Polestar is a rising name in the electric vehicle (EV) space, but many people are still wondering who owns Polestar. The company has gained global attention for its sleek design and strong sustainability focus. In this article, we’ll explore the full ownership, financial profile, leadership, and brand structure of Polestar.
Polestar Company Profile
Polestar is a Swedish electric performance vehicle manufacturer. It blends cutting-edge automotive technology with clean Scandinavian design. Though it’s now recognized as a leading electric vehicle (EV) brand, Polestar started with a different mission.
The company was originally founded in 1996 as a racing team under the name Flash Engineering by Jan “Flash” Nilsson, a Swedish racing driver. The team was focused on competing in the Swedish Touring Car Championship (STCC) using Volvo vehicles. In 2005, Christian Dahl, a motorsport engineer, took over and rebranded the team as Polestar Racing. This new name marked the brand’s deeper relationship with Volvo, both on the track and in engineering performance road cars.
In 2009, Polestar began producing performance-enhanced versions of Volvo’s standard models. These included more powerful engines, upgraded suspensions, and exclusive design features. This period was critical in building Polestar’s identity around performance and innovation.
A major shift happened in 2015 when Volvo Cars acquired Polestar. Volvo initially positioned it as an in-house performance sub-brand, similar to how Mercedes-Benz uses AMG or BMW uses M. But as electric mobility became a central focus globally, Volvo reimagined Polestar as a separate EV-focused company.
In 2017, Polestar was relaunched as a standalone electric performance brand. Its first vehicle, the Polestar 1, was a high-end hybrid grand tourer with a limited production run. It showcased Polestar’s design, luxury, and performance capabilities.
The next big milestone came with the launch of the Polestar 2 in 2020, a fully electric sedan that competed directly with Tesla’s Model 3. This car became the backbone of Polestar’s market presence, particularly in Europe and North America.
In 2022, Polestar became a publicly listed company through a merger with Gores Guggenheim, a SPAC (Special Purpose Acquisition Company). It started trading on the Nasdaq Stock Market under the ticker symbol PSNY.
By 2025, Polestar had expanded its model lineup to include the Polestar 3 (an electric SUV), with plans for the Polestar 4 and Polestar 5 underway. The company continues to operate out of Gothenburg, Sweden, with production facilities in China, leveraging Geely’s global manufacturing strength.
Major Milestones
- 1996: Founded as Flash Engineering by Jan Nilsson.
- 2005: Rebranded as Polestar Racing by Christian Dahl.
- 2009: Began building performance versions of Volvo cars.
- 2015: Acquired by Volvo Cars; became official performance brand.
- 2017: Relaunched as an independent EV brand; introduced Polestar 1.
- 2020: Launched Polestar 2, its first all-electric vehicle.
- 2022: Became a public company through SPAC merger with Gores Guggenheim.
- 2023–2025: Expanded EV lineup with Polestar 3, 4, and 5.
Polestar’s journey from racing to clean mobility represents one of the most successful brand evolutions in the automotive world. Its dual foundation in motorsport and Scandinavian design continues to define its electric future.
