BT, also known as British Telecommunications, is one of the UK’s most important telecom companies. For anyone wondering who owns BT, this article covers everything — from BT’s ownership structure to its subsidiaries and revenue figures. Let’s explore the company in detail.
BT Company Profile
BT Group plc, commonly referred to as BT, is the UK’s leading provider of fixed-line, broadband, mobile, and television services. As of 2025, BT also plays a central role in delivering digital infrastructure and IT services across the country and globally. It operates in more than 180 countries and serves over 30 million customers in the UK alone. Its mobile arm, EE, is the UK’s largest mobile network operator.
BT is listed on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) under the symbol BT.A and is a component of the FTSE 100 Index.
Company Details
- Full Name: BT Group plc
- Founded: Originally in 1846 (Electric Telegraph Company)
- Privatized: 1984
- Headquarters: London, England, UK
- CEO: Allison Kirkby (since 2024)
- Chairman: Adam Crozier
- Employees: Approximately 100,000 (globally)
- Revenue (2024): £20.8 billion
- Net Worth (Market Cap): ~£14 billion (as of mid-2025)
- Stock Exchange Listing: London Stock Exchange (BT.A)
BT operates several key business units:
- Consumer Services (BT, EE, Plusnet)
- Enterprise and Business Solutions
- Openreach (wholesale broadband and fiber network)
- Global Services (for multinational corporations)
Founders and Early History
BT traces its origins to The Electric Telegraph Company, founded in 1846 by William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone, inventors of the electric telegraph. This company was the world’s first public telegraph company. Over time, it merged with other entities to form the General Post Office (GPO), which later became the Post Office Telecommunications division.
In 1969, Post Office Telecommunications became a separate department. In 1980, it rebranded as British Telecommunications, and by 1984, it was officially privatized and became BT plc, the UK’s first major privatized utility.
Major Milestones
- 1984: BT is privatized; first shares offered to the public under Margaret Thatcher’s government.
- 1991: British Telecom merges its international operations to form Concert Communications with MCI (later dissolved).
- 2000: BT Cellnet (mobile arm) is spun off and becomes O2.
- 2002: BT rebrands its corporate identity to BT Group plc.
- 2005: Launches BT Vision, an IPTV service (precursor to BT TV).
- 2013: Launches BT Sport, acquiring rights to major football and rugby leagues.
- 2016: Acquires EE, making BT the largest mobile operator in the UK.
- 2021–2022: Begins nationwide rollout of fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) and 5G coverage.
- 2024: Allison Kirkby becomes the CEO, the first woman to lead the company.
- 2025: BT continues to expand its 5G and full fiber broadband networks, aiming to reach 25 million premises by 2026 through Openreach.
BT is central to the UK’s digital infrastructure development and remains at the forefront of 5G, fiber broadband, and enterprise connectivity. Its investments in AI, cybersecurity, and digital services are positioning it as more than a telecom provider — now a tech-driven digital platform business.
Who Owns BT: Major Shareholders of British Telecommunications
BT Group plc is a publicly traded company listed on the London Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol BT.A. The company is not owned by a single individual or entity. Instead, it is owned by institutional investors, retail shareholders, and international firms.
Ownership of BT is spread among a wide range of shareholders. The largest shareholder is typically an institutional investor, followed by pension funds and global asset managers. No single shareholder holds a controlling interest, which means decision-making is decentralized and board-driven.
