Chipotle Mexican Grill has become one of America’s most recognizable fast-casual restaurant chains. If you’re wondering who owns Chipotle, you’re not alone. Ownership details reveal a mix of institutional investors and individual stakeholders.
Let’s explore the company’s roots, ownership, and more.
History of Chipotle
Chipotle was founded in 1993 by Steve Ells, a classically trained chef. He opened the first restaurant in Denver, Colorado, with the idea of quickly serving gourmet burritos and tacos. The brand’s focus on high-quality ingredients and simple menus helped it grow fast.
In 1998, McDonald’s made a small investment in the brand.
By 2001, it was the largest investor and helped Chipotle expand nationwide. However, McDonald’s divested in 2006 before Chipotle went public that same year. The IPO marked a turning point as the company started trading on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker CMG.
Who Owns Chipotle? Major Shareholders
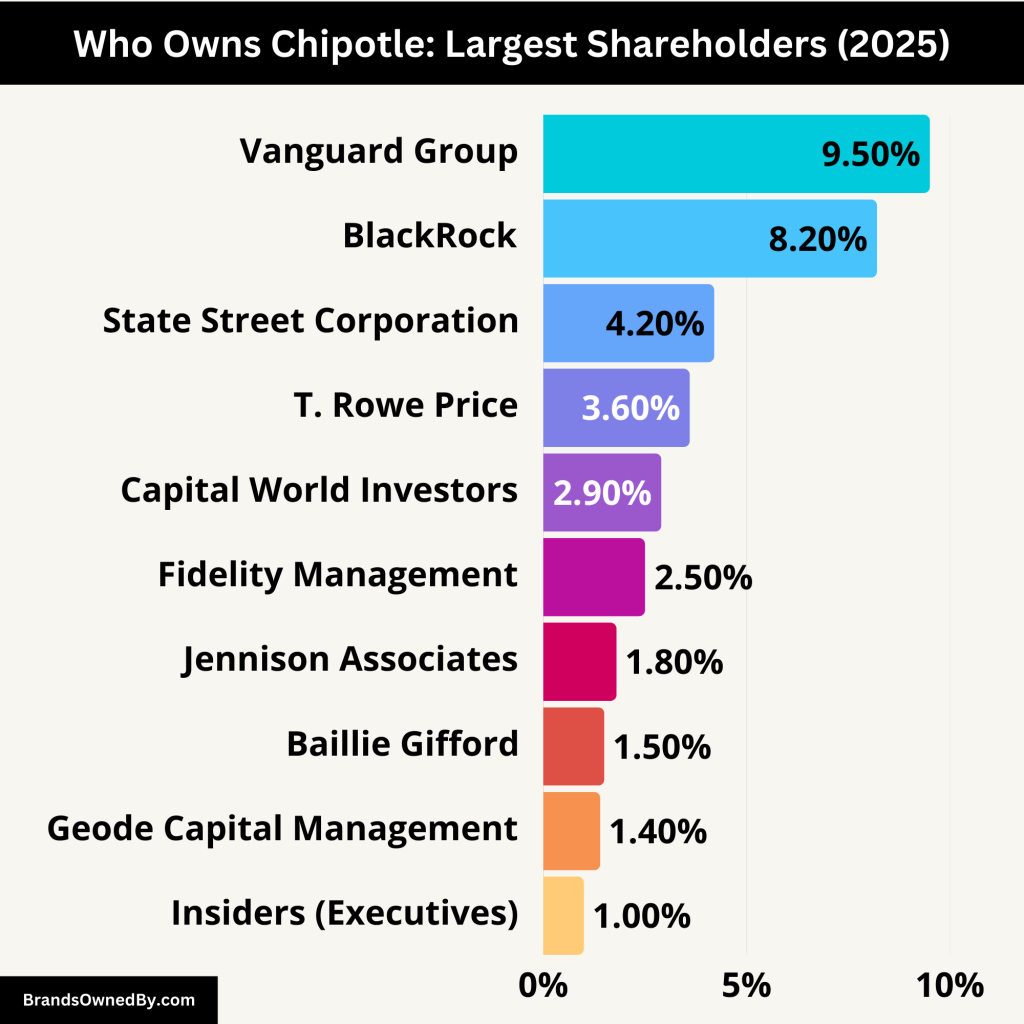
Chipotle is a publicly traded company. That means it doesn’t have one single owner but is owned by shareholders who hold its stock. The largest shareholders are typically institutional investors such as mutual funds, asset managers, and retirement funds. These investors hold significant control because of their large stakes.
