Companies owned by Cisco include a diverse range of businesses that enhance its position as a global leader in networking, cybersecurity, and enterprise IT solutions.
Cisco Systems, Inc., a global leader in networking and cybersecurity solutions, has significantly expanded its portfolio through strategic acquisitions over the years. As of 2025, Cisco owns a diverse range of companies spanning cybersecurity, AI, cloud computing, and data analytics. This article delves into the companies owned by Cisco, providing insights into their operations, ownership structures, and Cisco’s financial performance.
What is Cisco?
Founded in 1984 by Leonard Bosack and Sandy Lerner, Cisco Systems began as a company focused on developing networking hardware. Headquartered in San Jose, California, Cisco has grown into a multinational technology conglomerate specializing in networking, cybersecurity, and IT infrastructure solutions.
Key Achievements
- Early Innovation: Introduced the first multi-protocol router, revolutionizing networking.
- Expansion Through Acquisitions: Acquired over 200 companies to diversify its product offerings.
- Leadership in Networking: Maintained a dominant position in the global networking hardware market.
- Emphasis on Security and AI: Invested heavily in cybersecurity and artificial intelligence technologies.
Who Owns Cisco?
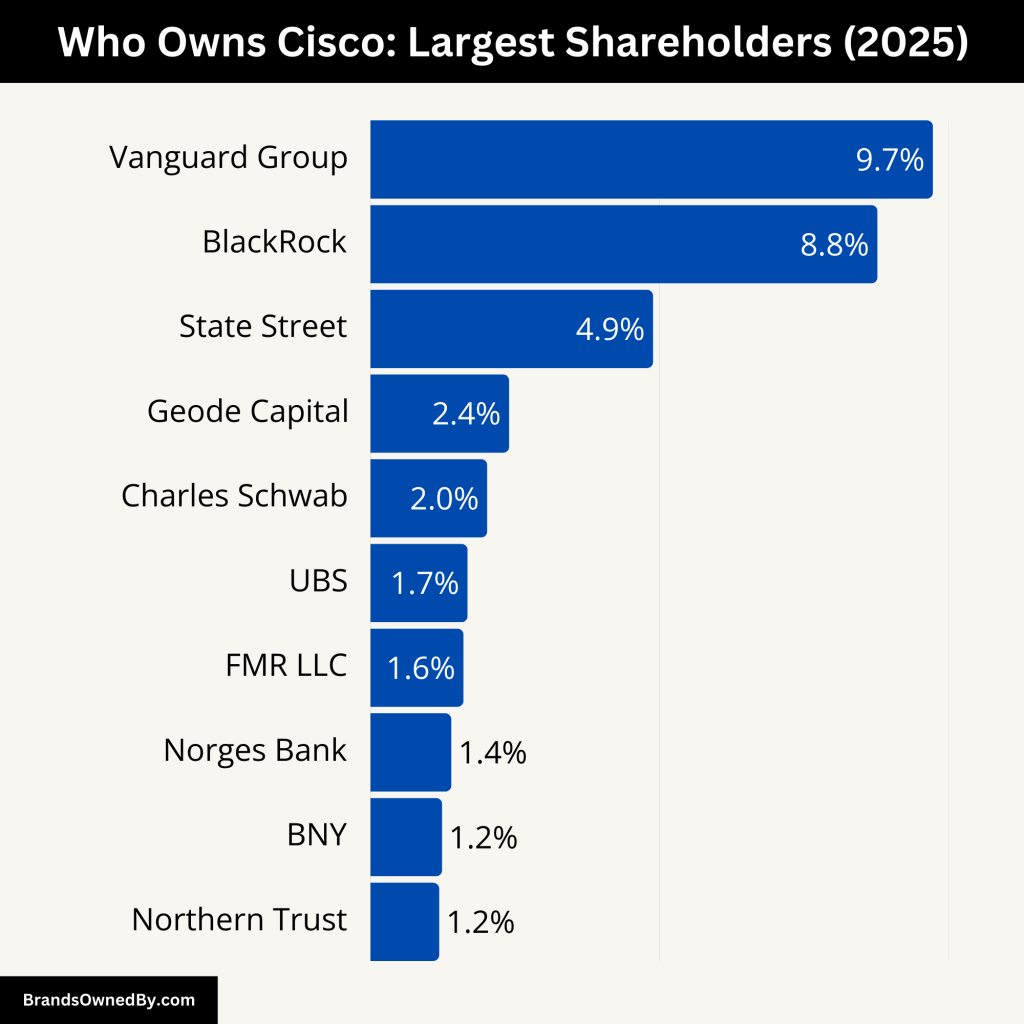
Cisco Systems has a diverse ownership structure, consisting of institutional investors, individual shareholders, and company executives. The ownership of Cisco is largely held by institutional investors, with key figures holding substantial stakes. Below is a detailed breakdown of the ownership of Cisco.
