If you’ve ever wondered “who owns Burger King,” you’re not alone. The popular fast-food chain, known for its flame-grilled burgers, has been through several ownership changes over the years. Today, it operates under the umbrella of Restaurant Brands International, a multinational holding company. This article explores the history of Burger King, its ownership structure, and the companies it owns.
History of Burger King
Burger King was founded in 1954 by James McLamore and David Edgerton in Miami, Florida. The company started with the idea of creating a fast-food restaurant that offered high-quality burgers, and it quickly grew in popularity.
Over the decades, Burger King changed hands several times. It was first acquired by Pillsbury Company in 1967.
Later, in the 1980s, it changed ownership again, moving through several private equity firms and conglomerates before being merged with Tim Hortons in 2014 to form Restaurant Brands International.
Who Owns Burger King?
The ownership of Burger King is currently held by Restaurant Brands International (RBI), a multinational holding company. RBI was established in 2014 after the merger of Burger King and Tim Hortons.
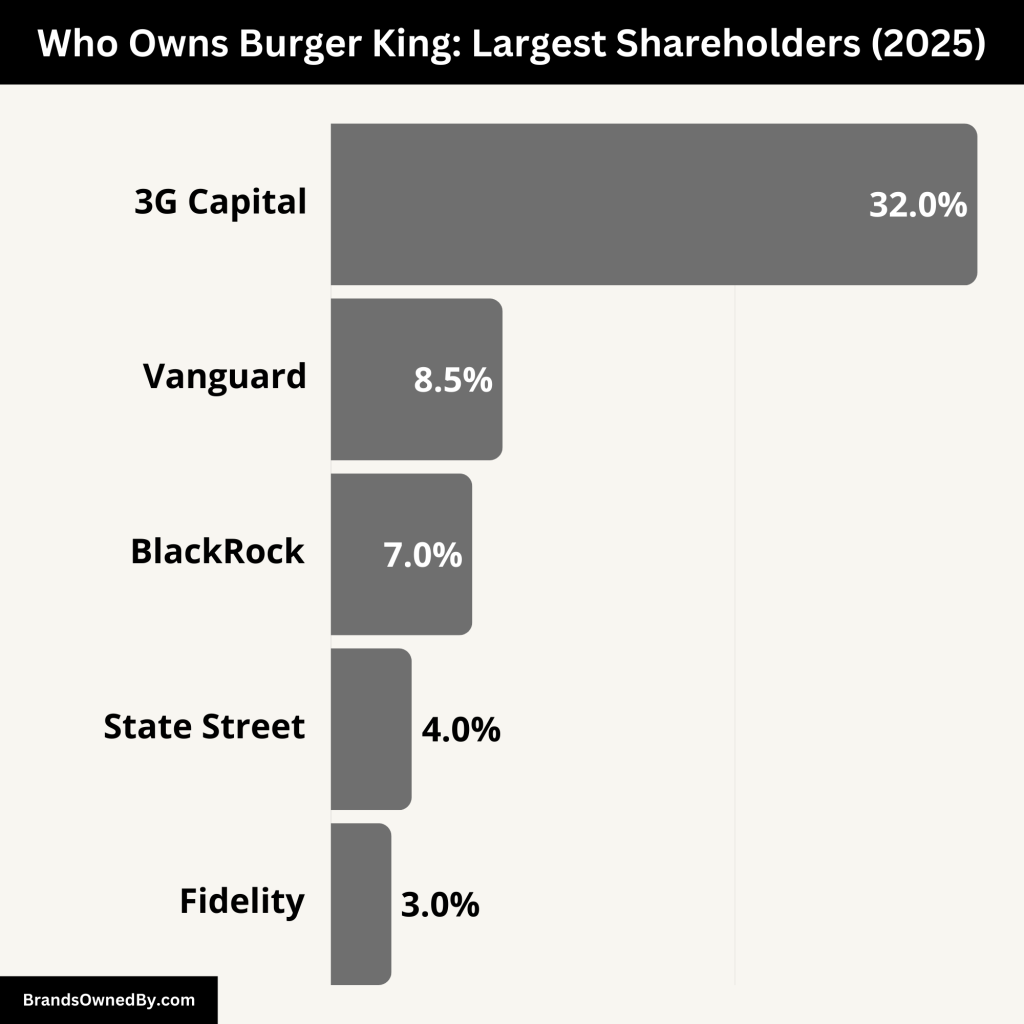
The majority stake in RBI is owned by 3G Capital, a Brazilian-American investment firm known for its involvement in large-scale mergers and acquisitions. 3G Capital holds a significant portion of the company, giving it substantial control over the operations and decisions of Burger King.