Who Owns Polestar: Top Shareholders
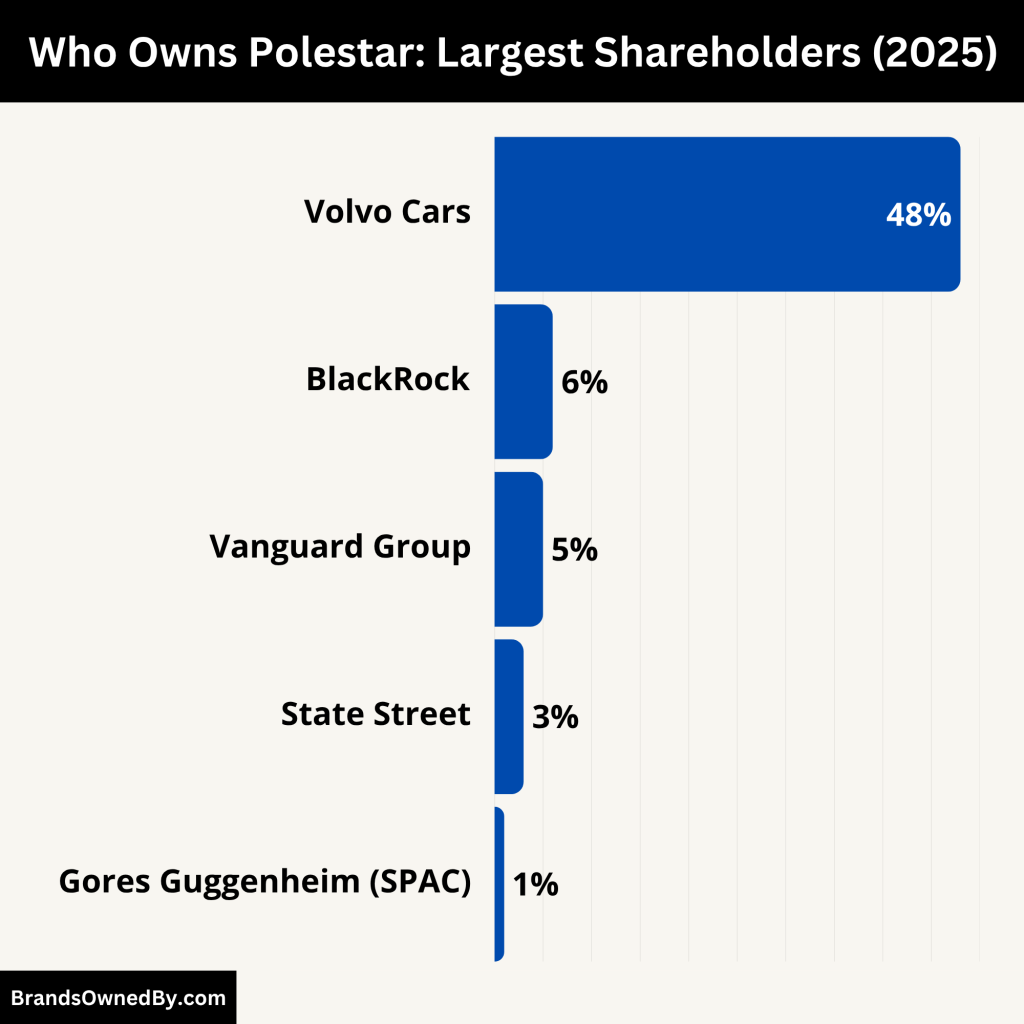
Polestar is owned jointly by Volvo Cars and Zhejiang Geely Holding Group, both of which are closely tied to Chinese billionaire Li Shufu. Geely is the ultimate parent company, while Volvo Cars is a majority stakeholder in Polestar.
This shared ownership gives Polestar a hybrid identity: Scandinavian in design and engineering but backed by major Chinese automotive capital. The company is listed publicly through a SPAC (Special Purpose Acquisition Company) merger with Gores Guggenheim, completed in 2022. After going public, ownership was distributed among institutional investors, Volvo Cars, and Geely-related entities.