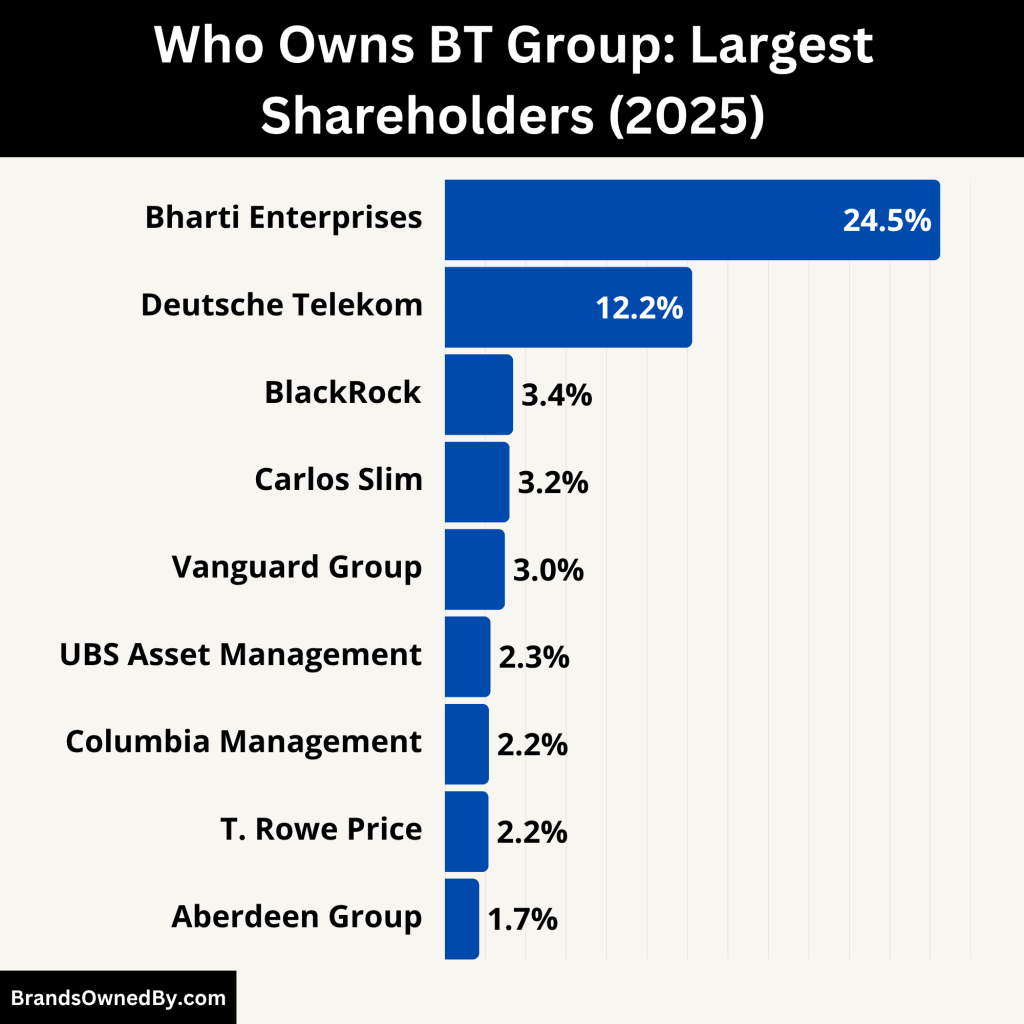
Here’s a list of the largest shareholders of BT Group as of July 2025:
| Shareholder | Ownership (%) | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Bharti Enterprises (Sunil Mittal) | 24.5% | Largest shareholder; strategic investor with potential for increased influence |
| Deutsche Telekom AG | 12.23% | Significant strategic stake; holds board representation |
| Carlos Slim | 3.2% | Passive strategic investment from respected telecom investor |
| BlackRock, Inc. | 3.38% | Major institutional investor, holds voting rights |
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | 2.97% | Passive index fund investor, exercises proxy voting |
| UBS Asset Management AG | 2.26% | Institutional owner with voting influence |
| Columbia Management Investment Advisers | 2.18% | Institutional investor via mutual funds |
| T. Rowe Price Group, Inc. | 2.16% | Institutional holder through equity funds |
| Aberdeen Group PLC | 1.70% | Institutional investor from the UK |
| Government Pension Fund Global (NBIM) | 1.36% | Sovereign wealth fund from Norway; governance focus |
| Other institutional & retail investors | ~45% | Diverse mix of global funds and individual shareholders |
Bharti Global / Bharti Enterprises (Sunil Bharti Mittal)
Ownership Stake: 24.5%
Bharti Enterprises, led by Indian telecom magnate Sunil Bharti Mittal, became the largest shareholder in BT Group in late 2024. Bharti acquired the entire 18% stake previously held by Patrick Drahi’s Altice Group and increased its holdings to 24.5% by mid-2025.
