Bernard Arnault is the mastermind behind the world’s largest luxury empire. As the chairman and CEO of LVMH, he controls an extensive portfolio of prestigious brands. His influence in the luxury industry is unmatched, with ownership of high-end fashion, jewelry, cosmetics, and spirits brands. The brands owned by Bernard Arnault span multiple sectors, making him one of the most powerful figures in global business.
Who is Bernard Arnault?

Bernard Arnault is a French business magnate, investor, and art collector. He was born on March 5, 1949, in Roubaix, France. He is best known as the Chairman and CEO of LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton, the world’s largest luxury goods company. Under his leadership, LVMH has grown into a powerhouse with brands spanning fashion, cosmetics, jewelry, and fine wines.
Arnault studied at the prestigious École Polytechnique, France’s top engineering school, and started his career in his family’s construction company, Ferret-Savinel. In the 1980s, he saw an opportunity in luxury brands and acquired Christian Dior, which became the foundation of his empire. Over the decades, he has transformed LVMH into a global leader in luxury.
Family and Personal Life
Bernard Arnault is married to Hélène Mercier, a Canadian concert pianist. The couple has three children together. He also has two children from his first marriage to Anne Dewavrin, bringing the total to five. His children play significant roles in his business empire:
- Delphine Arnault – She is the CEO of Christian Dior Couture and was previously Executive Vice President at Louis Vuitton. She is seen as one of the potential successors to her father.
- Antoine Arnault – He is the CEO of Berluti and Chairman of Loro Piana. He is also a key figure in LVMH’s strategic decisions.
- Alexandre Arnault – He is the Executive Vice President of Product and Communications at Tiffany & Co. and was previously CEO of Rimowa.
- Frédéric Arnault – He is the CEO of TAG Heuer, overseeing its innovation and expansion.
- Jean Arnault – He is the youngest and currently serves as the Director of Watches at Louis Vuitton.
Arnault is known for keeping his family closely involved in LVMH, ensuring that leadership remains within the family. His children have taken active roles in key brands, suggesting a long-term succession plan.
List of Companies and Brands Owned by Bernard Arnault
As the head of LVMH, Bernard Arnault controls a vast portfolio of prestigious brands across various industries. Below are the major brands he owns:
Here’s a detailed list of the companies and brands owned by Bernard Arnault through LVMH:
| Brand | Acquisition Year |
|---|---|
| Christian Dior | 1984 |
| Le Bon Marché | 1984 |
| Louis Vuitton | 1989 |
| Moët & Chandon | 1987 |
| Hennessy | 1987 |
| Parfums Christian Dior | 1987 |
| Givenchy | 1988 |
| Berluti | 1993 |
| Kenzo | 1993 |
| Guerlain | 1994 |
| Fred | 1995 |
| Loewe | 1996 |
| Celine | 1996 |
| Sephora | 1997 |
| Marc Jacobs | 1997 |
| DFS | 1997 |
| Château Cheval Blanc | 1998 |
| Benefit Cosmetics | 1999 |
| Make Up For Ever | 1999 |
| TAG Heuer | 1999 |
| Krug | 1999 |
| Château d’Yquem | 1999 |
| Chaumet | 1999 |
| Zenith | 1999 |
| Thomas Pink | 1999 |
| Cheval des Andes | 1999 |
| Fresh | 2000 |
| Emilio Pucci | 2000 |
| Newton Vineyard | 2001 |
| Fendi | 2001 |
| Donna Karan | 2001 |
| Acqua di Parma | 2001 |
| DKNY | 2001 |
| La Samaritaine | 2001 |
| Mercier | 1987 |
| Ruinart | 1987 |
| Veuve Clicquot | 1987 |
| Cloudy Bay | 2003 |
| Ardbeg | 2004 |
| Glenmorangie | 2004 |
| Belvedere | 2005 |
| 10 Cane Rum | 2005 |
| Wenjun | 2007 |
| Numanthia | 2008 |
| Hublot | 2008 |
| Bulgari | 2011 |
| Loro Piana | 2013 |
| Ao Yun | 2013 |
| Clos des Lambrays | 2014 |
| Rimowa | 2016 |
| Colgin Cellars | 2017 |
| Woodinville Whiskey Co. | 2017 |
| Maison Francis Kurkdjian | 2017 |
| Jean Patou | 2018 |
| Belmond | 2019 |
| Fenty | 2019 |
| Stella McCartney | 2019 |
| Château d’Esclans | 2019 |
| Tiffany & Co. | 2021 |
| Officine Universelle Buly | 2021 |
| Off-White | 2021 |
| Phoebe Philo | 2021 |
Louis Vuitton
Founded in 1854, Louis Vuitton began as a trunk-making company in Paris and has evolved into the most valuable luxury brand globally. Known for its monogrammed canvas bags, travel luggage, and leather accessories, it epitomizes luxury craftsmanship. Since Arnault’s LVMH took shape in 1987 through the merger of Louis Vuitton and Moët Hennessy, Louis Vuitton has remained the flagship brand.