| Shareholder | Ownership (%) | Type | Key Role / Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vanguard Group Inc. | ~9.5% | Institutional (Passive) | Largest shareholder; strong proxy voting influence |
| BlackRock Inc. | ~8.2% | Institutional (Passive) | Significant governance influence; ESG-focused policies |
| State Street Corporation | ~4.2% | Institutional (Passive) | Votes on board accountability, diversity, and governance issues |
| T. Rowe Price Associates | ~3.6% | Institutional (Active) | Engages with management; focuses on long-term strategy |
| Capital World Investors | ~2.9% | Institutional (Active) | Long-term investor; supports strategic planning |
| Fidelity Management | ~2.5% | Mutual Fund Manager | Moderate governance involvement; favors sustainable growth |
| Jennison Associates LLC | ~1.8% | Institutional (Active) | Growth-oriented firm; supports scalable business models |
| Baillie Gifford & Co. | ~1.5% | Institutional (Active) | International investor; focuses on ethical, global expansion |
| Geode Capital Management | ~1.4% | Institutional (Passive) | Manages index funds; affiliated with Fidelity; passive governance voting |
| Insiders (Executives) | <1% | Company Leadership | CEO and executives hold RSUs and options; direct control over day-to-day operations |
Vanguard Group Inc. – Largest Shareholder
Vanguard is the largest shareholder of Chipotle, owning around 9.5% of the outstanding shares as of early 2025. As one of the world’s largest asset management firms, Vanguard holds these shares through various index and mutual funds, including the Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund and Vanguard 500 Index Fund.
Vanguard is considered a passive investor. It typically does not interfere in day-to-day management but holds significant voting power in corporate governance matters, including board elections and shareholder resolutions.
BlackRock Inc. – Second-Largest Holder
BlackRock holds approximately 8.2% of Chipotle’s stock. Like Vanguard, BlackRock invests primarily through its iShares ETF range and other managed funds.
As a passive institutional investor, BlackRock tends to vote in alignment with governance policies and long-term shareholder interests. Its large stake means it can influence decisions during annual general meetings, especially regarding executive compensation and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices.
State Street Corporation – Third-Largest Institutional Investor
State Street owns roughly 4.2% of Chipotle’s outstanding shares. The firm manages assets through its SPDR ETFs and similar funds.
State Street has historically taken an active role in corporate governance despite being a passive investor. Its proxy voting guidelines often support diversity, board accountability, and risk mitigation.
T. Rowe Price Associates – Active Institutional Investor
T. Rowe Price holds around 3.6% of Chipotle’s shares. Unlike passive firms, T. Rowe Price is more actively managed and may engage with management on strategic issues.
The firm can influence decisions related to long-term growth, capital allocation, and competitive strategy. Though not the largest holder, it is often involved in deeper analysis of business fundamentals.
Capital World Investors – Long-Term Stakeholder
Capital World Investors owns approximately 2.9% of Chipotle’s stock. It is part of Capital Group, one of the oldest investment management companies in the United States.
Capital World tends to hold stocks for the long term. This stable ownership gives it influence in shaping the company’s strategy without the short-term pressures seen with hedge funds or activist investors.
Fidelity Management & Research – Mutual Fund Giant
Fidelity holds around 2.5% of Chipotle’s shares. It invests through multiple mutual funds managed by Fidelity Investments, one of the most well-known fund managers in the U.S.
Fidelity plays a moderate role in governance. It usually votes in favor of proposals that align with long-term shareholder value, such as those related to innovation, leadership succession, and expansion plans.
Jennison Associates LLC – Growth-Oriented Investment Firm
Jennison Associates owns about 1.8% of Chipotle. The firm specializes in growth investing, meaning it backs companies with strong future potential.
Jennison is known for focusing on companies with scalable business models. Its stake signals confidence in Chipotle’s ability to expand digitally and globally.
Baillie Gifford & Co. – International Institutional Investor
Edinburgh-based Baillie Gifford holds close to 1.5% of Chipotle stock. Known for its growth-oriented philosophy, the firm supports companies with global scalability and ethical practices.
Baillie Gifford’s ownership suggests an international perspective on Chipotle’s expansion, especially in emerging markets and sustainability initiatives.
Geode Capital Management – Index-Based Investment
Geode Capital, a close affiliate of Fidelity, owns about 1.4% of Chipotle. It manages index-based funds, primarily on behalf of Fidelity clients.
Although it follows a passive strategy, Geode casts important votes at shareholder meetings, especially in relation to board composition and shareholder returns.