Here’s an overview of the major shareholders of Burger King’s parent organization RBI:
| Shareholder | Approximate Ownership | Role/Control |
|---|---|---|
| 3G Capital | ~32% | Largest shareholder; exerts significant influence over strategic decisions. |
| The Vanguard Group | ~8.5% | Major institutional investor; votes on governance and corporate matters. |
| BlackRock | ~7% | Leading asset manager; influences financial strategies and long-term growth. |
| State Street Global Advisors | ~4% | Institutional investor focused on corporate responsibility and governance. |
| Fidelity Investments | ~3% | Holds shares via mutual funds; engages in shareholder voting and long-term strategies. |
| Public Shareholders | ~45% | Includes retail and institutional investors; votes on corporate governance but with less influence. |
| Management & Insider Holdings | ~1–2% | Includes RBI executives and board members; aligns with shareholder interests. |
3G Capital
3G Capital is a Brazilian-American investment firm founded by Jorge Paulo Lemann, Marcel Telles, and Beto Sicupira. The firm is known for its involvement in large-scale mergers and acquisitions. 3G Capital holds approximately 32% of RBI’s outstanding shares.
As the largest shareholder, 3G Capital exerts considerable influence over key board decisions and strategic direction. Its aggressive cost-cutting strategies are a hallmark, and it applies these principles across its portfolio, including Burger King.
The Vanguard Group
The Vanguard Group is one of the world’s largest asset management companies, with 8.5% of RBI’s shares. Vanguard’s investments are primarily in index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), representing a large pool of institutional investors. Although Vanguard does not play a direct role in the management of Burger King, it is a significant player in corporate governance through shareholder voting.
BlackRock
BlackRock, another major institutional investor, holds approximately 7% of RBI shares. As the world’s largest asset management firm, BlackRock’s influence is felt in both the financial and strategic decisions of RBI. BlackRock’s ownership allows it to engage with management on key issues such as growth strategies, operational efficiency, and governance.
State Street Global Advisors
State Street Global Advisors owns around 4% of RBI. Like Vanguard and BlackRock, State Street manages assets for institutional clients such as pension funds and mutual funds. The firm uses its shareholding to ensure that the RBI maintains strong governance practices, particularly on issues like corporate responsibility and environmental sustainability.
Fidelity Investments
Fidelity Investments holds about 3% of RBI shares through its mutual funds. While its stake is smaller than the other institutional investors, Fidelity still plays an important role in corporate governance and shareholder decisions, particularly in terms of long-term investment strategies.
Public Shareholders
Approximately 45% of RBI’s shares are held by the public, including both retail and institutional investors. These shares are traded on the New York Stock Exchange and the Toronto Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol QSR. Public shareholders have voting rights, but their influence is less significant compared to 3G Capital and the major institutional investors.
Management and Insider Holdings
Senior executives and board members of Restaurant Brands International, including CEO José Cil, own about 1–2% of the company’s outstanding shares. These insider holdings align the interests of management with those of the larger shareholders, ensuring that the company’s direction reflects the interests of both owners and leaders.
Who Controls Burger King?
Burger King is primarily controlled by 3G Capital. The investment firm has a significant role in setting the strategic direction of the company and its major brands, including Burger King.
It influences the decisions made by the executive team and has considerable sway over financial strategies. Although the company’s day-to-day operations are handled by the management teams of its brands, 3G Capital’s control is evident in high-level decisions.
The operational control is split between the management team, the board of directors, and the significant influence of its largest shareholder, 3G Capital. Here’s a breakdown of who controls Burger King and how decisions are made within the company:
3G Capital: Major Influence on Strategy and Operations
As the largest shareholder of Restaurant Brands International (RBI), 3G Capital holds approximately 32% of RBI’s shares. This private equity firm wields significant influence over the strategic direction of RBI, including Burger King.
3G Capital’s control over the company stems from its substantial ownership stake and its ability to appoint key members of the board. The firm is known for its aggressive cost-cutting measures and financial strategies, which it has applied across its portfolio, including Burger King. This control is particularly evident in high-level decision-making, where 3G Capital’s representatives have considerable sway over the board’s decisions and corporate policies.
CEO of Restaurant Brands International: José Cil
José Cil is the CEO of Restaurant Brands International (RBI), the parent company of Burger King. Appointed in 2017, Cil has played a pivotal role in shaping the company’s growth strategy, including overseeing Burger King’s operations.