This stake positions Bharti as a strategic cornerstone investor with significant influence. While not holding formal control, Bharti is expected to seek board representation and may influence key decisions, particularly in international strategy and telecom innovation. The move marks a strong India–UK corporate link in the telecom sector and aligns with Bharti’s broader global ambitions.
Deutsche Telekom AG
Ownership Stake: 12.23%
Deutsche Telekom has been a long-standing strategic investor in BT since the 2016 acquisition of EE. It received its stake in exchange for its share of EE and has retained it over time.
Deutsche Telekom continues to hold a seat on BT’s board of directors, giving it a formal role in corporate governance. While it does not exercise operational control, it collaborates with BT on network technology, mobile strategy, and European market coordination. The partnership is viewed as long-term and stable.
Carlos Slim (Grupo Carso / América Móvil)
Ownership Stake: 3.2%
Mexican billionaire Carlos Slim, through investment vehicles like Grupo Carso or América Móvil, acquired a 3.2% stake in BT in 2025. While not a controlling interest, this is a strategic minority investment and signals his interest in expanding his global telecom footprint.
Though Slim does not sit on BT’s board, his investment has been seen as a vote of confidence in BT’s growth potential, particularly in digital infrastructure and enterprise services. His involvement may pave the way for future collaboration or knowledge sharing.
BlackRock, Inc.
Ownership Stake: 3.38%
BlackRock remains one of BT’s top institutional investors. As the world’s largest asset manager, BlackRock holds its shares through passive index funds and long-term investment vehicles.
It does not seek strategic influence or board seats, but exercises significant voting power at BT’s Annual General Meetings (AGMs). BlackRock influences corporate governance policies, especially on sustainability, executive compensation, and shareholder rights.
The Vanguard Group, Inc.
Ownership Stake: 2.97%
Vanguard is another passive investor and a key holder of BT’s publicly traded shares. Like BlackRock, it invests through index and mutual funds. Vanguard supports governance initiatives but does not engage in day-to-day decision-making.
Its role is primarily financial, with a focus on long-term shareholder value and fiduciary responsibility to its investors.
UBS Asset Management AG
Ownership Stake: 2.26%
UBS holds a moderate but consistent stake in BT through various European and global equity portfolios. Its role is strictly institutional and focused on returns rather than direct influence.
It participates in shareholder voting and monitors ESG policies, but does not hold any executive or board-level control.
Columbia Threadneedle Investments (Columbia Management)
Ownership Stake: 2.18%
Columbia Threadneedle, the investment division of Ameriprise Financial, owns over 2% of BT as part of its European value and income-focused strategies. It does not seek board involvement but exercises proxy voting rights at AGMs.
T. Rowe Price Group, Inc.
Ownership Stake: 2.16%
T. Rowe Price is a U.S.-based asset management firm known for its active investing approach. Its BT stake represents confidence in BT’s long-term capital appreciation prospects.
While it is not involved in governance, T. Rowe Price often engages in private dialogues with management on performance metrics, capital allocation, and risk management.
abrdn (formerly Aberdeen Standard Investments)
Ownership Stake: 1.70%
abrdn is one of the UK’s largest investment firms. It holds BT shares in institutional and retail portfolios. It occasionally participates in stewardship discussions and shareholder resolutions but holds no operational power or board representation.
Norges Bank Investment Management (NBIM)
Ownership Stake: 1.36%
NBIM manages Norway’s sovereign wealth fund and maintains a long-term, governance-focused investment in BT. It advocates for transparency, ESG alignment, and executive accountability. NBIM rarely pushes for strategic influence but remains highly engaged through investor relations.
Other Institutional and Retail Shareholders
Ownership Stake: ~23% combined
The remaining ownership is held by UK pension funds, hedge funds, mutual funds, ETFs, and retail investors. While no single entity in this group has a large enough share to impact decisions, their collective votes during AGMs can influence governance outcomes.
This group includes shareholders from both the UK and international markets, many of whom invest passively or based on dividend income strategies.
Who is the CEO of BT?