Under Arnault, the brand expanded beyond leather goods into ready-to-wear fashion, shoes, watches, jewelry, and fragrances, collaborating with creative icons like Marc Jacobs, Nicolas Ghesquière, Virgil Abloh, and Pharrell Williams. Louis Vuitton contributes significantly to LVMH’s profits and maintains boutique dominance across more than 460 stores worldwide.
Christian Dior
Christian Dior was Arnault’s entry point into the luxury world. He acquired the struggling Boussac group in 1984, which owned Dior, and transformed it into a powerhouse. Dior operates under both Couture and Parfums divisions, producing haute couture, ready-to-wear, handbags (like the Lady Dior), and world-famous perfumes such as J’adore, Sauvage, and Miss Dior.
Through Christian Dior SE, Arnault also exercises controlling interest over LVMH itself. Maria Grazia Chiuri and Kim Jones currently lead its creative direction. Dior generates over €9 billion annually, and its stronghold in fashion weeks and flagship locations (like 30 Avenue Montaigne) cements its legacy.
Fendi
Founded in 1925 in Rome, Fendi is synonymous with Italian elegance and fur craftsmanship. It became part of the LVMH group in the early 2000s through a joint acquisition with Prada (LVMH later bought out Prada’s stake). The late Karl Lagerfeld was Fendi’s creative director for over 50 years.
Fendi is famous for its Baguette bag, Peekaboo line, and artisanal furs. Under Bernard Arnault, the brand grew into a multi-billion-euro label with flagship stores in Paris, Milan, and Tokyo. Fendi also launched Fendi Casa for luxury furniture and inaugurated its headquarters at Palazzo della Civiltà Italiana in Rome.
Bulgari
Bulgari, founded in 1884 in Rome, is a premier jewelry house famed for bold, colorful gemstone designs and luxury watches. LVMH acquired Bulgari in 2011 in a landmark €4.3 billion all-share deal, one of its largest acquisitions at the time.
Under Arnault, Bulgari expanded into ultra-high-end watches (e.g., Serpenti, Octo Finissimo), perfumes, and even hotels under Bulgari Hotels & Resorts in cities like Milan, Dubai, and London. Its presence in the fine jewelry market rivals Cartier and Tiffany.
TAG Heuer
TAG Heuer is a Swiss watch brand established in 1860. Known for its precision chronographs, racing-inspired timepieces, and sports endorsements, it joined LVMH in 1999.
Arnault has repositioned TAG Heuer as an affordable luxury brand and a tech-forward innovator through its Connected Watch collection. Endorsements by celebrities and athletes such as Cristiano Ronaldo and Naomi Osaka have strengthened its market appeal.
Hublot
Hublot, founded in 1980, is known for its philosophy of “The Art of Fusion,” combining traditional watchmaking with modern materials like carbon fiber and rubber. Acquired by LVMH in 2008, Hublot has thrived under CEO Ricardo Guadalupe and Arnault’s strategic support.
Famous models include the Big Bang, Classic Fusion, and Spirit of Big Bang. The brand maintains a bold presence in sports partnerships with FIFA, Ferrari, and Usain Bolt, reflecting Arnault’s penchant for aligning luxury with lifestyle.
Zenith
Zenith is a historic Swiss watch brand, established in 1865 and acquired by LVMH in 1999. It’s revered for the El Primero movement—one of the first automatic chronograph calibers. Zenith maintains a niche appeal among collectors, with a strong focus on technical horology.
Arnault’s LVMH group has helped Zenith modernize its offerings without sacrificing its legacy, especially with the Defy collection targeting younger audiences.
Celine
Celine, a French fashion house founded in 1945, was acquired by LVMH in 1996. Initially focused on women’s ready-to-wear and accessories, it rose in prominence under designer Phoebe Philo, whose minimalist aesthetic reshaped modern fashion.
Under current creative director Hedi Slimane, Celine adopted a rock-influenced, youth-oriented look. Arnault supported this pivot, expanding Celine into menswear, haute parfumerie, and flagship boutiques globally.
Loewe
Loewe, Spain’s oldest luxury fashion house (founded in 1846), became part of LVMH in 1996. Originally known for artisanal leather goods, it has gained new global appeal under Jonathan Anderson, whose avant-garde collections have redefined Loewe’s identity.