Here’s a list of the largest shareholders of Polestar as of 2025:
| Shareholder | Ownership % (2025 est.) | Type | Role & Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volvo Cars | 48% | Strategic/Corporate | Largest shareholder; controls product strategy and board participation |
| Zhejiang Geely Holding | Indirect via Volvo | Parent Company | Indirect control; shapes strategy via Volvo and global EV vision |
| Gores Guggenheim (SPAC) | <1% | Financial/Legacy | Former sponsor of SPAC merger; now minimal influence |
| Retail Investors | 20–22% | Public Investors | No direct control; impact share price and liquidity |
| Institutional Investors | 20% | Professional Funds | Strategic influence via voting rights and governance participation |
| → BlackRock Inc. | 5–6% | Institutional | ESG-focused; voting power on governance and long-term value alignment |
| → The Vanguard Group | 4–5% | Institutional | Passive investor; supports governance decisions through index fund exposure |
| → State Street Global Advisors | 2–3% | Institutional | Holds through ETFs; promotes ESG and diversity in leadership |
| → Fidelity, ARK, JPMorgan, Baillie Gifford | 3–5% combined | Institutional | Active and growth-focused funds; support long-term innovation |
| Management & Employees | <1% | Internal | Minor ownership; mostly stock options and performance-based equity |
Volvo Cars (Approx. 48%)
Volvo Cars is the largest single shareholder of Polestar, owning approximately 48% of the company as of 2025. Volvo was the first to fully acquire the Polestar performance division in 2015. It was also responsible for Polestar’s transformation into an independent electric vehicle manufacturer in 2017.
Even after Polestar’s public listing in 2022, Volvo retained a significant equity stake. This allows Volvo to maintain substantial influence over Polestar’s strategy, product development, and engineering alignment.
Operationally, Volvo provides Polestar access to its R&D infrastructure, vehicle platforms (like the CMA and SPA2), and software technologies. Polestar’s vehicles share key components with Volvo models, especially the XC40 and EX90 series.
Though Volvo operates separately from Polestar, it holds board representation and plays a role in long-term planning and alignment with the parent group.
Zhejiang Geely Holding Group (Indirect Control)
Zhejiang Geely Holding Group Co., Ltd., also known as Geely Holding, is a Chinese multinational automotive group. It is the ultimate parent company of both Volvo Cars and, indirectly, Polestar.
While Geely does not hold direct equity in Polestar, its full ownership of Volvo Cars gives it indirect control over nearly half of Polestar’s shares. This means Geely exerts strategic influence through Volvo’s board seats and voting rights at Polestar’s shareholder meetings.
Geely Holding’s founder, Li Shufu, plays a key role in shaping the direction of its global automotive brands, including Volvo, Lotus, Lynk & Co, Zeekr, and Polestar. While Geely avoids day-to-day involvement in Polestar, it aligns the brand with its global EV and mobility strategies.
Gores Guggenheim SPAC (Initial Stake, Now Minimal)
Gores Guggenheim Inc., the SPAC (Special Purpose Acquisition Company) that merged with Polestar to take it public in 2022, held an initial minority stake after the transaction.
As of 2025, Gores Guggenheim’s ownership has significantly declined, as is typical with post-merger SPAC entities. Most of its early equity was either sold off or diluted as public trading commenced. While no longer a major shareholder, Gores Guggenheim played a key role in facilitating Polestar’s market debut.
BlackRock Inc.
BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, owns an estimated 5–6% of Polestar shares. Through its iShares ETF products and actively managed funds, BlackRock has positioned itself as a long-term investor in the EV and clean energy space.
Its stake in Polestar aligns with its broader sustainability investment strategy. BlackRock also promotes ESG reporting and board accountability in its portfolio companies, including Polestar.
The Vanguard Group
Vanguard, another global asset management leader, holds about 4–5% of Polestar. Known for its passive index tracking strategies, Vanguard typically invests in companies included in indices like the Nasdaq Composite or other sustainability-focused ETFs.
While Vanguard remains a passive investor, its voting influence on governance and policy issues carries weight during annual general meetings (AGMs). Vanguard also tracks company performance on carbon emissions, product innovation, and financial returns.
State Street Global Advisors
State Street owns approximately 2–3% of Polestar. As a major index fund and institutional service provider, State Street holds shares primarily through ETFs and index funds that include publicly traded clean tech and EV firms.
It supports initiatives for diversity, transparent disclosures, and climate-related governance. State Street, like BlackRock and Vanguard, often advocates for long-term value creation and investor transparency.
Other Institutional Investors
Additional institutional shareholders include:
- Fidelity Investments – A mix of active and index-based exposure to EV and tech growth stocks.