As of 2025, Allison Kirkby is the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of BT Group plc. She assumed the role in early 2024, succeeding Philip Jansen. Kirkby is an experienced telecom executive with a strong record of leadership in major international telecom firms. Her appointment marks a significant milestone, as she is the first woman to lead BT in its long corporate history.
Background and Experience
Allison Kirkby was born in Scotland and began her career in finance. She trained as a Chartered Management Accountant and worked at Procter & Gamble and Virgin Media before transitioning fully into the telecom industry.
Before joining BT, she served as:
- CEO of Telia Company (2019–2023), the largest telecom operator in Sweden and one of the most influential in the Nordics.
- CEO of TDC Group in Denmark.
- A senior executive at Tele2 in Sweden.
Kirkby is known for her focus on digital transformation, cost efficiency, and customer-centric strategies. Her appointment was seen as a move to strengthen BT’s competitive edge in fiber broadband, 5G, and enterprise services.
Leadership Vision and Strategy
Under Kirkby’s leadership, BT continues its transformation into a digitally focused and infrastructure-driven company. Key strategic goals she is driving include:
- Accelerating the rollout of full-fiber broadband through Openreach, targeting 25 million premises by 2026.
- Expanding 5G coverage across the UK under the EE brand.
- Simplifying BT’s corporate structure, streamlining consumer and business divisions.
- Driving cost savings and operational efficiency, with BT aiming for billions in savings by 2027.
- Boosting innovation in AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity, especially in the enterprise segment.
Kirkby has emphasized sustainability and responsible business as part of BT’s future, reinforcing the company’s environmental and social commitments.
Executive Decision-Making Structure
BT Group is governed by a board of directors, led by Chairman Adam Crozier, with the CEO accountable to the board. Allison Kirkby leads the Executive Committee, which includes chief officers of finance, technology, strategy, and legal.
Key strategic decisions, such as mergers, investments, and infrastructure programs, are made by the CEO in consultation with the board. The CEO also communicates with shareholders, regulators, and the government, especially given BT’s national importance.
Past CEOs of BT
Over the past two decades, BT has seen several prominent CEOs:
- Philip Jansen (2019–2024): Focused on Openreach expansion and modernization. Initiated cost-cutting and 5G rollout. Stepped down in 2024.
- Gavin Patterson (2013–2018): Oversaw the EE acquisition and growth of BT Sport. His tenure ended amid concerns over BT’s performance.
- Ian Livingston (2008–2013): Focused on international operations and broadband expansion.
- Ben Verwaayen (2002–2008): Led BT’s early broadband and VoIP efforts.
BT Annual Revenue and Net Worth
In the fiscal year ending March 31, 2025, BT Group reported a total revenue of approximately £22.1 billion. This growth, compared to the previous year’s £20.8 billion, reflects ongoing expansion in both its fixed and mobile broadband divisions.
The acquisition of new full-fibre customers through Openreach and increased mobile service subscriptions under EE were key contributors. Additionally, higher business connectivity and global services contracts helped offset some competitive pressures and inflationary costs in the consumer segment.
These combined factors contributed to healthy top-line growth in 2025.
2025 Net Worth (Market Capitalization)
As of July 2025, BT’s market capitalization is estimated at around £19.5 billion, reflecting investor confidence in its digital infrastructure and growth strategy. This net worth is driven by strong performance in its core operations, optimistic projections for fibre and 5G expansion, and cost-saving initiatives under the current leadership.
The uplift from approximately £14 billion in 2024 indicates that markets are responding positively to investor communications about long‑term earnings potential, future profit margins, and debt reduction plans.