Bernard Arnault invested in expanding Casa Loewe concept stores, artist collaborations, and curated craft initiatives, reinforcing Loewe as both heritage-rich and forward-thinking.
Givenchy
Givenchy was founded by Hubert de Givenchy in 1952 and became part of LVMH in 1988. It gained global fame for dressing Audrey Hepburn and introducing elegant silhouettes to the post-war fashion world.
Under Arnault, Givenchy hired daring designers like Alexander McQueen, Riccardo Tisci, and Matthew M. Williams. The house also excels in fragrances (like Gentleman and L’Interdit) and plays a crucial role in LVMH’s prestige cosmetics division.
Sephora
Sephora, founded in France in 1969, revolutionized beauty retail with its open-sell model, letting customers try products before buying. LVMH acquired it in 1997, and under Arnault’s leadership, Sephora has grown into the world’s leading beauty chain, with over 3,000 stores across 35+ countries.
It carries thousands of brands, including private-label Sephora Collection and exclusive collaborations. Its digital app, loyalty program, and integration with TikTok and Instagram make it a top beauty retailer for Gen Z and Millennials.
Guerlain
Founded in 1828, Guerlain is one of the oldest and most prestigious perfume houses in the world. Known for classic fragrances like Shalimar, Mitsouko, and L’Heure Bleue, Guerlain also excels in skincare with its Abeille Royale and Orchidée Impériale lines.
LVMH acquired Guerlain in 1994. Arnault preserved its heritage while modernizing its operations. Guerlain’s Paris boutique on the Champs-Élysées remains a temple of perfumery, blending tradition with luxury innovation.
Rimowa
Rimowa, a German luggage brand founded in 1898, is famed for its grooved aluminum suitcases. LVMH acquired a majority stake in 2016, marking the group’s first acquisition of a German luxury brand.
Arnault appointed his son Alexandre Arnault as CEO, modernizing the brand through tech integrations, influencer campaigns, and high-profile collaborations with Off-White, Supreme, and Dior. Rimowa targets the luxury jet-set demographic.
Benefit Cosmetics
Founded in 1976 in San Francisco, Benefit is known for fun packaging and bestselling products like They’re Real! Mascara and Brow Bar services. Acquired by LVMH in 1999, it appeals to a youthful audience with quirky marketing and innovation in brow styling.
Make Up For Ever
Founded by makeup artist Dany Sanz in 1984, Make Up For Ever joined LVMH in 1999. It’s a favorite among professional artists for its pigmented, long-lasting formulas and artistry tools. LVMH has invested heavily in its global academies and creative campaigns.
Chaumet
Chaumet, founded in 1780 and associated with Napoleonic France, is a legacy jewelry house known for tiaras, bridal collections, and high jewelry. LVMH acquired Chaumet in 1999. It holds a prestigious location at Place Vendôme, where many LVMH jewelers operate.
Emilio Pucci
Italian brand Emilio Pucci is known for its colorful, psychedelic prints. It became part of LVMH in 2000. Though quieter in recent years, Arnault has preserved it as a niche artistic label with seasonal resort collections and high-end collaborations.
Le Parisien
Arnault owns Le Parisien, a major French newspaper, via his media group Groupe Les Échos-Le Parisien, acquired in 2015. Though not a luxury brand, it gives Arnault influence in public discourse and media strategy.
Belmond
LVMH acquired Belmond in 2019 for $3.2 billion. It operates ultra-luxury hotels, trains (like the Venice Simplon-Orient-Express), and cruises. Belmond complements LVMH’s luxury lifestyle positioning, offering experiences aligned with its core clientele.
Cheval Blanc
Cheval Blanc is LVMH’s in-house luxury hotel brand, launched in 2006. With locations in Courchevel, Paris, Maldives, and St. Barts, it offers bespoke hospitality and exclusive spa partnerships (e.g., Guerlain Spa). These hotels reflect the pinnacle of LVMH lifestyle branding.
Royal Van Lent (Feadship)
Through its acquisition of Royal Van Lent, LVMH entered the luxury yacht market. The Dutch shipyard builds custom superyachts under the Feadship name. This aligns with Arnault’s ambition to serve the ultra-wealthy across all touchpoints.
Officine Universelle Buly 1803
A revival of a historic Parisian apothecary, Buly 1803 was acquired by LVMH in 2021. Known for artisanal beauty products, vintage packaging, and water-based perfumes, it appeals to heritage luxury enthusiasts and complements LVMH’s high-end perfume division.