- JP Morgan Asset Management – Invests through actively managed equity portfolios.
- ARK Investment Management – Known for its focus on disruptive innovation, including electric vehicles and autonomous tech.
- Baillie Gifford – A long-term growth investor known to back EV and tech startups early.
Collectively, these institutional investors contribute to Polestar’s stability in capital markets. Their backing enhances credibility with analysts, suppliers, and global partners. Polestar’s investor relations team regularly engages with these firms during earnings calls, roadshows, and shareholder reports to ensure transparency and alignment with expectations.
Retail Investors (Approx. 20–22%)
Retail investors, including individual shareholders trading on the Nasdaq under the ticker PSNY, own an estimated 20% to 22% of Polestar as of 2025.
These investors participate through open-market trading and do not have operational control. However, their collective sentiment impacts Polestar’s stock price, public perception, and investor relations.
Polestar regularly engages with retail shareholders through earnings calls, reports, and product updates. Retail ownership provides liquidity and broadens brand awareness.
Management and Employees (Less than 1%)
Polestar’s executive leadership, board members, and employees collectively own less than 1% of the company through stock options, restricted shares, or employee stock purchase plans.
Though a small stake, this ownership incentivizes performance and aligns management’s interests with long-term shareholder value. CEO Thomas Ingenlath and other top executives are among the internal stakeholders with equity-based compensation.
Where is Polestar Made?
Polestar manufactures its vehicles in multiple locations around the world, with a strong focus on China and Europe. While the brand has Swedish roots, its production strategy is global. As of 2025, Polestar vehicles are built in highly specialized and sustainable factories. These production sites are operated either directly by Polestar or in collaboration with manufacturing partners.
Main Production Hub: Chengdu, China
The primary facility for Polestar production is located in Chengdu, in the Sichuan province of China. This state-of-the-art facility is wholly operated by Polestar and is known for its green manufacturing practices. It produces the Polestar 1, Polestar 2, and some early units of Polestar 3.
This factory has:
- Renewable energy integration
- Closed-loop water recycling
- ISO 14001 environmental certification
- Minimal landfill waste
Chengdu remains a core production site due to its high-volume capabilities and access to the Geely supply chain.
Secondary Facility: Taizhou, China
Polestar also produces vehicles at a shared Geely-Volvo plant in Taizhou, China. This location focuses on Polestar 3 and Polestar 4. While Polestar is a distinct company, this facility leverages economies of scale and uses shared EV platforms with Volvo for cost-efficiency and speed.
Taizhou is ideal for scaling production due to:
- Flexible modular platforms
- Established EV logistics
- Proximity to supply networks
Planned Manufacturing: South Carolina, USA
Starting in late 2024 and expanding in 2025, Polestar is beginning localized production of the Polestar 3 at the Volvo Cars plant in Ridgeville, South Carolina. This facility is important for the U.S. market, especially in response to inflation-reduction incentives and local sourcing regulations.
Key features of this site:
- Will serve North American demand
- Offers reduced import costs
- Supports local job creation and logistics efficiency
European Engineering & Assembly Support
Although no full-scale vehicle manufacturing occurs in Sweden, Polestar maintains its engineering and design headquarters in Gothenburg, Sweden. The team oversees prototype development, design verification, and final quality control processes.
Some pre-production assembly and component testing is handled in partnership with Volvo facilities in Europe.
Battery and Component Sourcing
Polestar sources EV batteries and components from multiple countries, including:
- China (majority of lithium-ion cells)
- South Korea (specialized EV modules and control units)
- Europe (future battery plant partnerships underway for localized sourcing)
These components are shipped to final assembly plants in China and the U.S.
Who is the CEO of Polestar?
Michael Lohscheller is the current CEO of Polestar, having taken the helm on October 1, 2024. He’s a seasoned automotive leader with a track record in both legacy and EV brands.
