by the descendants of the Cargill and MacMillan families. These two families have kept tight control of the business for generations.
The Cargill and MacMillan families maintain 88% majority control, effectively steering the company’s strategic direction, culture, and long-term vision. Their shared governance ensures the business remains private, stable, and focused on generational continuity rather than short-term shareholder returns.
Here’s a list of the top shareholders of Cargill as of August 2025:
| Shareholder Group | Ownership (%) | Role in Company | Level of Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cargill Family | 45% | Founders, board representation, family trusts | Very High |
| MacMillan Family | 43% | Founders, board participation, family trusts | Very High |
| Management & Former Executives | 6% | Senior leadership, incentive equity | Moderate |
| Employee Trusts & Retirement Plans | 3% | Long-term employee benefits | Low |
| Family Trusts & Charitable Entities | 3% | Philanthropic arms and intergenerational trusts | Low to Moderate |
| Silent Partners / Others | <1% | Legacy stakeholders, private holdings | Minimal |
Cargill Family
The Cargill family are the direct descendants of William Wallace Cargill, the founder of the company. The family has been involved in the company’s ownership since its inception in 1865. As of 2025, the Cargill family collectively owns approximately 45% of the company.
Although they are no longer involved in day-to-day management, several family members sit on the Board of Directors and family governance councils. Their control is exercised through private trusts, long-term agreements, and board representation. The family has remained committed to keeping the company private and maintaining long-term financial stability.
MacMillan Family
The MacMillan family joined the ownership lineage in the late 1800s when John MacMillan Sr. married into the Cargill family and later took over the company’s leadership. As of 2025, the MacMillan family owns approximately 43% of the company.
The MacMillans, like the Cargills, are involved in corporate governance but not in active business operations. Some members have served on the board or in advisory roles. Together with the Cargills, the MacMillans ensure the company remains private, independent, and focused on long-term growth.
Management and Former Executives
Roughly 6% of Cargill is held by current and former senior executives. These shares are typically granted through long-term incentive programs and reward packages for top leaders in the organization.
While this group does not hold controlling power, they benefit from profits and help align executive incentives with the company’s long-term strategy. Their shares are non-voting or limited in voting rights unless they serve on the board.
Employee Stock and Retirement Trusts
An estimated 3% of the company is owned through employee benefit trusts and retirement plans. These are non-controlling shares that provide financial benefits to long-serving employees and retirees.
While employees do not influence strategic decisions through this ownership, it serves as a loyalty and retention tool. Cargill has not pursued a widespread employee stock ownership plan (ESOP), but selected senior personnel may receive equity-linked benefits.
Charitable Foundations and Family Trusts
Approximately 3% of Cargill’s equity is held by private family trusts and charitable foundations linked to the Cargill and MacMillan families. These entities manage wealth across generations and may also contribute to philanthropic causes supported by the company or its founders.
These trusts and foundations usually have designated representatives and may have some indirect influence over how the company balances profit with social responsibility. Their votes are usually exercised in alignment with family governance policies.
Private Family Holdings and Silent Partners
A small portion—about less than 1%—is held by extended family members or silent private investors, often through historical inheritance or legacy arrangements. These investors play no role in management and typically have limited voting rights or access to insider information.
They do, however, benefit from the company’s strong dividend history and valuation growth.
Who is the CEO of Cargill?
As of 2025, Brian Sikes is the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Cargill. He took over the role in January 2023, becoming the 10th CEO in the company’s 160-year history. His appointment marked a significant moment, as he was the first internal executive in over 25 years to be promoted to the top position.
Brian Sikes has spent more than 30 years at Cargill, working in a wide range of business units and global leadership roles. Before becoming CEO, he served as the Chief Operating Officer (COO) and previously led the protein and salt division, which is one of Cargill’s largest and most profitable segments.
Sikes is known internally for his operational expertise, focus on innovation, and a strong commitment to food sustainability and digital transformation. He has held leadership roles in North America, Latin America, and Asia, giving him a broad global perspective of the company’s operations.
Leadership Style and Focus Areas
Under Brian Sikes’ leadership, Cargill has continued to invest in technology, regenerative agriculture, climate-friendly food systems, and supply chain digitization. He has emphasized the importance of making the global food system more secure, sustainable, and resilient.
He also supports expanding Cargill’s presence in emerging markets and investing in AI, blockchain, and real-time traceability platforms to modernize how commodities are traded and tracked.
Sikes is also known for pushing a collaborative leadership style, empowering regional leaders while maintaining strong centralized strategic oversight.