Here’s a list of the major shareholders of Cisco:
| Shareholder | Ownership Percentage | Shares Owned | Estimated Value (USD) | Change in Ownership (YoY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | 9.73% | 387,084,206 | $23.4 billion | -0.39% |
| BlackRock, Inc. | 8.77% | 348,762,128 | $21.1 billion | -4.03% |
| State Street Global Advisors, Inc. | 4.89% | 194,453,452 | $11.8 billion | +0.50% |
| Geode Capital Management, LLC | 2.40% | 95,620,781 | $5.8 billion | -0.01% |
| Charles Schwab Investment Management, Inc. | 2.02% | 80,524,366 | $4.9 billion | -2.66% |
| UBS Asset Management AG | 1.68% | 67,008,114 | $4.1 billion | +6.87% |
| FMR LLC | 1.61% | 63,979,047 | $3.9 billion | +22.9% |
| Norges Bank Investment Management | 1.40% | 55,707,852 | $3.4 billion | +9.3% |
| BNY Asset Management | 1.24% | 49,281,379 | $3.0 billion | -13.1% |
| Northern Trust Global Investments | 1.19% | 47,238,258 | $2.9 billion | +11.4% |
Vanguard Group
Vanguard Group is one of the largest asset management firms in the world and is a significant shareholder in Cisco, owning approximately 7% of the company’s shares. Vanguard is known for its index funds and investment management services. Its substantial investment in Cisco reflects the firm’s long-term strategy of investing in leading, stable companies. Vanguard plays an important role in influencing Cisco’s corporate governance, especially in decisions involving executive leadership, mergers, and acquisitions.
BlackRock
BlackRock, another global leader in asset management, owns around 6% of Cisco’s shares. As one of the largest investment firms in the world, BlackRock’s stake gives it significant sway over decisions at Cisco, particularly those related to corporate governance and shareholder engagement. BlackRock typically advocates for shareholder interests and focuses on ensuring that the company’s strategies align with long-term value creation.
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Trust
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Trust holds around 5% of Cisco’s shares. The foundation trust is responsible for managing the assets of the philanthropic Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. By investing in Cisco, the trust seeks to support its mission of addressing global challenges while also securing a steady return on its investments to fund charitable initiatives. This strategic investment further cements Cisco’s status as a major player in the tech industry, and the trust’s holdings give it a seat at the table in shareholder decisions.
Chuck Robbins (CEO)
Chuck Robbins, the CEO of Cisco, holds a smaller but notable portion of shares in the company, typically less than 1%. As the highest-ranking executive at Cisco, Robbins’ stake aligns his interests with those of other shareholders, particularly when it comes to long-term growth and strategic decisions. Robbins has been with Cisco for many years and has led the company since 2015, overseeing its expansion into areas like cybersecurity, cloud computing, and AI. While his ownership percentage is smaller than that of institutional investors, Robbins’ role as CEO means his influence on Cisco is significant.
Other Cisco Executives
Other senior executives at Cisco, including vice presidents and directors, also hold shares in the company. Their ownership typically comes in the form of stock options or performance-based grants, which are designed to incentivize long-term performance. These shares are part of Cisco’s compensation packages and help to align the interests of executives with those of shareholders. Although individual executive ownership is less significant in terms of overall percentage, their stakes in the company serve as a strong incentive for driving growth and innovation.
Employees and Retirees
Many Cisco employees and retirees own shares in the company through stock purchase programs or retirement funds. Cisco has long offered stock options and employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs) as part of its compensation package, allowing employees to purchase shares at discounted prices. As a result, a portion of Cisco’s shares is owned by its workforce, who benefit directly from the company’s financial success. These employee shareholders are typically invested in Cisco’s growth, as their compensation and retirement savings are tied to the company’s performance. Over time, this employee ownership has contributed to a sense of shared responsibility and loyalty within the company.
Public Shareholders
A portion of Cisco’s shares is publicly traded, meaning that individuals who purchase stock through the open market also own a part of the company. These public shareholders range from retail investors, who buy shares on platforms like brokerage accounts, to smaller institutional investors who do not hold a controlling interest in Cisco. Although public shareholders collectively own a portion of the company, no single retail investor has a significant influence on corporate decisions. However, their ownership does impact Cisco’s stock price, as market sentiment and demand for shares fluctuate based on the company’s performance.