Lohscheller earned his degrees from Osnabrück and Barcelona, followed by a Master’s in Marketing from Brunel University London. His career spans roles as CFO at Mitsubishi and Volkswagen, then CEO at Opel (under Stellantis), VinFast, and Nikola. These experiences equipped him to lead Polestar through a scaling and cost-management phase.
Under Lohscheller, Polestar has committed to increasing sales 30–35% over three years and achieving positive cash flow by 2027. His strategy includes expanding dealership presence in key markets, accelerating global model rollouts (Polestar 7 and Polestar 4), and pursuing operational efficiency to improve profitability.
Former CEO: Thomas Ingenlath (2017–Sept 2024)
Thomas Ingenlath served as Polestar’s first CEO, a role he held from June 2017 until stepping down on October 1, 2024.
Before his CEO appointment, Ingenlath was Senior Vice President of Design at Volvo Cars, having worked with Volkswagen, Škoda, and Volvo. His design leadership was pivotal in establishing the brand’s Scandinavian style DNA.
Ingenlath transitioned Polestar from a performance sub-brand into an independent EV maker. He oversaw the launch of the hybrid Polestar 1 and the fully electric Polestar 2, and supported the development of the Polestar 3 and 4. He emphasized sustainability, innovation, and design as core brand pillars.
He grew Polestar’s identity and market presence in the 2017–2024 period. As market dynamics shifted and sales slowed in early 2024, Volvo reduced funding, and the board decided it was time for a new phase; Ingenlath stepped aside for an executive with scaling expertise.
CEO Transition and Decision-Making Structure
Polestar’s executive and board structure includes the CEO, CFO, and independent board members—among them Chair Winfried Vahland, formerly of Škoda, who joined in June 2024. The board ensures alignment with strategic goals, investor accountability, and global rollout plans.
Under Lohscheller, the focus is on:
- Scaling up production and market presence
- Navigating geopolitical and tariff-related challenges linked to Chinese-built EVs
- Shifting toward a mixed sales model of online sales and traditional dealerships.
Polestar Annual Revenue and Net Worth
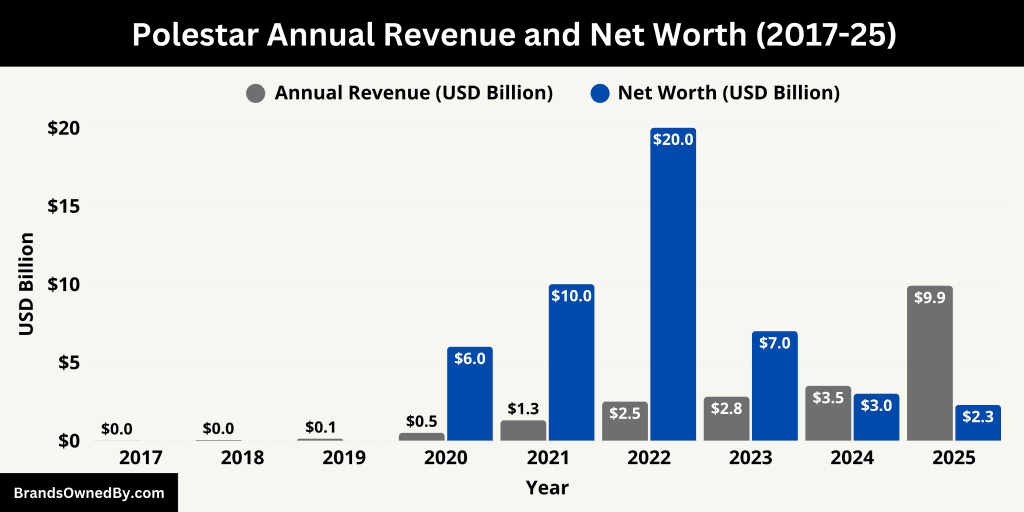
Polestar’s revenue soared by 84% year‑over‑year in Q1 2025, reaching $608 million, compared to $330 million in Q1 2024. The surge was driven by higher vehicle volume, especially from newer models like the Polestar 3 and 4, which carry stronger profit margins. Notably, the gross margin turned positive to 6.8%, up from –7.7% a year prior.