Cil’s leadership focuses on continuing the brand’s global expansion, particularly in emerging markets, while maintaining operational efficiencies that have been a hallmark of 3G Capital’s management style. Under his leadership, RBI has worked to increase the focus on digital innovations, improving the customer experience through mobile ordering, delivery, and other technological advancements.
Before becoming CEO, Cil was the global president of Burger King and was instrumental in developing and executing the brand’s turnaround strategy, which helped revitalize its global footprint. As CEO, Cil now manages the overall direction of Burger King and the other RBI brands, including Tim Hortons, Popeyes, and Firehouse Subs.
The RBI Board of Directors: Oversight and Decision-Making
The RBI Board of Directors plays a crucial role in overseeing the company’s operations and long-term strategies. The board is composed of experienced executives and independent directors, many of whom have strong ties to 3G Capital. The board’s responsibilities include approving major business decisions, setting executive compensation, and ensuring that the company adheres to its financial goals.
While the management team, led by CEO José Cil, handles day-to-day operations, the board’s influence is strong in shaping the company’s overall strategic direction. Board members are often appointed by 3G Capital, and this group of individuals plays a crucial role in guiding Burger King’s future.
Operational Control by Burger King Management
Although 3G Capital and the RBI board hold significant strategic control, the Burger King management team handles the operational decisions of the brand. The executive leadership of Burger King is responsible for overseeing its day-to-day operations, including managing franchises, marketing campaigns, and product innovation. Burger King’s leadership team reports to the RBI CEO, José Cil, and collaborates closely with other brands under RBI to implement shared strategies and initiatives.
Burger King’s Chief Marketing Officer (CMO), Chief Financial Officer (CFO), and other key executives focus on maintaining the brand’s position as one of the world’s largest fast-food chains. The management team also ensures that the company’s policies align with 3G Capital’s goals for efficiency and growth.
Burger King CEO José Cil’s Leadership and Vision
José Cil’s leadership of RBI and Burger King has been instrumental in the brand’s global expansion. Under his guidance, Burger King has significantly increased its presence in international markets, especially in regions such as Asia and Latin America. Cil’s focus has been on modernizing the brand, creating a stronger digital presence, and making the customer experience more seamless through innovations like delivery services and mobile ordering.
Before being named CEO of RBI, Cil was an executive at Burger King for many years, giving him deep knowledge of the brand’s operations. His ability to adapt Burger King’s business model to modern consumer trends while maintaining the efficiency principles established by 3G Capital has been key to the company’s success.
3G Capital’s Financial Control
3G Capital’s involvement in RBI is primarily financial, leveraging its expertise in operational efficiency, mergers, and acquisitions to drive growth and profitability. 3G Capital’s executives often serve on the board of directors and are responsible for guiding the company’s financial strategy. However, operational control remains with the CEO and the Burger King management team, although 3G Capital’s influence is felt in every major decision.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Burger King
As one of the largest fast-food chains in the world, Burger King has seen substantial growth over the years, contributing significantly to the success of its parent company, Restaurant Brands International (RBI). Here’s a closer look at Burger King’s 2024 revenue and 2025 net worth:
2024 Annual Revenue of Burger King
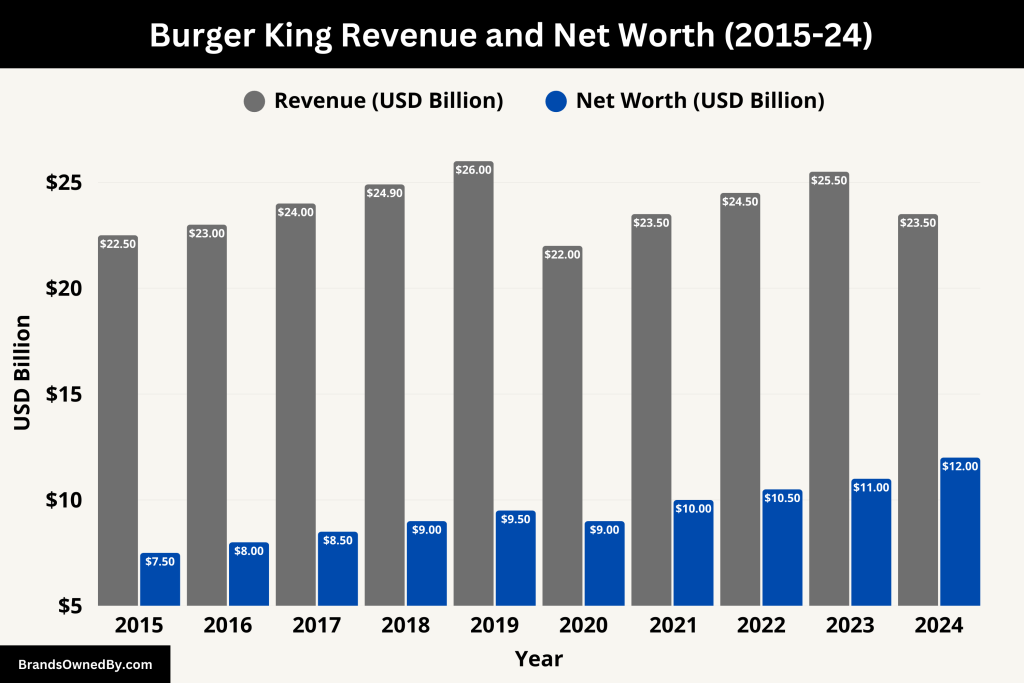
In 2024, Burger King reported global systemwide sales of approximately $23.5 billion, a significant increase from previous years. This growth is largely attributed to its expansion into new markets, a robust marketing strategy, and innovative digital solutions, such as mobile ordering and delivery services.