CEO’s Role in Company Governance
As CEO, Brian Sikes reports to the Board of Directors, which includes representatives from the Cargill and MacMillan families, independent directors, and former senior executives. Although Cargill is a private company, it operates with a structured and formal governance model.
The CEO leads the Executive Team, which consists of business group presidents and corporate function heads. Together, they are responsible for setting the company-wide strategy, approving major investments, and managing global risks.
Sikes also plays a public role as the face of the company during high-level partnerships, industry conferences, and global sustainability initiatives.
Previous CEOs of Cargill
Cargill has had relatively few CEOs in its long history, reflecting its culture of long-term leadership and internal development. Here are the most recent CEOs before Brian Sikes:
- David MacLennan (2013–2022): Led the company through global trade disruptions, digital transformation, and sustainability investments.
- Greg Page (2007–2013): Focused on global expansion and financial diversification.
- Warren Staley (2000–2007): Drove innovation and early adoption of bio-industrial products.
Each of these leaders played a key role in shaping Cargill’s direction while maintaining the company’s private and family-led structure.
CEO Succession Planning
Cargill maintains a formal succession planning process for executive roles. The selection of Brian Sikes in 2023 was the result of years of internal grooming and talent development. This approach is aligned with Cargill’s emphasis on stability, confidentiality, and cultural continuity, especially as a privately held firm not influenced by public market demands.
Cargill Annual Revenue and Net Worth
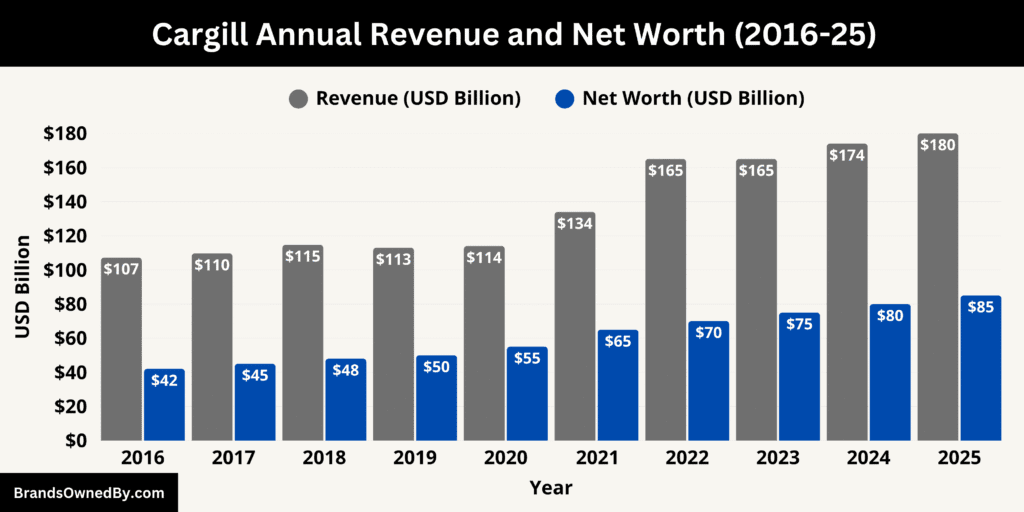
In the fiscal year ending 2024 (reported in early 2025), Cargill achieved record-breaking revenue of approximately $180 billion. This figure represents a modest increase compared to the $174 billion reported the previous year.
The growth was driven by higher global commodity prices, strong performance in the protein and crop businesses, and continued expansion in emerging markets. Cargill’s food and industrial segments both contributed significantly, while its risk management and financial services units helped stabilize margins amid market volatility.
Profit Margins and Net Income
Although Cargill does not disclose detailed financial results publicly, estimates indicate that net income for the same reporting period was around $4.5 billion. That suggests a net margin of about 2.5%. This reflects both operational scale and the impact of rising input costs.
Cargill’s operating efficiency measures, integrated supply chain management, and pricing power enabled it to maintain profitability despite macroeconomic pressures.
Cargill Net Worth
As a private company, Cargill’s market value is not derived from public equity markets. Analysts regularly estimate Cargill’s net worth by applying valuation multiples to revenue and earnings. As of August 2025, the company’s estimated net worth is around $85 billion.
It reflects strong recent performance, weather resilience, and strategic investments, while also accounting for fluctuations in global commodity valuations and currency exchange rates.