For Q4 2024, retail sales of 12,256 vehicles brought global annual deliveries to 44,851—down 15% from 2023 but bolstered by a 37% increase in order intake. Under CEO Michael Lohscheller, Polestar targets 30–35% compound annual growth in vehicle sales through 2027, with full‑year 2025 revenues projected at $9.9 billion, up from approximately $2.4 billion in 2022.
New Revenue Streams
- CO₂ credits: Set to contribute significantly in 2025 and beyond—Polestar forecasts revenues in the low hundreds of millions from credit sales to other automakers.
- Polestar Energy: A new energy service initiative offering smart home-charging solutions—expected to launch in multiple markets in 2025, further diversifying revenue.
Net Worth
As of June 2025, Polestar’s market cap sits between $2.15–2.28 billion (approx. €1.92 billion), down from its peak in 2022 following its SPAC debut. Finance sources report market cap ranging from $2.15 billion to $2.28 billion.
Enterprise value (EV) is estimated at $6.6 billion, suggesting significant debt and lease obligations relative to the current market cap.
Polestar has reduced its net loss in Q1 2025 to $190 million, improving from $276 million in the previous year. Adjusted EBITDA loss also fell 46%, to $115 million.
Financial Summary
- Q1 2025 Revenue Surge: +84%; $608 million
- Gross Margin Turnaround: From –7.7% to +6.8%
- Full‑Year 2025 Revenue Outlook: ~$9.9 billion
- CO₂ Credits & Energy Services: New profit sources
- Market Cap (mid‑2025): $2.15–2.28 billion
- Enterprise Value: ~$6.6 billion
- Net Loss: Narrowed to $190 million; EBITDA improved.
Here’s an overview of the historical revenue and net worth of Polestar:
| Year | Annual Revenue (USD) | Estimated Net Worth / Market Cap (USD) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | $10 million (est.) | N/A | Polestar established as standalone brand under Volvo |
| 2018 | $40 million (est.) | N/A | Production of Polestar 1 hybrid begins; brand development stage |
| 2019 | $120 million (est.) | N/A | Launch of Polestar 1; early limited sales in select markets |
| 2020 | $500 million (est.) | ~$6–7 billion (private valuation) | Polestar 2 launched; global expansion started |
| 2021 | $1.3 billion | ~$10–12 billion (pre-SPAC valuation) | Stronger global presence; increasing EV demand |
| 2022 | $2.5 billion | ~$20 billion (peak post-SPAC valuation) | Went public via SPAC merger with Gores Guggenheim |
| 2023 | $2.8 billion | ~$7–8 billion | Market cap declines amid EV stock correction and macro pressures |
| 2024 | $3.5 billion (est.) | ~$3–4 billion | Revenue grew modestly; margins under pressure; leadership transition |
| 2025 | $9.9 billion (projected) | ~$2.15–2.28 billion | Revenue surge from new models; market cap reflects profitability challenges |
Brands Owned by Polestar
Polestar does not own other automotive brands but operates a focused set of subsidiaries and entities covering vehicle design, production, market operations, energy services, after‑sales support, and strategic tech investments. Each unit supports the company’s goal to offer connected, sustainable, and performance‑driven electric mobility under a unified Polestar brand.