Burger King’s strong performance in both established and emerging markets, particularly in regions like Latin America, the U.S., and parts of Asia, has helped boost sales. The brand continues to leverage its popular items like the Whopper and its newer offerings, including plant-based options, to attract a broader customer base.
In addition to systemwide sales, Burger King’s direct revenue, which includes company-operated store revenue and franchising fees, contributed approximately $1.3 billion in 2024. This revenue stems from its vast network of franchises, with over 19,000 locations worldwide.
Net Worth of Burger King
While it’s difficult to isolate Burger King’s exact net worth separately from its parent company, Restaurant Brands International (RBI), experts estimate that Burger King’s brand value is approximately $10-12 billion in 2025. This valuation reflects the chain’s brand equity, global reach, and strong market presence in the fast-food industry.
Burger King’s estimated worth is also influenced by its performance in key markets, its diversified menu, and its increasing focus on modernizing its customer experience through digital platforms. Additionally, the brand’s growing emphasis on value for money, as well as sustainability initiatives, continues to strengthen its appeal to modern consumers, which contributes positively to its valuation.
Here’s an overview of the historical revenue and net worth of Burger King:
| Year | Revenue (Systemwide Sales) | Net Worth (Brand Value) |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | $22.5 billion | $7.5 billion |
| 2016 | $23.0 billion | $8.0 billion |
| 2017 | $24.0 billion | $8.5 billion |
| 2018 | $24.9 billion | $9.0 billion |
| 2019 | $26.0 billion | $9.5 billion |
| 2020 | $22.0 billion (decline due to COVID-19) | $9.0 billion (estimated decline) |
| 2021 | $23.5 billion | $10.0 billion |
| 2022 | $24.5 billion | $10.5 billion |
| 2023 | $25.5 billion | $11.0 billion |
| 2024 | $23.5 billion | $10-12 billion |
Brands Owned by Burger King
Burger King itself does not own a large portfolio of brands like its parent company, Restaurant Brands International (RBI). However, Burger King has launched or acquired a few sub-brands, spin-offs, and regional concepts over the years. These brands or initiatives are typically integrated within their global strategy to serve niche markets or test new business models.
Here is a breakdown of brands and concepts associated with or owned by Burger King:
| Brand/Concept | Type | Description | Current Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| BK Café | Sub-brand (Menu Category) | Coffee and beverage initiative to compete with McCafé and Starbucks | Active in many markets |
| Whopper Bar | Sub-brand/Concept Store | Premium fast-casual format with customizable Whoppers and upscale design | Mostly phased out |
| BK Fresh | Sub-brand/Menu Initiative | Health-focused menu with salads, wraps, and smoothies | Discontinued |
| Plant-Based Line | Product Line/Partnership | Includes the Impossible Whopper (U.S.) and Rebel Whopper (global) via suppliers | Active globally |
| Hungry Jack’s | Franchise Brand (Australia) | Operated independently by Competitive Foods Australia under Burger King rights | Active – Exclusive to Australia |
BK Café
BK Café is Burger King’s branded coffee initiative aimed at competing with major coffee chains like McDonald’s McCafé and Starbucks. It includes a variety of coffee beverages such as brewed coffee, iced coffee, lattes, and specialty drinks.
BK Café is not a standalone brand with separate locations but is integrated into Burger King’s regular menu in many markets. The introduction of BK Café was part of Burger King’s strategy to increase breakfast and beverage sales, particularly in the U.S.