Insiders: Executives and Board Members
Collectively, Chipotle insiders—executives, board members, and key employees—own less than 1% of the total shares. While this is small in percentage, their positions within the company give them a strong voice.
Brian Niccol, the CEO, has been awarded significant stock options and performance-based shares since taking leadership in 2018. Other top executives also hold restricted stock units (RSUs), which vest based on performance metrics.
These insider holdings align the leadership’s financial interests with those of shareholders, encouraging decisions that support long-term stock value.
Who Controls Chipotle?
Although Chipotle is publicly owned, control of the company lies in the hands of its executive leadership and board of directors. These individuals are responsible for making strategic, financial, and operational decisions. Institutional investors, while influential through voting rights, do not directly manage daily operations.
Executive Leadership: Day-to-Day Decision Makers
The executive team is responsible for running the company. The most influential figure is Brian Niccol, who has been the CEO and Chairman since 2018. Under his leadership, Chipotle has undergone a digital transformation, expanded its delivery services, and strengthened its brand image.
Brian Niccol came from Taco Bell, where he was known for creative marketing and menu innovation. At Chipotle, he introduced loyalty programs, digital ordering platforms, and opened more drive-thru-focused restaurants called “Chipotlanes.” His decisions directly shape the brand’s growth and consumer engagement.
Other key executives include:
- Jack Hartung – Chief Financial Officer since 2002, responsible for financial strategy and long-term planning.
- Curt Garner – Chief Customer and Technology Officer, leading the company’s digital platforms and innovation.
- Scott Boatwright – Chief Operating Officer, in charge of restaurant operations and employee training.
These executives collectively handle everything from menu changes to store expansion and employee management.
Board of Directors: Governance and Oversight
Chipotle’s Board of Directors oversees the company’s overall direction and governance. They are responsible for:
- Approving strategic plans
- Reviewing performance
- Setting executive compensation
- Hiring or removing the CEO
The board includes independent members from various industries, adding expertise in technology, finance, supply chain, and food service. Some notable members:
- Brian Niccol – Also serves as Chairman
- Mary Winston – Former CFO of Family Dollar and current board member of other public companies
- Matthew Paull – Former CFO at McDonald’s, offering valuable insight from Chipotle’s early investor days
The board meets several times a year to review strategy, risk, and performance. Their decisions are binding and they hold the CEO accountable.
Shareholder Voting Power: Indirect Influence
Large institutional shareholders like Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street do not run the company, but they have power during shareholder votes. These votes determine:
- Election of board members
- Approval of compensation plans
- Major policy shifts
- Share buybacks or capital allocation
Though most vote in line with board recommendations, they can oppose moves they see as harmful to long-term value. For instance, if they believe executive pay is too high, they can vote against it.
Proxy Advisory Firms: Behind-the-Scenes Influence
Chipotle’s large shareholders often rely on proxy advisory firms like ISS (Institutional Shareholder Services) or Glass Lewis. These firms provide recommendations on how to vote during shareholder meetings. While they don’t hold shares, their reports shape institutional investor decisions.
So even though they aren’t official decision-makers, these firms can indirectly affect governance outcomes, especially on sensitive topics like board diversity or environmental policies.
Annual Revenue and Net Worth of Chipotle
Chipotle’s financial performance has been strong in recent years. For fiscal year 2024, the company reported annual revenue of $9.9 billion. Net income reached around $1.1 billion, showing strong profitability.
Its market capitalization, often viewed as net worth in public markets, fluctuates but is around $85 billion as of April 2025. The company’s strong brand, loyal customer base, and digital innovation have helped boost its valuation.
Here’s a breakdown of the historical revenue and net worth of Chipotle Mexican Grill:
| Year | Annual Revenue (USD) | Net Word (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | $4.50 billion | ~$19 billion |
| 2016 | $3.90 billion | ~$11 billion |
| 2017 | $4.48 billion | ~$10.5 billion |
| 2018 | $4.86 billion | ~$13 billion |
| 2019 | $5.59 billion | ~$22 billion |
| 2020 | $5.98 billion | ~$41 billion |
| 2021 | $7.55 billion | ~$49 billion |
| 2022 | $8.63 billion | ~$48 billion |
| 2023 | $9.23 billion | ~$65 billion |
| 2024 | $9.90 billion | ~$85 billion |
Key Insights from Financial Trends
- 2016 Dip: Revenue dropped significantly due to the E. coli and norovirus outbreaks in 2015, which severely affected customer trust and traffic. Market value also declined.
- 2018 Recovery: The appointment of Brian Niccol as CEO marked a major turnaround. New strategies began to take effect, improving revenue and investor sentiment.