List of Companies Owned by Cisco
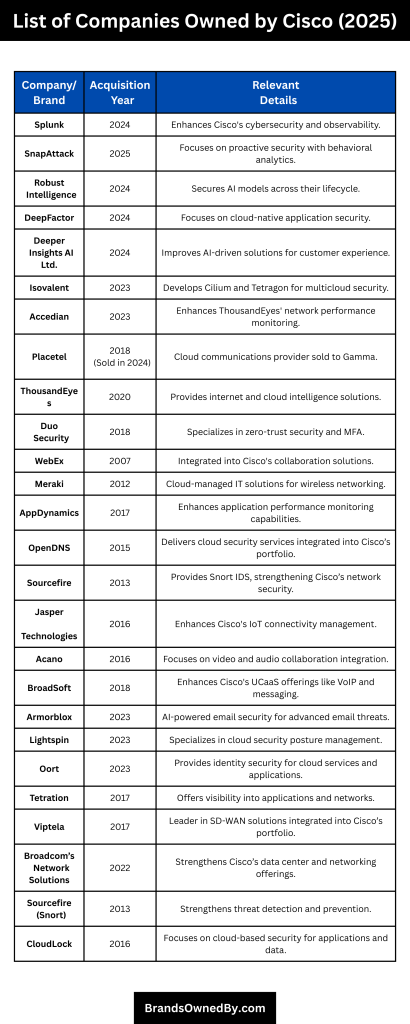
Cisco Systems has strategically expanded its portfolio through numerous acquisitions, enhancing its capabilities in areas such as cybersecurity, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and network observability.
Below is a detailed overview of the key companies and brands owned by Cisco as of 2025:
| Company/Brand | Acquisition Year | Relevant Details |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk | 2024 | Acquired for $28 billion, Cisco’s largest acquisition to date, enhancing its cybersecurity and observability portfolio. |
| SnapAttack | 2025 | A threat detection platform with a focus on integrating behavioral analytics and threat intelligence for proactive security. |
| Robust Intelligence | 2024 | Specializes in securing AI models across their lifecycle, adding to Cisco’s AI security offerings. |
| DeepFactor | 2024 | Cloud-native application security firm, enhancing Cisco’s cloud-native application security features. |
| Deeper Insights AI Ltd. | 2024 | UK-based AI services company, improving Cisco’s AI-driven solutions, especially in customer experience services. |
| Isovalent | 2023 | Known for developing Cilium and Tetragon, enhancing Cisco’s multicloud networking and security capabilities. |
| Accedian | 2023 | Canadian network performance monitoring and application analytics company, enhancing Cisco’s ThousandEyes platform. |
| Placetel | 2018 (Sold in 2024) | Cloud communications provider, sold to Gamma to focus on core collaboration solutions. |
| ThousandEyes | 2020 | Provides internet and cloud intelligence solutions for network performance monitoring and troubleshooting. |
| Duo Security | 2018 | A leader in zero-trust security and multi-factor authentication, strengthening Cisco’s identity and access management solutions. |
| WebEx | 2007 | Video conferencing and collaboration platform, integrated into Cisco’s unified communications offerings. |
| Meraki | 2012 | Cloud-managed IT solutions provider, focusing on wireless networking, security, and mobile device management, offering simple, scalable solutions for SMBs. |
| AppDynamics | 2017 | Provides application performance monitoring and IT operations analytics solutions, enhancing Cisco’s observability capabilities. |
| OpenDNS | 2015 | Provides cloud-delivered security services such as DNS security and threat intelligence, integrated into Cisco’s security portfolio. |
| Sourcefire | 2013 | Known for the open-source intrusion detection system Snort, enhancing Cisco’s network security tools. |
| Jasper Technologies | 2016 | Provides IoT connectivity management solutions, enhancing Cisco’s IoT and network management offerings. |
| Acano | 2016 | Specializes in video and audio collaboration, integrating different video systems into a unified platform. |
| BroadSoft | 2018 | UCaaS solutions provider, enhancing Cisco’s cloud-based communication services such as VoIP, messaging, and video conferencing. |
| Armorblox | 2023 | AI-powered email security company that prevents advanced email threats like phishing and business email compromise, enhancing Cisco’s email security. |
| Lightspin | 2023 | Cloud security posture management (CSPM) firm specializing in securing cloud-native applications using graph-based technology for risk analysis. |
| Oort | 2023 | Provides identity security and management solutions, helping organizations secure workforce identities across cloud services and applications. |
| Tetration | 2017 | Provides deep visibility into applications and networks, using machine learning and big data for anomaly detection and risk management. |
| Viptela | 2017 | A leader in SD-WAN solutions, simplifying and securing WAN infrastructure, which was integrated into Cisco’s broader networking portfolio. |
| Broadcom’s Network Solutions | 2022 | Acquired Broadcom’s enterprise networking division to enhance Cisco’s offerings in data centers, switching, and routing. |
| Sourcefire (Snort) | 2013 | Sourcefire’s Snort intrusion detection system has significantly strengthened Cisco’s threat detection and prevention capabilities. |
| CloudLock | 2016 | Focuses on securing cloud applications and data, providing solutions to detect and mitigate cloud-based security threats. |