Whopper Bar
Whopper Bar was a premium sub-brand concept launched by Burger King in 2009. These locations featured an upscale, modern design and offered a customizable gourmet Whopper menu with unique toppings and ingredients not available at standard Burger King locations.
Whopper Bars were launched in select urban and tourist locations such as Miami, Las Vegas, and international airports. The concept was experimental and is no longer widely promoted, but it represented an effort to create a more premium image for Burger King.
BK Fresh (formerly BK Whopper Bar in some regions)
BK Fresh (also known in some pilot markets as part of the Whopper Bar initiative) was a short-lived effort to market healthy and fresh menu items including salads, wraps, and smoothies. It was launched to respond to growing demand for healthier fast-food options. However, due to limited market success, this initiative did not expand widely.
Plant-Based Offerings (in partnership with Impossible Foods and The Vegetarian Butcher)
While Burger King doesn’t own these external companies, it has developed strong partnerships for its plant-based product lines:
- Impossible Whopper (U.S. and other markets): Developed with Impossible Foods, this burger features a plant-based patty and caters to vegetarian and flexitarian customers.
- Rebel Whopper or Plant-Based Whopper (Europe and Latin America): Made in partnership with The Vegetarian Butcher, owned by Unilever.
Burger King markets these under its own branding but relies on supplier partnerships for the core product ingredients.
Hungry Jack’s (Burger King Australia)
Hungry Jack’s is the exclusive Australian master franchise of Burger King. While not a brand Burger King “owns” in the traditional sense, it functions as the local representation of Burger King in Australia. The brand is owned and operated by Competitive Foods Australia, under a long-term agreement with Burger King.
Hungry Jack’s uses a menu and branding very similar to Burger King’s and is often seen by consumers as the same brand under a different name due to trademark issues in Australia. Burger King maintains influence through branding and supply agreements.
Conclusion
Burger King is owned by Restaurant Brands International, with the majority of the shares controlled by 3G Capital. The company plays a significant role in the global fast-food industry, competing alongside other brands like McDonald’s and Wendy’s. While 3G Capital has the final say in decision-making, the management team, led by CEO José Cil, handles daily operations. RBI’s portfolio also includes Tim Hortons, Popeyes, and Firehouse Subs, contributing to its strong position in the global foodservice market.
FAQs
Who owns Burger King in 2025?
Burger King is owned by Restaurant Brands International, with 3G Capital holding the largest stake.
Is Burger King owned by McDonald’s?
No, Burger King is not owned by McDonald’s. It is owned by Restaurant Brands International, with 3G Capital as the largest shareholder.
How many Burger King restaurants are there worldwide?
As of 2025, there are over 18,000 Burger King restaurants in more than 100 countries.
Who is the CEO of Burger King?
The CEO of Burger King is José Cil, who also serves as the CEO of Restaurant Brands International.
Is Burger King owned by Jollibee?
No, Burger King is not owned by Jollibee. It is owned by Restaurant Brands International (RBI), a Canadian multinational fast-food holding company.
Are KFC and Burger King the same company?
No, KFC and Burger King are not the same company. KFC is owned by Yum! Brands, while Burger King is owned by Restaurant Brands International.
Is Burger King halal?
Burger King serves halal-certified food in some countries like the UAE, Malaysia, and parts of the UK. However, it is not universally halal, so it depends on the location.
Is Burger King 100% meat?
Burger King uses 100% beef patties for its burgers, with no fillers or preservatives. However, it also offers plant-based options like the Impossible Whopper.
What country is Burger King owned by?
Burger King is owned by Restaurant Brands International, which is headquartered in Canada.
Who owns Restaurant Brands International?
The largest shareholder of Restaurant Brands International is 3G Capital, a Brazilian-American investment firm. Other major shareholders include institutional investors like Vanguard, BlackRock, and T. Rowe Price.
Who owns Burger King restaurants?
Most Burger King restaurants are owned by independent franchisees. Over 90% of locations are franchised globally.
Is Burger King privately owned?
No, Burger King is not privately owned. It is part of Restaurant Brands International, which is a publicly traded company listed on the NYSE and TSX under the ticker QSR.
Who owns Burger King franchisees?
Individual franchisees or franchise groups own Burger King restaurants. These may be small local operators or large multinational franchise companies.
Who bought Burger King?
3G Capital bought Burger King in 2010 and later merged it with Tim Hortons in 2014 to create Restaurant Brands International.
What is Burger King’s owner’s name?
The corporate owner of Burger King is Restaurant Brands International, primarily controlled by 3G Capital.
Who is the corporate owner of Burger King?
The corporate owner of Burger King is Restaurant Brands International (RBI).