Bernard Arnault Net Worth
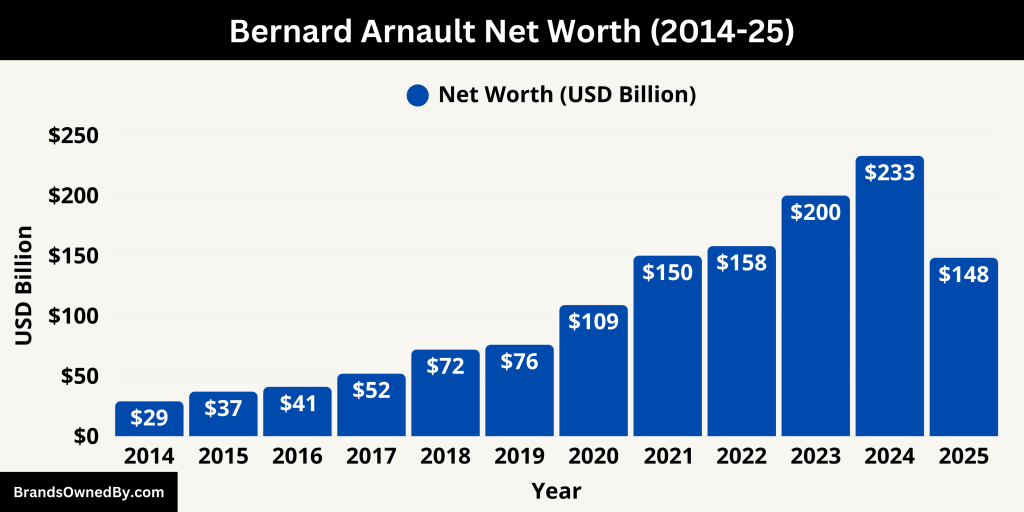
As of May 2025, his estimated net worth is around $148.3 billion, driven primarily by his ownership stake in LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton, the world’s largest luxury goods company.
Sources of Wealth
Arnault’s wealth comes from multiple sources, but the most significant is his controlling stake in LVMH. Through his family holding company, Groupe Arnault, he owns over 48% of LVMH’s shares and controls around 64% of its voting rights. This gives him a commanding position in the company’s operations and decision-making. LVMH’s continued growth in fashion, cosmetics, wines, and jewelry has been a major factor in Arnault’s rising net worth.
In addition to LVMH, he also has significant investments in other industries, including media, technology, and real estate. He has acquired stakes in Carrefour (a major French supermarket chain) and owns the luxury hotel group Cheval Blanc. His family’s investment firm has also backed tech startups and financial services firms.
LVMH’s Role in His Wealth
LVMH is a dominant force in the global luxury market, with brands like Louis Vuitton, Dior, Tiffany & Co., and Moët & Chandon driving revenue. The company’s annual revenue surpasses $80 billion, with high profitability margins. Arnault’s wealth is heavily tied to LVMH’s stock price, meaning that fluctuations in the luxury market can impact his net worth significantly.
During times of economic downturns, his fortune has seen temporary declines. However, LVMH’s ability to maintain high demand for luxury goods worldwide has ensured consistent long-term growth. The company’s expansion into China, the Middle East, and North America has further increased its valuation, adding billions to Arnault’s net worth.
Luxury Real Estate and Art Collection
Beyond corporate holdings, Arnault has a vast real estate portfolio. He owns multiple luxury properties in France and internationally, including private mansions and estates. He is also a passionate art collector, owning works from artists like Pablo Picasso, Jean-Michel Basquiat, and Andy Warhol. His Fondation Louis Vuitton, a contemporary art museum in Paris, showcases major art exhibitions and highlights his commitment to the arts.
Yearly Net Worth Growth
Arnault’s net worth has surged dramatically in the last decade. In 2010, he was worth around $25 billion. By 2019, he had crossed the $100 billion mark, and in 2021, he briefly became the richest person in the world. By 2024, his fortune had more than doubled in just five years, largely due to LVMH’s rising stock value and expansion into new markets.