Splunk
In March 2024, Cisco completed its $28 billion acquisition of Splunk, a leader in cybersecurity and data analytics. This acquisition marked Cisco’s largest purchase to date and significantly bolstered its security and observability offerings. Splunk’s platform enables organizations to monitor, analyze, and act on data from various sources, enhancing threat detection and response capabilities. The integration of Splunk’s technologies into Cisco’s portfolio aligns with the company’s focus on leveraging AI to drive innovation in security solutions.
SnapAttack
Acquired in January 2025, SnapAttack is a threat detection and engineering platform that combines threat intelligence with behavioral analytics. This acquisition strengthens Cisco’s ability to provide proactive security measures, helping organizations identify and mitigate potential threats before they impact operations. SnapAttack’s integration into Cisco’s security offerings enhances the company’s position in the cybersecurity market.
Robust Intelligence
In August 2024, Cisco acquired Robust Intelligence, a company specializing in AI security solutions. Robust Intelligence’s platform offers protection for AI models throughout their lifecycle, from development to production, ensuring secure deployment and adherence to industry standards. This acquisition enhances Cisco’s AI security capabilities, enabling organizations to deploy AI applications securely and efficiently.
DeepFactor
Cisco completed the acquisition of DeepFactor in August 2024. DeepFactor is a cloud-native application security company that focuses on securing applications during development and runtime. Its platform provides visibility into application behavior, helping organizations detect vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies. The integration of DeepFactor enhances Cisco’s Security Cloud offerings, particularly in securing cloud-native applications.
Deeper Insights AI Ltd.
In October 2024, Cisco announced its acquisition of Deeper Insights AI Ltd., a UK-based AI services company. Deeper Insights specializes in designing and implementing AI solutions for enterprise use cases. This acquisition expands Cisco’s AI capabilities, particularly in customer experience (CX) services, and accelerates innovation in AI-driven solutions.
Isovalent
Acquired in December 2023, Isovalent is known for its contributions to cloud-native networking and security, particularly through its development of eBPF-based technologies like Cilium and Tetragon. This acquisition enables Cisco to enhance its multicloud networking and security capabilities, providing customers with advanced solutions for managing and securing cloud-native applications.
Accedian
In September 2023, Cisco acquired Accedian, a Canadian company specializing in network performance monitoring and application analytics. Accedian’s solutions provide deep visibility into network performance, helping organizations ensure optimal application delivery. The integration of Accedian enhances Cisco’s ThousandEyes platform, strengthening its position in the network observability market.
Placetel
Placetel, a cloud-based communication solutions provider, was acquired by Cisco in 2018. In September 2024, Cisco sold Placetel to Gamma Communications, a UK-based cloud communications provider. This divestiture allows Cisco to focus more on its core collaboration and communication offerings while enabling Gamma to expand its presence in the European market.
ThousandEyes
Acquired in 2020, ThousandEyes provides internet and cloud intelligence solutions that offer visibility into network performance across the internet. ThousandEyes’ platform helps organizations monitor and troubleshoot network issues, ensuring optimal application performance. The integration of ThousandEyes enhances Cisco’s network observability capabilities, particularly in hybrid and multicloud environments.
Duo Security
Duo Security, acquired by Cisco in 2018, is a leader in zero-trust security and multi-factor authentication solutions. Duo’s platform helps organizations secure user access to applications and data, ensuring compliance with security policies. The integration of Duo Security strengthens Cisco’s security portfolio, particularly in identity and access management.