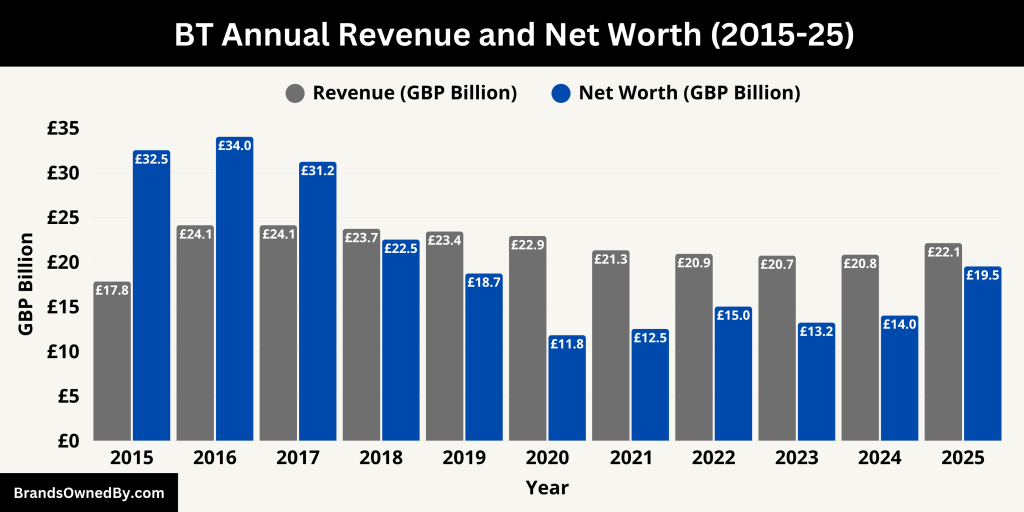
Here is a 10-year overview of BT Group’s revenue and net worth (market capitalization) from 2015 to 2025:
| Year | Revenue (£ Billion) | Net Worth / Market Cap (£ Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | 22.1 | 19.5 |
| 2024 | 20.8 | 14.0 |
| 2023 | 20.7 | 13.2 |
| 2022 | 20.9 | 15.0 |
| 2021 | 21.3 | 12.5 |
| 2020 | 22.9 | 11.8 |
| 2019 | 23.4 | 18.7 |
| 2018 | 23.7 | 22.5 |
| 2017 | 24.1 | 31.2 |
| 2016 | 24.1 | 34.0 |
| 2015 | 17.8 | 32.5 |
Financial Position and Key Indicators
BT’s financial position in 2025 shows steady improvement in profitability and debt metrics. Operating margins have risen due to ongoing cost efficiency programs, including network modernization and streamlined operations.
The enterprise and global services units have posted improved earnings, benefiting from digital transformation contracts in both public and private sectors. On the balance sheet, BT has continued to reduce net debt through disciplined cash flow management, strengthening its credit profile, and reducing interest expense.
Outlook and Forecast
BT’s outlook for the coming year remains cautiously optimistic. The company aims to sustain revenue growth above 5% through continued fiber rollout and mobile penetration. With fibre expansion expected to cover 25 million premises by 2026 and EE’s 5G network reaching rural and underserved areas, BT’s growth drivers remain robust.
Analysts also highlight BT’s strategic shift toward higher-margin software, cybersecurity, and cloud services as factors that could enhance net worth and support a higher valuation multiple in public markets.
Brands and Companies Owned by BT
As of 2025, BT Group plc operates through several subsidiaries, brands, and business units that serve both consumers and enterprises. These entities are either wholly owned or fully operated under the BT Group umbrella. They contribute to BT’s telecommunications, broadband, digital TV, mobile, IT services, and infrastructure operations.