Here is Cargill’s estimated historical revenue and net worth over the past 10 years (2016–2025):
| Year | Estimated Revenue (USD) | Estimated Net Worth (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | $180 billion | $70–85 billion |
| 2024 | $174 billion | $65–80 billion |
| 2023 | $165 billion | $60–75 billion |
| 2022 | $165 billion | $60–70 billion |
| 2021 | $134 billion | $55–65 billion |
| 2020 | $114 billion | $45–55 billion |
| 2019 | $113 billion | $42–50 billion |
| 2018 | $114.7 billion | $40–48 billion |
| 2017 | $109.7 billion | $38–45 billion |
| 2016 | $107.2 billion | $35–42 billion |
Wealth of the Owner Families
Because most of Cargill is owned by the Cargill and MacMillan families, the estimated net worth of the company largely corresponds to their collective personal wealth. Both families are estimated to place on lists of wealthiest individuals in the United States.
The majority of their compensation comes from retained earnings and dividends rather than public equity dividends. Their wealth grows as Cargill reinvests in sustainable agriculture, food innovation, and global infrastructure.
Financial Outlook and Future Expectations
Under the leadership of CEO Brian Sikes, Cargill has signaled plans to sustain and slightly accelerate growth. Investment in regenerative agriculture, digital platforms, and expanded protein production are expected to support revenue growth in the low to mid-single-digit percentage range in 2025.
Analysts anticipate net income to remain robust, though margins may be under pressure from ongoing energy and input cost inflation. The long‑term financial outlook remains positive, anchored by a diversified, global footprint and financial discipline built over decades.
Companies Owned by Cargill
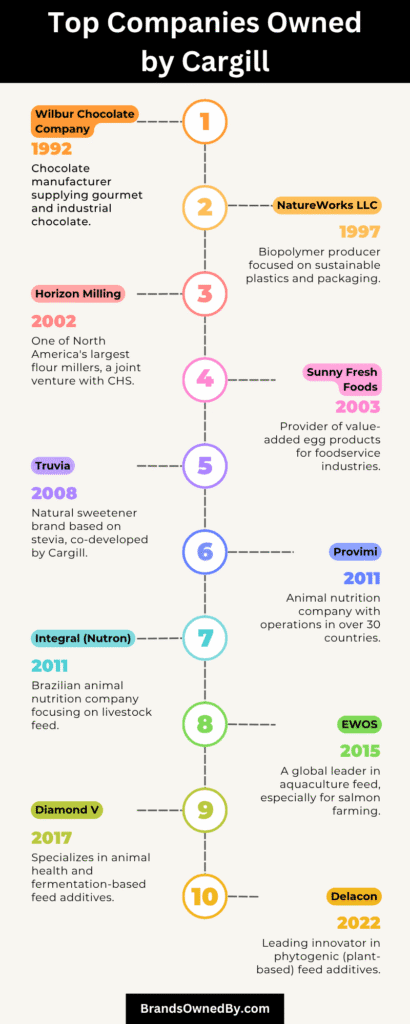
Cargill owns and operates a wide range of businesses across agriculture, food production, and industrial sectors. Here’s a list of the major brands, subsidiaries, and companies owned by Cargill as of 2025:
| Name | Type | Year Acquired / Founded | Business Focus / Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cargill Protein | Division | N/A | Meat processing; beef, poultry, turkey, and prepared foods |
| EWOS | Acquisition | 2015 | Global aquaculture nutrition and fish feed |
| Provimi | Acquisition | 2011 | Animal nutrition and feed solutions |
| NatureWax | Brand | Early 2000s | Plant-based waxes for candles, cosmetics, and bio-industrial use |
| Wilbur Chocolate | Brand | Legacy (Pre-2000s) | Specialty chocolate coatings and ingredients |
| Peter’s Chocolate | Brand | Legacy | Premium chocolate brand for gourmet and industrial use |
| Diamond Crystal (assets) | Acquisition (partial) | 2021 | Portion-control condiments and foodservice ingredients |
| Sunny Fresh | Brand | 1990s | Fully cooked egg products for institutional foodservice |
| Honeysuckle White | Brand | 1990s | Turkey products with family-farm sourcing in the U.S. Midwest |
| Shady Brook Farms | Brand | 1990s | Turkey products marketed in the U.S. East |
| Truvia | Brand | 2008 | Stevia-based natural sweetener, calorie-free |
| Ardent Mills | Joint Venture | 2014 | Largest flour milling company in North America (Cargill owns a major stake) |
| Cargill Cocoa & Chocolate | Division | N/A | Global cocoa processing and chocolate production (brands include Gerkens, Peter’s, etc.) |
| Cargill Bioindustrial | Division | N/A | Renewable industrial products: chemicals, lubricants, foams |
| Starches, Sweeteners & Texturizers | Division | N/A | Food and beverage ingredients: syrups, maltodextrins, stabilizers |
| Front Range Energy | Acquisition | 2023 | Bioethanol production and renewable fuel manufacturing |
| Croda Industrial Business | Acquisition | 2022 | Bio-based industrial ingredients for personal care, lubricants, and more |
| Delacon | Acquisition | 2022 | Plant-based feed additives (phytogenics) |
| Aalst Chocolate | Acquisition | 2021 | Premium chocolate manufacturer in Asia-Pacific |
| Konspol | Acquisition | 2018 | Integrated poultry producer in Poland and Eastern Europe |
Cargill Protein
Cargill Protein is one of the company’s most valuable and strategic divisions. It produces beef, turkey, chicken, and prepared foods for major retailers and foodservice clients across North America. Headquartered in Wichita, Kansas, it operates multiple processing facilities and has expanded its sustainable protein offerings, including plant-based alternatives and traceable supply chain solutions. This division contributes significantly to Cargill’s annual revenue.