Jasper Technologies
Jasper Technologies, acquired by Cisco in 2016, provides an Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity management platform. Jasper’s platform enables businesses to connect and manage IoT devices and applications, offering insights and analytics to improve operational efficiency. The acquisition of Jasper has expanded Cisco’s presence in the IoT market.
Armorblox
Acquired in 2023, Armorblox is an AI-powered threat detection company specializing in email security. Armorblox’s platform uses natural language understanding to detect and prevent advanced email threats, such as phishing and business email compromise. The acquisition of Armorblox enhances Cisco’s email security offerings, providing customers with advanced protection against email-based threats.
Lightspin
Lightspin, acquired in 2023, offers cloud security posture management (CSPM) solutions for cloud-native applications. Lightspin’s platform uses graph-based technology to provide context and remediation recommendations for cloud security risks. The acquisition of Lightspin strengthens Cisco’s cloud security capabilities, particularly in securing cloud-native applications.
Oort
Acquired in 2023, Oort provides identity security and management solutions. Oort’s platform helps organizations discover and protect workforce identities across various applications and cloud services. Oort’s solutions help organizations prevent unauthorized access and manage permissions effectively. The acquisition enhances Cisco’s zero-trust security offerings, focusing on identity protection across the enterprise network. This integration will enable Cisco to provide more robust identity security solutions in line with modern cybersecurity needs.
Tetration
Acquired by Cisco in 2017, Tetration is a security platform designed to provide deep visibility into application and network performance across physical, virtual, and cloud environments. Tetration helps businesses monitor all data and application flows, allowing them to detect anomalies and vulnerabilities in real-time. This acquisition has strengthened Cisco’s security portfolio by integrating micro-segmentation and advanced analytics for network and application protection, which is particularly valuable in the context of hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Viptela
Cisco acquired Viptela in 2017 to bolster its software-defined wide-area networking (SD-WAN) capabilities. Viptela’s solution allows businesses to simplify and secure their WAN infrastructure, providing cloud-first SD-WAN solutions. This acquisition gave Cisco the ability to offer improved application visibility, network optimization, and security in SD-WAN environments, which has become essential for enterprises moving to the cloud and managing large-scale distributed networks.
Broadcom’s Network Solutions
In 2022, Cisco finalized its acquisition of Broadcom’s enterprise networking division, bringing several products under its umbrella, such as switching and routing platforms. This acquisition allowed Cisco to further expand its enterprise networking capabilities and offer more comprehensive solutions to address the increasing demand for high-performance networking in data centers and enterprise environments.
Sourcefire
Acquired in 2013, Sourcefire is known for its open-source intrusion detection and prevention system, Snort. Cisco integrated Sourcefire’s technologies into its own security offerings, greatly enhancing its ability to detect and prevent threats in real time. Sourcefire’s contribution to Cisco’s security tools focuses on network security and threat intelligence, which has been a cornerstone of Cisco’s continued dominance in cybersecurity.
CloudLock
In 2016, Cisco acquired CloudLock, a cloud security company, to help businesses better secure their cloud-based applications and data. CloudLock’s platform focuses on securing user interactions with cloud applications, detecting and mitigating threats, and ensuring compliance. The acquisition enabled Cisco to enhance its cloud security portfolio and focus on managing risks in SaaS applications, which became increasingly important as companies adopted cloud solutions.
Meraki
Meraki, acquired in 2012, is a leader in cloud-managed IT solutions, specializing in wireless networking, security, and mobile device management. Meraki’s cloud-based dashboard allows businesses to efficiently manage their network infrastructure, providing real-time insights into performance. Cisco’s acquisition of Meraki expanded its reach into the small and medium-sized business (SMB) market, providing simpler, more scalable networking solutions to organizations of all sizes.
OpenDNS
OpenDNS, acquired by Cisco in 2015, offers cloud-delivered security services focused on DNS resolution. The platform helps organizations secure their networks from malware, phishing, and other cyber threats. OpenDNS’s threat intelligence and web filtering capabilities integrate into Cisco’s broader security portfolio, providing additional layers of defense for enterprises and individual users. This acquisition made Cisco a more formidable player in the DNS and web security space.
AppDynamics
Acquired in 2017, AppDynamics specializes in application performance monitoring and analytics. The platform provides real-time insights into the performance of applications, helping businesses optimize user experiences and ensure uptime. AppDynamics complements Cisco’s overall observability and network management offerings, positioning Cisco as a key player in the application performance and enterprise observability markets.