The following are the key companies, brands, acquisitions, and business entities owned and operated directly by BT Group as of July 2025:
| Name | Type | Year Acquired/Founded | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| EE Limited | Mobile Network Operator | Acquired in 2016 | Provides 4G/5G mobile services, broadband, and SIM-only deals; BT’s flagship mobile brand. |
| Openreach | Network Infrastructure | Created in 2006 (separate legal entity) | Builds and manages UK broadband and fiber infrastructure; wholesale access for ISPs. |
| Plusnet | Budget Broadband Provider | Acquired in 2007 | Offers low-cost broadband and landline services with UK-based support. |
| BT Consumer | Telecom Services (Retail) | Internal BT division | Sells broadband, landline, TV, and mobile packages under the BT brand. |
| BT Business | Enterprise Telecom Services | Restructured in 2023 | Offers broadband, IT, VoIP, and managed services to SMEs and public sector. |
| BT Global | Multinational Connectivity | Internal BT division | Provides networking, cybersecurity, and digital services to global enterprises. |
| BT Wholesale | Telecom Wholesale Services | Internal BT division | Sells broadband, Ethernet, and voice solutions to telecom resellers and ISPs. |
| TNT Sports (JV) | Sports Broadcasting (Joint Venture) | Formed in 2022 (from BT Sport) | Offers live sports via BT TV and EE TV in partnership with Warner Bros. Discovery. |
| Adastral Park | Innovation & R&D Campus | Developed in 2000s | BT’s primary innovation center for AI, networking, and emerging tech research. |
| BT Ireland | Enterprise Division (Ireland) | Internal BT division | Provides enterprise and government telecom and IT services in Ireland. |
EE Limited
EE is the UK’s largest mobile network operator and a core brand within BT’s consumer division. BT acquired EE in 2016 from Deutsche Telekom and Orange S.A. EE operates independently in terms of branding but is fully integrated operationally within BT.
EE provides 4G and 5G mobile services, SIM-only deals, and broadband bundles. It is also central to BT’s 5G rollout strategy, offering high-speed mobile data services across the UK. As of 2025, EE has expanded 5G coverage to over 85% of the UK population. EE also contributes to BT’s business mobile offerings and partners with BT Business for enterprise-grade mobile connectivity.
Openreach
Openreach is a wholly owned but legally separate subsidiary of BT Group. It is responsible for building and maintaining the UK’s fiber and broadband infrastructure. Openreach provides wholesale access to its network to multiple ISPs, including BT, Sky, TalkTalk, and Vodafone.
In 2025, Openreach remains central to BT’s strategic growth. It aims to deliver full-fiber (FTTP) broadband to 25 million premises by 2026. Though operationally independent due to regulatory requirements, Openreach’s revenues contribute directly to BT’s consolidated financial performance.
Plusnet
Plusnet is a BT-owned broadband and landline provider operating as a value-focused, independent brand. Acquired by BT in 2007, Plusnet offers affordable broadband and phone packages with UK-based customer service.
It targets cost-conscious consumers and small businesses, distinguishing itself from the more premium BT and EE offerings. As of 2025, Plusnet continues to operate with its own website, support center, and customer base while leveraging BT’s network infrastructure.
BT Consumer
BT Consumer is the division through which BT sells broadband, landline, TV, and mobile services directly under the BT brand. It includes bundled packages with BT TV and access to premium sports and entertainment content.
In 2025, BT Consumer also offers BT Halo, a premium service that integrates Wi-Fi, mobile, and customer support. BT continues to maintain and expand its BT TV service, although it has transitioned much of its sports content into partnerships with other providers.
BT Business
BT Business serves small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and public sector clients. It offers broadband, VoIP, cloud-based communications, managed IT services, and security solutions.
In 2023–2024, BT merged its Enterprise and Global units into a simplified BT Business division. As of 2025, it focuses on delivering unified communications, smart solutions, and IT services to UK businesses. The unit plays a critical role in supporting the digital transformation of SMEs and local government entities.
BT Global
BT Global (previously BT Global Services) is responsible for BT’s international operations. It provides network connectivity, cybersecurity, cloud services, and managed communications to large multinational corporations and government clients in over 180 countries.
Although partially streamlined during internal restructuring, BT Global remains a vital part of BT’s enterprise services in 2025. It has retained key contracts in finance, logistics, and defense sectors and plays a strategic role in cross-border digital services.
BT Wholesale
BT Wholesale provides telecom services to other providers using BT’s core network infrastructure. It offers wholesale broadband, Ethernet, voice, and managed services to UK-based telecom companies, MVNOs, and ISPs.
This division enables BT to generate revenue from other network providers, even those competing in the consumer market. BT Wholesale plays an important role in leveraging the company’s nationwide infrastructure.
BT Sport (Merged with TNT Sports)
BT Sport, launched in 2013, was BT’s dedicated sports broadcasting brand. In 2022, BT Sport merged with Warner Bros. Discovery’s Eurosport UK, creating TNT Sports. As of 2025, BT no longer owns the brand independently but maintains a joint venture stake in TNT Sports, which airs via BT TV and EE TV platforms.