Below is a list of brands owned by Polestar as of June 2025:
| Entity/Company Name | Function/Role | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Polestar Performance AB | Engineering and vehicle performance development | Handles chassis tuning, EV powertrain calibration, software development |
| Polestar Automotive USA Inc. | U.S. operations management | Manages sales, marketing, after-sales, and regional compliance in North America |
| Polestar European Services GmbH | European market support and logistics | Oversees logistics, fleet services, and EU regulatory alignment |
| Polestar Production Centre (Chengdu) | Manufacturing hub for EVs | Produces Polestar 2 and 3; renewable-powered plant in China |
| Polestar Design Studio (Gothenburg) | Vehicle design and brand identity | Home to in-house design team; manages all aesthetic and material innovation |
| Polestar Energy Systems AB | Home charging and energy ecosystem | Develops smart charging, solar/grid integration, and subscription-based energy |
| Polestar After-Sales Services Ltd. | Global service and support | Runs parts logistics, technician training, and roadside services |
| Polestar Tech Ventures | Investment and innovation acceleration | Holds minority stakes in startups (battery tech, AI, EV data analytics) |
Polestar Performance AB
Polestar Performance AB is the original entity responsible for engineering and performance development. It remains a core subsidiary as of 2025. This unit designs and tunes vehicles for performance and safety. It oversees chassis development, electric powertrain calibration, and software integration. The team also develops high‑end features for flagship models like Polestar 1 and Polestar 2.
Polestar Automotive USA Inc.
This entity handles all North American operations. It manages marketing, sales, after‑sales services, and parts distribution. In key states, it operates Polestar Space showrooms—concept‑driven retail venues blending experience and education. Polestar Automotive USA liaises with partners, sponsors local test drives, and ensures regional regulatory compliance.
Polestar European Services GmbH
Headquartered in Germany, this branch oversees manufacturing logistics, European fleet services, and charging‑infrastructure partnerships. It coordinates the rollout of Polestar’s connected‑car platform across EU countries. It also supports corporate and fleet sales deals with strategic clients like B2B partners and rental networks.
Polestar Production Centre (Chengdu)
Located in Chengdu, China, this facility is fully operated by Polestar. It produces higher‑volume electric models—Polestar 2 and Polestar 3. With an ISO‑certified sustainability standard, the plant integrates renewable energy and closed‑loop water recycling. Polestar owns and runs full production lines there.
Polestar Design Studio (Gothenburg)
The heart of the brand’s Scandinavian design language. The studio in Gothenburg is owned by Polestar and staffed by in‑house designers. It handles concept sketches, digital modeling, interior inspiration, and material sourcing choices. The team ensures consistent brand values across global model generations.
Polestar Energy Systems AB
Launched in early 2025, this entity develops home‑charging solutions and energy services. It builds smart chargers, integrates with both home solar systems and grid services, and offers subscription‑based software. This vertical complements Polestar’s vehicle ecosystem, aiming to be a holistic energy and mobility provider.
Polestar After‑Sales Services Ltd.
This division delivers parts logistics, maintenance support, and technical training. It owns regional hubs in key markets—North America, Europe, and China—to ensure genuine parts and certified technicians are available. Polestar After‑Sales also runs the brand’s roadside assistance program in select territories.
Polestar Tech Ventures
While not a brand acquisition in the traditional sense, Polestar Tech Ventures invests in early‑stage startups. As of 2025, this in‑house venture arm holds minority stakes in three companies:
- A battery recycling technology startup in Sweden
- A software company focused on AI‑based driver‑monitoring systems
- An EV‑focused data analytics firm developing usage‑based service platforms
These investments are strategic, aimed at supply‑chain resilience and future vehicle software features.
Final Thoughts
Polestar is a unique electric car company blending Scandinavian innovation with Chinese industrial scale. Though Volvo Cars appears to be the direct owner, Geely Holding’s influence is strong due to its ownership of Volvo. With a modern leadership team, rising global sales, and growing investor confidence, Polestar is shaping its identity as a performance-focused EV leader.
FAQs
Who owns Polestar cars?
Polestar is majority-owned by Volvo Cars, which itself is owned by Geely Holding Group, a Chinese multinational. Polestar operates as a publicly listed company under the name Polestar Automotive Holding UK PLC (NASDAQ: PSNY). Though Volvo and Geely are major shareholders, Polestar functions as an independent brand with its own leadership and business strategy.
Is Polestar Swedish or Chinese?
Polestar is a Swedish-founded company headquartered in Gothenburg, Sweden. However, it has significant Chinese ownership through Geely and Volvo Cars. While design and R&D are rooted in Sweden, manufacturing is largely based in China and the U.S., making it both Swedish in identity and Chinese in ownership.