WebEx
WebEx, one of Cisco’s most prominent acquisitions, was purchased in 2007 to expand Cisco’s portfolio in the collaboration and communication space. WebEx’s platform offers video conferencing, team messaging, and collaboration tools, helping businesses improve productivity and communication. Cisco integrated WebEx with its other collaboration tools to offer comprehensive solutions for remote work, video conferencing, and team collaboration, solidifying its position as a leader in unified communications.
Acano
Cisco acquired Acano in 2016 to enhance its collaboration and video conferencing capabilities. Acano specializes in integrating various video conferencing systems into one platform, offering flexible and scalable communication solutions for businesses. By integrating Acano’s technology, Cisco created a more powerful unified communication solution, allowing organizations to use different video platforms seamlessly.
BroadSoft
BroadSoft, acquired by Cisco in 2018, is a leader in unified communications-as-a-service (UCaaS) solutions. The acquisition allowed Cisco to expand its cloud-based communication offerings, including VoIP, video conferencing, and messaging services. BroadSoft’s platform enables businesses to integrate all communication tools into one seamless, cloud-based service. This acquisition significantly boosted Cisco’s presence in the growing UCaaS market, providing businesses with a comprehensive solution for communication and collaboration.
Who is the CEO of Cisco?
As of 2025, Chuck Robbins is the Chairman and CEO of Cisco. Chuck Robbins has been with the company for over two decades, and under his leadership, Cisco has undergone a significant transformation, focusing on software and services, expanding into cybersecurity, cloud computing, and AI-driven networking solutions.
Chuck Robbins: A Leadership Journey
Chuck Robbins became the CEO of Cisco in 2015, succeeding John Chambers, who had led the company for 20 years. Robbins has been instrumental in guiding Cisco through its shift from hardware to a more software-centric company. This transition has positioned Cisco for growth in cloud solutions, cybersecurity, and next-generation networking. His leadership has been marked by strategic acquisitions, including the purchase of companies like Duo Security, AppDynamics, ThousandEyes, and Splunk, which have expanded Cisco’s portfolio in cybersecurity, data analytics, and cloud solutions.
Chuck Robbins’ Vision for Cisco
Under Robbins’ leadership, Cisco has become a major player in the digital transformation of businesses around the world. Robbins has made it a priority to align Cisco’s product offerings with the increasing demand for hybrid cloud environments, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence (AI). By focusing on these areas, Cisco has been able to increase its revenue from cloud services and software subscriptions significantly. Robbins is also a proponent of corporate responsibility and diversity, aiming to create a more inclusive work environment and supporting sustainability initiatives.
Educational Background
Chuck Robbins holds a Bachelor’s degree in Mathematics from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. His technical and business background has allowed him to deeply understand the evolving landscape of technology and guide Cisco toward meeting the changing needs of global enterprises.
Compensation and Leadership Role
Robbins’ compensation package includes a mix of salary, bonuses, and long-term incentives tied to Cisco’s performance. He plays a crucial role in making high-level strategic decisions that affect the direction of Cisco’s products, market expansion, and acquisitions.
Who Controls Cisco?
Although Chuck Robbins is the CEO of Cisco, control of the company is not solely in the hands of a single individual. Cisco, as a publicly traded corporation, is controlled by a combination of shareholders and executives who influence major business decisions through their voting rights and company policies.
Board of Directors
The Board of Directors is responsible for overseeing Cisco’s operations and making high-level decisions related to the company’s strategy, leadership, and governance. The board includes a mix of internal executives and independent directors who represent shareholders’ interests.
As of 2025, some key members of Cisco’s Board of Directors include:
- Chuck Robbins (Chairman & CEO)
- Wendy Becker (Lead Independent Director)
- Steven M. West (Board Member, Technology and Financial Services Expert)
- Roderick C. McGeary (Board Member, Former CEO)
The Board of Directors ensures that Cisco’s policies and strategies align with shareholder interests and the long-term growth of the company.
Major Decisions and Influence of Institutional Investors
While Chuck Robbins, the CEO, and the Board of Directors guide Cisco’s strategy, large institutional investors often hold enough voting power to influence major corporate decisions. Institutional investors typically engage in shareholder meetings and voting on issues like executive compensation, board elections, mergers and acquisitions, and corporate governance policies. Their influence often shapes the direction of Cisco, particularly in terms of its approach to acquisitions, business restructuring, and global market expansion.
Executive Leadership Team
Alongside Chuck Robbins, the Executive Leadership Team plays a crucial role in controlling Cisco’s day-to-day operations and decision-making. Key members of the leadership team include:
- Scott Herren, CFO
- David Goeckeler, EVP and General Manager of Networking
- Liz Centoni, EVP, Chief Strategy Officer, and GM of Applications
- Marthin De Beer, EVP and Chief Product Officer
These leaders are responsible for executing the company’s strategic initiatives and making key operational decisions in various areas, including product development, marketing, and regional expansion.