BT continues to offer sports content through its platforms, but it is now done in partnership rather than through a fully owned media unit.
Adastral Park
Adastral Park is BT’s main research and innovation campus located in Martlesham Heath, Suffolk. Although not a consumer-facing brand, it is a wholly owned entity operated by BT for R&D in networking, AI, and cybersecurity.
It serves as the hub for BT’s innovation programs and partnerships with universities, startups, and technology vendors. In 2025, it continues to support BT’s technological roadmap, especially in areas like 6G research, smart cities, and autonomous networks.
BT Ireland
BT Ireland is a division of BT Group operating in both Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. It provides business connectivity, IT solutions, and managed services to public and private sector clients.
While it doesn’t serve consumer markets like BT UK, it plays an important role in BT’s international enterprise strategy. It is especially active in sectors like government communications, healthcare IT, and data center services.
Conclusion
BT is a legacy telecom provider with a strong presence in the UK and around the world. For those asking who owns BT, it is a publicly owned company with a mix of institutional investors and strategic shareholders like Deutsche Telekom. Its diversified business model and extensive infrastructure make it a major player in the telecom sector. With a strong leadership team and focus on 5G and fiber, BT is positioned for future growth.
FAQs
Who are the main shareholders of BT?
As of 2025, the main shareholders of BT Group include Bharti Enterprises (24.5%), Deutsche Telekom AG (12.23%), and Carlos Slim (3.2%). Other significant institutional shareholders include BlackRock (3.38%), Vanguard Group (2.97%), UBS Asset Management, T. Rowe Price, Columbia Threadneedle, and Norges Bank Investment Management (NBIM). Together, these shareholders represent a mix of strategic and financial stakeholders.
Who is BT owned by?
BT Group is a publicly traded company listed on the London Stock Exchange. It is not owned by any single entity but rather by a group of shareholders. The largest current shareholder is Bharti Enterprises, followed by Deutsche Telekom. Ownership is spread across institutional investors, sovereign funds, and individual shareholders globally.
Who owns BT and EE?
BT Group plc owns EE Limited. BT acquired EE in 2016, integrating it as its mobile division. As of 2025, BT fully owns and operates EE as part of its consumer services. BT itself is majority-owned by shareholders including Bharti Enterprises and Deutsche Telekom, making them key indirect stakeholders in both BT and EE.
Who invested in BT?
Several entities have invested in BT over the years. In 2025, major investors include:
- Bharti Enterprises (the largest investor)
- Deutsche Telekom (strategic partner)
- Carlos Slim
- Institutional investors like BlackRock, Vanguard, UBS, Columbia, and NBIM
These investors hold varying levels of equity and influence, depending on their shareholding percentages and board representation.
Who founded BT?
BT’s origins trace back to The Electric Telegraph Company, founded in 1846 by Sir William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone. The modern BT Group evolved through mergers, nationalization, and eventually privatization in 1984. The British government initially owned it as part of the General Post Office (GPO) before it was privatized under the name British Telecom.
Who owns British Telecom?
British Telecom, now officially known as BT Group plc, is owned by a combination of global shareholders. The largest stake is held by Bharti Enterprises, followed by Deutsche Telekom. It is a publicly listed company, and its shares are traded on the London Stock Exchange, meaning it is owned by both institutional and retail investors. No single party holds complete control.
Is BT a private or public company?
BT is a public company listed on the London Stock Exchange.
Does the UK government own BT?
No. The UK government fully privatized BT in 1984 and no longer owns any shares.
Is EE part of BT?
Yes. BT acquired EE in 2016, and it is now a key part of BT’s mobile services.
Who is the CEO of BT?
Allison Kirkby is the current CEO of BT Group as of 2025.
What companies does BT own?
BT owns EE, Openreach, Plusnet, BT Global, BT Consumer, and BT Business.
What is BT’s revenue?
BT reported revenue of about £22.1 billion for the year ending 2025.
What is BT’s net worth?
BT’s market capitalization is estimated at around £19.5 billion as of July 2025.