- 2020–2021 Surge: Despite the pandemic, Chipotle benefited from a digital-first approach and contactless ordering, boosting revenue and valuation.
- 2022 Onward: Continued investment in drive-thru locations (“Chipotlanes”), mobile app orders, and loyalty programs drove steady revenue and a sharp increase in market capitalization.
Companies Owned by Chipotle
Unlike many large restaurant groups, Chipotle has chosen to focus on a single flagship brand—Chipotle Mexican Grill. Over the years, the company has experimented with other restaurant concepts, but it eventually returned to concentrating its resources on the Chipotle brand. Below is a detailed look at the brands Chipotle has owned or operated.
Chipotle Mexican Grill – The Flagship Brand
Chipotle Mexican Grill is the company’s core and only currently operating brand. It was founded in 1993 by Steve Ells in Denver, Colorado, with a mission to bring high-quality ingredients to fast-casual dining.
The brand is known for:
- Customizable burritos, bowls, tacos, and salads.
- “Food with Integrity” philosophy, emphasizing sustainability and ethically sourced ingredients.
- A strong digital presence, including app-based ordering, rewards programs, and delivery integrations.
- Expansion through “Chipotlanes”, drive-thru lanes designed for mobile order pickups.
As of 2024, Chipotle operates over 3,400 locations across the United States and select international markets. It is the company’s only active brand today, accounting for 100% of its revenue.
ShopHouse Southeast Asian Kitchen (2011–2017)
ShopHouse was a Southeast Asian fast-casual concept launched by Chipotle in 2011. The first location opened in Washington, D.C., with a menu inspired by Thai, Vietnamese, and Malaysian cuisines. It featured:
- Customizable bowls with rice or noodles.
- Meats marinated in bold flavors like lemongrass or tamarind.
- Southeast Asian vegetables, sauces, and garnishes.
While the brand mirrored Chipotle’s model of customization and ethically sourced ingredients, ShopHouse never gained widespread popularity. Customers found the flavors too niche or unfamiliar, and the brand failed to scale efficiently.
By 2017, Chipotle announced it would shut down all ShopHouse locations, stating the brand didn’t meet performance expectations. The closure allowed the company to refocus on strengthening the core Chipotle business.
Tasty Made (2016–2018)
Tasty Made was a Chipotle experiment in the burger category. It launched in 2016 in Lancaster, Ohio, with the idea of using Chipotle’s principles—simple menu, quality ingredients, and made-to-order service—in a burger format.
The menu included:
- Grass-fed beef burgers
- Hand-cut fries
- Milkshakes and sodas
Despite its simplicity, Tasty Made failed to attract enough traffic to justify expansion. Customers did not see enough differentiation from existing burger chains. In 2018, the brand was closed after only one location operated for two years.
Pizzeria Locale (2013–2020, reduced operations after)
Pizzeria Locale was a fast-casual pizza concept co-founded by restaurateurs Bobby Stuckey and Lachlan Mackinnon-Patterson. Chipotle partnered with them in 2013 to bring Neapolitan-style pizzas to a broader audience.
Highlights of the concept:
- Fast-fired pizzas made in under 3 minutes
- High-quality ingredients like mozzarella di bufala and San Marzano tomatoes
- Customizable pizza toppings with artisanal crust
At its peak, the brand had multiple locations in Colorado and Ohio, but expansion stalled, and Chipotle eventually pulled back its support. While a few Pizzeria Locale locations still operate independently in Boulder under the original founders, Chipotle no longer manages or grows the chain.
Final Words on Chipotle Ownership
So, who owns Chipotle?
The answer lies with its shareholders—primarily large investment firms like Vanguard and BlackRock. These institutions hold the largest stakes but don’t manage operations. Control is in the hands of the leadership team, led by CEO Brian Niccol.
The company continues to grow its financial power and brand reach. It has remained focused on a single brand strategy, which has helped it stay consistent and innovative.
FAQs
Who is the largest shareholder of Chipotle?
The largest shareholder is Vanguard Group Inc., owning about 9.5% of Chipotle’s stock.
Is Chipotle privately owned?
No, Chipotle is a publicly traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker CMG.
Does McDonald’s still own Chipotle?
No. McDonald’s fully exited its investment in Chipotle in 2006, before the company went public.
Who is the CEO of Chipotle?
Brian Niccol is the current CEO. He joined in 2018 and previously worked at Taco Bell.
How much is Chipotle worth?
As of early 2025, Chipotle’s market capitalization is around $85 billion.