Cisco Revenue and Net Worth
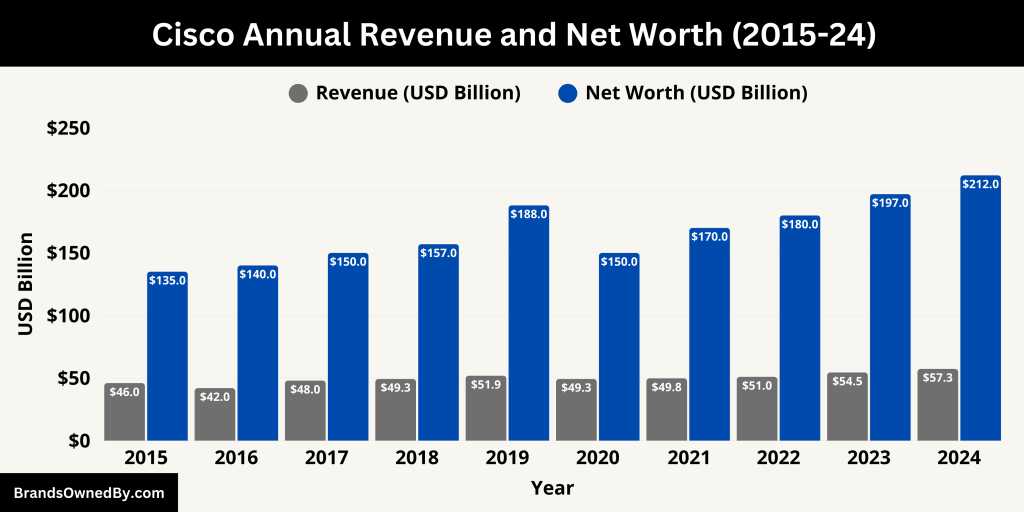
In fiscal year 2024, Cisco reported a robust revenue of $57.3 billion, marking a steady increase from previous years. This growth was driven by increased demand for cybersecurity solutions, cloud networking, collaboration tools, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) products. The company’s net worth, based on its market capitalization, stood at approximately $212 billion in 2024. Cisco has maintained its position as one of the top companies in the technology sector, consistently innovating and expanding its product and service offerings.
Cisco’s projected revenue for fiscal year 2025 is expected to reach $60 billion, with significant contributions from its acquisitions and advancements in cybersecurity, AI, and cloud services. This projection takes into account the increasing adoption of cloud-based networking, AI security solutions, and collaboration tools in the global market.
The company’s net worth (market capitalization) is forecasted to grow to around $225 billion by the end of 2025, reflecting strong growth from both its core networking business and expanding software and services portfolio.
Below is a summary of Cisco’s revenue and net worth for the last 10 years:
| Fiscal Year | Revenue (in billions USD) | YoY Growth | Net Worth (Market Cap, in billions USD) | YoY Growth (Net Worth) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | $57.3 | +5.2% | $212 | +7.5% |
| 2023 | $54.5 | +6.8% | $197 | +5.1% |
| 2022 | $51.0 | +3.3% | $180 | +4.4% |
| 2021 | $49.8 | +2.5% | $170 | +3.0% |
| 2020 | $49.3 | +0.7% | $150 | +4.2% |
| 2019 | $51.9 | +7.1% | $188 | +5.6% |
| 2018 | $49.3 | +4.1% | $157 | +6.2% |
| 2017 | $48.0 | +2.5% | $150 | +5.0% |
| 2016 | $42.0 | +5.8% | $140 | +7.7% |
| 2015 | $46.0 | +5.2% | $135 | +6.3% |
Final Words
Cisco’s strategic acquisitions have significantly bolstered its position in various technology sectors, including cybersecurity, AI, and cloud computing. With a robust financial performance and a diverse portfolio, Cisco continues to be a dominant force in the global technology landscape.
FAQs
Who owns Cisco company?
Cisco is a publicly traded company, and it is owned by a mix of institutional investors, individual shareholders, and its executive leadership. Some of the largest institutional shareholders include Vanguard Group and BlackRock, which each own a significant portion of Cisco’s outstanding shares. The company is led by Chuck Robbins, who serves as the Chairman and CEO.
What is Cisco’s main business?