EWOS
EWOS is a global leader in fish feed and aquaculture nutrition, acquired by Cargill in 2015 for $1.5 billion. Based in Norway, EWOS helps Cargill dominate the salmon feed market in Europe, Chile, and Southeast Asia. This acquisition marked Cargill’s entry into aquaculture, a fast-growing sector aligned with global protein demand.
Provimi
Cargill acquired Provimi, a Dutch-based animal nutrition company, in 2011 for over $2 billion. Provimi operates across Europe, Asia, and Latin America, providing customized feed solutions for swine, poultry, and ruminants. It helped position Cargill as a top-three global animal nutrition company.
NatureWax
NatureWax is a producer of natural, sustainable waxes made from renewable plant-based sources such as soy and palm. It serves candle manufacturers and cosmetic producers globally. Owned and operated by Cargill since the early 2000s, NatureWax aligns with Cargill’s focus on bio-industrial products and green innovation.
Wilbur Chocolate
Wilbur is a legacy chocolate brand that manufactures chocolate coatings and specialty ingredients for bakeries and confectioners. Operated by Cargill under its Cocoa & Chocolate division, Wilbur is known for high-quality melting chocolate used in commercial baking.
Peter’s Chocolate
Peter’s Chocolate was one of the earliest U.S. chocolate brands and is now a key part of Cargill’s chocolate division. It provides premium chocolate products to bakeries, gourmet brands, and candy manufacturers. It emphasizes quality craftsmanship and is frequently used in artisanal confections.
Diamond Crystal Brands (Select Assets)
In 2021, Cargill acquired select assets from Diamond Crystal Brands, strengthening its foodservice operations. The acquisition included portion-control condiments, sauces, and seasoning blends used in restaurants, hotels, and institutional foodservice.
Sunny Fresh
Sunny Fresh is Cargill’s brand of fully cooked egg products, serving schools, healthcare facilities, and foodservice operators. The brand is recognized for food safety, convenience, and innovation in pre-cooked egg solutions.
Honeysuckle White
Honeysuckle White is a retail turkey brand owned by Cargill, offering fresh and frozen turkey products with a focus on transparency and independent farming. It is popular across U.S. grocery chains and continues to evolve with consumer demand for antibiotic-free and natural protein options.
Shady Brook Farms
A sister brand to Honeysuckle White, Shady Brook Farms serves the Eastern U.S. market. Both brands operate under the same turkey production system, emphasizing traceability and family-farm sourcing.
Truvia
Truvia is a natural, plant-based sweetener made from stevia, launched by Cargill in partnership with Coca-Cola in 2008 and fully owned by Cargill today. It is a calorie-free sugar alternative available globally and used in many food and beverage products.
Ardent Mills (Joint Venture)
Ardent Mills is a joint venture between Cargill, ConAgra Foods, and CHS, formed in 2014. It is the largest flour milling company in North America, with over 35 mills. While not wholly owned by Cargill, it is partially controlled through Cargill’s majority stake and operational influence.
Cargill Cocoa & Chocolate
This division operates several brands and production facilities across Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Americas. It processes raw cocoa into cocoa powder, butter, and liquor, and supplies chocolate to some of the world’s largest food manufacturers. Brands like Gerkens and Peter’s fall under this division.
Cargill Bioindustrial
Cargill Bioindustrial is a fast-growing unit that produces chemicals, lubricants, foams, and binders from renewable sources like soy and corn. It provides sustainable alternatives to petroleum-based chemicals for industries such as construction, automotive, and packaging.
Cargill Starches, Sweeteners & Texturizers
This global business segment includes the manufacturing of food-grade starches, sweeteners, and food additives. It serves industries ranging from bakery and dairy to beverage and snacks. Cargill is a major producer of corn syrup, maltodextrin, and texturizers used in thousands of processed foods.