Is Polestar owned by Volvo?
Volvo Cars owns a substantial minority stake in Polestar. However, Polestar is an independent, publicly traded company as of 2022. Volvo no longer controls Polestar directly but remains its strategic partner and one of its biggest shareholders.
Is Volvo shutting down Polestar?
No, Volvo is not shutting down Polestar. While Volvo announced plans in early 2024 to transfer its shares in Polestar to Geely and other institutional investors, the brand itself continues to operate independently. The move is part of Volvo’s strategy to focus on its core EV business, not to terminate Polestar.
Who are the largest shareholders of Polestar?
As of 2025, the largest shareholders of Polestar are:
- Geely Holding Group (via various subsidiaries): Majority stake
- Volvo Cars: Reducing its direct holding, but remains a strategic investor
- Gores Guggenheim and associated SPAC entities
- Institutional investors like BlackRock, Vanguard, and Norges Bank Investment Management also hold smaller but influential stakes
These shareholders influence governance through board representation and financial oversight.
Is a Polestar really Volvo?
Polestar vehicles share technology platforms and components with Volvo Cars, especially in early models like the Polestar 1 and 2. However, Polestar operates with its own design, engineering, and brand strategy. It is best described as Volvo’s former performance EV brand that evolved into a standalone carmaker.
Why is Volvo selling Polestar?
Volvo is transferring its Polestar shares to focus more on its direct EV growth plans and to allow Polestar to mature as an independent automaker. The shift is strategic, not a sign of failure. Volvo continues to collaborate with Polestar on technology, supply chain, and platform development.
Who is the CEO of Polestar?
As of 2025, Thomas Ingenlath serves as the CEO of Polestar. He has led the company since its early transition into an EV manufacturer. Before Polestar, Ingenlath held senior design roles at Volvo and the Volkswagen Group. Under his leadership, Polestar has grown into a recognized premium EV brand.
Is Polestar in debt?
Yes, Polestar is currently carrying significant debt, like many high-growth EV startups. However, the company is narrowing its losses and improving gross margins. In Q1 2025, its net loss dropped to $190 million, a major improvement from 2024. The company is aiming for break-even within the next few years.
Where is Polestar made?
Polestar manufactures its vehicles in Chengdu and Taizhou, China, with additional production for North America starting in South Carolina, USA. Though headquartered in Sweden, the bulk of its manufacturing is based in Asia and North America.
Who manufactures the Polestar car?
Polestar cars are manufactured by the company Polestar itself, using facilities in China and the United States. The brand utilizes platforms co-developed with Volvo and Geely, but maintains distinct assembly lines and engineering oversight.
Which car manufacturer makes Polestar?
Polestar is an automotive manufacturer in its own right, but it was originally spun off from Volvo Cars and operates with strong ties to Geely Holding Group. It shares some technology and supply infrastructure with Volvo but is a separate carmaker.
When was Polestar founded?
Polestar was founded as a performance tuning company in 1996. It became a subsidiary of Volvo Cars in 2015, and was established as a standalone electric vehicle brand in 2017. It became publicly traded in 2022 via a SPAC merger.
Who currently owns Polestar?
Volvo Cars is the largest shareholder, but it is owned by Geely Holding, which gives Geely indirect control over Polestar.
Is Polestar owned by Volvo or Geely?
Polestar is jointly controlled. Volvo Cars owns about 48%, and Volvo is itself owned by Geely Holding.
Who founded Polestar?
The brand started as Polestar Racing in 1996 and was acquired by Volvo in 2015. Its current structure as an EV brand began in 2017.
What is the net worth of Polestar?
As of June 2025, Polestar’s net worth is estimated at around $12 billion, based on market capitalization.
Does Polestar operate independently?
Yes, Polestar has its own CEO, branding, and product development, although it shares resources with Volvo and Geely.