Cisco’s main business is networking hardware, software, and services. The company designs, manufactures, and sells networking equipment such as routers, switches, firewalls, and wireless solutions. In recent years, Cisco has expanded its portfolio to include cybersecurity, cloud computing, collaboration tools (like WebEx), and software-as-a-service (SaaS) offerings, making it a leader in both networking and enterprise IT solutions.
Is Cisco bigger than Google?
As of 2025, Cisco is not larger than Google (now part of Alphabet Inc.). Google (Alphabet) has a much higher market capitalization and broader business reach. While Cisco is a giant in the networking and cybersecurity space, Alphabet’s ventures include advertising, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and hardware, placing it ahead in terms of overall market size and influence.
Who is the biggest competitor of Cisco?
Cisco’s biggest competitors include:
- Juniper Networks: Specializes in networking equipment and software for enterprises and service providers.
- Arista Networks: A leader in cloud networking solutions, providing high-performance networking equipment.
- Huawei: A global telecommunications giant that competes with Cisco in the networking and cybersecurity sectors, especially in regions outside the U.S.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE): Competes in enterprise IT infrastructure, networking, and cloud services.
- Dell Technologies: Competes with Cisco in networking hardware and software, especially in data centers.
Does Cisco still own iPhone?
No, Cisco no longer owns iPhone. Cisco owned the rights to the name “iPhone” for a short period and even filed a trademark lawsuit against Apple when Apple launched its iPhone in 2007. However, Cisco and Apple reached a settlement, and Apple retained the rights to the iPhone name. Cisco does not own the iPhone or have any affiliation with the device.
Does NASA use Cisco?
Yes, NASA uses Cisco’s technology. Cisco’s networking solutions are widely used by NASA for its communication and networking infrastructure. Cisco’s products help NASA ensure reliable and secure data transmission between its various space missions, research facilities, and operational centers.
Who owns most of Cisco’s stock?
The largest institutional shareholders of Cisco are Vanguard Group and BlackRock, each holding significant stakes in the company, approximately 7-8% of Cisco’s outstanding shares. These large institutional investors exercise considerable influence over the company’s governance and strategic decisions.
Does Cisco own Linksys?
Yes, Cisco owns Linksys, which it acquired in 2003. Linksys is a well-known brand that produces networking hardware such as routers, modems, and wireless networking equipment for home and small business use. However, Cisco sold Linksys to Belkin in 2013, and it is no longer part of Cisco’s portfolio.
Did Cisco buy Accedian?
Yes, Cisco acquired Accedian in 2023. Accedian is a network performance monitoring and application analytics company, and its acquisition strengthened Cisco’s position in providing solutions for monitoring network performance in real-time, especially in service provider and enterprise environments.
How many companies has Cisco acquired?
As of 2025, Cisco has acquired more than 200 companies. These acquisitions have helped Cisco expand into new areas, including cybersecurity, cloud networking, AI, and SaaS. Some of Cisco’s most notable acquisitions include Duo Security, AppDynamics, ThousandEyes, and Splunk.
What are the major Cisco acquisitions?
Some of the major acquisitions by Cisco include:
- Duo Security (2018): A leader in zero-trust security and multi-factor authentication.
- AppDynamics (2017): Provides application performance monitoring and IT operations analytics.
- ThousandEyes (2020): A network intelligence company that provides internet and cloud performance monitoring solutions.
- Splunk (2024): A leader in data analytics and cybersecurity.
- Meraki (2012): A cloud-managed IT solutions provider focusing on wireless networking, security, and mobile device management.
- Sourcefire (2013): Known for its intrusion detection system, Snort, and network security tools.
- WebEx (2007): A leading video conferencing platform for enterprise communication and collaboration.
- Jasper Technologies (2016): Provides IoT connectivity management solutions, enabling the management of connected devices.
- Viptela (2017): Known for its SD-WAN solutions, enhancing Cisco’s enterprise networking capabilities.
These acquisitions have enabled Cisco to broaden its portfolio and become a comprehensive player in networking, security, cloud computing, and digital collaboration.
How much did Cisco acquire Splunk for?
Cisco acquired Splunk in 2023 for $28 billion.
What is Cisco’s revenue for 2024?
Cisco’s revenue for 2024 was $56.3 billion.
Who are the major shareholders of Cisco?
Major shareholders of Cisco include Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Trust.
When was Cisco founded?
Cisco was founded in 1984 by Leonard Bosack and Sandy Lerner.
Where is Cisco headquartered?
Cisco is headquartered in San Jose, California, USA.