| Year | Net Worth (USD) | Notes |
|---|
| 2014 | $29 billion | Arnault’s wealth was bolstered by LVMH’s strong performance and successful brand acquisitions. |
| 2015 | $37 billion | Continued growth in the luxury market contributed to an increase in net worth. |
| 2016 | $41 billion | LVMH’s expansion into new markets and product lines supported further wealth accumulation. |
| 2017 | $52 billion | A surge in demand for luxury goods, particularly in Asia, led to significant financial gains. |
| 2018 | $72 billion | Record-breaking revenues for LVMH propelled Arnault’s net worth upward. |
| 2019 | $76 billion | Strategic acquisitions, including the announcement to purchase Tiffany & Co., enhanced LVMH’s market position. |
| 2020 | $109 billion | Despite global challenges, LVMH’s resilience in the luxury sector resulted in substantial wealth growth. |
| 2021 | $150 billion | Arnault’s net worth continued to rise, reflecting LVMH’s dominance in the luxury market. |
| 2022 | $158 billion | Steady performance and brand strength maintained Arnault’s financial standing. |
| 2023 | $200 billion | Expansion into emerging markets and sustained demand for luxury products contributed to wealth accumulation. |
| 2024 | $233 billion | As of 2024, Arnault’s net worth is estimated at $233 billion, reaffirming his status as one of the world’s wealthiest individuals. |
Comparison to Other Billionaires
Arnault is frequently compared to other billionaires such as Elon Musk (Tesla, SpaceX), Jeff Bezos (Amazon), and Mark Zuckerberg (Meta). While their fortunes are often tied to tech and innovation, Arnault’s wealth is deeply rooted in heritage, craftsmanship, and brand prestige. The luxury sector has proven to be resilient, with high-income consumers continuing to buy premium products even during economic downturns.
Final Words
Bernard Arnault has built a luxury empire through strategic acquisitions and brand development. The brands owned by Bernard Arnault cover fashion, jewelry, cosmetics, and spirits, making LVMH the leader in the luxury sector. His ability to grow and sustain these brands ensures his influence remains strong in the global market.
FAQs
How many brands does Bernard Arnault own?
Bernard Arnault, through LVMH, owns over 70 luxury brands across fashion, beauty, jewelry, and spirits.
What is Bernard Arnault’s most famous brand?
Louis Vuitton is the most famous brand owned by Bernard Arnault. It is the flagship of LVMH and one of the most valuable luxury brands in the world.
How did Bernard Arnault become so rich?
Arnault built his wealth through strategic acquisitions and investments in luxury brands. His leadership of LVMH has driven massive growth and increased his net worth.
Does Bernard Arnault own Sephora?
Yes, Sephora is owned by LVMH, which is controlled by Bernard Arnault. It is one of the largest beauty retailers in the world.
What is Bernard Arnault’s role at LVMH?
He is the chairman and CEO of LVMH, overseeing the company’s operations and strategic growth.
Does Bernard Arnault own Gucci?
No, Bernard Arnault does not own Gucci. Gucci is owned by Kering, a rival French luxury group led by François-Henri Pinault. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, Arnault made several attempts to acquire Gucci, but after a fierce legal and financial battle, he lost control to Pinault’s then-named PPR Group (now Kering). Since then, Gucci has remained a flagship brand of Kering, not LVMH.
Is Celine owned by Louis Vuitton?
No, Celine is not owned by Louis Vuitton directly. Both Celine and Louis Vuitton are owned by LVMH, the parent company controlled by Bernard Arnault. While Louis Vuitton is a flagship brand within LVMH, Celine is its own independent fashion house under the same corporate umbrella. Each brand has its own creative leadership and distinct identity within LVMH’s fashion and leather goods division.
Why did Bernard Arnault buy Dior?
Bernard Arnault acquired Christian Dior in 1984 as part of a broader strategy to build a luxury empire. At the time, Dior was part of the bankrupt Boussac textile group. Arnault bought Boussac with government support and sold off its non-luxury assets, retaining Dior for its brand power. This acquisition was his entry into the luxury fashion world and later became a strategic linchpin, as Christian Dior SE also serves as the major shareholder of LVMH, giving Arnault control over the entire group.
What religion is Bernard Arnault?
Bernard Arnault was born into a Catholic family and is considered to be Roman Catholic by upbringing. However, he is known to be very private about his personal beliefs and does not publicly discuss religion or spirituality. There are no verified reports of him being devoutly religious or actively involved in religious institutions.
Who was Bernard Arnault’s first wife?
Bernard Arnault’s first wife was Anne Dewavrin. They married in 1973 and had two children together: Delphine Arnault (who is now CEO of Dior) and Antoine Arnault (who plays key roles in Berluti and Loro Piana). The couple later divorced in 1990. Arnault later married Hélène Mercier, a Canadian concert pianist, with whom he has three more sons.
What is the Bernard Arnault family’s net worth?
As of 2025, the Arnault family’s net worth is estimated at over $210 billion, making Bernard Arnault one of the richest individuals in the world. The family’s wealth is largely derived from their controlling stake in LVMH, held through Christian Dior SE and the Groupe Arnault holding company. Several family members also hold executive roles in LVMH’s brands, ensuring long-term dynastic control.