Front Range Energy (Acquisition)
In 2023, Cargill acquired Front Range Energy, a Colorado-based bioethanol plant. This strengthened Cargill’s presence in renewable fuels and low-carbon energy solutions, aligning with its broader climate and emissions goals.
Croda’s Industrial Business (Acquisition)
Cargill completed its acquisition of Croda International’s bio-based industrial business in 2022. This added a portfolio of natural-based polyols and esters used in personal care, lubricants, and other non-food sectors.
Delacon (Acquisition)
In 2022, Cargill acquired Delacon, an Austrian company that specializes in plant-based feed additives. This investment expanded Cargill’s offering in phytogenic solutions, an area growing in demand due to restrictions on antibiotics in animal feed.
Aalst Chocolate (Acquisition)
Cargill acquired Singapore-based Aalst Chocolate in 2021, marking its first chocolate production site in Asia. Aalst serves the premium baking and foodservice markets in Asia-Pacific and complements Cargill’s existing chocolate operations.
Konspol (Acquisition)
In 2018, Cargill acquired Konspol, one of Poland’s top poultry producers. This acquisition expanded Cargill’s integrated poultry business across Central and Eastern Europe, where protein demand has been steadily growing.
Final Thoughts
Cargill remains one of the most powerful private companies in the world. Its ownership has stayed within the Cargill and MacMillan families for more than 150 years. Despite its size, it has avoided public markets and operates largely out of the public eye. With vast revenues, strategic acquisitions, and a global footprint, Cargill continues to shape the future of food and agriculture worldwide.
FAQs
Who owns Cargill?
Cargill is primarily owned by the Cargill and MacMillan families, who together control about 88% of the company.
Is Cargill a public company?
No, Cargill is not a public company. It is a privately held corporation and has never been listed on any stock exchange. Its shares are owned primarily by the Cargill and MacMillan families.
Who owns the majority of Cargill?
The majority of Cargill is owned by the Cargill and MacMillan families, who together control about 88% of the company. The remaining shares are held by executives, family trusts, and a small number of other stakeholders.
Who owns Cargill Incorporated?
Cargill Incorporated is owned by descendants of its founder William Wallace Cargill and his extended family through the MacMillan line. These families have passed ownership through generations and maintain tight control over the company’s governance and decisions.
Is Cargill owned by Monsanto?
No, Cargill is not owned by Monsanto. Cargill and Monsanto have operated independently. Monsanto was acquired by Bayer in 2018, while Cargill has remained privately owned by its founding families. The two companies may have collaborated in agriculture sectors in the past, but Cargill has never been owned by Monsanto or Bayer.
What is the Cargill family net worth?
The combined net worth of the Cargill and MacMillan families is estimated to be over $45 billion as of 2025. Several family members rank among the wealthiest individuals in the United States due to their long-standing ownership in the company. Their wealth is largely tied to dividends, reinvestments, and long-term company valuation.
What companies does Cargill own?
Cargill owns a wide range of subsidiaries, brands, and business units. These include:
- Cargill Protein
- EWOS
- Provimi
- NatureWax
- Wilbur Chocolate
- Peter’s Chocolate
- Sunny Fresh
- Honeysuckle White
- Shady Brook Farms
- Truvia
- Cargill Cocoa & Chocolate
- Cargill Bioindustrial
- Front Range Energy
- Aalst Chocolate
- Delacon
- Konspol
It also has joint ventures like Ardent Mills, and partial ownership in various other industrial and agricultural operations globally.
How many family members own Cargill?
As of 2025, around 90 family members from the Cargill and MacMillan families own shares in the company. While not all of them are involved in operations, several serve on the board or in family governance roles.
What does Cargill do?
Cargill is a global agribusiness and industrial conglomerate. It operates across food production, grain trading, meat processing, animal nutrition, cocoa and chocolate manufacturing, bio-industrials, and risk management. The company connects farmers with markets, processes raw materials, and delivers food, feed, and industrial products in more than 70 countries.
Is Cargill a US company?
Yes, Cargill is an American company. It was founded in 1865 in Iowa and is currently headquartered in Minnesota. It is one of the largest privately held companies in the United States by both revenue and employee count.
Where is Cargill headquartered?
Cargill is headquartered in Minnetonka, Minnesota, a suburb of Minneapolis. Its headquarters manage global operations, business development, sustainability, and innovation strategies.
Who is the largest privately owned company in the US?
As of 2025, Cargill remains the largest privately owned company in the United States by revenue. It consistently ranks at the top of private company lists due to its massive global footprint, annual revenues exceeding $180 billion, and its position in critical supply chains across agriculture, food, and industry.

